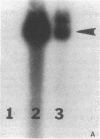
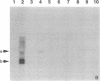
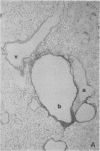
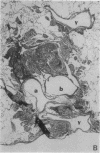
Abstract
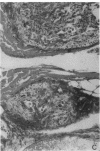
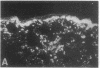
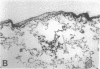
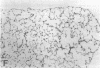
Increased production of EGF or TGF-alpha by the respiratory epithelial cells has been associated with the pathogenesis of various forms of lung injury. Growth factors and cytokines are thought to act locally, via paracrine and autocrine mechanisms, to stimulate cell proliferation and matrix deposition by interstitial lung cells resulting in pulmonary fibrosis. To test whether TGF-alpha mediates pulmonary fibrotic responses, we have generated transgenic mice expressing human TGF-alpha under control of regulatory regions of the human surfactant protein C (SP-C) gene. Human TGF-alpha mRNA was expressed in pulmonary epithelial cells in the lungs of the transgenic mice. Adult mice bearing the SP-C-TGF-alpha transgene developed severe pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrotic lesions were observed in peribronchial, peribronchiolar, and perivascular regions, as well as subjacent to pleural surfaces. Lesions consisted of fibrous tissue that included groups of epithelial cells expressing endogenous SP-C mRNA, consistent with their identification as distal respiratory epithelial cells. Peripheral fibrotic regions consisted of thickened pleura associated with extensive collagen deposition. Alveolar architecture was disrupted in the transgenic mice with loss of alveoli in the lung parenchyma. Pulmonary epithelial cell expression of TGF-alpha in transgenic mice disrupts alveolar morphogenesis and produces fibrotic lesions mediated by paracrine signaling between respiratory epithelial and interstitial cells of the lung.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. C., Schuyler M., Martin R. J., Starcher B. C., Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Wedig K. E. Risk factors for the degradation of lung elastic fibers in the ventilated neonate. Implications for impaired lung development in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):204–212. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterton W. Z., Escobedo M. B., Sexson W. R., Gray M. E., Sundell H. W., Stahlman M. T. Effect of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal rabbits. Pediatr Res. 1979 Feb;13(2):104–108. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197902000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G. Human epidermal growth factor: isolation and chemical and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1317–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Fox C. F. Molecular mechanism of mitogen action: processing of receptor induced by epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Das M. Internalization and processing of the EGF receptor in the induction of DNA synthesis in cultured fibroblasts: the endocytic activation hypothesis. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(2):199–214. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganser G. L., Stricklin G. P., Matrisian L. M. EGF and TGF alpha influence in vitro lung development by the induction of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Int J Dev Biol. 1991 Dec;35(4):453–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Bruno M. D., Dey C., Whitsett J. A. Structure and expression of the pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C gene in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21986–21991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. D., Gray M. E., Carpenter G., Pepinsky R. B., Sundell H., Stahlman M. T. Ontogeny of epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase and of lipocortin-1 in the ovine lung. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):535–541. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubiak J., Mitra M. M., Steve A. R., Hunt J. D., Davies P., Pitt B. R. Transforming growth factor-alpha gene expression in late-gestation fetal rat lung. Pediatr Res. 1992 Mar;31(3):286–290. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199203000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rochford R., Todaro G. J., Villarreal L. P. Developmental expression of rat transforming growth factor-alpha mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3644–3646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Sakariassen K. S., Assoian R. K., Sporn M. B., Bell G. I., Ross R. Induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in activated human alveolar macrophages. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Todaro G. J. Rat transforming growth factor type 1: structure and relation to epidermal growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6320373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plopper C. G., St George J. A., Read L. C., Nishio S. J., Weir A. J., Edwards L., Tarantal A. F., Pinkerton K. E., Merritt T. A., Whitsett J. A. Acceleration of alveolar type II cell differentiation in fetal rhesus monkey lung by administration of EGF. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L313–L321. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaberg L., Nexø E., Damsgaard Mikkelsen J., Seier Poulsen S. Immunohistochemical localisation and developmental aspects of epidermal growth factor in the rat. Histochemistry. 1988;89(4):351–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00500636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaberg L., Poulsen S. S., Nexø E. Epidermal growth factor in the rat lung. Histochemistry. 1991;95(5):471–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00315742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Todaro G. J., Fryling C., Stephenson J. R. Human transforming growth factors induce tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptors. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):259–262. doi: 10.1038/292259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Luetteke N. C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lee D. C. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1121–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90075-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sannes P. L., Burch K. K., Khosla J. Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor and acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in postnatal developing and adult rat lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Aug;7(2):230–237. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snead M. L., Luo W., Oliver P., Nakamura M., Don-Wheeler G., Bessem C., Bell G. I., Rall L. B., Slavkin H. C. Localization of epidermal growth factor precursor in tooth and lung during embryonic mouse development. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):420–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman M. T., Orth D. N., Gray M. E. Immunocytochemical localization of epidermal growth factor in the developing human respiratory system and in acute and chronic lung disease in the neonate. Lab Invest. 1989 Apr;60(4):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandjord T. P., Clark J. G., Hodson W. A., Schmidt R. A., Madtes D. K. Expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in mid-gestation human fetal lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;8(3):266–272. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell H. W., Gray M. E., Serenius F. S., Escobedo M. B., Stahlman M. T. Effects of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal lambs. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):707–726. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D., Seth R., Shum L., Horcher P. G., Hall F. L., Werb Z., Slavkin H. C. Epigenetic role of epidermal growth factor expression and signalling in embryonic mouse lung morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90269-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wert S. E., Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Whitsett J. A. Transcriptional elements from the human SP-C gene direct expression in the primordial respiratory epithelium of transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1993 Apr;156(2):426–443. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Dey C. R., Stripp B. R., Wikenheiser K. A., Clark J. C., Wert S. E., Gregory R. J., Smith A. E., Cohn J. A., Wilson J. M. Human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator directed to respiratory epithelial cells of transgenic mice. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):13–20. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Lieberman M. A., Clark J. C., Daugherty C. Differential effects of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta on synthesis of Mr = 35,000 surfactant-associated protein in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7908–7913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikenheiser K. A., Clark J. C., Linnoila R. I., Stahlman M. T., Whitsett J. A. Simian virus 40 large T antigen directed by transcriptional elements of the human surfactant protein C gene produces pulmonary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5342–5352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispé J. R., Warner B. B., Clark J. C., Dey C. R., Neuman J., Glasser S. W., Crapo J. D., Chang L. Y., Whitsett J. A. Human Mn-superoxide dismutase in pulmonary epithelial cells of transgenic mice confers protection from oxygen injury. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23937–23941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]