Abstract
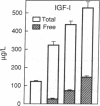
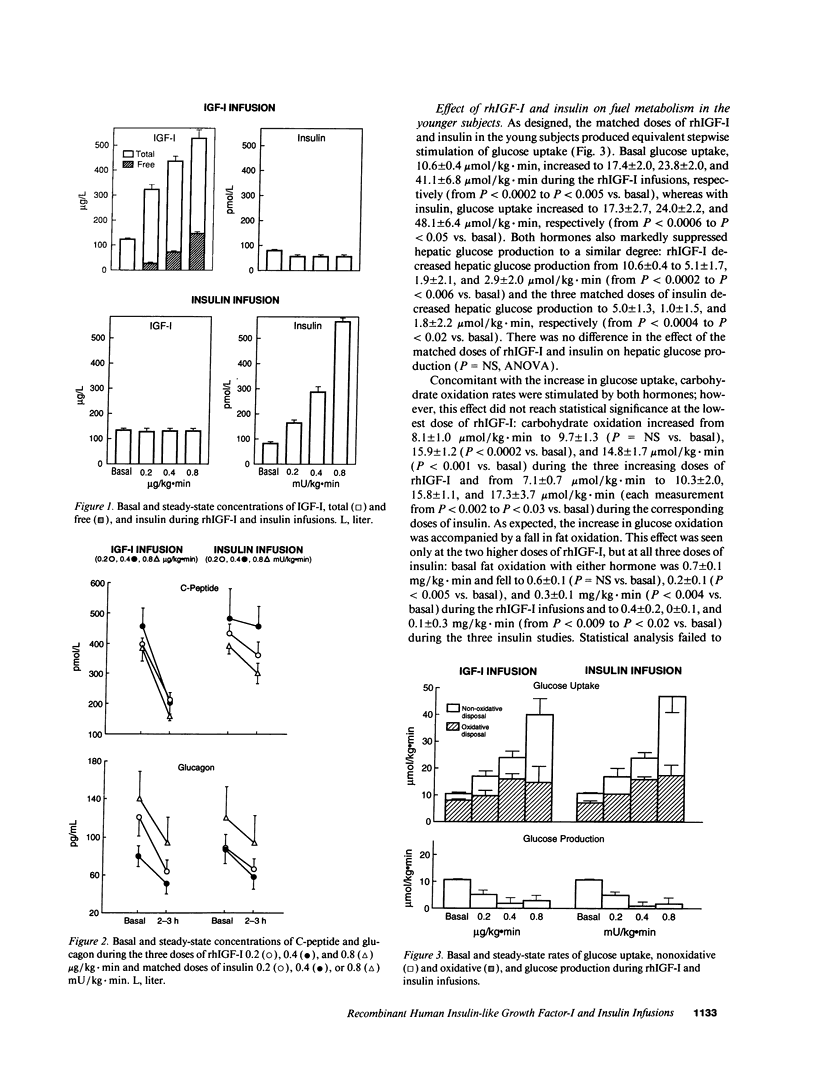
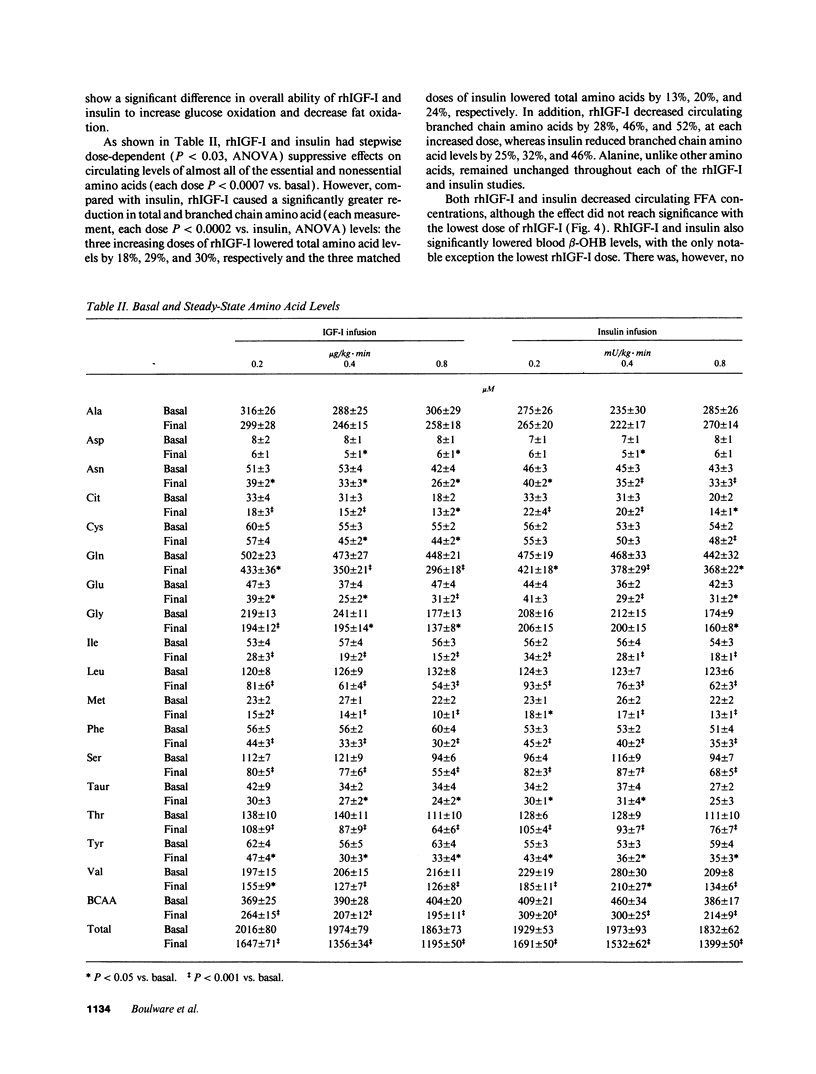
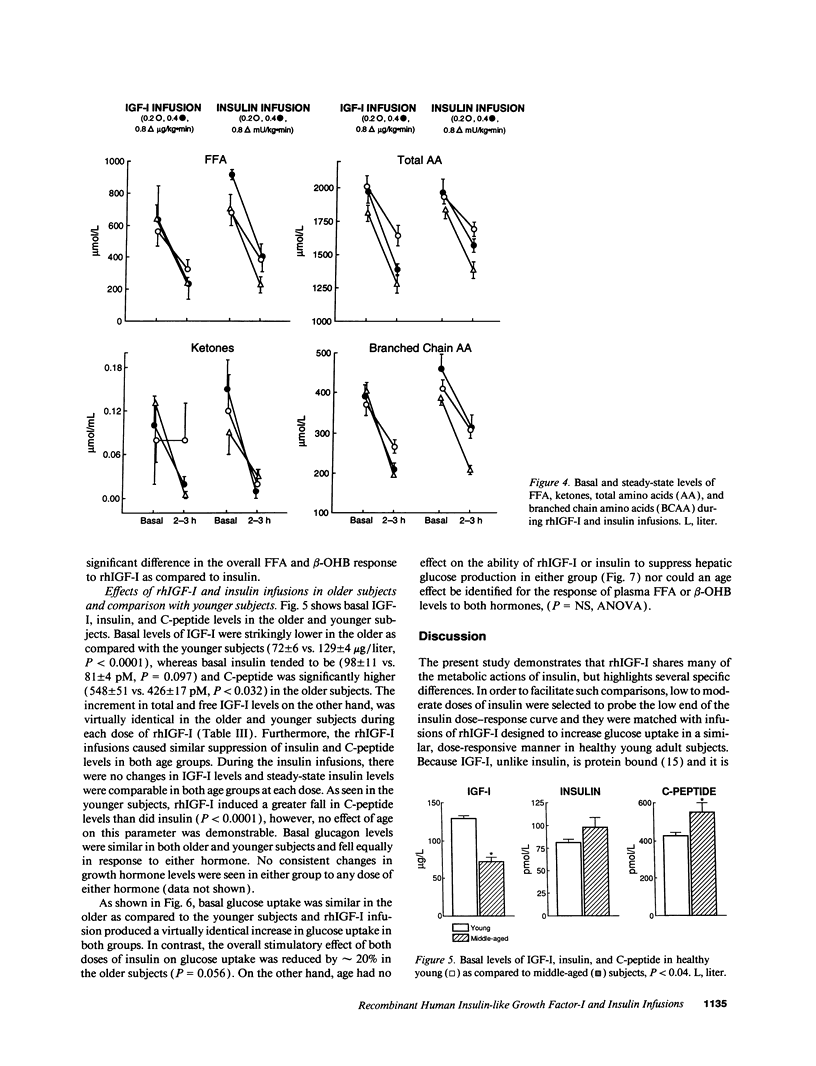
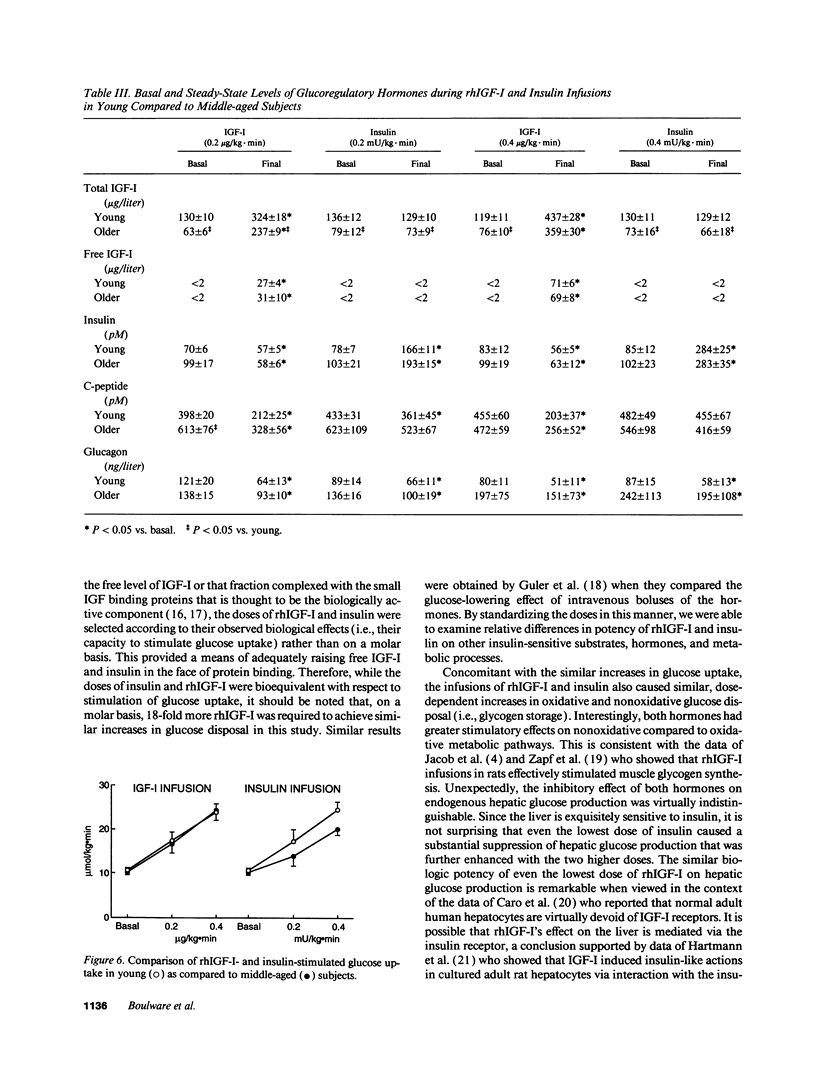
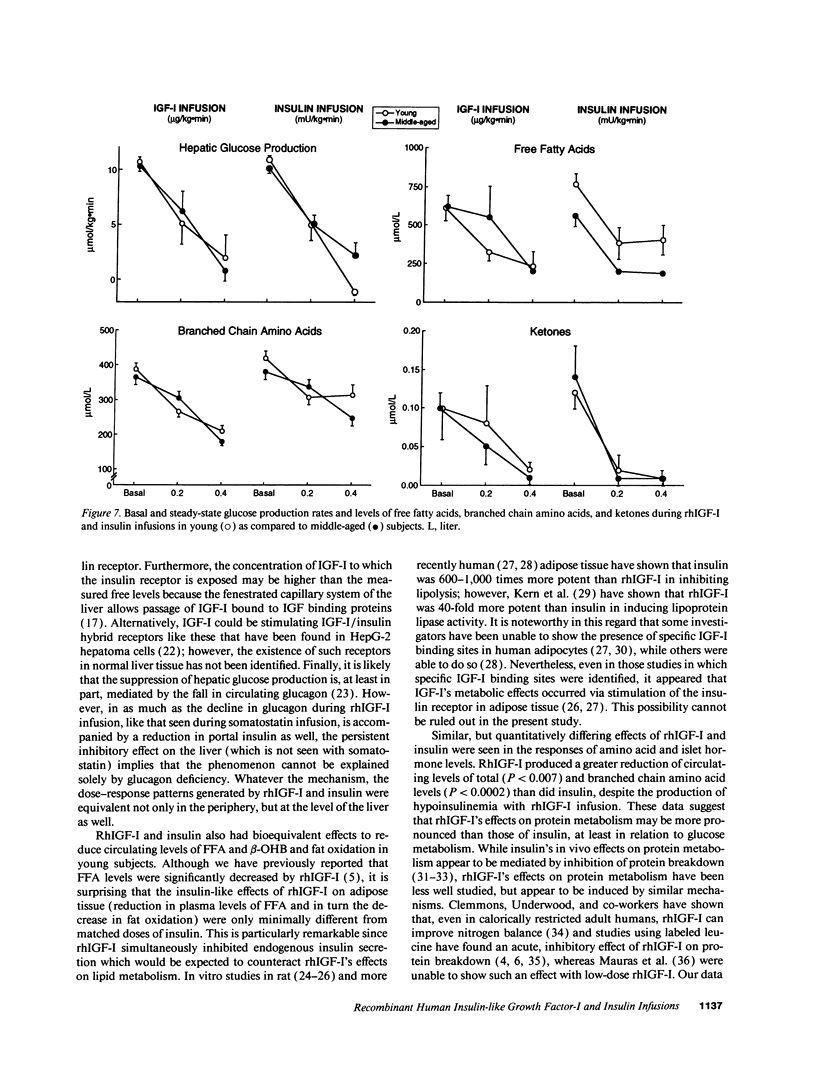
The actions of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I (rhIGF-I) and insulin were compared in 21 healthy young (24 +/- 1 yr) and 14 healthy middle-aged (48 +/- 2 yr) subjects during 3-h paired euglycemic clamp studies using one of three doses (rhIGF-I 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 micrograms/kg.min and insulin 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 mU/kg.min, doses chosen to produce equivalent increases in glucose uptake). In younger subjects, rhIGF-I infusions suppressed insulin by 19-33%, C-peptide by 47-59% and glucagon by 33-47% (all, P < 0.02). The suppression of C-peptide was less pronounced with insulin than with rhIGF-I (P < 0.007). The metabolic responses to rhIGF-I and insulin were remarkably similar: not only did both hormones increase glucose uptake and oxidation in a nearly identical fashion, but they also produced similar suppression of glucose production, free fatty acid levels, and fat oxidation rates. In contrast, rhIGF-I had a more pronounced amino acid-lowering effect than did insulin (P < 0.004). In middle-aged subjects, basal IGF-I levels were 44% lower (P < 0.0001) whereas basal insulin and C-peptide were 20-25% higher than in younger subjects. Age did not alter the response to rhIGF-I. However, insulin-induced stimulation of glucose uptake was blunted in older subjects (P = 0.05). Our data suggest that absolute IGF-I and relative insulin deficiency contribute to adverse metabolic changes seen in middle age.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binoux M., Hossenlopp P. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding proteins: comparison of human serum and lymph. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Sep;67(3):509–514. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Lindblad A., Engfeldt P., Arner P. Studies of acute effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II in human fat cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):732–737. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Poulos J., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Sinha M. K. Insulin-like growth factor I binding in hepatocytes from human liver, human hepatoma, and normal, regenerating, and fetal rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):976–981. doi: 10.1172/JCI113451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Smith-Banks A., Underwood L. E. Reversal of diet-induced catabolism by infusion of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):234–238. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland K. C., Colletti R. B., Devlin J. T., McAuliffe T. L. The relationship between insulin-like growth factor-I, adiposity, and aging. Metabolism. 1990 Jun;39(6):584–587. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Glucose intolerance and aging. Diabetes Care. 1981 Jul-Aug;4(4):493–501. doi: 10.2337/diacare.4.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A., Sherwin R. S. Transient hepatic response to glucagon in man: role of insulin and hyperglycemia. Am J Physiol. 1982 Feb;242(2):E73–E81. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.2.E73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Prinz P. N., Vitiello M. V., Hintz R. L. Somatomedin-C levels in healthy young and old men: relationship to peak and 24-hour integrated levels of growth hormone. J Gerontol. 1985 Jan;40(1):2–7. doi: 10.1093/geronj/40.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa N. K., Minaker K. L., Rowe J. W., Goodman M. N., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Young V. R. Insulin-mediated reduction of whole body protein breakdown. Dose-response effects on leucine metabolism in postabsorptive men. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2306–2311. doi: 10.1172/JCI112240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand R. A., Barrett E. J. Effect of physiologic hyperinsulinemia on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI113033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F. Demonstration of specific plasma protein binding sites for somatomedin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):988–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Barrett E., Plewe G., Fagin K. D., Sherwin R. S. Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1717–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI114072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P. A., Marshall S., Eckel R. H. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase in primary cultures of isolated human adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):199–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI111675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Tamborlane W. V., Rife F., Sherwin R. S. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 on the responses to and recognition of hypoglycemia in humans. A comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):141–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI116163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Vandekerkhove K. M. Insulin-like growth factor-I at physiological concentrations is a potent inhibitor of insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1593–1598. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauras N., Horber F. F., Haymond M. W. Low dose recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I fails to affect protein anabolism but inhibits islet cell secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Nov;75(5):1192–1197. