Abstract
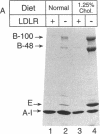
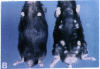
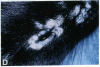
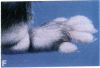
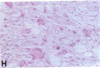
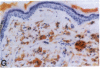
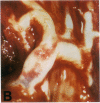
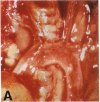
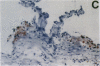
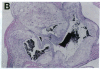
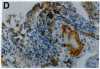
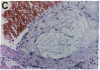
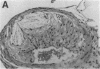
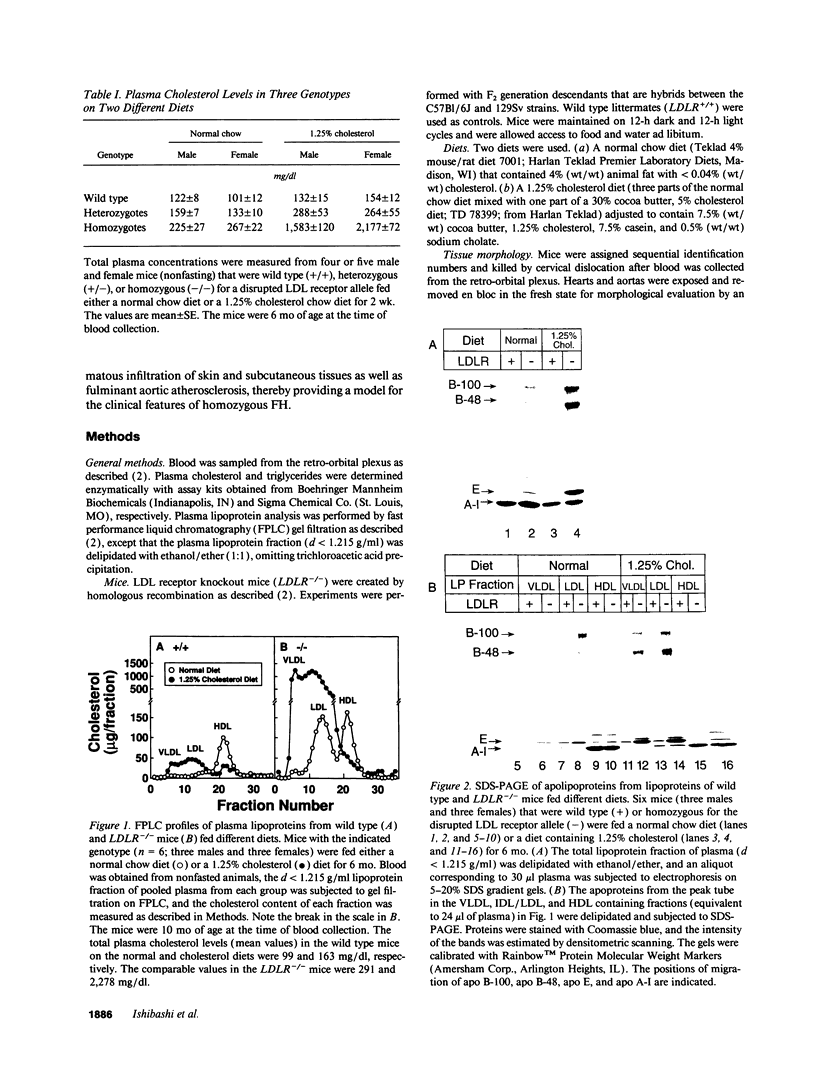
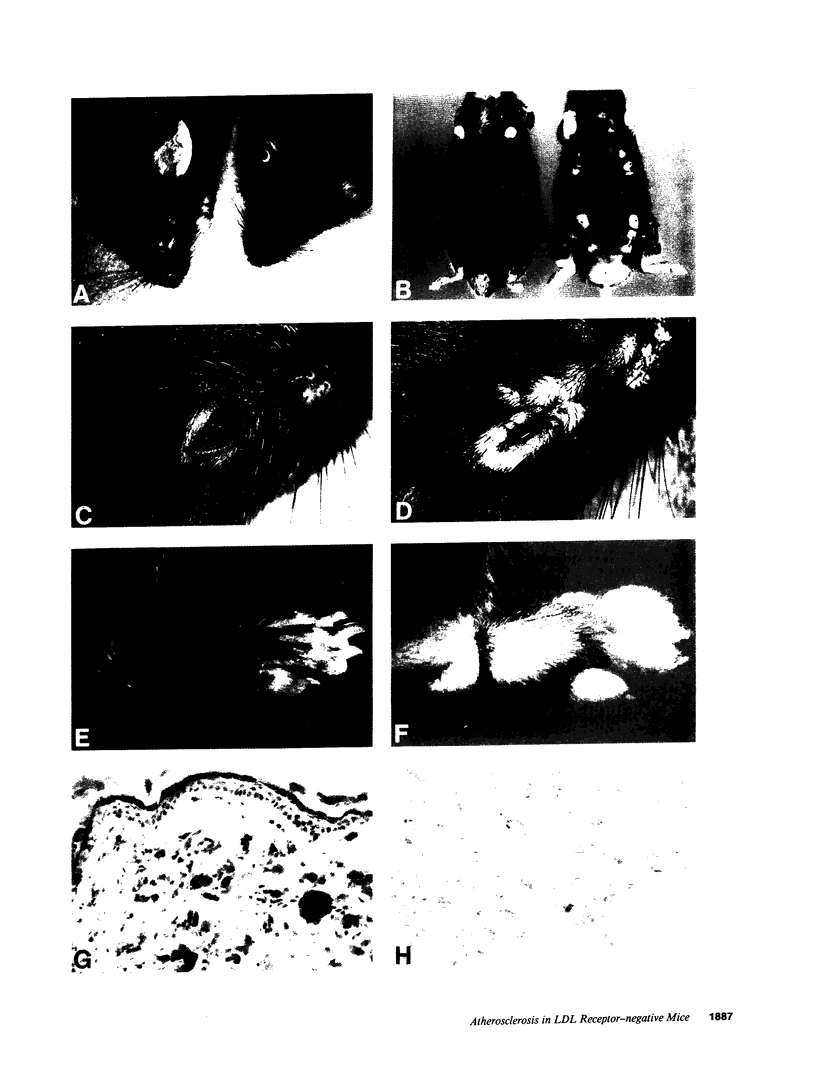
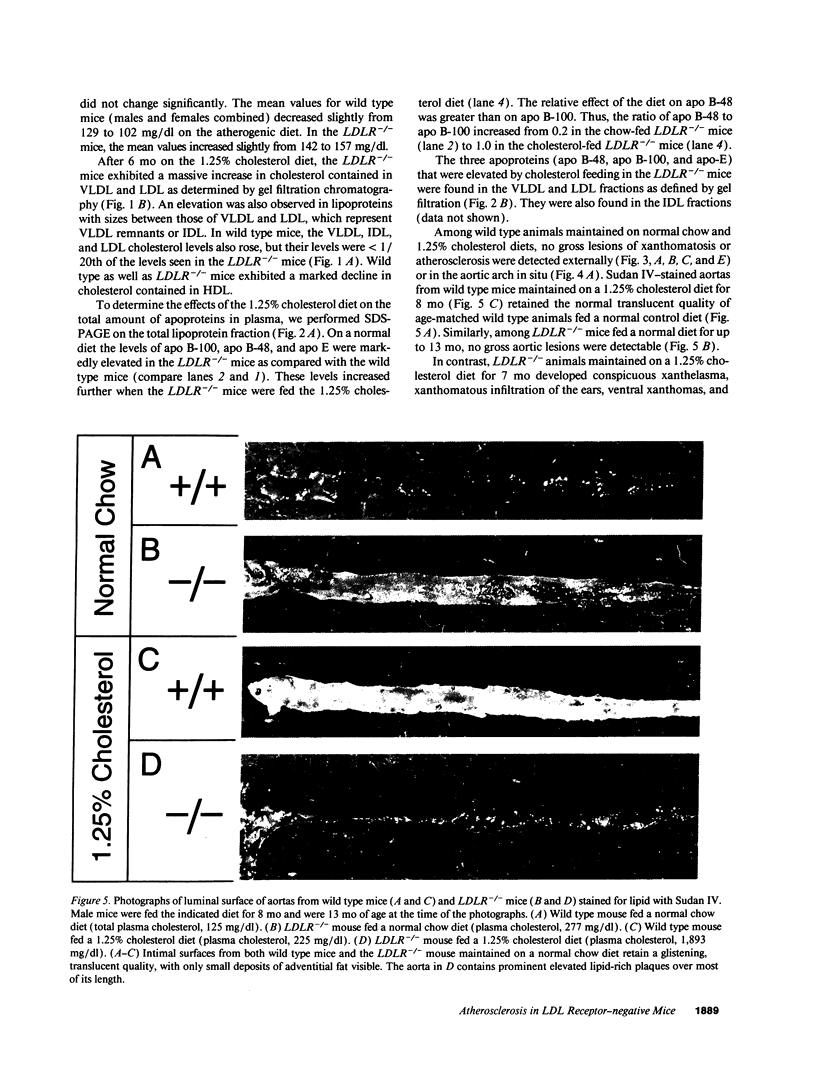
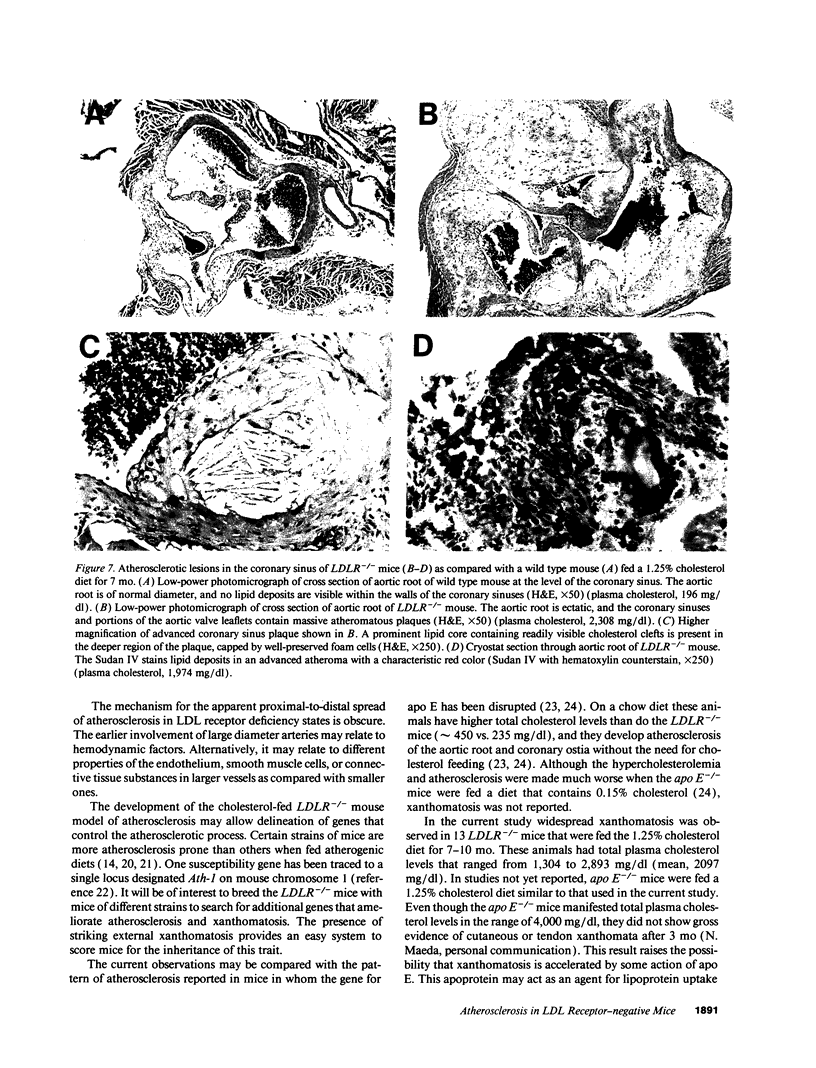
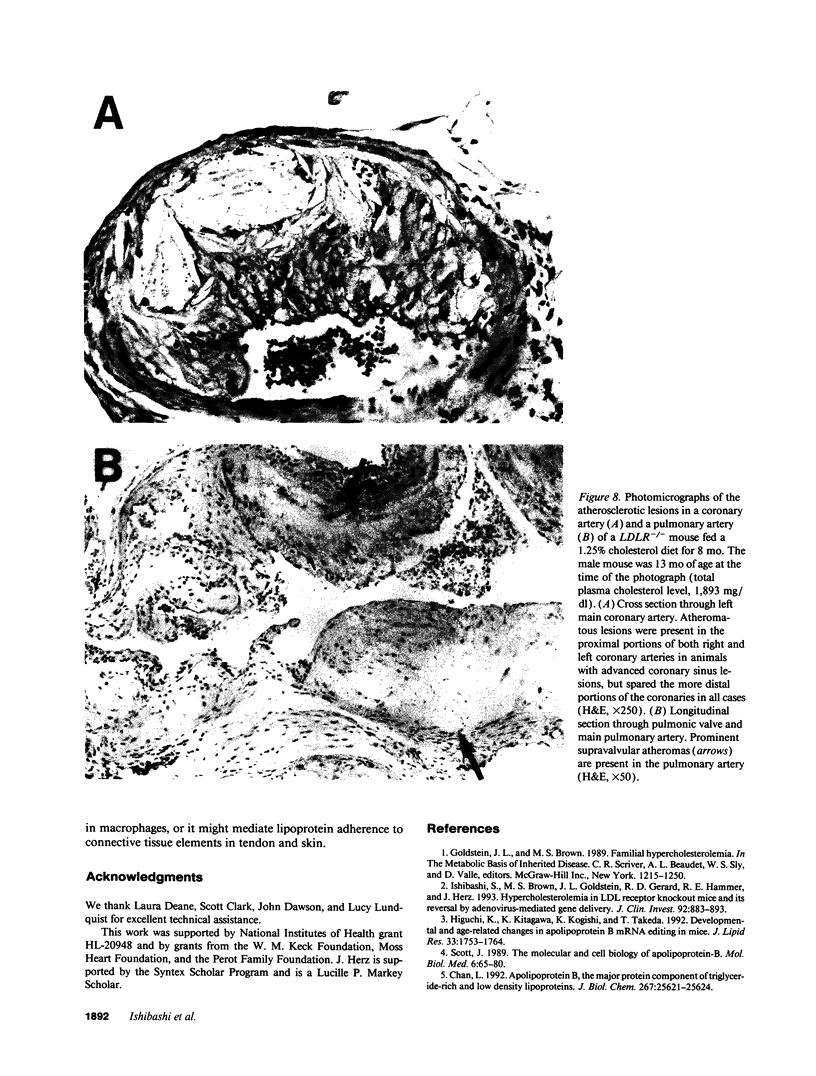
Mice that are homozygous for a targeted disruption of the LDL receptor gene (LDLR-/- mice) were fed a diet that contained 1.25% cholesterol, 7.5% cocoa butter, 7.5% casein, and 0.5% cholic acid. The total plasma cholesterol rose from 246 to > 1,500 mg/dl, associated with a marked increase in VLDL, intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL), and LDL cholesterol, and a decrease in HDL cholesterol. In wild type littermates fed the same diet, the total plasma cholesterol remained < 160 mg/dl. After 7 mo, the LDLR-/- mice developed massive xanthomatous infiltration of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The aorta and coronary ostia exhibited gross atheromata, and the