Abstract
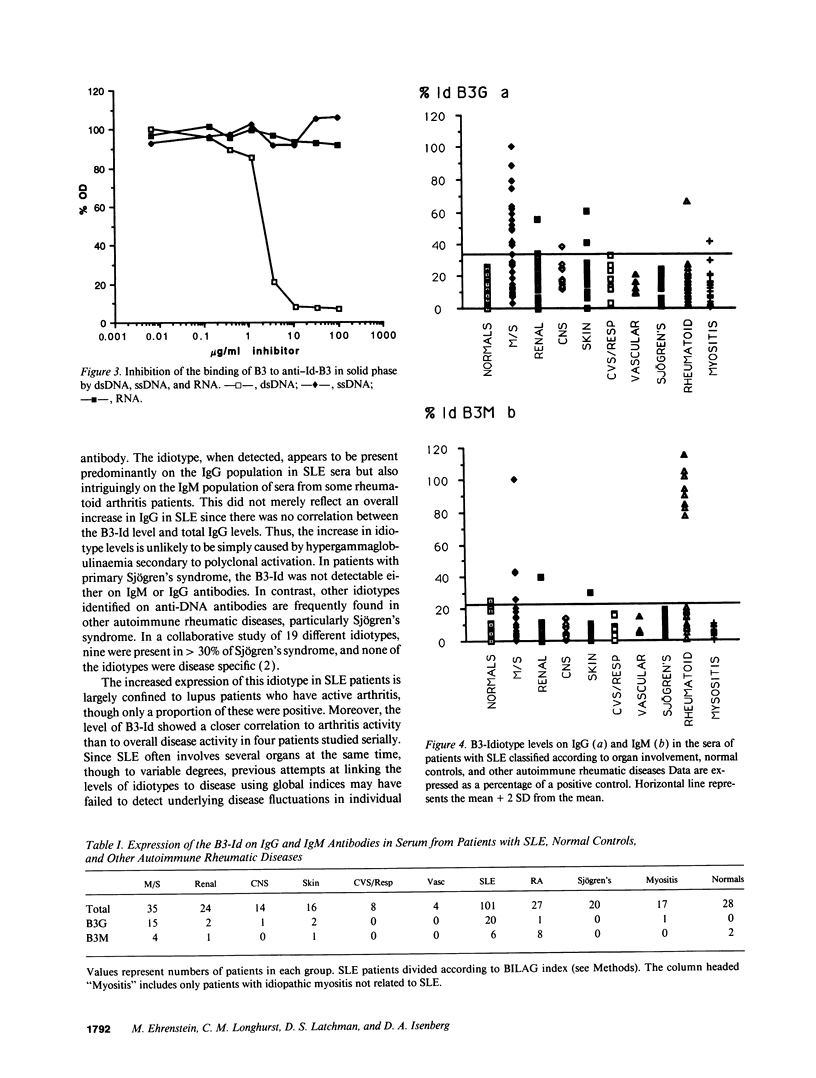
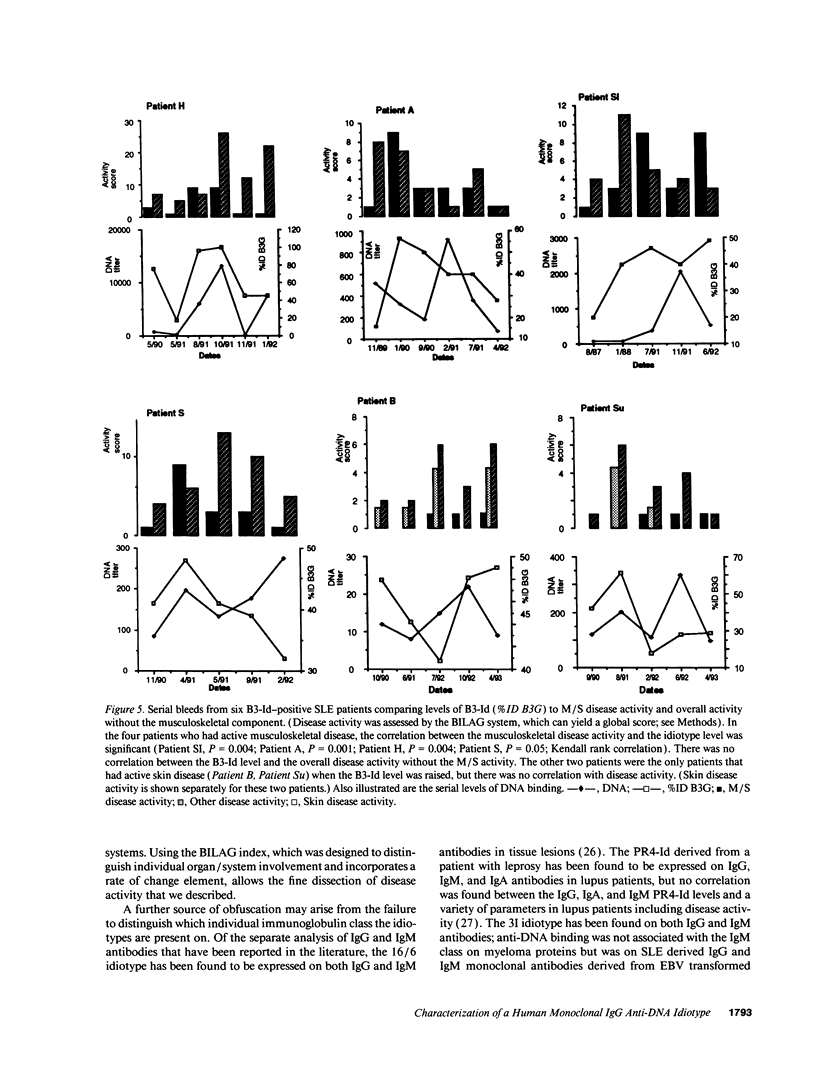
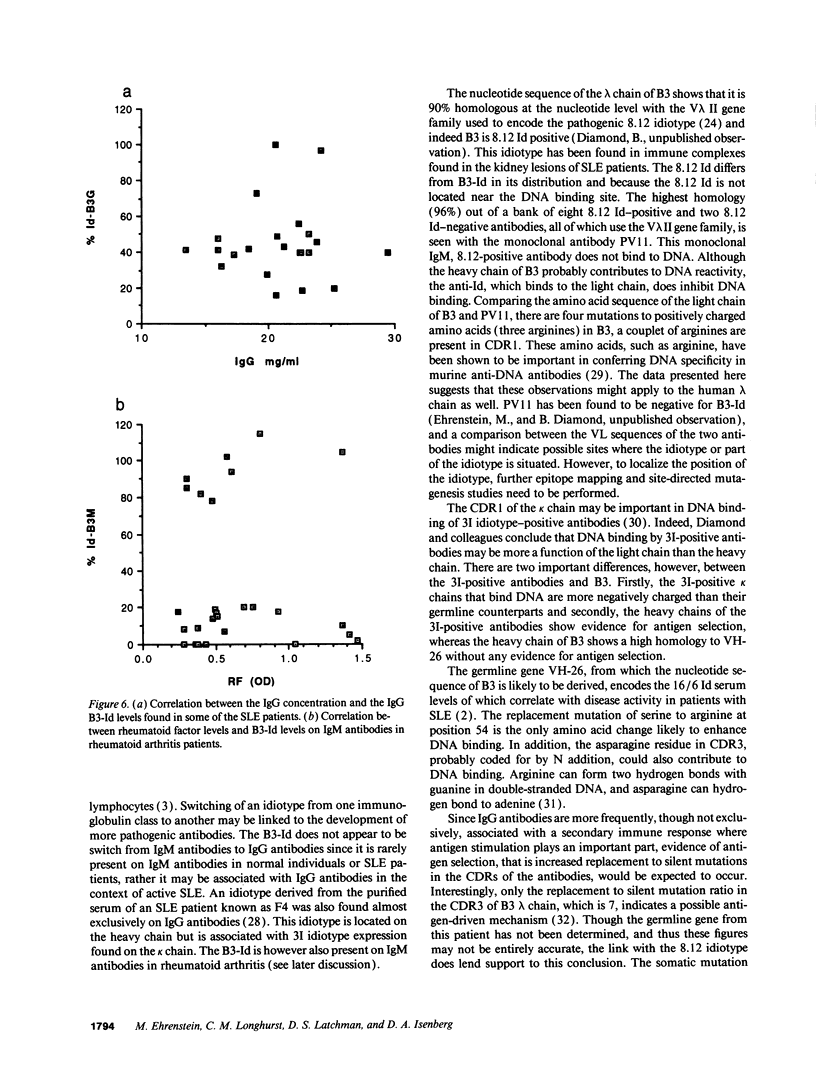
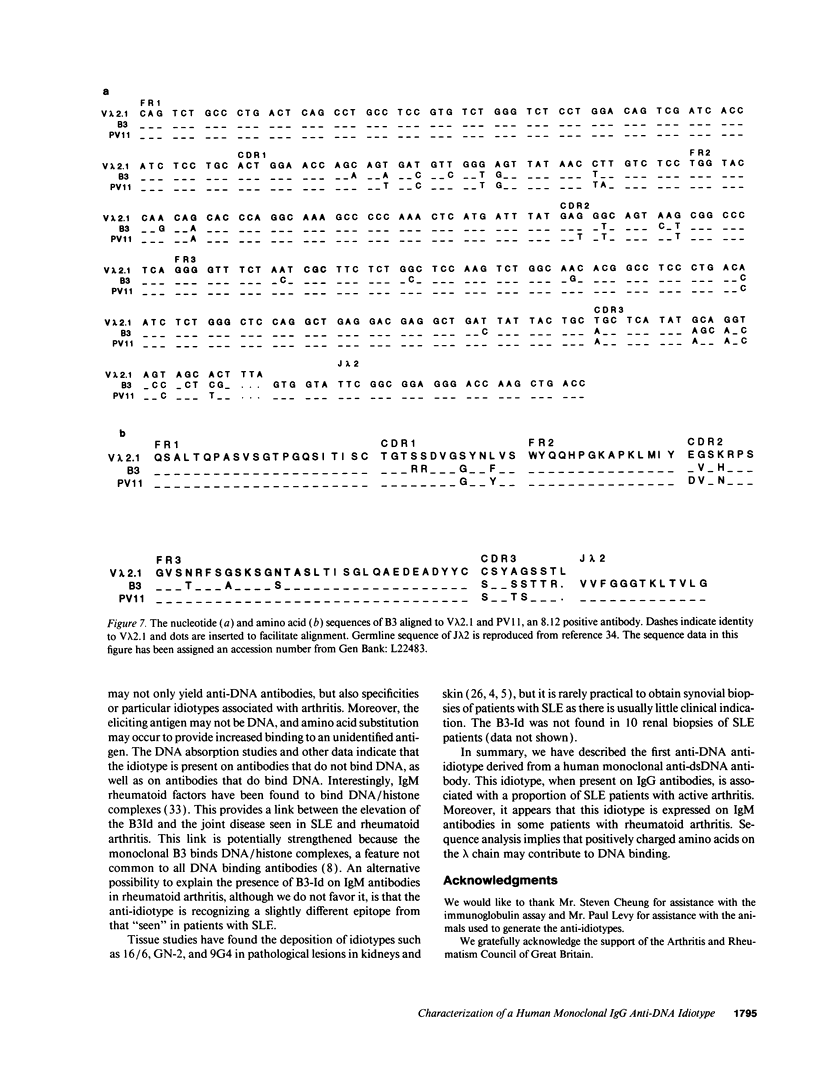
This study analyzed the distribution of an idiotype, B3-Id, in patients with active SLE, classified according to organ involvement, normal controls, and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases. A polyclonal anti-idiotype was raised by immunizing a rabbit with a monoclonal IgG anti-double-stranded (ds) DNA antibody, B3, generated from a patient with SLE who had active arthritis. The idiotype is present on the lambda chain and is at or near the binding site for double-stranded DNA. The lambda chain, which was characterized by nucleotide sequencing, was 90% homologous to the V lambda 2.1 germline, which is known to be involved in coding for nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies carrying the 8.12 idiotype. There were four changes to positively charged amino acids, known to be involved in DNA binding, in the complementarity determining regions of B3 lambda chain compared with a non-DNA binding, 8.12 positive antibody, PV11. Only one change to a positively charged amino acid occurs in the heavy chain of B3, which is 93.5% homologous to VH-26. The B3-Id was present on IgG antibodies in the serum of 20% of patients with SLE but was not found in the normal controls. Within the SLE group, there is a statistically significant association of B3-Id on IgG in the arthritis group (42%) compared to the other manifestations (9%) (P < 0.001). In four B3-Id-positive SLE patients tested serially, the level of B3-Id reflected the arthritis disease activity more closely than the overall disease activity (P < 0.05). The B3-Id was also present on IgM antibodies in one third of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. This idiotype is the first to be derived from a human monoclonal anti-DNA antibody of the IgG class, the isotype associated with active disease. Sequence analysis shows that positively charged amino acids on the lambda chain may contribute to DNA binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Arbetter A., Ibanez de Kasep G., Powell R., Tan E. M., Joslin F. Evidence for a subset of rheumatoid factors that cross-react with DNA-histone and have a distinct cross-idiotype. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1514–1527. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockly F., Alexandre D., Chuchana P., Huck S., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. First nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin variable lambda gene belonging to subgroup II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3976–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Liu M. F., Sinha S., Carson D. A. A 16/6 idiotype-positive anti-DNA antibody is encoded by a conserved VH gene with no somatic mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1429–1431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Smith A., Katz J., Preud'Homme J. L., Solomon A., Diamond B. A cross-reactive idiotype on anti-DNA antibodies defines a H chain determinant present almost exclusively on IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Katz J. B., Paul E., Aranow C., Lustgarten D., Scharff M. D. The role of somatic mutation in the pathogenic anti-DNA response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:731–757. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein M., Longhurst C., Isenberg D. A. Production and analysis of IgG monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Apr;92(1):39–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladman D. D., Goldsmith C. H., Urowitz M. B., Bacon P., Bombardier C., Isenberg D., Kalunian K., Liang M. H., Maddison P., Nived O. Crosscultural validation and reliability of 3 disease activity indices in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1992 Apr;19(4):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. M., Bacon P. A., Gordon C., Isenberg D. A., Maddison P., Snaith M. L., Symmons D. P., Viner N., Zoma A. The BILAG index: a reliable and valid instrument for measuring clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1993 Jul;86(7):447–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Collins C. Detection of cross-reactive anti-DNA antibody idiotypes on renal tissue-bound immunoglobulins from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI111959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Rowe D., Tookman A., Hopp A., Griffiths M., Paice E., Stewart J., Beverley P. C. An immunohistological study of secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Jun;43(3):470–476. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D., Spellerberg M., Williams W., Griffiths M., Stevenson F. Identification of the 9G4 idiotope in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Oct;32(10):876–882. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.10.