Abstract
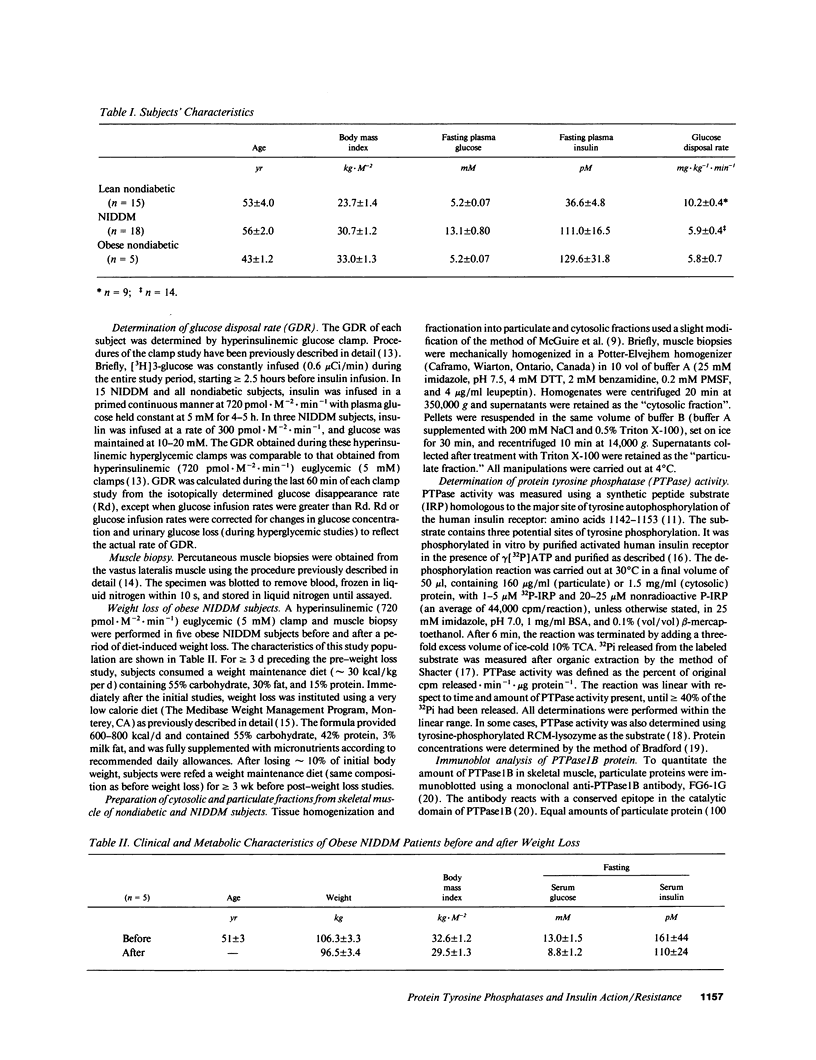
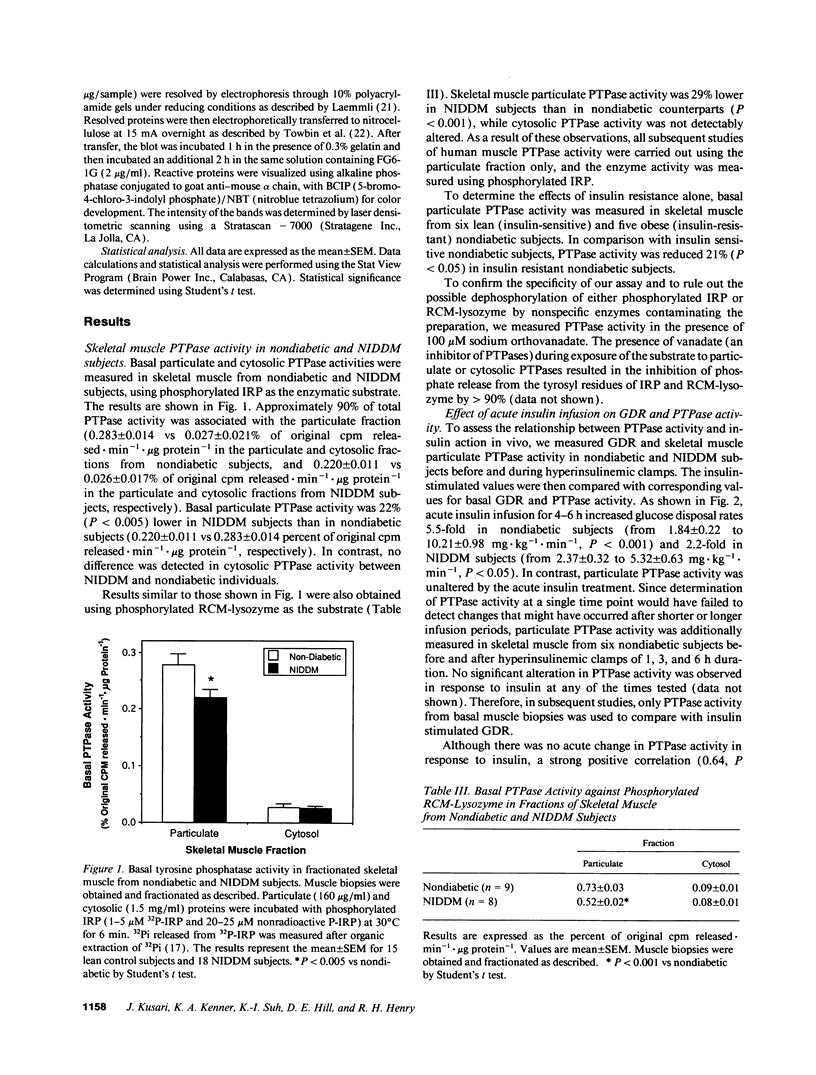
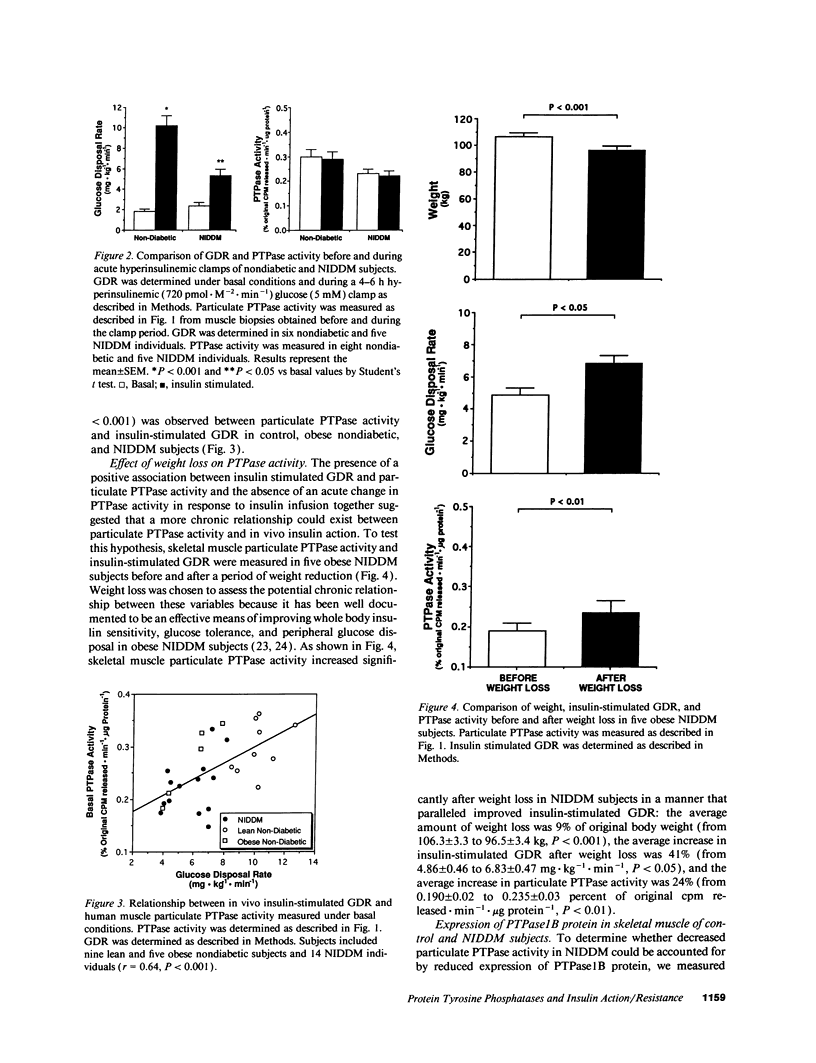
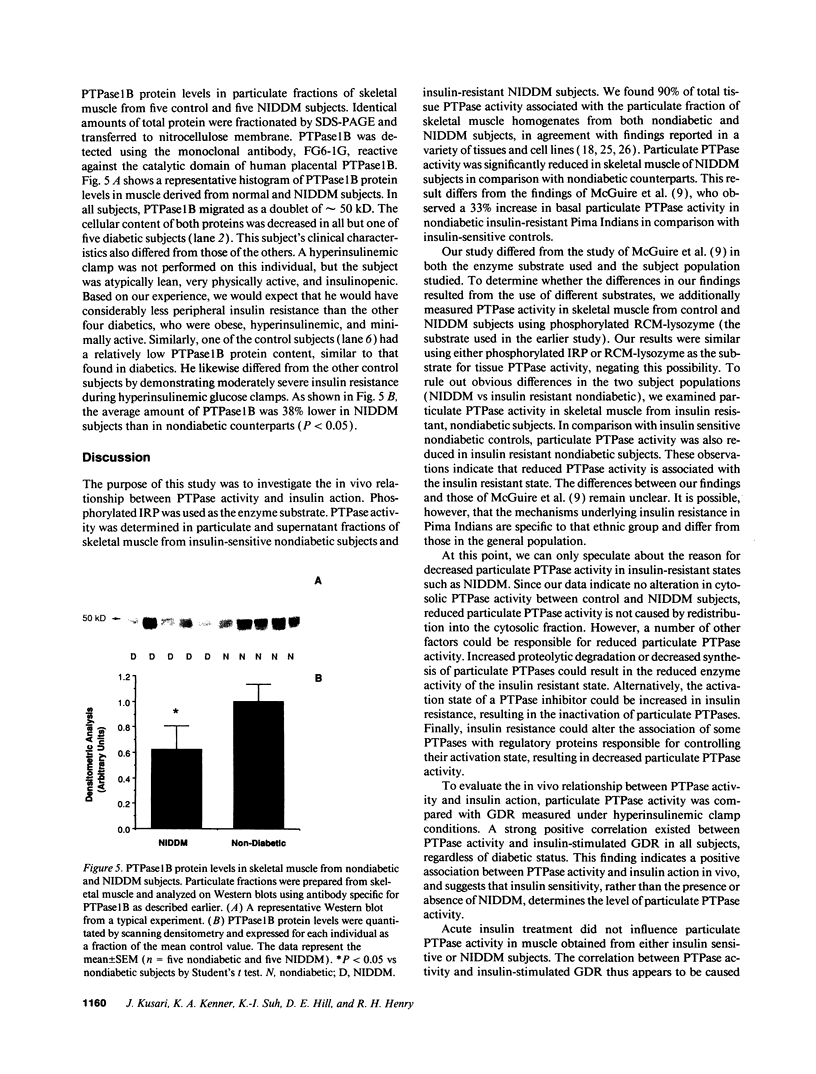
Particulate and cytosolic protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) activity was measured in skeletal muscle from 15 insulin-sensitive subjects and 5 insulin-resistant nondiabetic subjects, as well as 18 subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Approximately 90% of total PTPase activity resided in the particulate fraction. In comparison with lean nondiabetic subjects, particulate PTPase activity was reduced 21% (P < 0.05) and 22% (P < 0.005) in obese nondiabetic and NIDDM subjects, respectively. PTPase1B protein levels were likewise decreased by 38% in NIDDM subjects (P < 0.05). During hyperinsulinemic glucose clamps, glucose disposal rates (GDR) increased approximately sixfold in lean control and twofold in NIDDM subjects, while particulate PTPase activity did not change. However, a strong positive correlation (r = 0.64, P < 0.001) existed between particulate PTPase activity and insulin-stimulated GDR. In five obese NIDDM subjects, weight loss of approximately 10% body wt resulted in a significant and corresponding increase in both particulate PTPase activity and insulin-stimulated GDR. These findings indicate that skeletal muscle particulate PTPase activity and PTPase1B protein content reflect in vivo insulin sensitivity and are reduced in insulin resistant states. We conclude that skeletal muscle PTPase activity is involved in the chronic, but not acute regulation of insulin action, and that the decreased enzyme activity may have a role in the insulin resistance of obesity and NIDDM.