Abstract
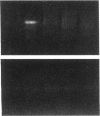
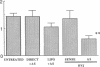
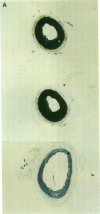
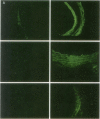
The cell cycle regulatory enzyme, cdk (cyclin-dependent kinase) 2 kinase, is activated in the rat carotid artery after balloon angioplasty injury, and may mediate smooth muscle proliferation. To test the hypothesis that inhibition of the expression of this key enzyme can inhibit intimal hyperplasia, we studied the effect of antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) against cdk 2 kinase administered by intraluminal delivery using hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ)-liposome-mediated transfer. The specificity of antisense cdk 2 ODN was confirmed by the observation that mRNA level of cdk 2 kinase in injured vessels was markedly diminished by the antisense ODN treatment. At 2 wk after transfection, antisense cdk 2 ODN treatment (15 microM) resulted in a significant inhibition (60%) in neointima formation, compared with sense ODN-treated and untreated vessels. Since we have previously observed that cell division cycle 2 kinase mRNA was also activated after vascular injury, we administered the combination of antisense cdc 2 and cdk 2 ODN in this study. Antisense cdc 2 ODN alone (15 microM) only reduced intimal formation by 40%. Combined antisense treatment resulted in near complete inhibition of neointima formation. To understand the mechanism of the sustained effect of a single antisense ODN administration, we examined kinetics of ODN in the vessel wall. Using phosphorothioate FITC-labeled ODN, we transfected carotid artery using the HVJ-liposome method. Fluorescence localized immediately to the medial layer, and persisted up to 2 wk after transfection. These results demonstrate that a single intraluminal administration of antisense ODN directed to cell cycle regulatory genes (e.g., cdk 2 kinase) using the HVJ method can result in a sustained inhibition of neointima formation after balloon angioplasty in rat carotid injury model.
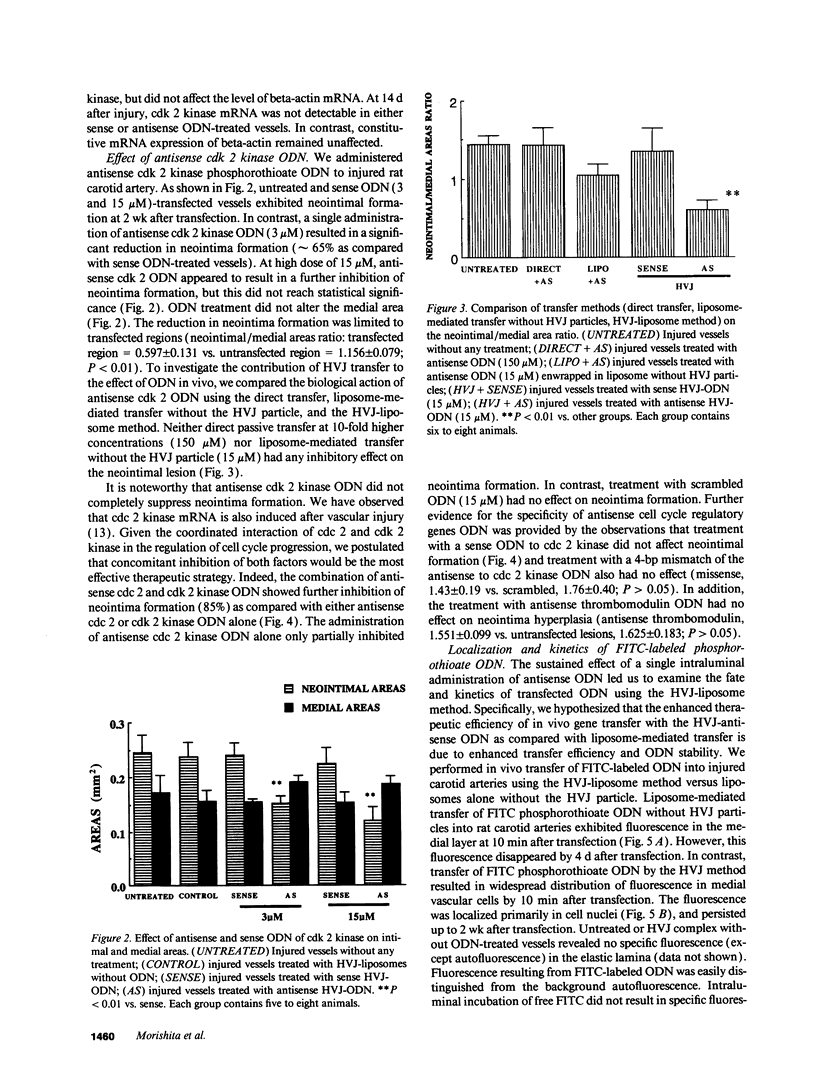
Full text
PDF

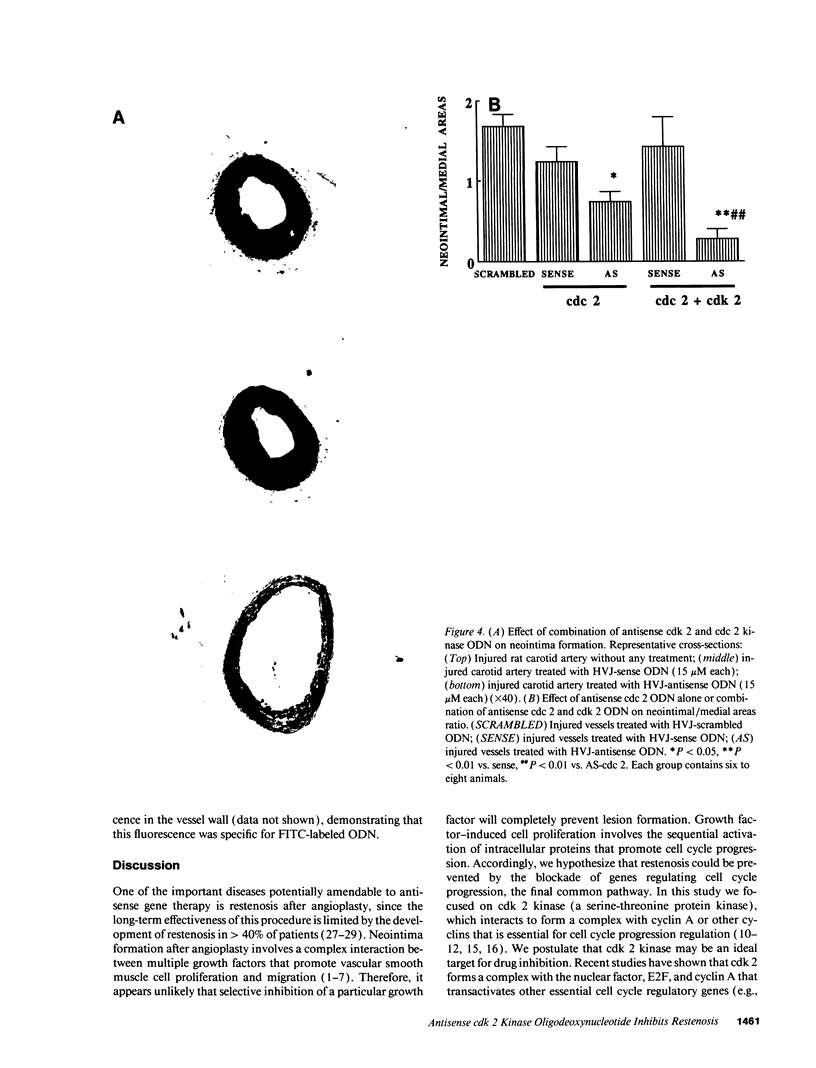



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar S., Juliano R. L. Cellular uptake and intracellular fate of antisense oligonucleotides. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 May;2(5):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Chiang M. Y., Chan H., Shoemaker J. E., Mirabelli C. K. Cationic lipids enhance cellular uptake and activity of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1023–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cercek B., Fishbein M. C., Forrester J. S., Helfant R. H., Fagin J. A. Induction of insulin-like growth factor I messenger RNA in rat aorta after balloon denudation. Circ Res. 1990 Jun;66(6):1755–1760. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.6.1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns G. A., Raines E. W., Sprugel K. H., Motani A. S., Reidy M. A., Ross R. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1653454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerle J., Johnson R., Clowes A. W., Majesky M. W., Reidy M. A. Role of platelets in smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration after vascular injury in rat carotid artery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8412–8416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., Piwnica-Worms H., Ernst T. J., Kanakura Y., Griffin J. D. cdc2 gene expression at the G1 to S transition in human T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):805–808. doi: 10.1126/science.2237430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Mukoyama M., Pratt R. E., Gibbons G. H., Dzau V. J. Multiple autocrine growth factors modulate vascular smooth muscle cell growth response to angiotensin II. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2268–2274. doi: 10.1172/JCI116454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda Y., Iwai K., Uchida T. Increased expression of DNA cointroduced with nuclear protein in adult rat liver. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):375–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2911748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Nakanishi M., Kaneda Y., Uchida T., Okada Y. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen in adult rat liver. Co-introduction of DNA and nuclear protein by a simplified liposome method. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3361–3364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittelberger R., Davis P. F., Stehbens W. E. An improved immunofluorescence technique for the histological examination of blood vessel tissue. Acta Histochem. 1989;86(2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(89)80082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Ohtsuki M., Polyak K., Roberts J. M., Massagué J. Negative regulation of G1 in mammalian cells: inhibition of cyclin E-dependent kinase by TGF-beta. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):536–539. doi: 10.1126/science.8475385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Mechti N., Degols G., Gagnor C., Lebleu B. Intracellular distribution of microinjected antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2702–2706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majesky M. W., Lindner V., Twardzik D. R., Schwartz S. M., Reidy M. A. Production of transforming growth factor beta 1 during repair of arterial injury. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):904–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI115393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus-Sekura C. J. Techniques for using antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides to study gene expression. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride W., Lange R. A., Hillis L. D. Restenosis after successful coronary angioplasty. Pathophysiology and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 30;318(26):1734–1737. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806303182606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalescot G., Faraggi M., Drobinski G., Messian O., Evans J., Grosgogeat Y., Thomas D. Myocardial viability in patients with Q wave myocardial infarction and no residual ischemia. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):47–55. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Novel and effective gene transfer technique for study of vascular renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2580–2585. doi: 10.1172/JCI116496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Koseki I., Kim J., Maeda Y., Hashimoto T. Modification of cell membranes with viral envelopes during fusion of cells with HVJ (Sendai virus). Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):368–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Edelman E. R., DeKeyser J. L., Langer R., Rosenberg R. D. Antisense c-myb oligonucleotides inhibit intimal arterial smooth muscle cell accumulation in vivo. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):67–70. doi: 10.1038/359067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller D. G., Tidd D. M. The uptake kinetics of chimeric oligodeoxynucleotide analogues in human leukaemia MOLT-4 cells. Anticancer Drug Des. 1992 Apr;7(2):115–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cohen J. S. Oligodeoxynucleotides as inhibitors of gene expression: a review. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2659–2668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita N., Higaki J., Morishita R., Kato K., Mikami H., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T. Direct in vivo gene introduction into rat kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80784-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]