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D., Williams W., Axford J., Bakimer R., Bell D., Casaseca-Grayson T., Diamond B., Ebling F., Hahn B., Harkiss G. Comparison of DNA antibody idiotypes in human sera: an international collaborative study of 19 idiotypes from 11 different laboratories. J Autoimmun. 1990 Aug;3(4):393–414. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalunian K. C., Panosian-Sahakian N., Ebling F. M., Cohen A. H., Louie J. S., Kaine J., Hahn B. H. Idiotypic characteristics of immunoglobulins associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Studies of antibodies deposited in glomeruli of humans. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;32(5):513–522. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manheimer-Lory A. J., Davidson A., Watkins D., Hannigan N. R., Diamond B. A. Generation and analysis of clonal IgM- and IgG-producing human B cell lines expressing an anti-DNA-associated idiotype. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI115162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manheimer-Lory A., Katz J. B., Pillinger M., Ghossein C., Smith A., Diamond B. Molecular characteristics of antibodies bearing an anti-DNA-associated idiotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1639–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Tristem M., Karpas A., Winter G. Oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reaction amplification of human immunoglobulin variable genes and design of family-specific oligonucleotide probes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):985–991. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura M., Kanayama Y., Amastu K., Negoro N., Kohda S., Takeda T., Inoue T. Significance of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies to double stranded and single stranded DNA in patients with lupus nephritis: correlation with severity of renal histology. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jan;52(1):14–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Iliev A. A., Livneh A., Diamond B. The anti-DNA-associated idiotype 8.12 is encoded by the V lambda II gene family and maps to the vicinity of L chain CDR1. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3588–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher C., Williams W., Isenberg D. A. Assessment of common idiotype PR4-Id in serial bleeds from lupus patients. Autoimmunity. 1991;9(1):7–12. doi: 10.3109/08916939108997118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radic M. Z., Mackle J., Erikson J., Mol C., Anderson W. F., Weigert M. Residues that mediate DNA binding of autoimmune antibodies. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4966–4977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Longhurst C., Chapman C. J., Ehrenstein M., Spellerberg M. B., Hamblin T. J., Ravirajan C. T., Latchman D., Isenberg D. Utilization of the VH4-21 gene segment by anti-DNA antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 1993 Dec;6(6):809–825. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1993.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symmons D. P., Coppock J. S., Bacon P. A., Bresnihan B., Isenberg D. A., Maddison P., McHugh N., Snaith M. L., Zoma A. S. Development and assessment of a computerized index of clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Members of the British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG). Q J Med. 1988 Nov;69(259):927–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udey J. A., Blomberg B. Human lambda light chain locus: organization and DNA sequences of three genomic J regions. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00768834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. A., Hillson J. L., Oppliger I. R., Mackenzie L., Lydyard P. M., Mackworth Young C. G., Brown C., Staines N. A., Isenberg D. A. Sequence analysis and idiotypic relationships of BEG-2, a human fetal antibody reactive with DNA. Lupus. 1991 Nov;1(1):9–17. doi: 10.1177/096120339100100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. A., Ravirajan C. T., Staines N. A., Isenberg D. A. A human fetal monoclonal DNA-binding antibody shares idiotypes with fetal and adult murine monoclonal DNA-binding antibodies. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):348–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. A., Williams W., Le Page S., Norden A., Soltys A., Swana G., Addison I., Hay F. C., Isenberg D. A. Analysis of autoantibody reactivity and common idiotype PR4 expression of myeloma proteins. J Autoimmun. 1989 Oct;2(5):689–700. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(89)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R., Isenberg D. DNA antibody idiotypes: an analysis of their clinical connections and origins. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):279–293. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W., Zumla A., Behrens R., Locniskar M., Voller A., McAdam K. P., Isenberg D. A. Studies of a common idiotype PR4 in autoimmune rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1097–1104. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]