Abstract
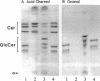
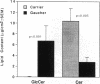
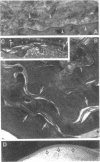
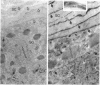
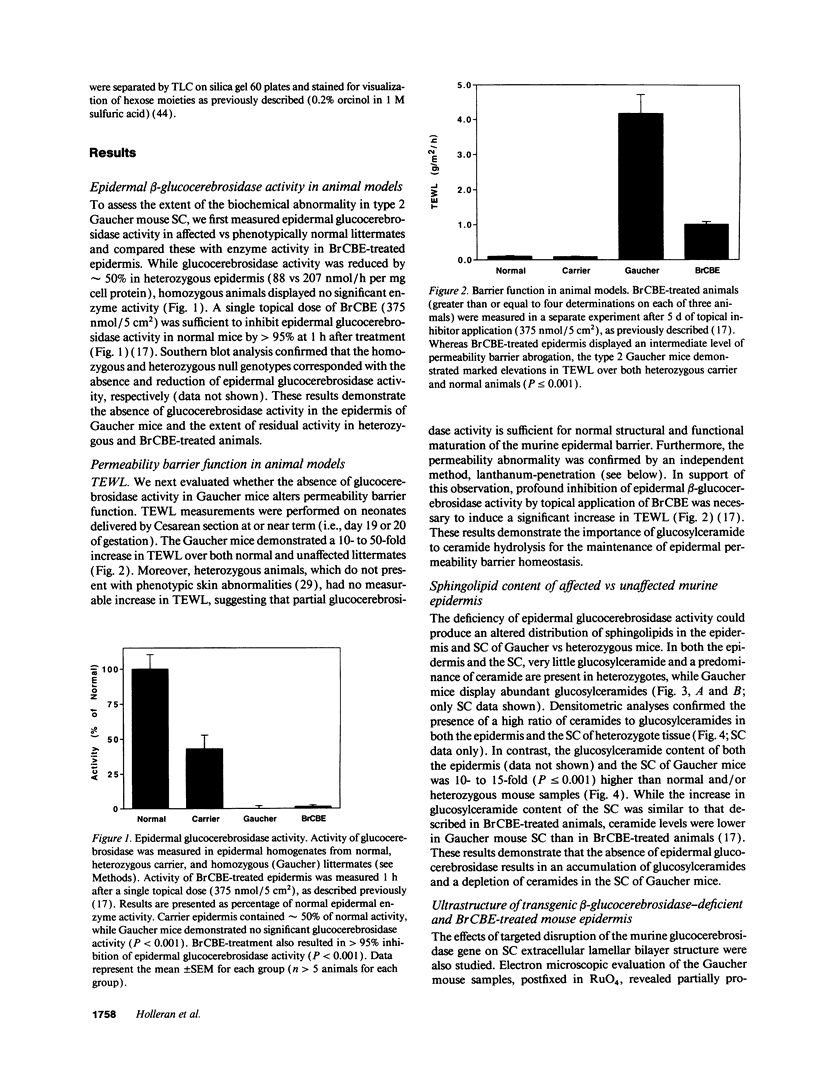
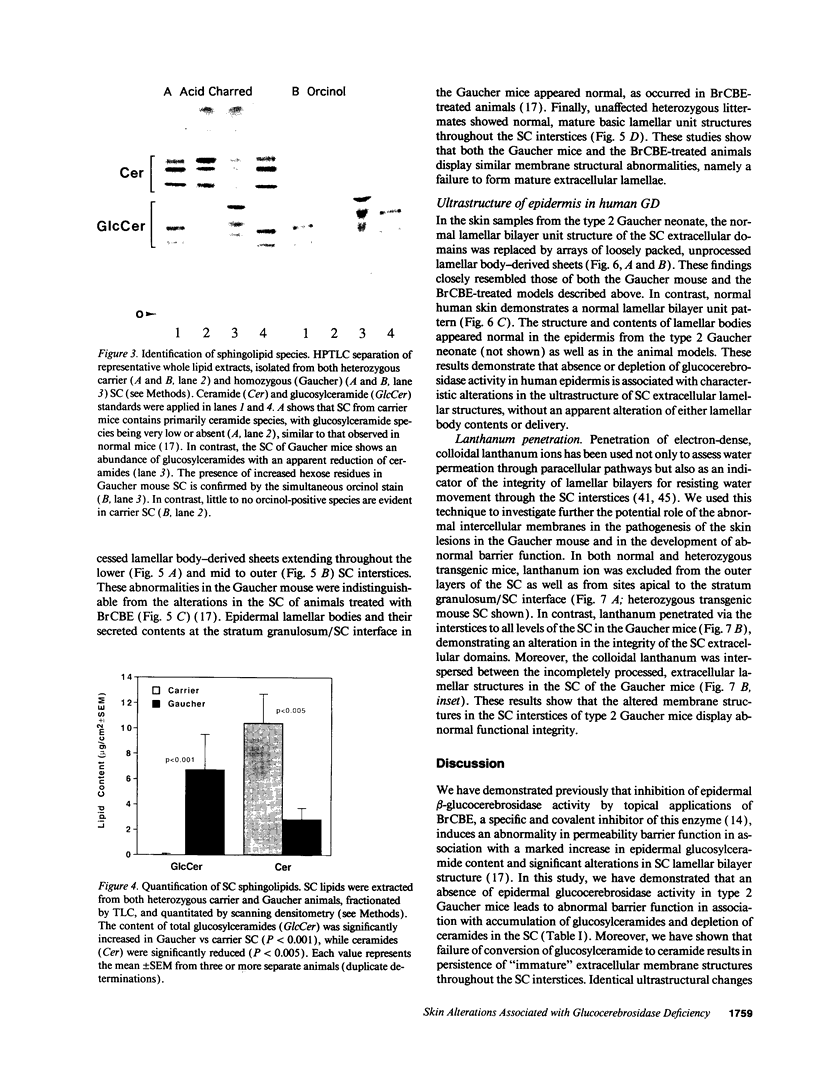
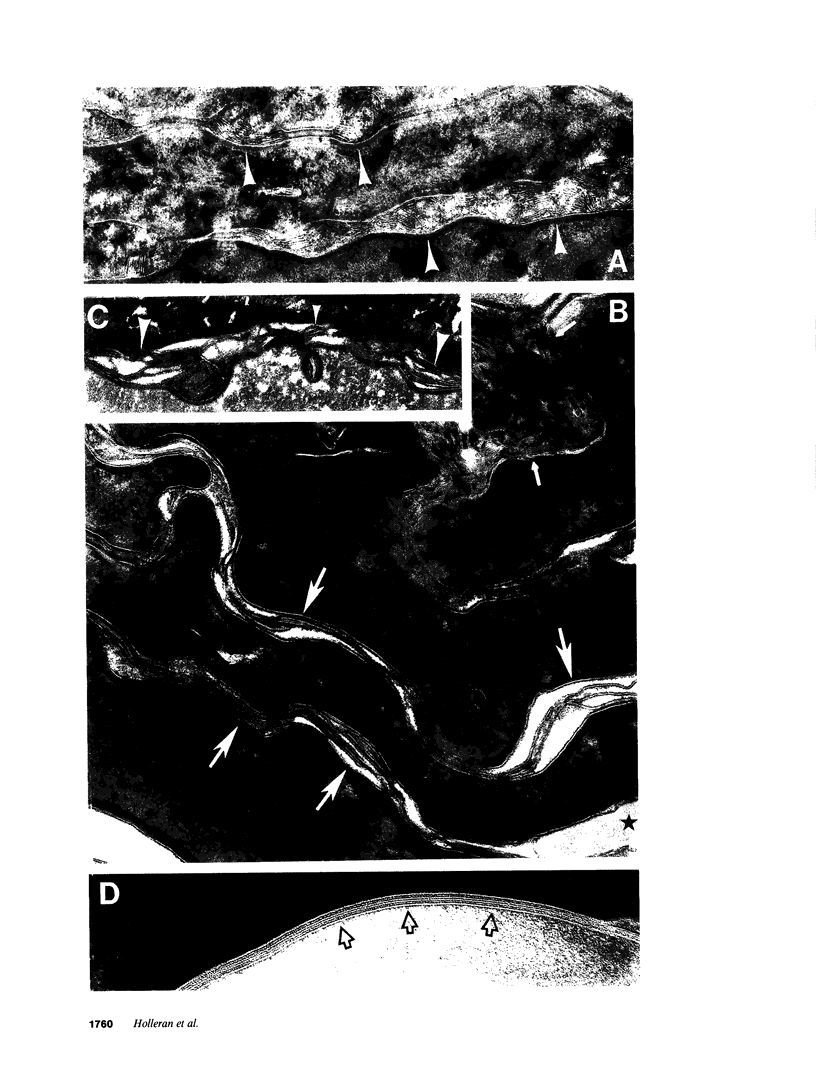
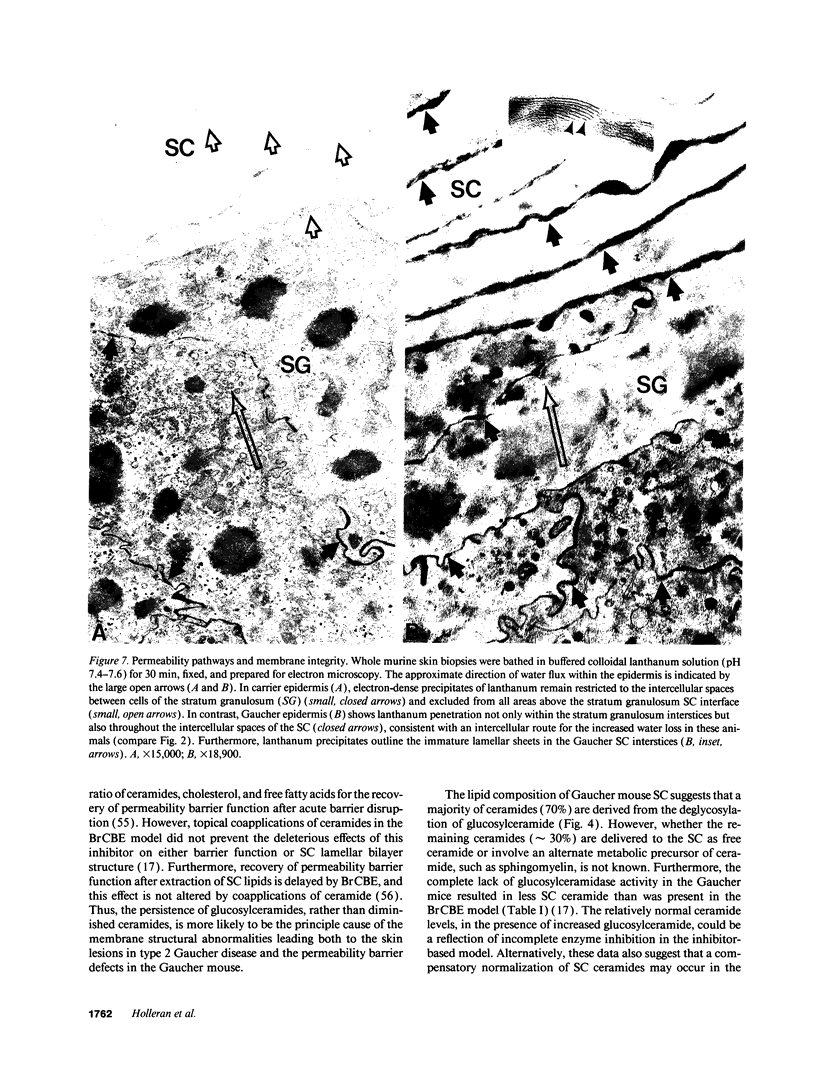
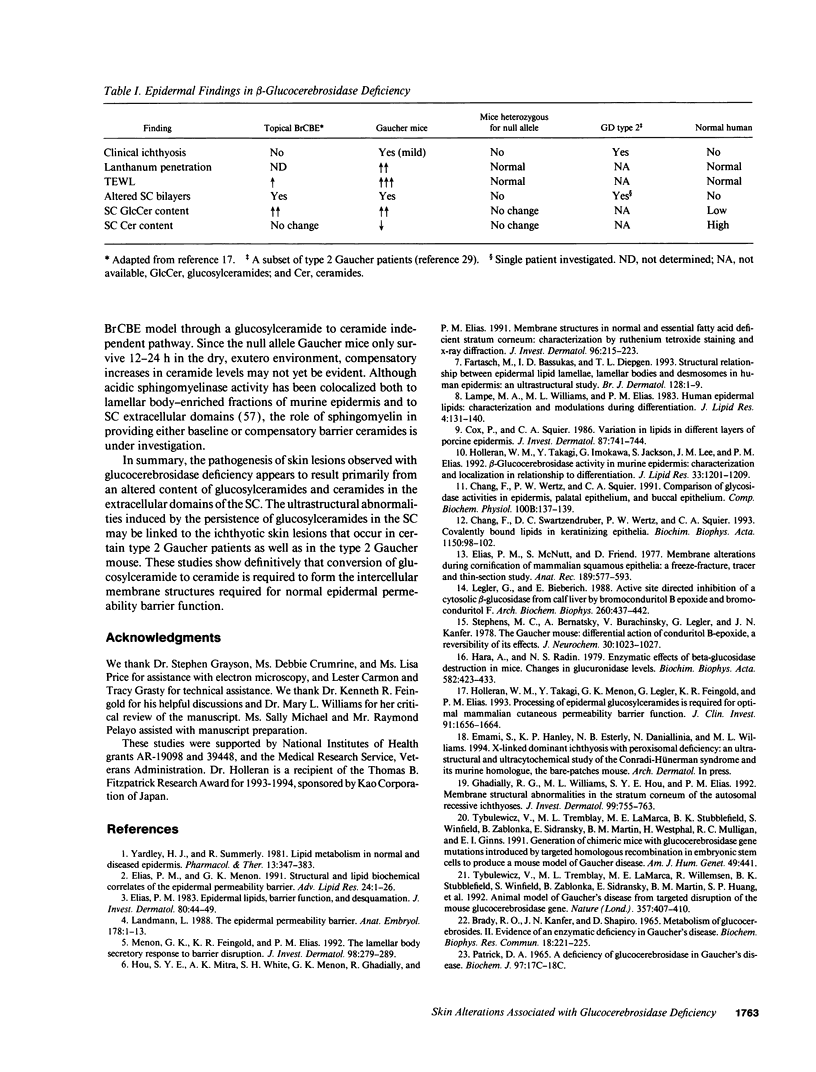
Hydrolysis of glucosylceramide by beta-glucocerebrosidase results in ceramide, a critical component of the intercellular lamellae that mediate the epidermal permeability barrier. A subset of type 2 Gaucher patients displays ichthyosiform skin abnormalities, as do transgenic Gaucher mice homozygous for a null allele. To investigate the relationship between glucocerebrosidase deficiency and epidermal permeability barrier function, we compared the stratum corneum (SC) ultrastructure, lipid content, and barrier function of Gaucher mice to carrier and normal mice, and to hairless mice treated topically with bromoconduritol B epoxide (BrCBE), an irreversible inhibitor of glucocerebrosidase. Both Gaucher mice and BrCBE-treated mice revealed abnormal, incompletely processed, lamellar body-derived sheets throughout the SC interstices, while transgenic carrier mice displayed normal bilayers. The SC of a severely affected type 2 Gaucher's disease infant revealed similarly abnormal ultrastructure. Furthermore, the Gaucher mice demonstrated markedly elevated transepidermal water loss (4.2 +/- 0.6 vs < 0.10 g/m2 per h). The electron-dense tracer, colloidal lanthanum, percolated between the incompletely processed lamellar body-derived sheets in the SC interstices of Gaucher mice only, demonstrating altered permeability barrier function. Gaucher and BrCBE-treated mice showed < 1% and < 5% of normal epidermal glucocerebrosidase activity, respectively, and the epidermis/SC of Gaucher mice demonstrated elevated glucosylceramide (5- to 10-fold), with diminished ceramide content. Thus, the skin changes observed in Gaucher mice and infants may result from the formation of incompetent intercellular lamellar bilayers due to a decreased hydrolysis of glucosylceramide to ceramide. Glucocerebrosidase therefore appears necessary for the generation of membranes of sufficient functional competence for epidermal barrier