Abstract
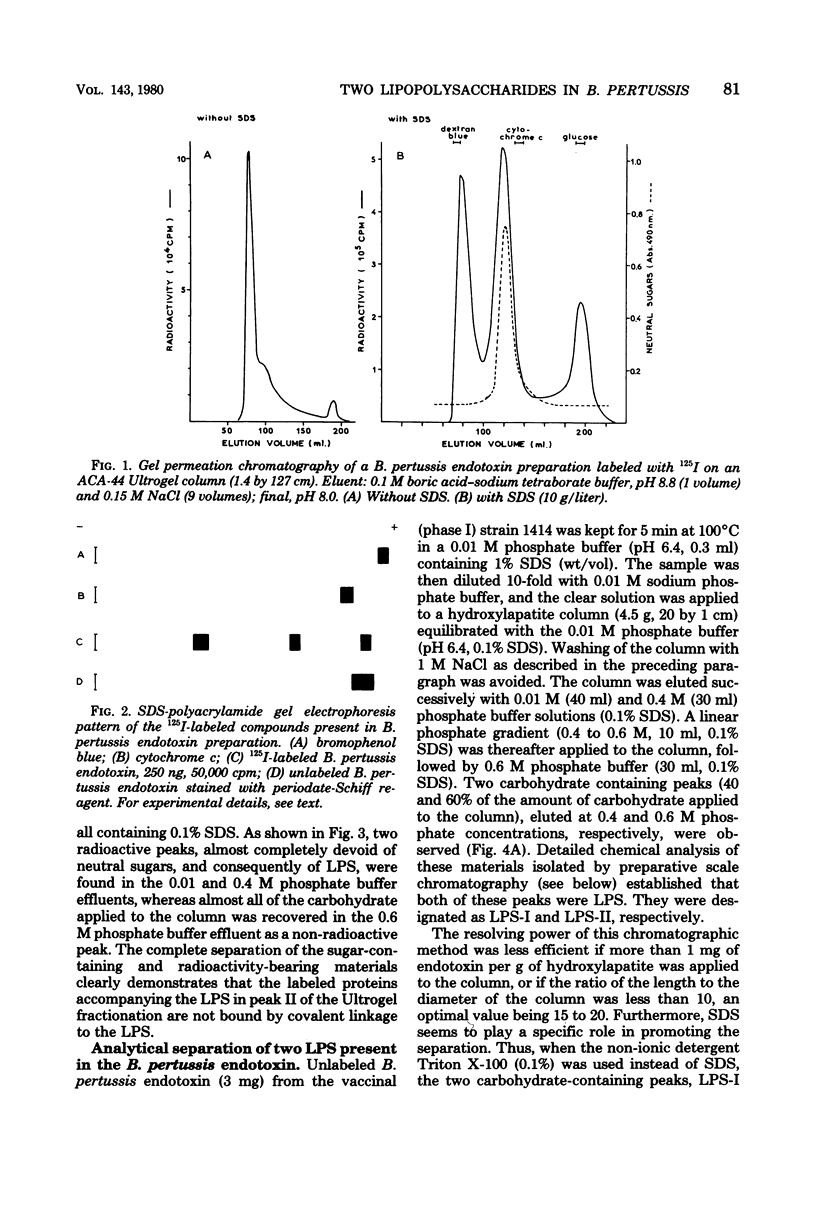
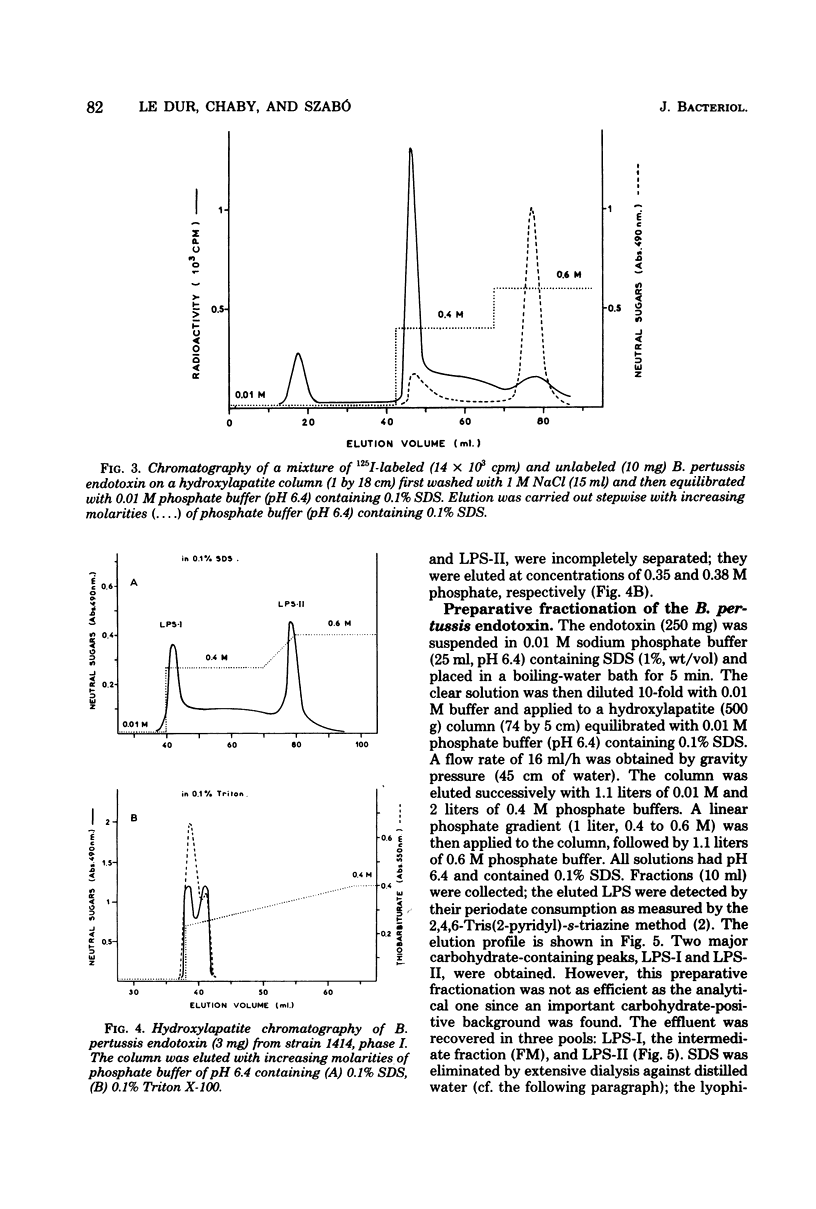
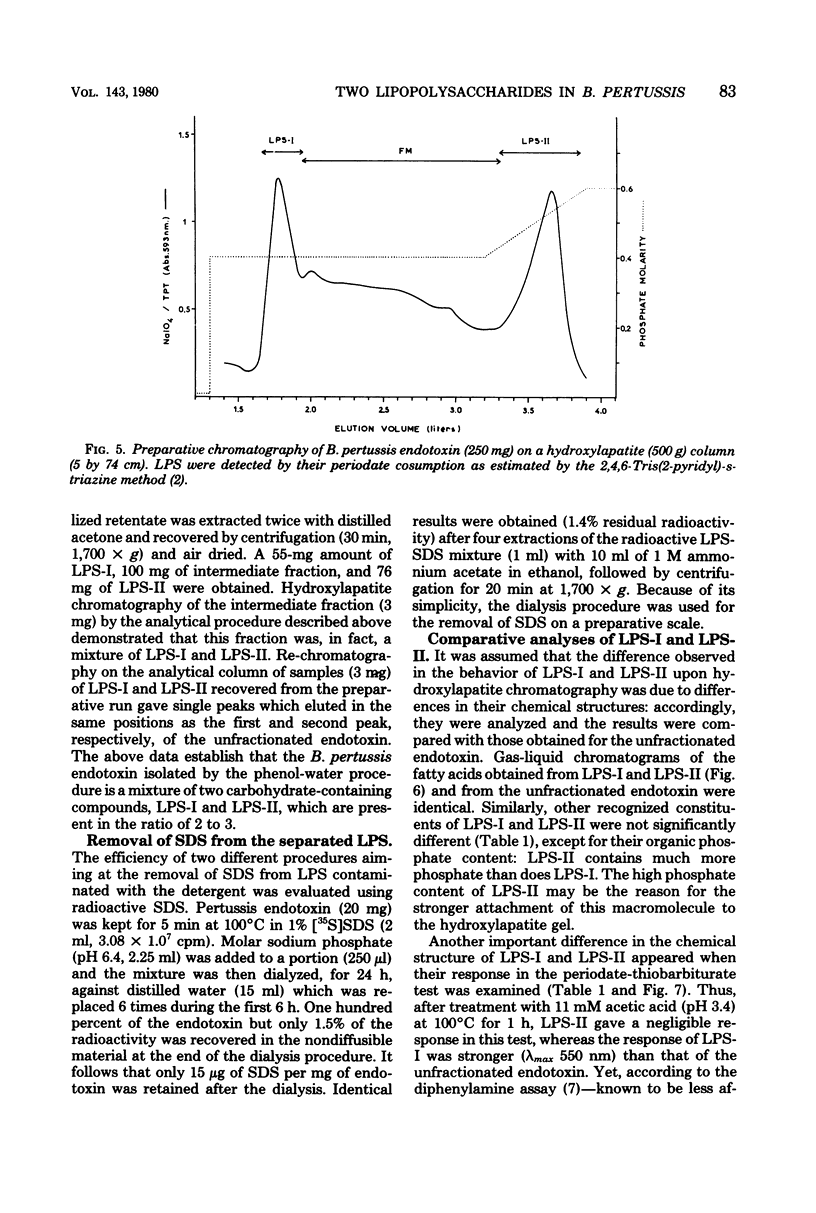
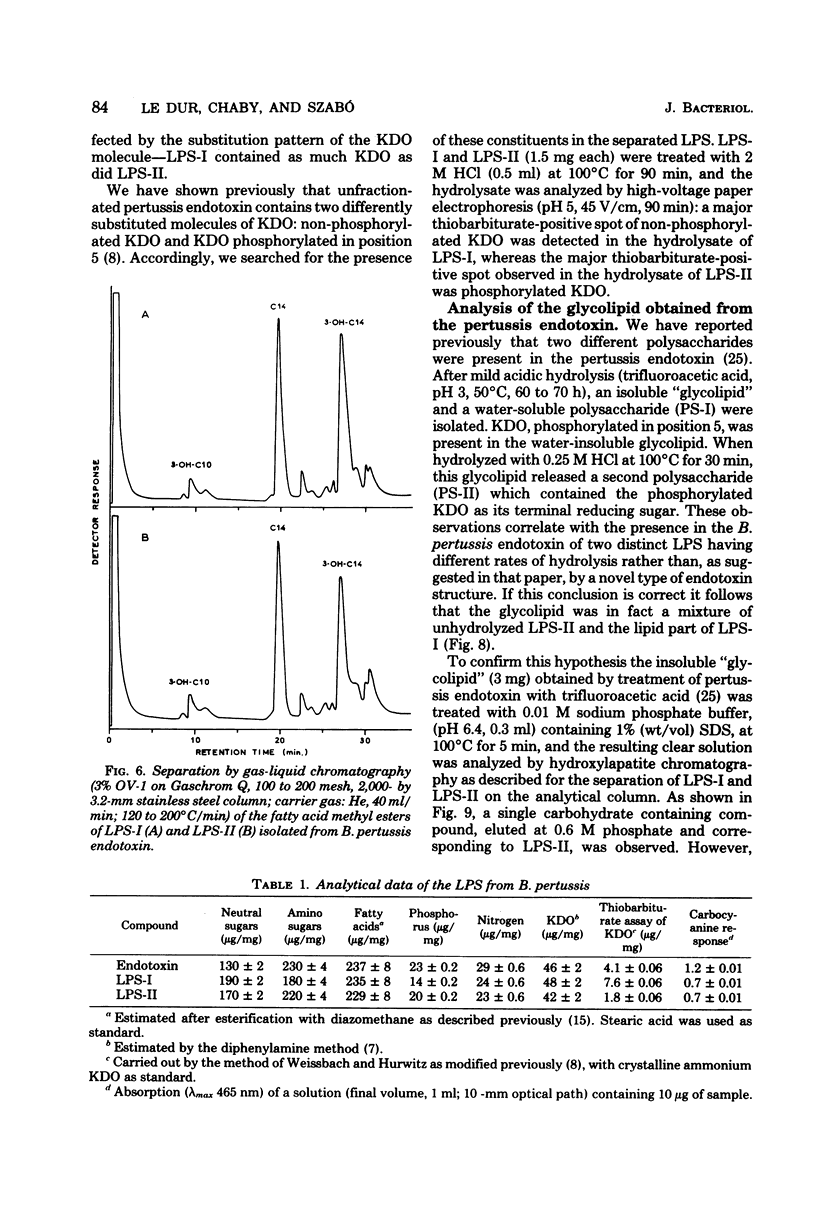
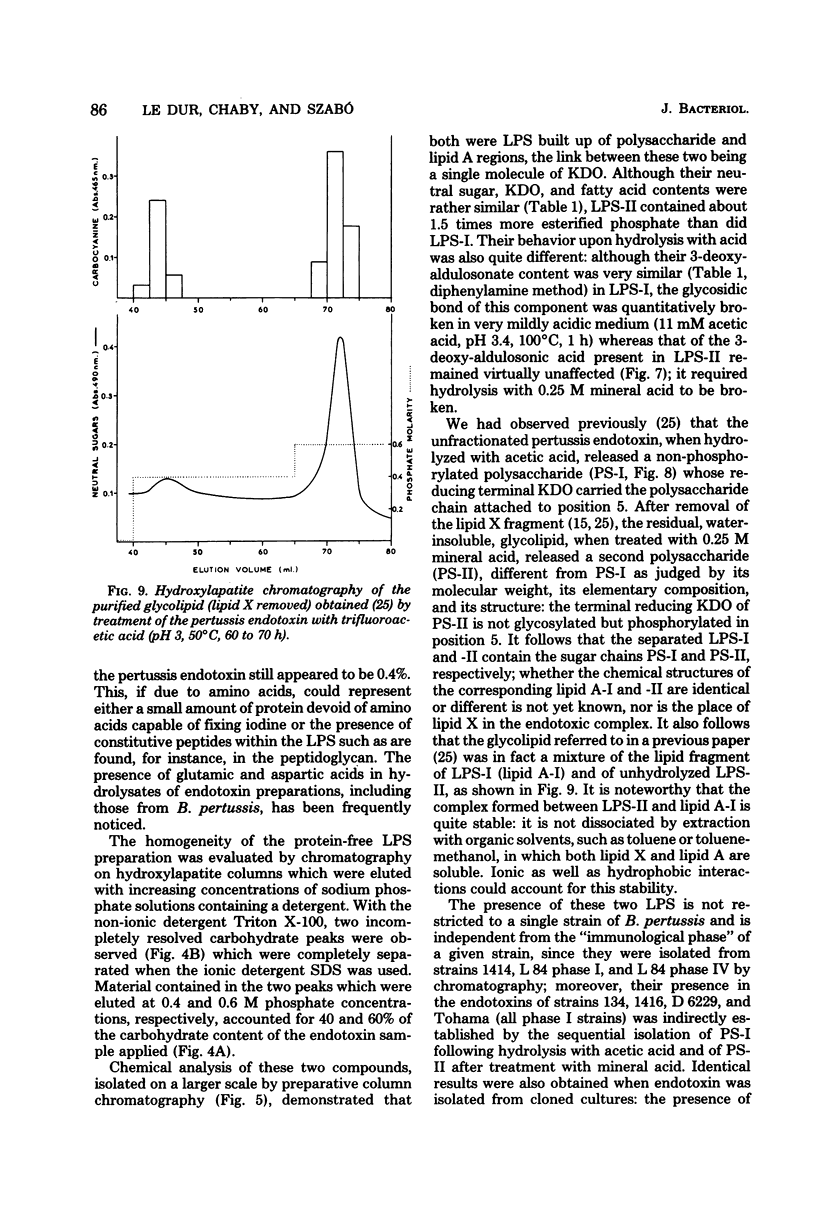
Endotoxin prepared from several Bordetella pertussis strains in both immunological phases I and IV gave two lipopolysaccharide peaks (LPS-I and LPS-II) when analyzed on hydroxylapatite columns in a phosphate buffer containing 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate; these lipopolysaccharides, present in the ratio of 2:3, are true endotoxins by both chemical and biological criteria. Endotoxins isolated from Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Shigella flexneri gave single lipopolysaccharide peaks when analyzed by the same procedure. Upon hydrolysis with acetic acid (pH 3.4) at 100 degrees C for 1 h, LPS-I released a polysaccharide (PS-I); the linkage broken was that of the glycosidic bond of a non-phosphorylated 3-deoxy-oct-2-ulosonic acid. Treatment with 0.25 M mineral acid at 100 degrees C for 30 min was required to free the polysaccharide moiety (PS-II) of LPS-II, the linkage broken being the glycosidic bond of a phosphorylated 3-deoxy-oct-2-ulosonic acid. Chemical and physical differences of the polysaccharide moieties PS-I and PS-II present in LPS-I and LPS-II have been described previously (25). By using the technique of 125I labeling, it was shown that the totality of labeled proteins present in the endotoxin extracted from Bordetella pertussis by the phenol-water procedure could be separated from the lipopolysaccharide by column chromatography on hydroxylapatite; it follows that these proteins are not linked by covalent bonds to the lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERER F. A. [Reversible denaturization of protein from tobacco mosaic virus]. Z Naturforsch B. 1959 Oct;14B:642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayme G., Caroff M., Chaby R., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Le Dur A., Moreau M., Muset M., Mynard M. C., Roumiantzeff M., Schulz D. Biological activities of fragments derived from Bordetella pertussis endotoxin: isolation of a nontoxic, Shwartzman-negative lipid A possessing high adjuvant properties. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):739–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.739-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON A. J., CARTER H. E. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LIPID A COMPONENT OF THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:411–418. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. Chromatography of nucleic acids on hydroxyapatite. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):779–783. doi: 10.1038/206779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaby R., Sarfati S. R., Szabó L. Colorimetric estimation of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid in oligosaccharides with diphenylamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaby R., Szabó L. 3-Deoxy-2-octulosonic acid 5-phosphate: a component of the endotoxin of Bordetella pertussis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):277–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon D., Szabó L. The synthesis of 3-deoxy-5-O-methyloctulosonic acid and its behaviour in the Warren reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 18;29(1):184–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Wheeler M. W. Pertussis Vaccine Prepared with Phase-I Cultures Grown in Fluid Medium. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 Apr;36(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Petris S. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Escherichia coli and chemical nature of its constituent layers. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jul;19(1):45–83. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Deneke C. F., MacLeod R. A. Heterogeneity and distribution of lipopolysaccharide in the cell wall of a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.148-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. G., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Modulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated function by structural differences of two physically distinct fractions of Escherichia coli K235 LPS. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1852–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner N., Chaby R., Szabó L. Identification of 2-methyl-3-hydroxydecanoic and 2-methyl-3-hydroxytetradecanoic acids in the 'lipid X' fraction of the Bordetella pertussis endotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Alkaline phosphatase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the mechanism of secretion and release of the enzyme from whole cells. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1407–1415. doi: 10.1139/m73-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B., McDonald I. J., Russel R. R. Cellular and free lipopolysaccharides of some species of Neisseria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):1969–1980. doi: 10.1139/m75-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeltzow D. E., Conrad H. E. Structural heterogeneity in the lipopolysaccharide of Aerobacter aerogenes NCTC 243. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):214–224. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotelko K., Gromska W., Sidorczyk Z., Zwoliński J. Further investigations on the antigenic structure of Proteus mirabilis. I. The presence and role of uronic acids. Bull Acad Pol Sci Biol. 1968;16(12):739–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacave C., Asselineau J., Serre A., Roux J. Comparaison de la composition chimique d'une fraction lipopolysaccharidique et d'une fraction polysaccharidique isolées de Brucella melitensis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Dur A., Caroff M., Chaby R., Szabó L. A novel type of endotoxin structure present in Bordetella pertussis. Isolation of two different polysaccharides bound to lipid A. