Abstract
Microbial methanogenesis was examined in thermal waters, muds, and decomposing algal-bacterial mats associated with volcanic activity in Yellowstone National Park. Radioactive tracer studies with [14C]glucose, acetate, or carbonate and enrichment culture techniques demonstrated that methanogenesis occurred at temperatures near 70°C but below 80°C and correlated with hydrogen production from either geothermal processes or microbial fermentation. Three Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum strains (YT1, YTA, and YTC) isolated from diverse volcanic habitats differed from the neotype sewage strain ΔH in deoxyribonucleic acid guanosine-plus-cytosine content and immunological properties. Microbial methanogenesis was characterized in more detail at a 65°C site in the Octopus Spring algal-bacterial mat ecosystem. Here methanogenesis was active, was associated with anaerobic microbial decomposition of biomass, occurred concomitantly with detectable microbial hydrogen formation, and displayed a temperature activity optimum near 65°C. Enumeration studies estimated more than 109 chemoorganotrophic hydrolytic bacteria and 106 chemolithotrophic methanogenic bacteria per g (dry weight) of algal-bacterial mat. Enumeration, enrichment, and isolation studies revealed that the microbial population was predominantly rod shaped and asporogenous. A prevalent chemoorganotrophic organism in the mat that was isolated from an end dilution tube was a taxonomically undescribed gram-negative obligate anaerobe (strain HTB2), whereas a prevalent chemolithotrophic methanogen isolated from an end dilution tube was identified as M. thermoautotrophicum (strain YTB). Taxonomically recognizable obligate anaerobes that were isolated from glucose and xylose enrichment cultures included Thermoanaerobium brockii strain HTB and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum strain 39E. The nutritional properties, growth temperature optima, growth rates, and fermentation products of thermophilic bacterial strains 39E, HTB2, and YTB were determined.
