Abstract
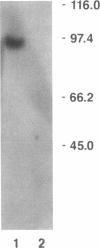
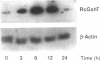
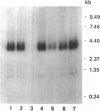
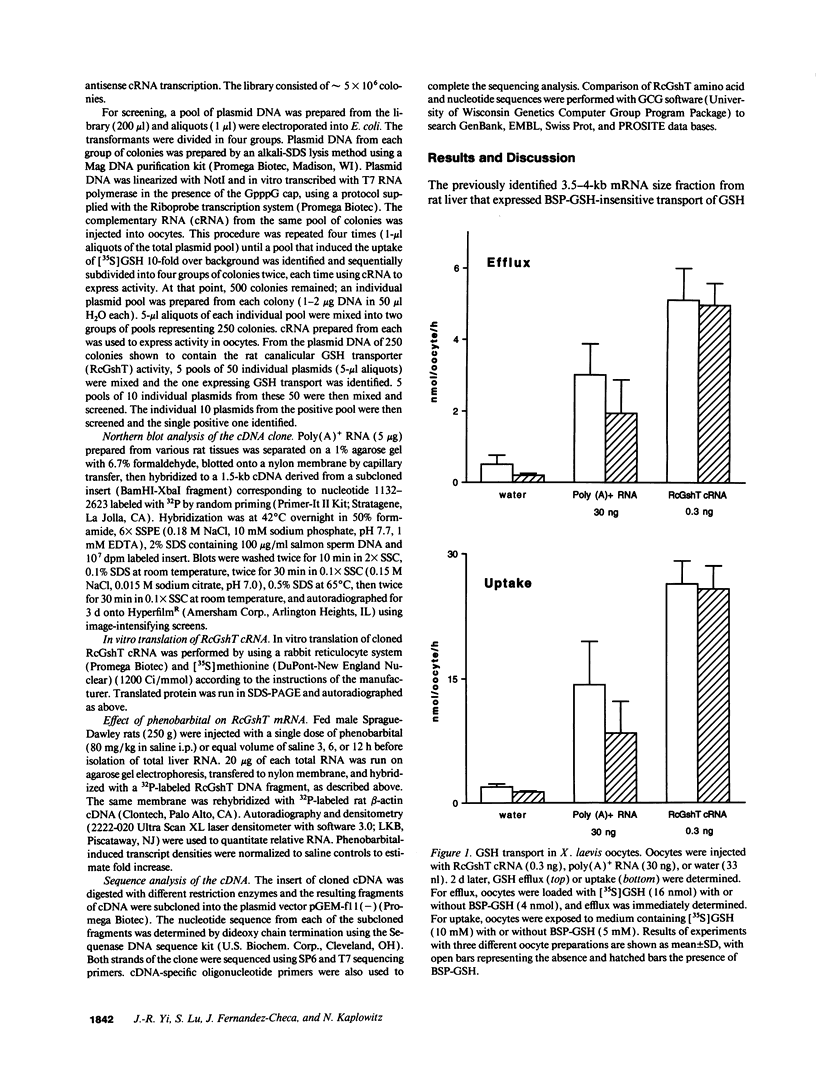
Using the Xenopus oocyte expression system, we have previously identified an approximately 4-kb fraction of mRNA from rat liver that expresses sulfobromophthalein-glutathione (BSP-GSH)-insensitive reduced glutathione (GSH) transport (Fernandez-Checa, J., J. R. Yi, C. Garcia-Ruiz, Z. Knezic, S. Tahara, and N. Kaplowitz. 1993. J. Biol. Chem. 268:2324-2328). Starting with a cDNA library constructed from this fraction, we have now isolated a single clone that expresses GSH transporter activity. The cDNA for the rat canalicular GSH transporter (RcGshT) is 4.05 kb with an open reading frame of 2,505 nucleotides encoding for a polypeptide of 835 amino acids (95,785 daltons). No identifiable homologies were found in searching various databases. An approximately 96-kD protein is generated in in vitro translation of cRNA for RcGshT. Northern blot analysis reveals a single 4-kb transcript in liver, kidney, intestine, lung, and brain. The abundance of mRNA for RcGshT in rat liver increased 3, 6, and 12 h after a single dose of phenobarbital. Insensitivity to BSP-GSH and induction by phenobarbital, unique characteristics of canalicular GSH secretion, suggest that RcGshT encodes for the canalicular GSH transporter.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballatori N., Truong A. T. Relation between biliary glutathione excretion and bile acid-independent bile flow. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):G22–G30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.1.G22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., North S. L., Hubbard R. C., Crystal R. G. Normal alveolar epithelial lining fluid contains high levels of glutathione. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jul;63(1):152–157. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Selective induction by phenobarbital of the electrogenic transport of glutathione and organic anions in rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10836–10841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Takikawa H., Horie T., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Canalicular transport of reduced glutathione in normal and mutant Eisai hyperbilirubinemic rats. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1667–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Yi J. R., Garcia-Ruiz C., Knezic Z., Tahara S. M., Kaplowitz N. Expression of rat liver reduced glutathione transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2324–2328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz C., Fernández-Checa J. C., Kaplowitz N. Bidirectional mechanism of plasma membrane transport of reduced glutathione in intact rat hepatocytes and membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22256–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan R., Kuhlenkamp J. F., Jeandidier E., Trinh H., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Evidence for carrier-mediated transport of glutathione across the blood-brain barrier in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2009–2013. doi: 10.1172/JCI114666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan R., Kuhlenkamp J. F., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Transport of glutathione at blood-brain barrier of the rat: inhibition by glutathione analogs and age-dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Dec;263(3):964–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M. The regulation of hepatic glutathione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:715–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Eberle D. E., Petrini J., Touloukian J., Corvasce M. C., Kuhlenkamp J. Factors influencing the efflux of hepatic glutathione into bile in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Anderson M. E. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkoff M., Pleasure D., Cregar L., Lin Z. P., Nissim I., Stern J., Nissim I. Glutathione turnover in cultured astrocytes: studies with [15N]glutamate. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]