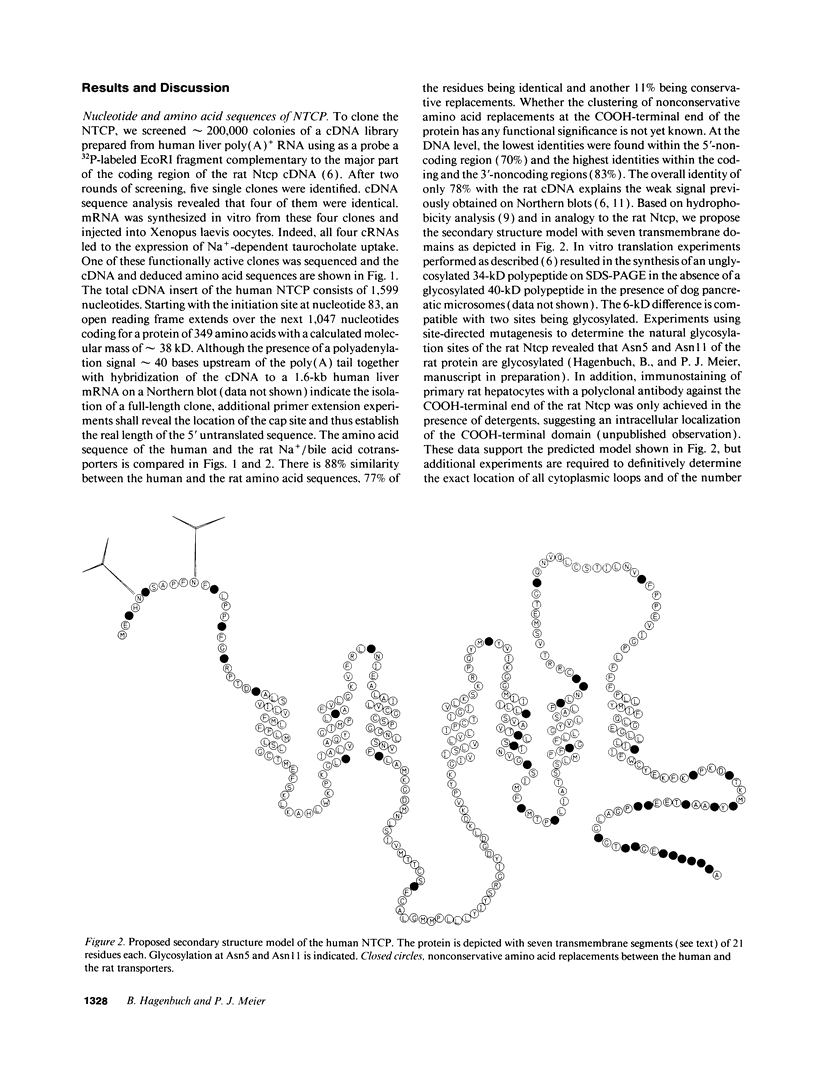
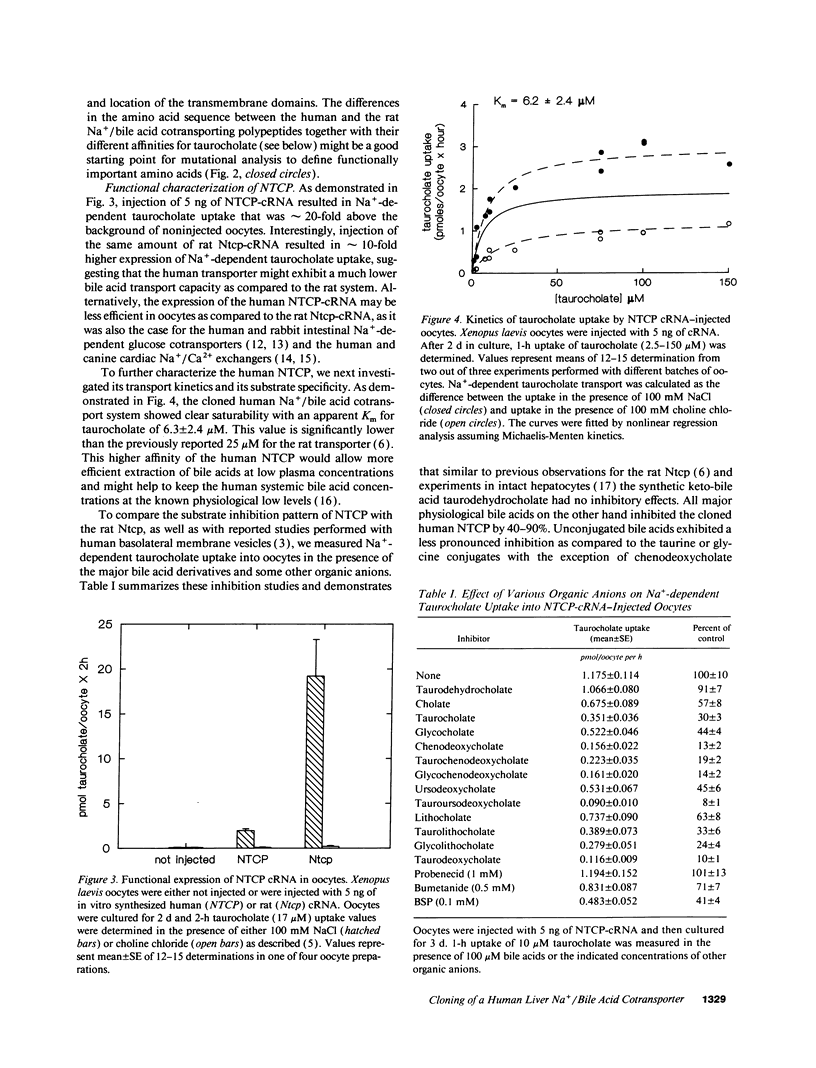
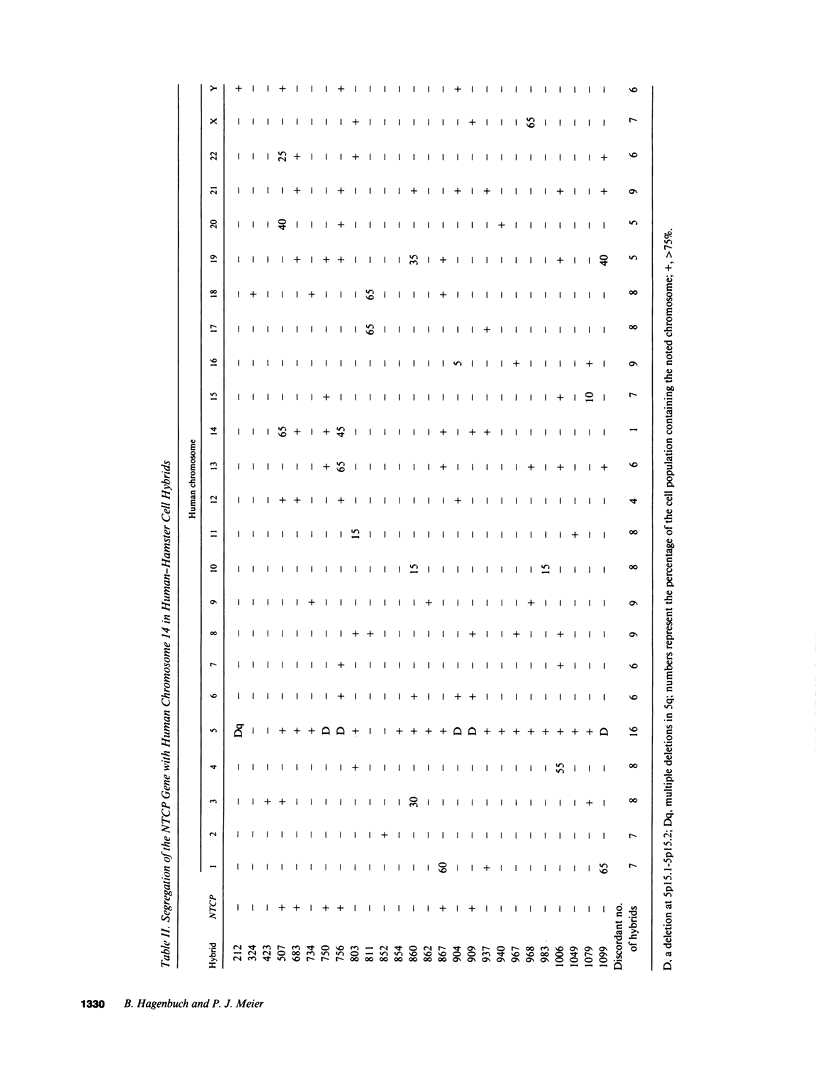
Abstract
We have used a cDNA probe from a cloned rat liver Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (Ntcp) to screen a human liver cDNA library. A 1,599-bp cDNA clone that encodes a human Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) was isolated. The human NTCP consists of 349 amino acids (calculated molecular mass of 38 kD) and exhibits 77% amino acid homology with the rat Ntcp. In vitro translation experiments indicate that the protein is glycosylated and has a molecular weight similar to the rat Ntcp. Injection of in vitro transcribed cRNA into Xenopus laevis oocytes resulted in the expression of Na(+)-dependent taurocholate uptake. Saturation kinetics indicated that the human NTCP has a higher affinity for taurocholate (apparent Km = 6 microM) than the previously cloned rat protein (apparent Km = 25 microM). NTCP-mediated taurocholate uptake into oocytes was inhibited by all major bile acid derivatives (100 microM), bumetanide (500 microM), and bromosulphophthalein (100 microM). Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from a panel of human/hamster somatic cell hybrids mapped the human NTCP gene to chromosome 14.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. L., Hagenbuch B., Ananthanarayanan M., Suchy F., Stieger B., Meier P. J. Phylogenic and ontogenic expression of hepatocellular bile acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):435–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimmer M., Ziegler K. The transport of bile acids in liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):75–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Lübbert H., Stieger B., Meier P. J. Expression of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5357–5360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Lowe P. J., Gosink E. Nature of taurodehydrocholic acid uptake in rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):G269–G274. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.2.G269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Turk E., Wright E. M. Homology of the human intestinal Na+/glucose and Escherichia coli Na+/proline cotransporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5748–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Wolkoff A. W., Meier P. J. Expression of the hepatocellular chloride-dependent sulfobromophthalein uptake system in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2146–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI115546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Wenninger K. E., Philipson K. D., Izumo S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4769–4773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll D. A., Longoni S., Philipson K. D. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1700476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak D. A., Ryckman F. C., Suchy F. J. Taurocholate transport by basolateral plasma membrane vesicles isolated from human liver. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):447–453. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke R. W., Stephens J. E., Scharschmidt B. F. Bile acid transport in cultured rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):G484–G492. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.6.G484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli B., Valantinas J., Meier P. J. Multispecificity of Na+-dependent taurocholate uptake in basolateral (sinusoidal) rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