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):579–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison G. R. Microchemical determination of organic nitrogen with Nessler reagent. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N. Hydroxylapatite chromatography of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. A new method for the separation of polypeptide subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5194–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nghiêm H. O., Staub A. M. Molecular immunological heterogeneity of the Salmonella zuerich [1, 9, 12, (46), 27] cell-wall polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):153–169. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82678-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Cundy K. R., Neale N. L., Nowotny A. M., Radvany R., Thomas S. P., Tripodi D. J. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. IV. Fractionation of the components. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):586–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Weinbaum G. An envelope-specific glycoprotein from Escherichia coli B. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2819–2825. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. W. A SIMPLE METHOD FOR PREPARING ANTIGENIC SUBSTANCES FROM THE TYPHOID BACILLUS. Science. 1940 Aug 16;92(2381):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.92.2381.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. W., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Characterization of a protein-lipopolysaccharide complex released from cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):743–748. doi: 10.1139/m69-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Tang J., Barzilay I., Khorana H. G. Structure of the lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. I. Chemical degradations and identification of products. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5906–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman-Kothencz M. Synthesis and assembly of bacterial membrane components. A lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid-protein complex excreted by living bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):477–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. M., Conrad H. E. Structural heterogeneity in the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella newington. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Jann B., Jann K. Immunochemistry of R lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli. Different core regions in the lipopolysaccharides of O group 8. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):501–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer M., Hindennach I., Garten W., Henning U. Major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Interaction of protein II with lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Horowitz M. I. Separation of polar lipids by column chromatography on hydroxylapatite. J Chromatogr. 1970 Jun 24;49(3):455–461. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang J. C., Wang C. S., Alaupovic P. Degradative effect of phenol on endotoxin and lipopolysaccharide preparations from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):786–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.786-795.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. C., Heath E. C. Isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharide protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2572–2576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman D. H., Gregory S., Kern M. Differentiation of lymphoid cells: the preferential binding of the lipid A moiety of lipopolysaccharide to B lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1018–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


