Abstract
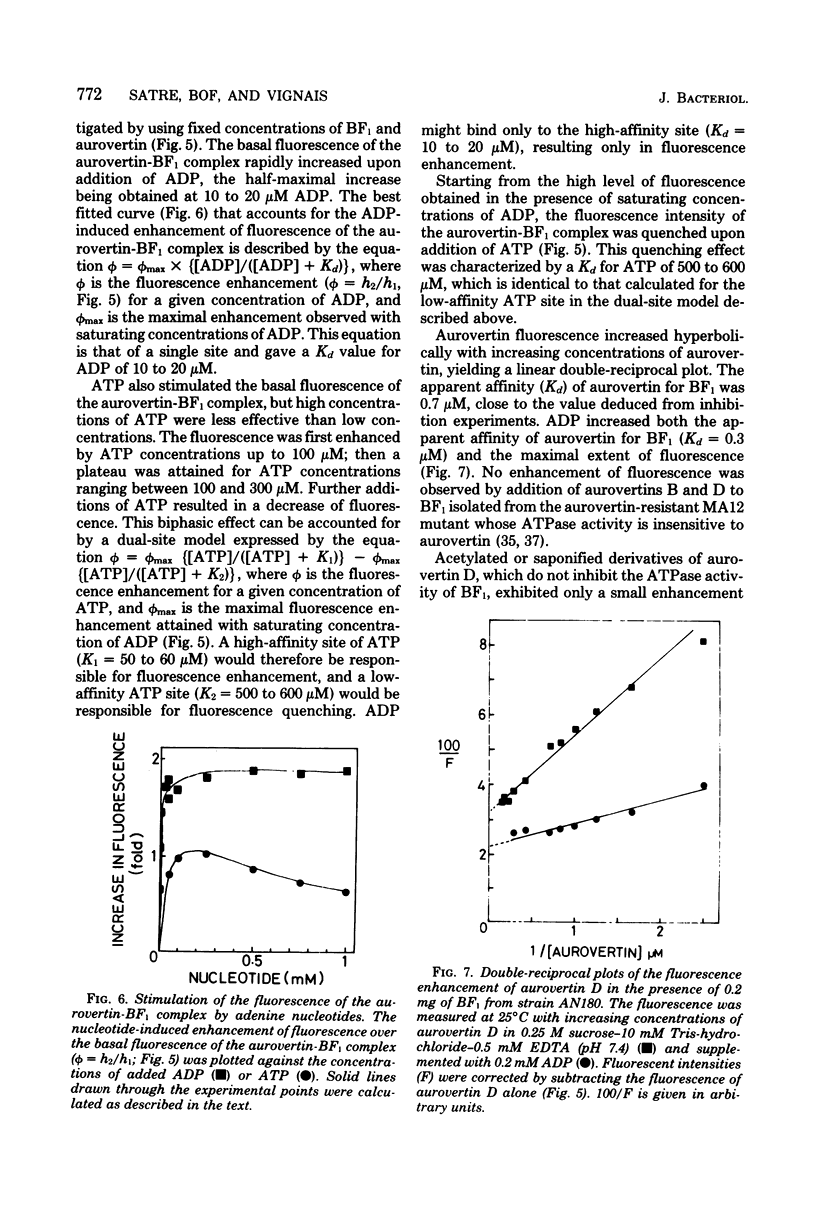
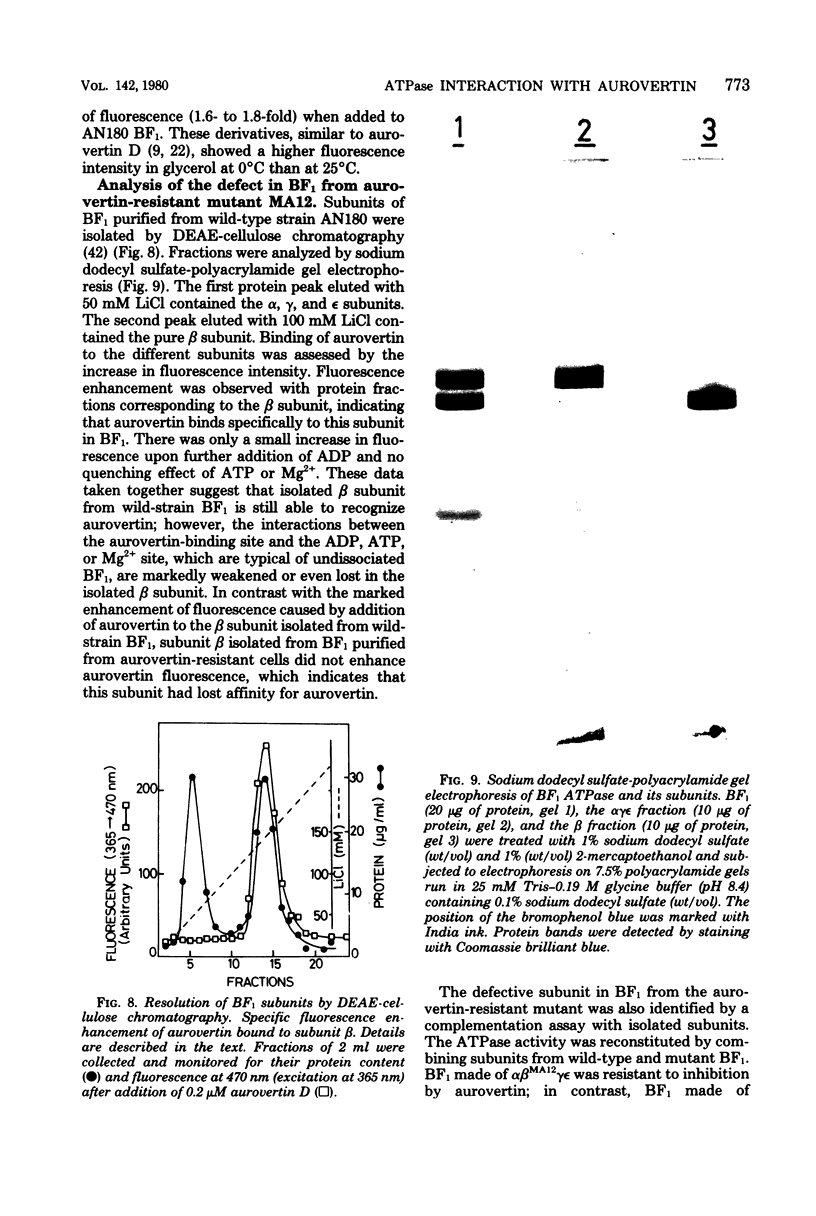
Aurovertins B and D inhibited the adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity of soluble Escherichia coli coupling factor ATPase (BF1) isolated from wile-type E. coli K-12. Half inhibition was obtained with 2 microns aurovertin B and 0.9 microns aurovertin D. Aurovertins B and D had no inhibitory effect on BF1 isolated from the aurovertin-resistant E. coli mutant MA12. Acetylation or saponification of aurovertin D yielded a derivative which was devoid of inhibitory effect on BF1. Citreoviridin also inhibited wild-type BF1 but with much less efficiency (half inhibition at 60 microns) than aurovertin. Citreoviridin had no effect on the aurovertin-resistant BF1. The fluorescence intensity of aurovertins B and D was markedly enhanced upon addition to purified BF1. There was no enhancement of fluorescence when the aurovertins were added to BF1 isolated from the aurovertin-resistant mutant. The fluorescence of the aurovertin-BF1 complex was enhanced by adenosine 5'-diphosphate and by low concentrations of adenosine 5'-triphosphate. The adenosine 5'-diphosphate-enhanced fluorescence of the aurovertin-BF1 complex was quenched by high concentrations of adenosine 5'-triphosphate or by MG2+. Aurovertin bound selectively to the beta subunit of BF1 isolated from wile-type cells. By complementation assays in vitro, using a reconstituted system made of subunits isolated from wild-type and aurovertin-resistant BF1, it was shown that the altered peptide in aurovertin-resistant BF1 was the beta subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolfsen R., Moudrianakis E. N. Molecular polymorphism and mechanisms of activation and deactivation of the hydrolytic function of the coupling factor of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4163–4170. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechey R. B., Hubbard S. A., Linnett P. E., Mitchell A. D., Munn E. A. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of adenosine triphosphatase from submitochondrial particles. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):533–537. doi: 10.1042/bj1480533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Schrier P. I., Slater E. C. The binding of aurovertin to mitochondria, and its effect on mitochondrial respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 28;305(3):503–518. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragg P. D., Hou C. Purification and characterization of the inactive Ca2+, Mg2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase of the unc A- mutant Escherichia coli AN120. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):486–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K-12: the genetic and biochemical characterisations of a strain carrying a mutation in the uncB gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. M., Penefsky H. S. Energy-dependent enhancement of aurovertin fluorescence. An indicator of conformational changes in beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1090–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Penefsky H. S. Aurovertin, a fluorescent probe of conformational change in beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2746–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Fayle D. R., Gibson F., Radik J. Inhibition, by a protease inhibitor, of the solubilization of the F1-portion of the Mg2+-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.287-292.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., Koh Y., Dockter M. E., Schatz G. Aurovertin binds to the beta subunit of yeast mitochondrial ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8333–8335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Gibson F., Cox G. B. Membrane adenosine triphosphatases of prokaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:103–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D., Futai M. Reconstitution of a functional coupling factor from the isolated subunits of Escherichia coli F1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel R. E., Lardy H. A. Influence of aurovertin on mitochondrial ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4992–4995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., John P., Radda G. K. Tightly bound nucleotides of the energy-transducing ATPase, and their role in oxidative phosphorylation. I. The Paracoccus denitrificans system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 11;459(3):546–559. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Anraku Y. Membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Partial purification and properties. J Biochem. 1972 Mar;71(3):387–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARDY H. A., CONNELLY J. L., JOHNSON D. ANTIBIOTIC STUDIES. II. INHIBITION OF PHOSPHORYL TRANSFER IN MITOCHONDRIA BY OLIGOMYCIN AND AUROVERTIN. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1961–1968. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton D., Azzi A., Graziotti P. The use of the fluorescent probe aurovertin, to monitor energy linked conformational changes in mitochondrial ATPases. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnett P. E., Beechey R. B. Inhibitors of the ATP synthethase system. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:472–518. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnett P. E., Mitchell A. D., Beechey R. B., Baum H. A reiteration of the equation derived by Easson & Stedman (1936) and its application to the inhibition of mitochondrial energy-linked functions by the aurovertins [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1510–1511. doi: 10.1042/bst0051510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnett P. E., Mitchell A. D., Osselton M. D., Mulheirn L. J., Beechey R. B. Citreoviridin, a specific inhibitor of the mitochondiral adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):503–510. doi: 10.1042/bj1700503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melandri A. B., Fabbri E., Melandri B. A. Energy transduction in photosynthetic bacteria. VIII. Activation of the energy-transducing ATPase by inorganic phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 31;376(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller J. L., Rosing J., Slater E. C. The binding of aurovertin to isolated F1 (mitochondrial ATPase). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 17;462(2):422–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravizzini R. A., Lescano W. I., Vallejos R. H. Effect of aurovertin on energy transfer reactions in Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton A. M., Beechey R. B., Holloway C. T., Knight I. G. The effect of aurovertin on a soluble mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):54C–55C. doi: 10.1042/bj1040054c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roisin M. P., Kepes A. The membrane ATPase of Escherichia coli. I. Ion dependence and ATP-ADP exchange reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):333–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saphon S., Jackson J. B., Witt H. T. Electrical potential changes, H+ translocation and phosphorylation induced by short flash excitation in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 10;408(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satre M., Klein G., Vignais P. V. Isolation of Escherichia coli mutants with an adenosine triphosphatase insensitive to aurovertin. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):17–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.17-23.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satre M., Lunardi J., Pougeois R., Vignais P. V. Inactivation of Escherichia coli BF1-ATPase by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Chemical modification of the beta subunit. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3134–3140. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschoor G. J., van der Sluis P. R., Slater E. C. The binding of aurovertin to isolated beta subunit of F1 (mitochondrial ATPase). Stoicheiometry of beta subunit in F1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 17;462(2):438–449. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel G., Steinhart R. ATPase of Escherichia coli: purification, dissociation, and reconstitution of the active complex from the isolated subunits. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):208–216. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK B., COHEN J. Automatic analysis of tissue culture proteins with stable Folin reagents. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Sep;6:665–670. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Stadt R. J., van Dam K. Binding of aurovertin to phosphorylating submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 22;347(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Stadt R. J., van Dam K., Slater E. C. Interaction of aurovertin with submitochondrial particles, deficient in ATPase inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 22;347(2):224–239. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]