function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W. The diagnosis of the adult type of Gaucher's disease and its carrier state by demonstration of deficiency of beta-glucosidase activity in peripheral blood leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):747–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommannan D., Menon G. K., Okuyama H., Elias P. M., Guy R. H. Sonophoresis. II. Examination of the mechanism(s) of ultrasound-enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Pharm Res. 1992 Aug;9(8):1043–1047. doi: 10.1023/a:1015806528336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. The new mouse genetics: altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Swartzendruber D. C., Wertz P. W., Squier C. A. Covalently bound lipids in keratinizing epithelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 25;1150(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90126-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Wertz P. W., Squier C. A. Comparison of glycosidase activities in epidermis, palatal epithelium and buccal epithelium. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1991;100(1):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox P., Squier C. A. Variations in lipids in different layers of porcine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):741–744. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W. The physical properties of glycolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 24;906(2):111–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Brown B. E. The mammalian cutaneous permeability barrier: defective barrier function is essential fatty acid deficiency correlates with abnormal intercellular lipid deposition. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):574–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., McNutt N. S., Friend D. S. Membrane alterations during cornification of mammalian squamous epithelia: a freeze-fracture, tracer, and thin-section study. Anat Rec. 1977 Dec;189(4):577–594. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091890404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Menon G. K. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:1–26. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024924-4.50005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fartasch M., Bassukas I. D., Diepgen T. L. Structural relationship between epidermal lipid lamellae, lamellar bodies and desmosomes in human epidermis: an ultrastructural study. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Jan;128(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially R., Williams M. L., Hou S. Y., Elias P. M. Membrane structural abnormalities in the stratum corneum of the autosomal recessive ichthyoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Dec;99(6):755–763. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12614489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Beighton P. Cutaneous manifestations of Gaucher disease. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Sep;111(3):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Radin N. S. Enzymic effects of beta-glucosidase destruction in mice. Changes in glucuronidase levels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 1;582(3):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., DeGregorio M. W., Ganapathi R., Wilbur J. R., Macher B. A. Characterization of cellular lipids in doxorubicin-sensitive and -resistant P388 mouse leukemia cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1986;17(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00299859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Feingold K. R., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Lee J. M., Elias P. M. Regulation of epidermal sphingolipid synthesis by permeability barrier function. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jul;32(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Menon G. K., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Sphingolipids are required for mammalian epidermal barrier function. Inhibition of sphingolipid synthesis delays barrier recovery after acute perturbation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1338–1345. doi: 10.1172/JCI115439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Takagi Y., Imokawa G., Jackson S., Lee J. M., Elias P. M. beta-Glucocerebrosidase activity in murine epidermis: characterization and localization in relation to differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1201–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Takagi Y., Menon G. K., Legler G., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Processing of epidermal glucosylceramides is required for optimal mammalian cutaneous permeability barrier function. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1656–1664. doi: 10.1172/JCI116374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou S. Y., Mitra A. K., White S. H., Menon G. K., Ghadially R., Elias P. M. Membrane structures in normal and essential fatty acid-deficient stratum corneum: characterization by ruthenium tetroxide staining and x-ray diffraction. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Feb;96(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. A., Williams M. L., Elias P. M. Human epidermal lipids: characterization and modulations during differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann L. The epidermal permeability barrier. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;178(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00305008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. E., Worthington C. R., Glew R. H. The bilayer nature of deposits occurring in Gaucher's disease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Bieberich E. Active site directed inhibition of a cytosolic beta-glucosidase from calf liver by bromoconduritol B epoxide and bromoconduritol F. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson A. H., Rogers M., Berry A. Collodion babies with Gaucher's disease--a further case. Arch Dis Child. 1991 May;66(5):667–667. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.5.667-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui K., Commens C., Choong R., Jaworski R. Collodion babies with Gaucher's disease. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Jul;63(7):854–856. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.7.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man M. Q., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Exogenous lipids influence permeability barrier recovery in acetone-treated murine skin. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Jun;129(6):728–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Lamellar body secretory response to barrier disruption. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Mar;98(3):279–289. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12497866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Grayson S., Elias P. M. Cytochemical and biochemical localization of lipase and sphingomyelinase activity in mammalian epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 May;86(5):591–597. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12355263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O., Månsson J. E., Håkansson G., Svennerholm L. The occurrence of psychosine and other glycolipids in spleen and liver from the three major types of Gaucher's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 14;712(3):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O., Svennerholm L. Accumulation of glucosylceramide and glucosylsphingosine (psychosine) in cerebrum and cerebellum in infantile and juvenile Gaucher disease. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):709–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascher I., Lundmark M., Nyholm P. G., Sundell S. Crystal structures of membrane lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 11;1113(3-4):339–373. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponec M., Weerheim A., Kempenaar J., Mommaas A. M., Nugteren D. H. Lipid composition of cultured human keratinocytes in relation to their differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):949–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo W. B., Dammann A. L., Craft D. A. Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. Impaired fatty alcohol oxidation in cultured fibroblasts due to deficient fatty alcohol:nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidoreductase activity. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):738–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI113379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherer D. M., Metlay L. A., Sinkin R. A., Mongeon C., Lee R. E., Woods J. R., Jr Congenital ichthyosis with restrictive dermopathy and Gaucher disease: a new syndrome with associated prenatal diagnostic and pathology findings. Obstet Gynecol. 1993 May;81(5 ):842–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky E., Sherer D. M., Ginns E. I. Gaucher disease in the neonate: a distinct Gaucher phenotype is analogous to a mouse model created by targeted disruption of the glucocerebrosidase gene. Pediatr Res. 1992 Oct;32(4):494–498. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199210000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegenthaler U., Laine A., Polak L. Studies on contact sensitivity to chromium in the guinea pig. The role of valence in the formation of the antigenic determinant. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jan;80(1):44–47. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens M. C., Bernatsky A., Burachinsky V., Legler G., Kanfer J. N. The Gaucher mouse: differential action of conduritol B epoxide and reversibility of its effects. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1023–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Crawford C. E., Jackson P. K., Bronson R. T., Mulligan R. C. Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Tremblay M. L., LaMarca M. E., Willemsen R., Stubblefield B. K., Winfield S., Zablocka B., Sidransky E., Martin B. M., Huang S. P. Animal model of Gaucher's disease from targeted disruption of the mouse glucocerebrosidase gene. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):407–410. doi: 10.1038/357407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Mirejovsky D., King G. I. Structure of lamellar lipid domains and corneocyte envelopes of murine stratum corneum. An X-ray diffraction study. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3725–3732. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L., Elias P. M. From basket weave to barrier. Unifying concepts for the pathogenesis of the disorders of cornification. Arch Dermatol. 1993 May;129(5):626–629. doi: 10.1001/archderm.129.5.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L., Elias P. M. Stratum corneum lipids in disorders of cornification: increased cholesterol sulfate content of stratum corneum in recessive x-linked ichthyosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1404–1410. doi: 10.1172/JCI110391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L., Koch T. K., O'Donnell J. J., Frost P. H., Epstein L. B., Grizzard W. S., Epstein C. J. Ichthyosis and neutral lipid storage disease. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;20(4):711–726. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley H. J., Summerly R. Lipid composition and metabolism in normal and diseased epidermis. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;13(2):357–383. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]