Abstract
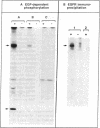
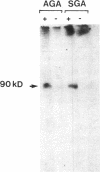
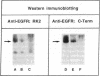
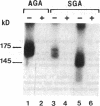
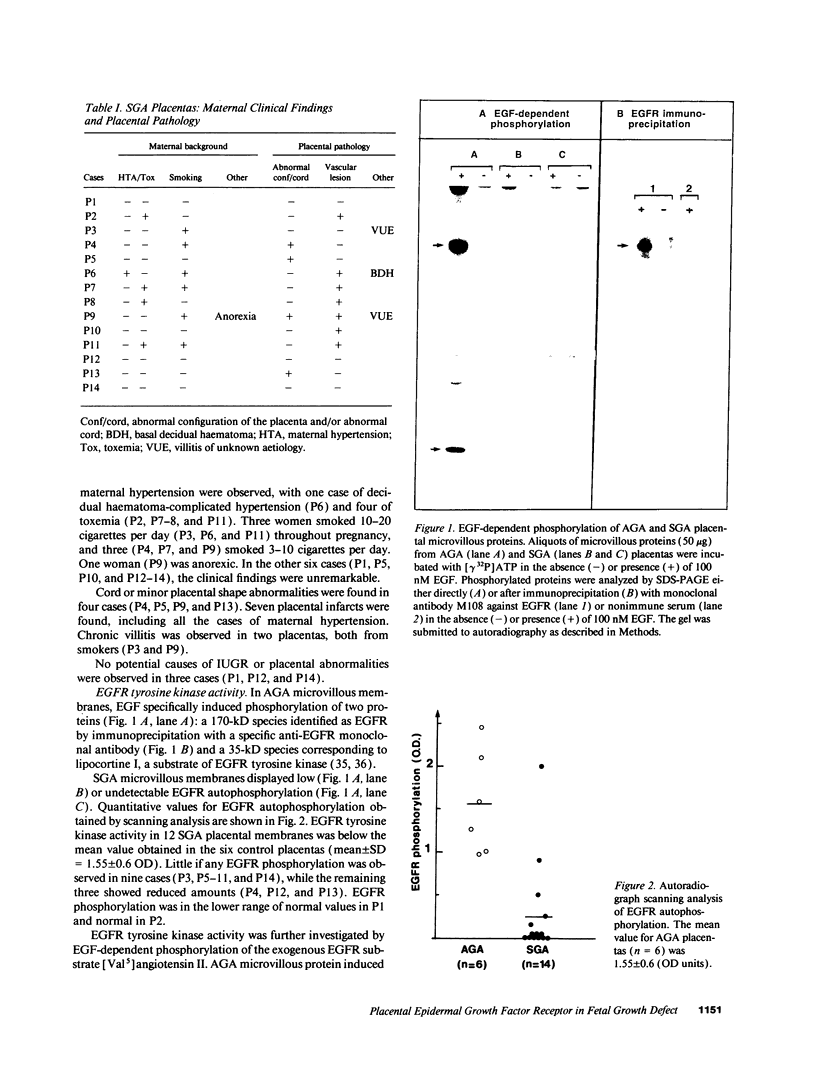
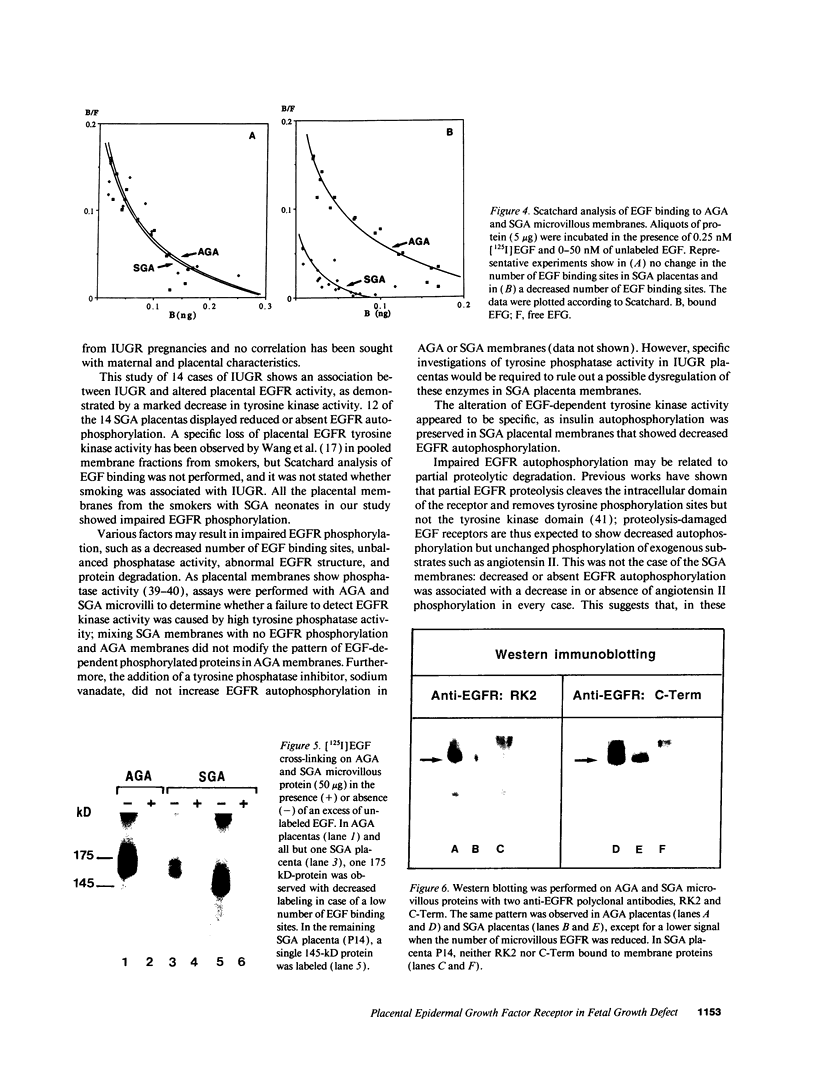
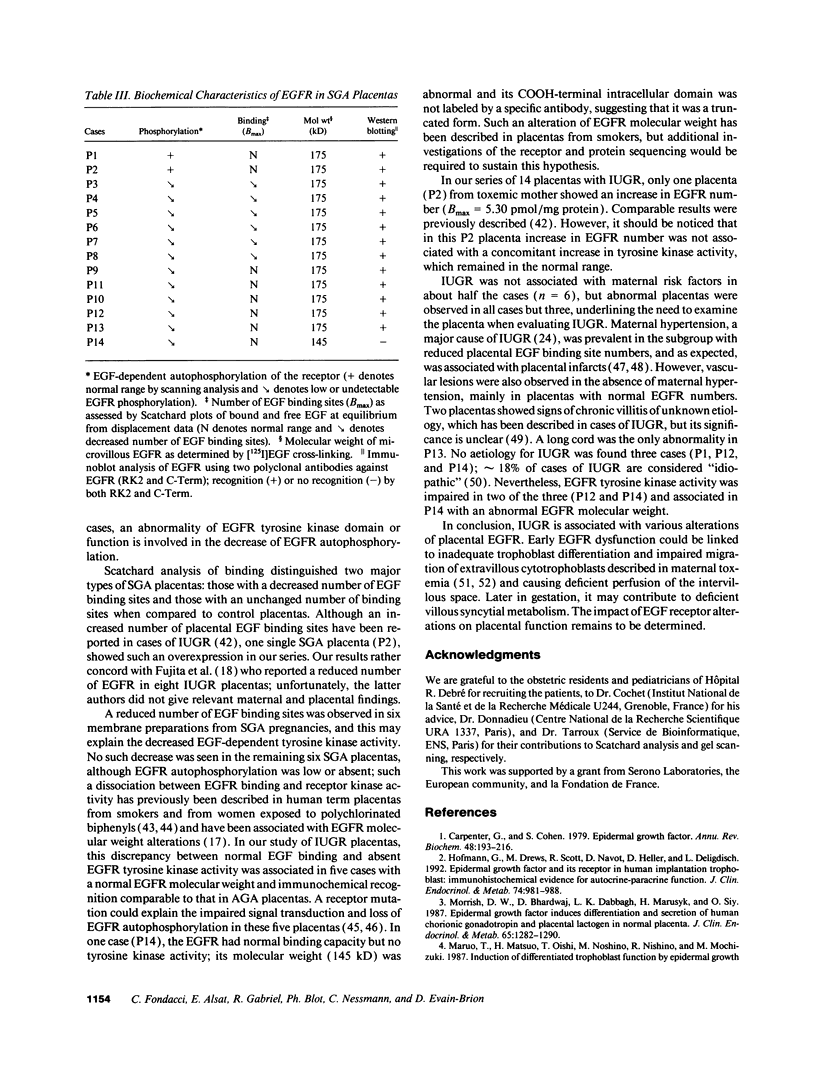
We studied human placental microvillous EGF receptor (EGFR) and its relationship with maternal and placental features in 14 cases of intrauterine growth retardation. Placental EGFR phosphorylation was significantly decreased or absent in 12 cases of small for gestational age neonates, as shown by SDS-PAGE, autoradiography, and scanning analysis. Specific [125I]EGF binding and Scatchard plots of the binding data showed a decreased number of EGFR in 6 of the 12 cases, with a mean maximal binding capacity of 1.09 +/- 0.32 pmol/mg for high affinity sites (mean control value = 2.30 +/- 0.23 pmol/mg). Most of the hypertensive women and smokers belonged to this subgroup. In three of the remaining six cases of small gestational age placentas with low EGFR phosphorylation, there was no maternal pathology or significant parenchymatous placental lesions. Five showed a 175-kD EGFR species when probed by [125I]EGF cross-linking and Western blotting with RK2 and C-Term, two polyclonal anti-EGFR antibodies, suggesting abnormal transduction of the EGF-induced signal. The sixth placenta yielded a single 145-kD EGFR band consistent with an abnormal EGFR structure; Western blot analysis showed no immunoreactive band. In conclusion, maternal and placental pathologies in intrauterine growth retardation are associated with various alterations of placental EGFR, pointing out the importance of EGFR ligands in the regulatory pathway of placental and fetal growth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht E. D., Pepe G. J. Placental steroid hormone biosynthesis in primate pregnancy. Endocr Rev. 1990 Feb;11(1):124–150. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-1-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen M. C. Developmental outcome and followup of the small for gestational age infant. Semin Perinatol. 1984 Apr;8(2):123–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsat E., Bouali Y., Goldstein S., Malassiné A., Laudat M. H., Cedard L. Characterization of specific low-density lipoprotein binding sites in human term placental microvillous membranes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Nov-Dec;28(3):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsat E., Haziza J., Evain-Brion D. Increase in epidermal growth factor receptor and its messenger ribonucleic acid levels with differentiation of human trophoblast cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Jan;154(1):122–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsat E., Mirlesse V., Fondacci C., Dodeur M., Evain-Brion D. Parathyroid hormone increases epidermal growth factor receptors in cultured human trophoblastic cells from early and term placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Aug;73(2):288–295. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-2-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Althabe O., Labarrere C. Chronic villitis of unknown aetiology and intrauterine growth-retarded infants of normal and low ponderal index. Placenta. 1985 Jul-Aug;6(4):369–373. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnea E. R., Feldman D., Kaplan M., Morrish D. W. The dual effect of epidermal growth factor upon human chorionic gonadotropin secretion by the first trimester placenta in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Oct;71(4):923–928. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-4-923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. A., Chase R., Ulep E., Scommegna A., Benveniste R. Ontogenesis and characteristics of epidermal growth factor receptors in human placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Dec 15;147(8):932–939. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. F., Kurachi H., Fujita Y., Terakawa N., Miyake A., Tanizawa O. Changes in epidermal growth factor receptor and its messenger ribonucleic acid levels in human placenta and isolated trophoblast cells during pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1171–1177. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Schievella A. R., Jost C. A., Erikson R. L., Neel B. G. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Brugge J. S. Characterization of structural domains of the human epidermal growth factor receptor obtained by partial proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11534–11542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Kurachi H., Morishige K., Amemiya K., Terakawa N., Miyake A., Tanizawa O. Decrease in epidermal growth factor receptor and its messenger ribonucleic acid levels in intrauterine growth-retarded and diabetes mellitus-complicated pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jun;72(6):1340–1345. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyda H. J., Mathieu L., Lai W., Manchester D., Wang S. L., Ogilvie S., Shiverick K. T. Benzo(a)pyrene inhibits epidermal growth factor binding and receptor autophosphorylation in human placental cell cultures. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann G. E., Drews M. R., Scott R. T., Jr, Navot D., Heller D., Deligdisch L. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor in human implantation trophoblast: immunohistochemical evidence for autocrine/paracrine function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):981–988. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1569175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann G. E., Rao C. V., Carman F. R., Jr, Siddiqi T. A. 125I-human epidermal growth factor specific binding to placentas and fetal membranes from various pregnancy states. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Apr;117(4):485–490. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1170485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Szapary D., Komoriya A., Kris R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Kinetic parameters of the protein tyrosine kinase activity of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3053–3060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawagoe K., Akiyama J., Kawamoto T., Morishita Y., Mori S. Immunohistochemical demonstration of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors in normal human placental villi. Placenta. 1990 Jan-Feb;11(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy B., Lefort F. A propos du poids et de la taille des nouveau-nés à la naissance. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Jun-Jul;66(6):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W. L., Jr, Boyd F. T., Clarke D. W., Raizada M. K., Hart C., LeRoith D. Development of brain insulin receptors: structural and functional studies of insulin receptors from whole brain and primary cell cultures. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):25–35. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruo T., Matsuo H., Murata K., Mochizuki M. Gestational age-dependent dual action of epidermal growth factor on human placenta early in gestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Nov;75(5):1362–1367. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.5.1430098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruo T., Matsuo H., Oishi T., Hayashi M., Nishino R., Mochizuki M. Induction of differentiated trophoblast function by epidermal growth factor: relation of immunohistochemically detected cellular epidermal growth factor receptor levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Apr;64(4):744–750. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrish D. W., Bhardwaj D., Dabbagh L. K., Marusyk H., Siy O. Epidermal growth factor induces differentiation and secretion of human chorionic gonadotropin and placental lactogen in normal human placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Dec;65(6):1282–1290. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-6-1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nessmann-Emmanuelli C., Sturbois G., Kone-Pale B., Goujard J., Bréart G., Sureau C., Lepage F. Examen macroscopique de placenta frais. Analyse statistique de 1200 cas. Confrontation avec la pathologie maternelle et néo-natale. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1976 Apr-May;5(3):397–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijnenborg R. Establishment of uteroplacental circulation. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1988;28(6B):1581–1586. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19881004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent S. A., Lemoine N. R. The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1992;4(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(92)90002-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. V., Ramani N., Chegini N., Stadig B. K., Carman F. R., Jr, Woost P. G., Schultz G. S., Cook C. L. Topography of human placental receptors for epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1705–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Honegger A. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Cytoplasmic domains determine signal specificity, cellular routing characteristics and influence ligand binding of epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2943–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Allosteric regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2067–2072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets E. E., Giugni T. D., Coates G. G., Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Epidermal growth factor dependent phosphorylation of a 35-kilodalton protein in placental membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1164–1172. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara G. I., Nelson K. G., Wong T. K., Lucier G. W. Decreased human birth weights after in utero exposure to PCBs and PCDFs are associated with decreased placental EGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation capacity. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):572–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H. Protein tyrosine dephosphorylation and signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Dec;14(12):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine-Braun K. A., Hollenberg M. D., Fraser E., Northup J. K. Isolation of a major human placental substrate for the epidermal growth factor (urogastrone) receptor kinase: immunological cross-reactivity with transducin and sequence homology with lipocortin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Dec;259(2):262–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. L., Lucier G. W., Everson R. B., Sunahara G. I., Shiverick K. T. Smoking-related alterations in epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors in human placenta. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Damsky C. H., Chiu K., Roberts J. M., Fisher S. J. Preeclampsia is associated with abnormal expression of adhesion molecules by invasive cytotrophoblasts. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):950–960. doi: 10.1172/JCI116316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]