Abstract
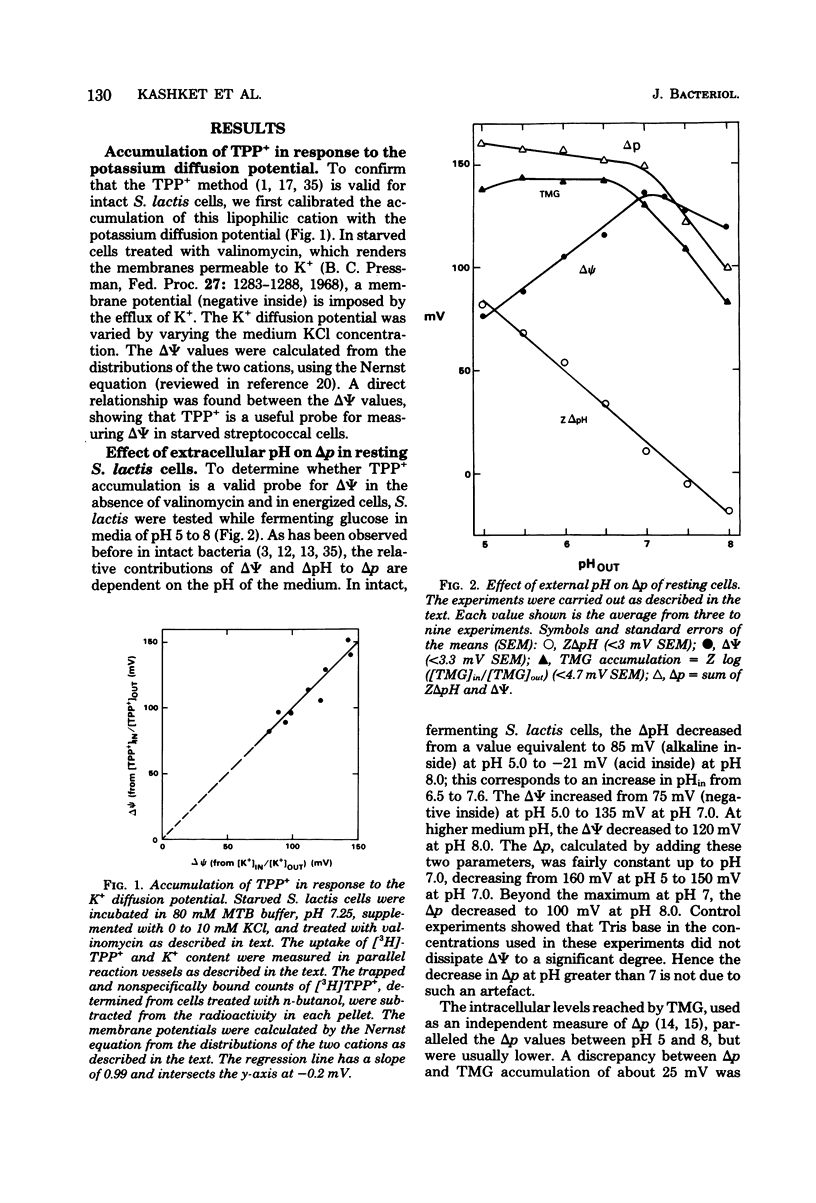
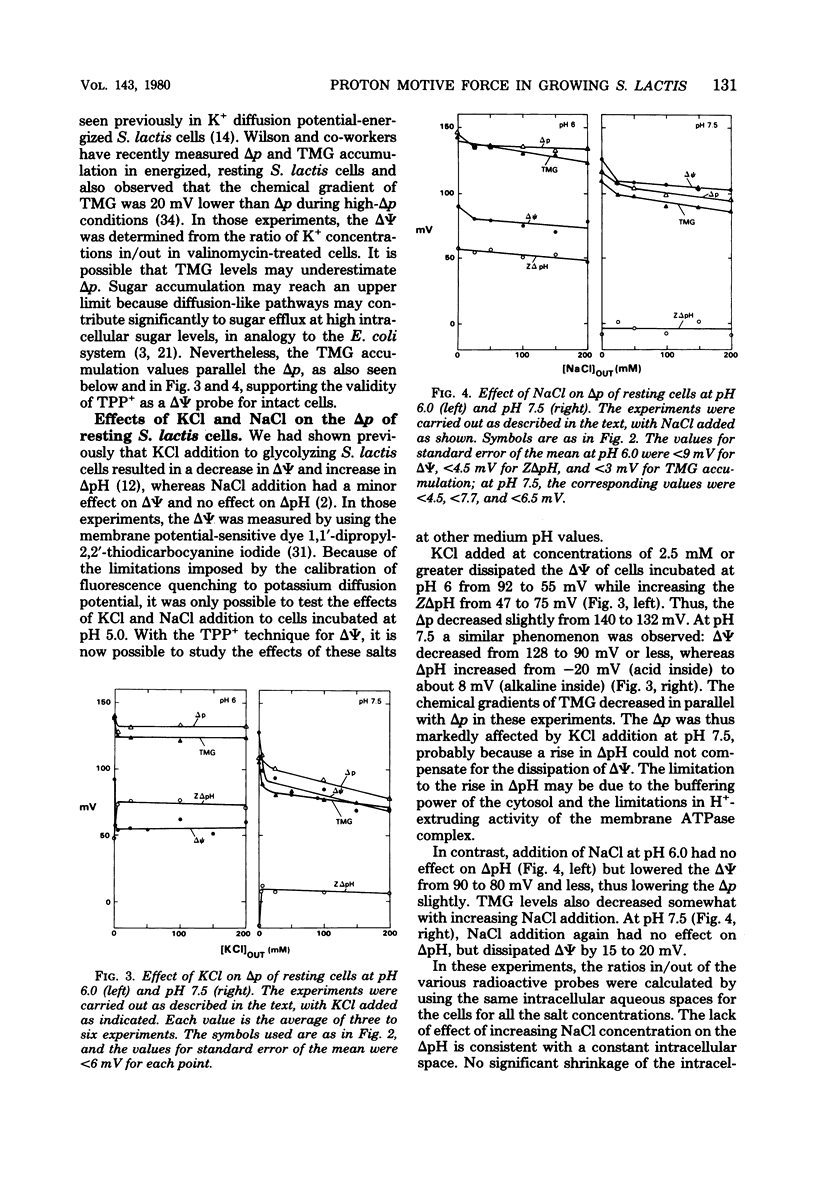
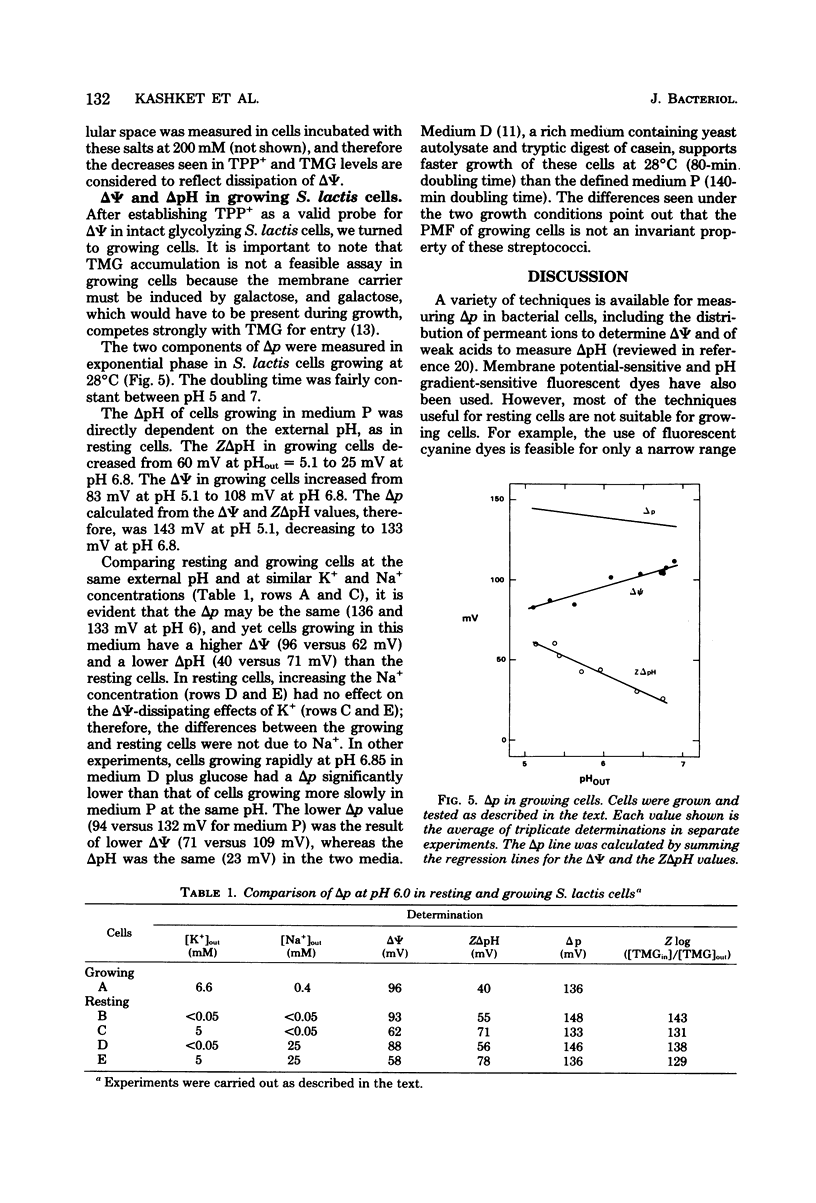
Experiments with the aerotolerant anaerobe Streptococcus lactis provide the opportunity for determining the proton motive force (Δp) in dividing cells. The two components of Δp, ΔΨ (the transmembrane potential) and ΔpH (the chemical gradient of H+), were determined by the accumulation of radiolabeled tetraphenylphosphonium (TPP+) and benzoate ions. The ΔΨ was calibrated with the K+ diffusion potential in starved, valinomycin-treated cells. With resting, glycolyzing cells, the Δp was measured also by the accumulation of the non-metabolizable sugar thiomethyl-β-galactoside (TMG). In resting cells the Δp, calculated either by adding ΔΨ and ZΔpH or from the levels of TMG, was relatively constant between pH 5 to 7, decreasing from 160 to 150 mV and decreasing further to 100 mV at pH 8.0. With the TPP+ probe for ΔΨ, we confirmed our previous finding that the K+ ions dissipate ΔΨ and increase ΔpH, whereas Na+ ions have little effect on ΔΨ and no effect on ΔpH. [3H]TPP+ and [14C]benzoate were added during exponential phase to S. lactis cells growing at pH 5 to 7 at 28°C in a defined medium with glucose as energy source. As with resting cells, the ΔpH and ΔΨ were dependent on the pH of the medium. At pH 5.1, the ΔpH was equivalent to 60 mV (alkaline inside) and decreased to 25 mV at pH 6.8. The ΔΨ increased from 83 mV (negative inside) at pH 5.1 to 108 mV at pH 6.8. The Δp, therefore, was fairly constant between pH 5 and 7, decreasing from 143 to 133 mV. The values for Δp in growing cells, just as