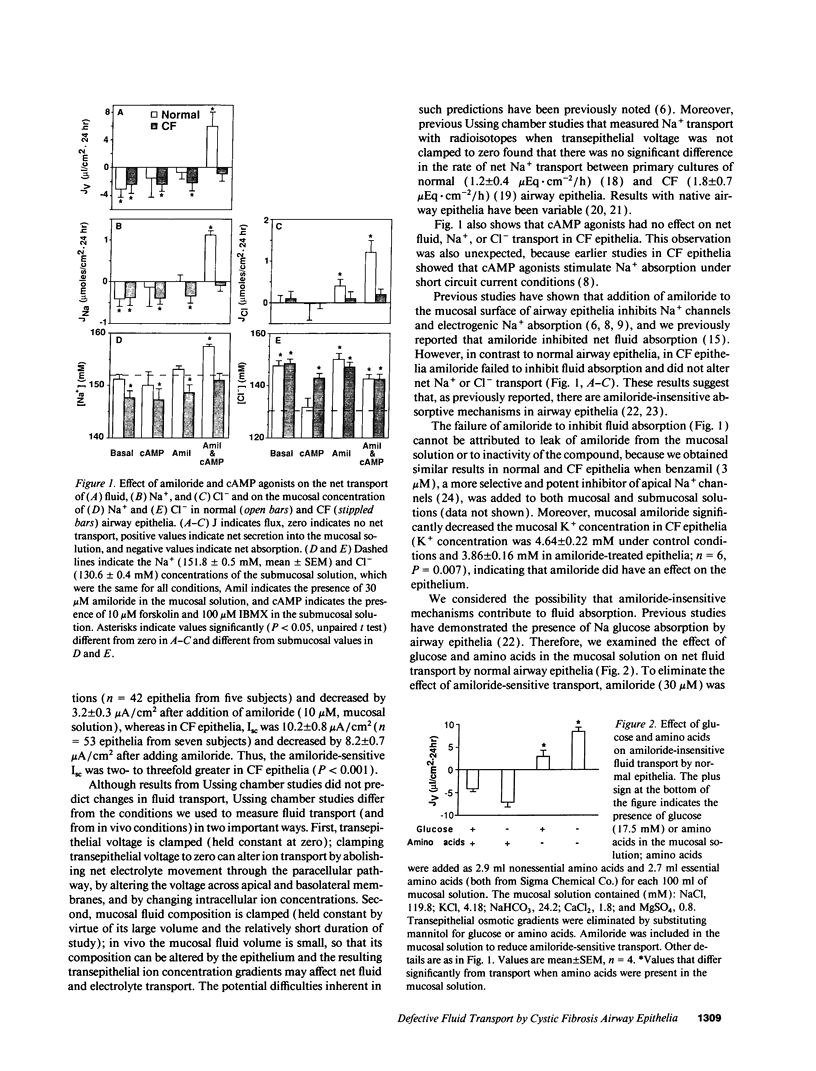
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis (CF) airway epithelia exhibit defective transepithelial electrolyte transport: cAMP-stimulated Cl- secretion is abolished because of the loss of apical membrane cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl- channels, and amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption is increased two- to threefold because of increased amiloride-sensitive apical Na+ permeability. These abnormalities are thought to alter respiratory tract fluid, thereby contributing to airway disease, the major source of mortality in this genetic disease. However, the underlying hypothesis, that fluid transport is abnormal in CF airway epithelia, has not been tested. Most conjecture about fluid transport is based on measurements of Na+ and Cl- transport performed under short circuit conditions in Ussing chambers. But such studies differ from in vivo conditions in that transepithelial voltage and mucosal fluid composition are held constant. Therefore, we measured fluid transport and mucosal electrolyte composition in primary cultures of CF airway epithelia without holding transepithelial voltage and ion concentration gradients at zero. In normal epithelia, cAMP agonists plus amiloride stimulated NaCl and fluid secretion. In CF epithelia, cAMP agonists failed to stimulate fluid or electrolyte secretion, changes consistent with the loss of CFTR Cl- channels. But in striking contrast to predictions based on Ussing chamber studies, CF epithelia absorbed fluid at a rate no greater than normal epithelia. Moreover, amiloride, which inhibits Na+ channels, failed to inhibit fluid absorption by CF epithelia. These results have important implications for understanding the pathogenesis of CF airway disease and for the design and evaluation of therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton E. W., Rogers D. F., Logan-Sinclair R., Yacoub M., Barnes P. J., Geddes D. M. Bioelectric properties of cystic fibrosis airways obtained at heart-lung transplantation. Thorax. 1992 Dec;47(12):1010–1014. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.12.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Welsh M. J. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- App E. M., King M., Helfesrieder R., Köhler D., Matthys H. Acute and long-term amiloride inhalation in cystic fibrosis lung disease. A rational approach to cystic fibrosis therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):605–612. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cotton C. U., Gatzy J. T., Knowles M. R., Yankaskas J. R. Evidence for reduced Cl- and increased Na+ permeability in cystic fibrosis human primary cell cultures. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:77–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNICK W. S., BARBERO G. J. Composition of tracheobronchial secretions in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and bronchiectasis. Pediatrics. 1959 Nov;24:739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Cystic fibrosis: molecular biology and therapeutic implications. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):774–779. doi: 10.1126/science.1375392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Uchic M., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Kornhaus J., Grantham J. A., Donoso V., Mangoo-Karim R., Evan A., McAteer J. Chemical modification of cell proliferation and fluid secretion in renal cysts. Kidney Int. 1989 Jun;35(6):1379–1389. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Finkbeiner W. E., Widdicombe J. H., McCray P. B., Jr, Miller S. S. Altered fluid transport across airway epithelium in cystic fibrosis. