Abstract
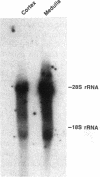
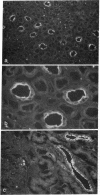
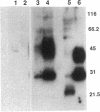
We recently cloned a cDNA of the collecting duct apical membrane water channel of rat kidney, which is important for the formation of concentrated urine (Fushima, K., S. Uchida, Y. Hara, Y. Hirata, F. Marumo, and S. Sasaki. 1993. Nature [Lond.]. 361:549-552). Since urine concentrating ability varies among mammalian species, we examined whether an homologous protein is present in human kidney. By screening a human kidney cDNA library, we isolated a cDNA clone, designated human aquaporin of collecting duct (hAQP-CD), that encodes a 271-amino acid protein with 91% identity to rat AQP-CD. mRNA expression of hAQP-CD was predominant in the kidney medulla compared with the cortex, immunohistochemical staining of hAQP-CD was observed only in the collecting duct cells, and the staining was dominant in the apical domain. Functional expression study in Xenopus oocytes confirmed that hAQP-CD worked as a water channel. Western blot analysis of human kidney medulla indicated that the molecular mass of hAQP-CD is 29 kD, which is the same mass expected from the amino acid sequence. Chromosomal mapping of the hAQP-CD gene assigned its location to chromosome 12q13. These results could be important for future studies of the pathophysiology of human urinary concentration mechanisms in normal and abnormal states.
Full text
PDF

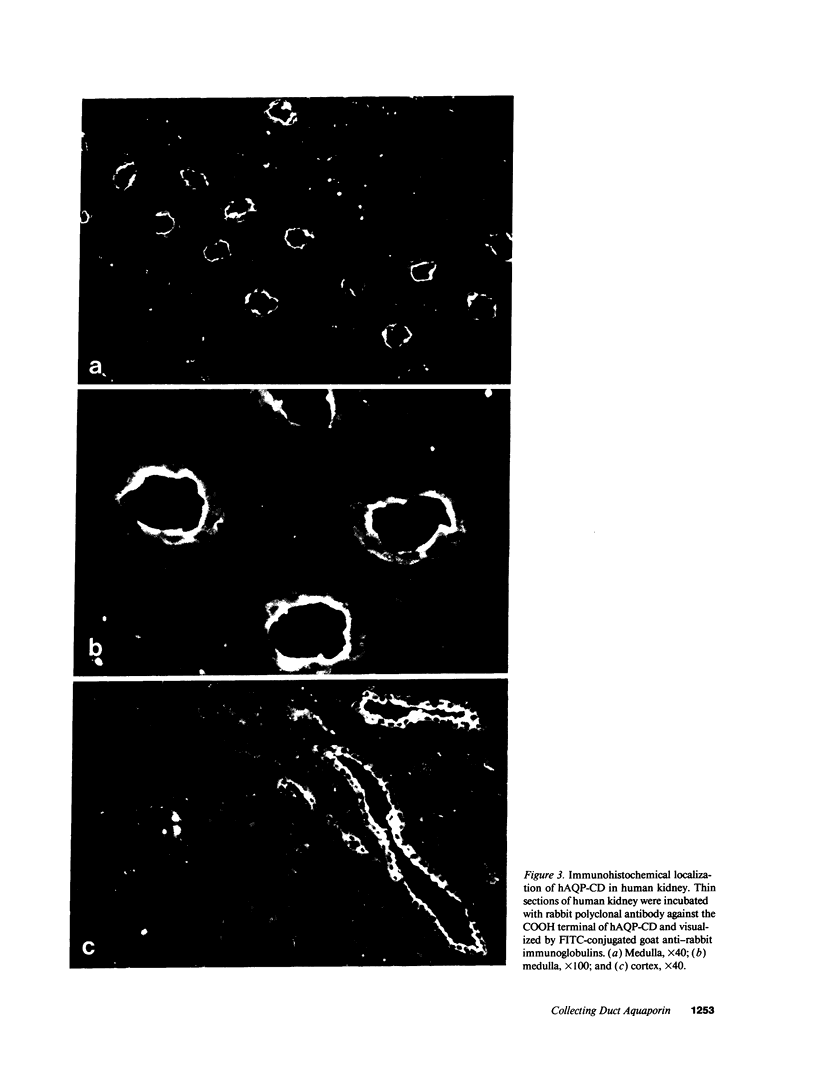
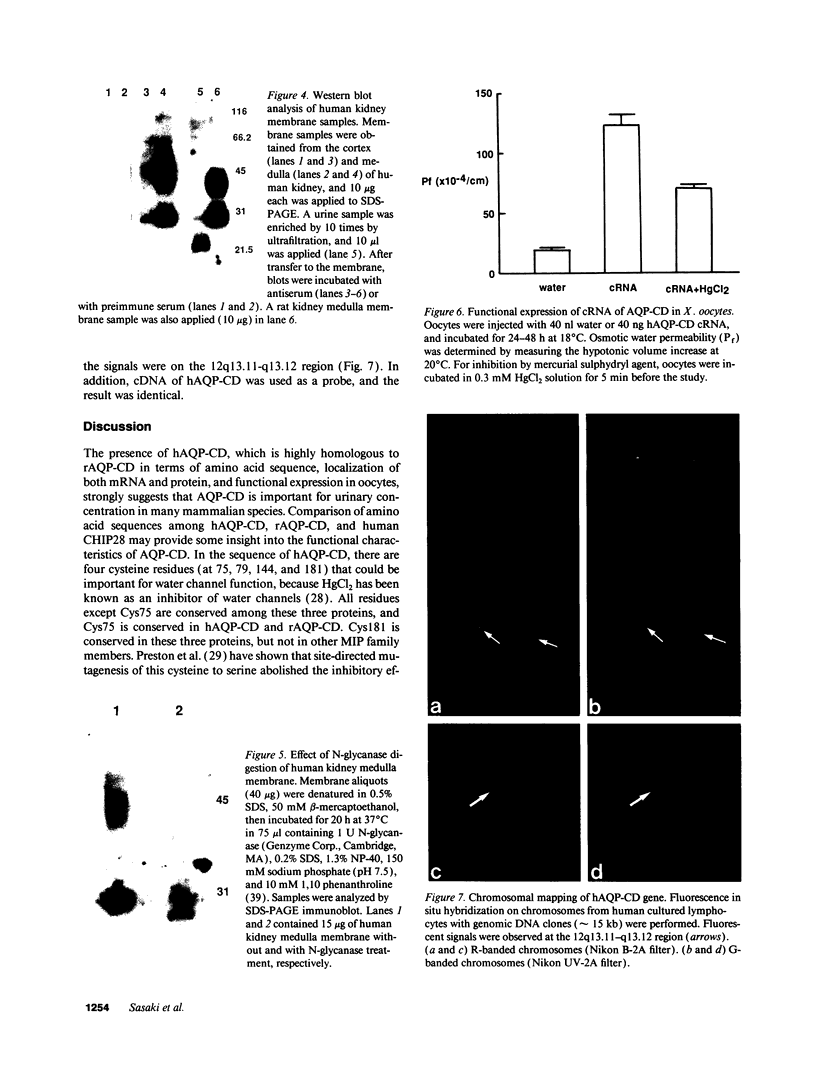


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Zahid G., Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L., Andreoli T. E. Effect of antidiuretic hormone on water and solute permeation, and the activation energies for these processes, in mammalian cortical collecting tubules: evidence for parallel ADH-sensitive pathways for water and solute diffusion in luminal plasma membranes. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):103–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01869401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E., Saier M. H., Jr A common ancestor for bovine lens fiber major intrinsic protein, soybean nodulin-26 protein, and E. coli glycerol facilitator. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):185–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90731-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell N. H., Clark C. M., Jr, Avery S., Sinha T., Trygstad C. W., Allen D. O. Demonstration of a defect in the formation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in vasopressin-resistant diabetes insipidus. Pediatr Res. 1974 Apr;8(4):223–230. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197404000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Smith B. L., Kuhajda F. P., Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15634–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehring G. R., Lagos N., Zampighi G. A., Hall J. E. Phosphorylation modulates the voltage dependence of channels reconstituted from the major intrinsic protein of lens fiber membranes. J Membr Biol. 1992 Feb;126(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00233462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
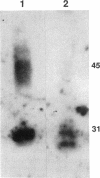
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland D., Russell P. Phosphorylation of lens fiber cell membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Yancey S. B., Cline J., Revel J. P., Horwitz J. The major intrinsic protein (MIP) of the bovine lens fiber membrane: characterization and structure based on cDNA cloning. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S. Antidiuretic hormone moves membranes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F375–F382. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Jr, Handler J. S. The role of membrane turnover in the water permeability response to antidiuretic hormone. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;103(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01993980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Jr, Strange K., Zeidel M. L. Current understanding of the cellular biology and molecular structure of the antidiuretic hormone-stimulated water transport pathway. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI115263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori T., Takahashi E., Ayusawa D., Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Seno T. Regional assignment of the human thymidylate synthase (TS) gene to chromosome band 18p11.32 by nonisotopic in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;85(6):576–580. doi: 10.1007/BF00193577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lampe P. D., Hur K. C., Louis C. F., Johnson R. G. A lens intercellular junction protein, MP26, is a phosphoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1334–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe P. D., Johnson R. G. Amino acid sequence of in vivo phosphorylation sites in the main intrinsic protein (MIP) of lens membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. M., Balfe J. W., Selander T., Ray P. N., Clarke J. T. Autosomal recessive inheritance of vasopressin-resistant diabetes insipidus. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jan;38(1):90–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolait S. J., O'Carroll A. M., McBride O. W., Konig M., Morel A., Brownstein M. J. Cloning and characterization of a vasopressin V2 receptor and possible link to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):336–339. doi: 10.1038/357336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I. Transport of water and urea in red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C195–C203. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F. Sites of hormone action in the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F159–F164. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohzeki T., Igarashi T., Okamoto A. Familial cases of congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus type II: Remarkable increment of urinary adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in response to antidiuretic hormone. J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;104(4):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff J., Handler J. The role of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in the action of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):757–768. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Metzenberg A., Das S., Jing B., Gitschier J. Mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene are associated with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):103–106. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Jung J. S., Guggino W. B., Agre P. The mercury-sensitive residue at cysteine 189 in the CHIP28 water channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Agre P. Erythrocyte Mr 28,000 transmembrane protein exists as a multisubunit oligomer similar to channel proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6407–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi E., Yamakawa K., Nakamura Y., Hori T. A high-resolution cytogenetic map of human chromosome 3: localization of 291 new cosmid markers by direct R-banding fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90018-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S. Mechanisms and regulation of water permeability in renal epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):C837–C850. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.5.C837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Stetson D. L., Lewis S. A. ADH action: evidence for a membrane shuttle mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:106–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Pisano M. M., Chepelinsky A. B. Tandem sequence repeats in transmembrane channel proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):170–171. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Dreesen J. C., Verdijk M., Knoers N. V., Monnens L. A., Rocchi M., van Oost B. A. Mutations in the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) associated with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):99–102. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]