in resting cells, are consistent with a system in which the net efflux of H+ ions is effected by a membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase and glycolytically generated adenosine triphosphate. The data suggest that in both growing and resting cells the pH of the medium and its K+ concentration are the two principal factors that determine the relative contribution of ΔpH and ΔΨ to the proton motive force.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker S. L., Kashket E. R. Effects of sodium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(3):383–388. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Mitchell W. J., Hamilton W. A. Quantitative analysis of proton-linked transport systems. The lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):687–696. doi: 10.1042/bj1820687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Ion currents and physiological functions in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:181–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. II. Proton and sodium extrusion. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):45–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01868094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Hunt A. G., Masters P. S., Lieberman M. A. Requirements of acetyl phosphate for the binding protein-dependent transport systems in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Active transport of thallous ions by Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8129–8131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Proton-coupled accumulation of galactoside in Streptococcus lactis 7962. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2866–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Protonmotive force in fermenting Streptococcus lactis 7962 in relation to sugar accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):879–886. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Use of a lipophilic cation for determination of membrane potential in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. A protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Obligatory coupling between proton entry and the synthesis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.564-575.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Wilson T. H. Quantitative aspects of active transport by the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 13;330(2):196–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Takeda K. Extrusion of sodium ions energized by respiration and glycolysis in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. Optical probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1976 Jun 30;27(4):317–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01869143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Stoicheiometry of lactose-H+ symport across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):587–592. doi: 10.1042/bj1320587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Janssen D. B., van Wezenbeek P. M. Hydrolysis and synthesis of ATP by membrane-bound ATPase from a motile Streptococcus. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):31–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00407924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