aortic valve leaflets were thickened by cholesterol-laden macrophages. No such changes were seen in the LDLR-/- mice on a normal chow diet, nor in wild type mice that were fed either a chow diet or the high-fat diet. We conclude that LDL receptors are largely responsible for the resistance of wild type mice to atherosclerosis. The cholesterol-fed LDLR-/- mice offer a new model for the study of environmental and genetic factors that modify the processes of atherosclerosis and xanthomatosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Thompson G. R., Myant N. B., Steiner R., Oakley C. M. Cadiovascular complications of homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Br Heart J. 1980 Oct;44(4):361–368. doi: 10.1136/hrt.44.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein receptors in the liver. Control signals for plasma cholesterol traffic. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buja L. M., Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Watanabe Y., Brown M. S. Cellular pathology of progressive atherosclerosis in the WHHL rabbit. An animal model of familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):87–101. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buja L. M., Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W. Cellular pathology of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Pathol. 1979 Nov;97(2):327–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. Apolipoprotein B, the major protein component of triglyceride-rich and low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25621–25624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN R. L., McGILL H. C., Jr, STRONG J. P., GEER J. C. Technics for studying atherosclerotic lesions. Lab Invest. 1958 Jan-Feb;7(1):42–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haitas B., Baker S. G., Meyer T. E., Joffe B. I., Seftel H. C. Natural history and cardiac manifestations of homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Q J Med. 1990 Jul;76(279):731–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Lipid transport function of lipoproteins in blood plasma. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):E1–E5. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry W. G., Seed M. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia with supravalvar aortic stenosis treated by surgery. J R Soc Med. 1985 Apr;78(4):334–335. doi: 10.1177/014107688507800412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi K., Kitagawa K., Kogishi K., Takeda T. Developmental and age-related changes in apolipoprotein B mRNA editing in mice. J Lipid Res. 1992 Dec;33(12):1753–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Gerard R. D., Hammer R. E., Herz J. Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):883–893. doi: 10.1172/JCI116663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Hornick C. A., Havel R. J. Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in WHHL rabbits: a mechanism genetically distinct from the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Mitchell D., Reue K., Morrow A., Lusis A. J., LeBoeuf R. C. Ath-1, a gene determining atherosclerosis susceptibility and high density lipoprotein levels in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Morrow A., Brandon C., Mitchell D., Holmes P. Variation in susceptibility to atherosclerosis among inbred strains of mice. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Oct;57(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Cohen J. C., Berger G. M., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A., Gevers W. Chylomicron remnant clearance from the plasma is normal in familial hypercholesterolemic homozygotes with defined receptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1306–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI114839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. The molecular and cell biology of apolipoprotein-B. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Feb;6(1):65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van't Hooft F. M., Hardman D. A., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Apolipoprotein B (B-48) of rat chylomicrons is not a precursor of the apolipoprotein of low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):179–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]