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.5.1430078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J., Glasscock R., Aikens J., Gerich J., Haymond M. A microfluorometric method for the determination of free fatty acids in plasma. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Duronio V., Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13238–13244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert N. J., Caprio S., Sherwin R. S. Insulin-like growth factor I inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion but does not impair glucose metabolism in normal humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Mar;76(3):804–806. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.3.8445040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Minaker K. L., Pallotta J. A., Flier J. S. Characterization of the insulin resistance of aging. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1581–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI110914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlechter N. L., Russell S. M., Spencer E. M., Nicoll C. S. Evidence suggesting that the direct growth-promoting effect of growth hormone on cartilage in vivo is mediated by local production of somatomedin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7932–7934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., DeFronzo R., Wahren J., Felic P. Glucose homeostasis during prolonged suppression of glucagon and insulin secretion by somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Buchanan C., Leggett N., Martin L., Khazanie P. G., Dimarchi R., Pories W. J., Caro J. F. Mechanism of IGF-I-stimulated glucose transport in human adipocytes. Demonstration of specific IGF-I receptors not involved in stimulation of glucose transport. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1217–1225. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Trevisan R., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Nosadini R., De Kreutzenberg S. V., Duner E., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Dose-response curves of effects of insulin on leucine kinetics in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):E334–E342. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.3.E334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkalj I., Keller U., Ninnis R., Vosmeer S., Stauffacher W. Effect of increasing doses of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose, lipid, and leucine metabolism in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Nov;75(5):1186–1191. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.5.1430077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk C. F., Foriers A., Van den Brande J. L., Pipeleers D. G. Evidence for the presence of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors on rat pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1784–1788. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk C. F., Heylen L., Van den Brande J. L., Pipeleers D. G. Direct effect of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I on the secretory activity of rat pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia. 1990 Nov;33(11):649–653. doi: 10.1007/BF00400565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1768–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI112500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Waldvogel M., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Effect of trypsin treatment of rat adipocytes on biological effects and binding of insulin and insulin-like growth factors: further evidence for the action of insulin-like growth factors through the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]