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Pinault F. M. Activation of membrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase involving cAMP- and Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6696–6700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Meelheim D., Flickinger E. G., Thomas F., Jenquin M., Silverman J. F., Khazanie P. G., Sinha M. K. Studies on the mechanism of insulin resistance in the liver from humans with noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes, insulin receptor structure, and kinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):249–258. doi: 10.1172/JCI112558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Raju S. M., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Dohm G. L. Insulin receptor kinase in human skeletal muscle from obese subjects with and without noninsulin dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1330–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI112958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidenberg G. R., Henry R. R., Klein H. H., Reichart D. R., Olefsky J. M. Decreased kinase activity of insulin receptors from adipocytes of non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):240–250. doi: 10.1172/JCI112789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Dohm G. L., Leggett-Frazier N., Elton C. W., Tapscott E. B., Pories W. P., Caro J. F. Restoration of insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of morbidly obese patients after weight loss. Effect on muscle glucose transport and glucose transporter GLUT4. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):701–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI115638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J. Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and the regulation of insulin action. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Jan;48(1):33–42. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240480107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Polonsky K. S., Beltz W. F., Griver K., Wallace P., Brechtel G., Henry R. R. Effects of weight loss and reduced hyperglycemia on the kinetics of insulin secretion in obese non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jun;70(6):1594–1602. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-6-1594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauguel-de Mouzon S., Peraldi P., Alengrin F., Van Obberghen E. Alteration of phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity in tissues from diabetic and pregnant rats. Endocrinology. 1993 Jan;132(1):67–74. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.1.8419148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. R., Gumbiner B., Flynn T., Thorburn A. W. Metabolic effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on fate of intracellular glucose in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):149–156. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. R., Wallace P., Olefsky J. M. Effects of weight loss on mechanisms of hyperglycemia in obese non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1986 Sep;35(9):990–998. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.9.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. J., Sale G. J. Assay of phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase using synthetic peptide 1142-1153 of the insulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 12;237(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao K., Hoffman R. D., Lane M. D. Phosphotyrosyl turnover in insulin signaling. Characterization of two membrane-bound pp15 protein tyrosine phosphatases from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6544–6553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire M. C., Fields R. M., Nyomba B. L., Raz I., Bogardus C., Tonks N. K., Sommercorn J. Abnormal regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase activities in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant humans. Diabetes. 1991 Jul;40(7):939–942. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerovitch J., Rothenberg P., Shechter Y., Bonner-Weir S., Kahn C. R. Vanadate normalizes hyperglycemia in two mouse models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1286–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI115131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Garvey W. T., Henry R. R., Brillon D., Matthaei S., Freidenberg G. R. Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetes. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):86–105. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E. Organic extraction of Pi with isobutanol/toluene. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Caro J. F. Insulin-receptor kinase activity of adipose tissue from morbidly obese humans with and without NIDDM. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):620–625. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A. W., Gumbiner B., Bulacan F., Wallace P., Henry R. R. Intracellular glucose oxidation and glycogen synthase activity are reduced in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetes independent of impaired glucose uptake. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):522–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI114468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truglia J. A., Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Insulin resistance: receptor and post-binding defects in human obesity and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1985 Aug 23;79(2B):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90580-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