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):424–427. doi: 10.1126/science.8211164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris L., Quinton P. M. Evidence for electrogenic Na-glucose cotransport in tracheal epithelium. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Oct;415(1):118–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00373149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Church N. L., Waltner W. E., Yankaskas J. R., Gilligan P., King M., Edwards L. J., Helms R. W., Boucher R. C. A pilot study of aerosolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1189–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS L. W., SPECTOR S., LEMM J., POTTER J. L. STUDIES ON PULMONARY SECRETIONS. I. THE OVER-ALL CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF PULMONARY SECRETIONS FROM PATIENTS WITH CYSTIC FIBROSIS, BRONCHIECTASIS, AND LARYNGECTOMY. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 Aug;88:199–204. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.88.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangoo-Karim R., Uchic M. E., Grant M., Shumate W. A., Calvet J. P., Park C. H., Grantham J. J. Renal epithelial fluid secretion and cyst growth: the role of cyclic AMP. FASEB J. 1989 Dec;3(14):2629–2632. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.14.2480260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton P. M. Cystic fibrosis: a disease in electrolyte transport. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2709–2717. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2197151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:609–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.003141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. J., Welsh M. J. Fluid and electrolyte transport by cultured human airway epithelia. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1590–1597. doi: 10.1172/JCI116365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Welsh M. J., Stoff J. S., Frizzell R. A. Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: I. Role of intracellular c AMP levels. J Membr Biol. 1982;70(3):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Anderson M. P., Rich D. P., Berger H. A., Denning G. M., Ostedgaard L. S., Sheppard D. N., Cheng S. H., Gregory R. J., Smith A. E. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator: a chloride channel with novel regulation. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90196-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Electrolyte transport by airway epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1143–1184. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Molecular mechanisms of CFTR chloride channel dysfunction in cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1251–1254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90353-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Boucher R. C. Sodium transport and intracellular sodium activity in cultured human nasal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C319–C331. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Boucher R. C. Transcellular sodium transport in cultured cystic fibrosis human nasal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C332–C341. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. L., Sivarajah K., Wu R., Nettesheim P., Eling T. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins by isolated and cultured airway epithelial cells. Exp Lung Res. 1986;10(1):101–114. doi: 10.3109/01902148609057506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]