Full text
PDF


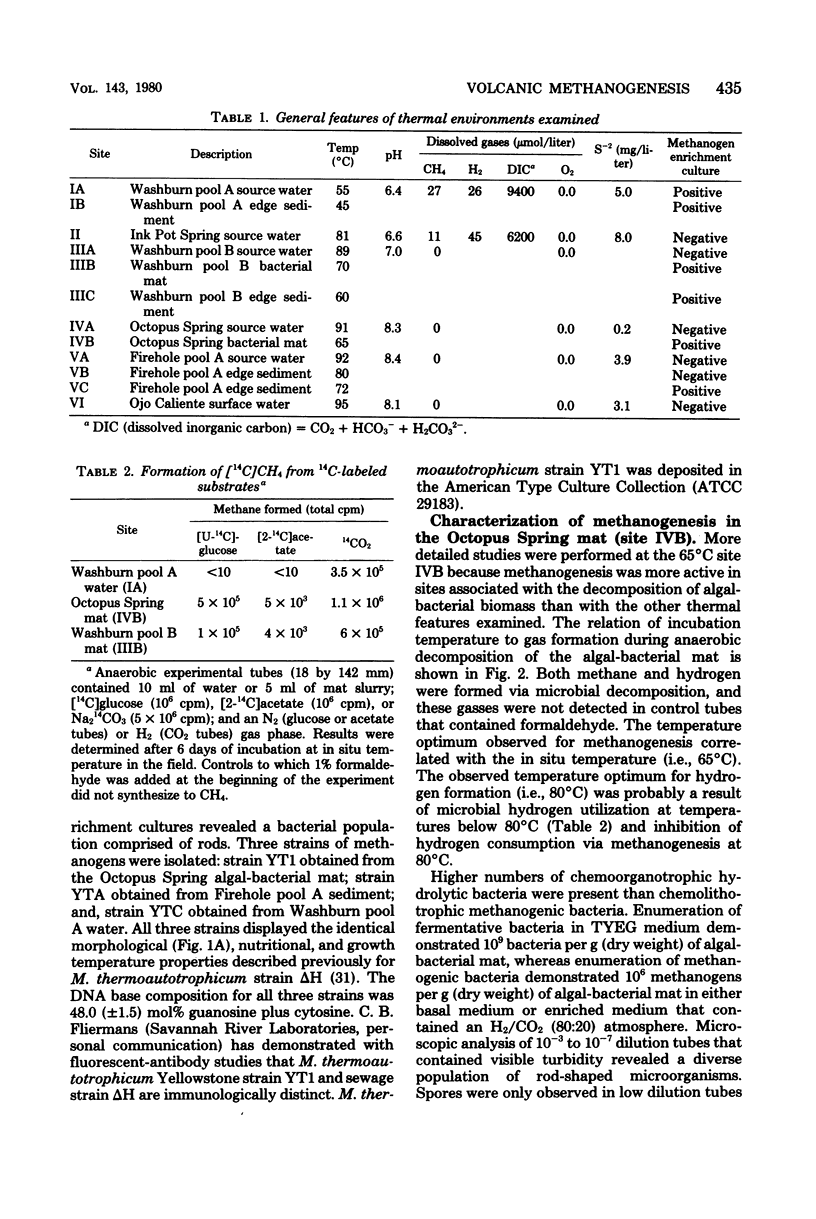
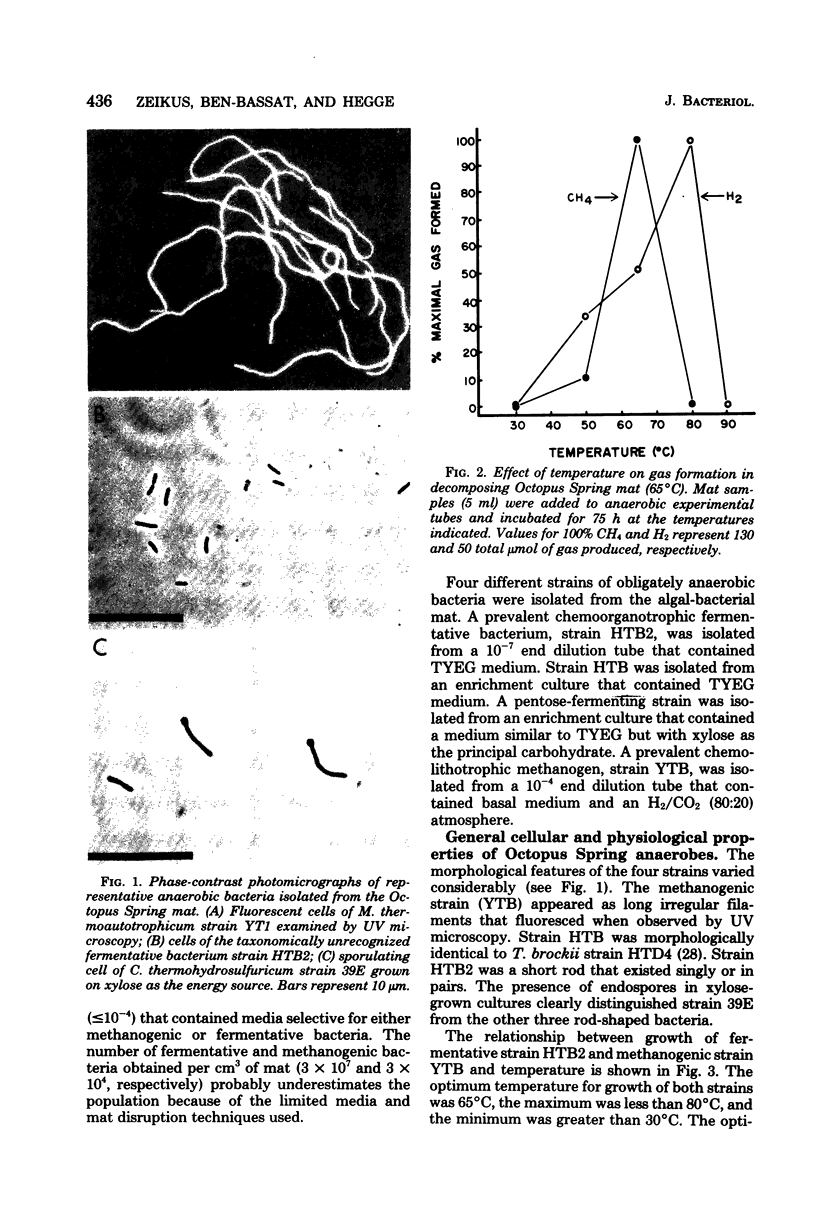
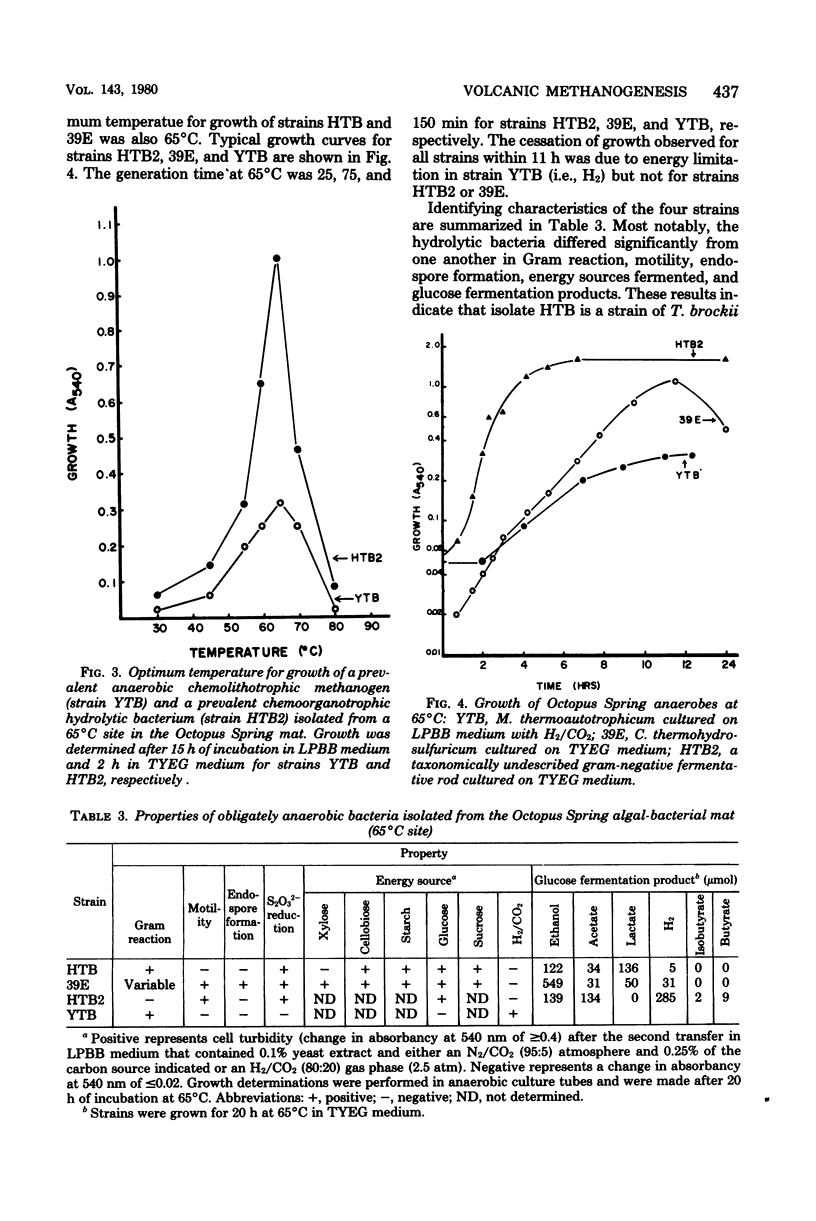



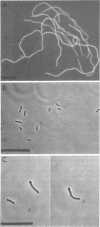
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D., Brock M. L., Bott T. L., Edwards M. R. Microbial life at 90 C: the sulfur bacteria of Boulder Spring. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):303–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.303-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):738–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.738-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuser W. G., Degens E. T., Harvey G. R., Rubin M. Methane in lake kivu: new data bearing on its origin. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):51–54. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doddema H. J., van der Drift C., Vogels G. D., Veenhuis M. Chemiosmotic coupling in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: hydrogen-dependent adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis by subcellular particles. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1081–1089. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1081-1089.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doemel W. N., Brock T. D. Structure, growth, and decomposition of laminated algal-bacterial mats in alkaline hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):433–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.433-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollaus F., Sleytr U. On the taxonomy and fine structure of some hyperthermophilic saccharolytic Clostridia. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(2):129–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00413368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M. Thermophilic methanogenesis in a hot-spring algal-bacterial mat (71 to 30 degrees C). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1019-1026.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegel J., Ljungdahl L. G., Rawson J. R. Isolation from soil and properties of the extreme thermophile Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):800–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.800-810.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Microbial methanogenesis and acetate metabolism in a meromictic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):213–221. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.213-221.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Bowen V. G. Comparative ultrastructure of methanogenic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;21(2):121–129. doi: 10.1139/m75-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Henning D. L. Methanobacterium arbophilicum sp.nov. An obligate anaerobe isolated from wetwood of living trees. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(4):543–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02565096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Winfrey M. R. Temperature limitation of methanogenesis in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.99-107.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder S. H., Mah R. A. Isolation and Characterization of a Thermophilic Strain of Methanosarcina Unable to Use H(2)-CO(2) for Methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):996–1008. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.996-1008.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]