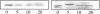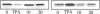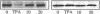Abstract
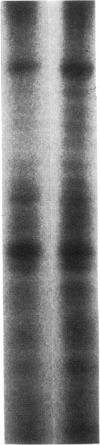
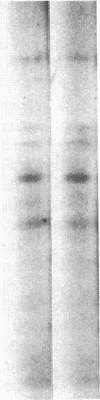
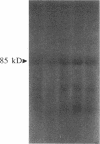
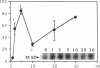
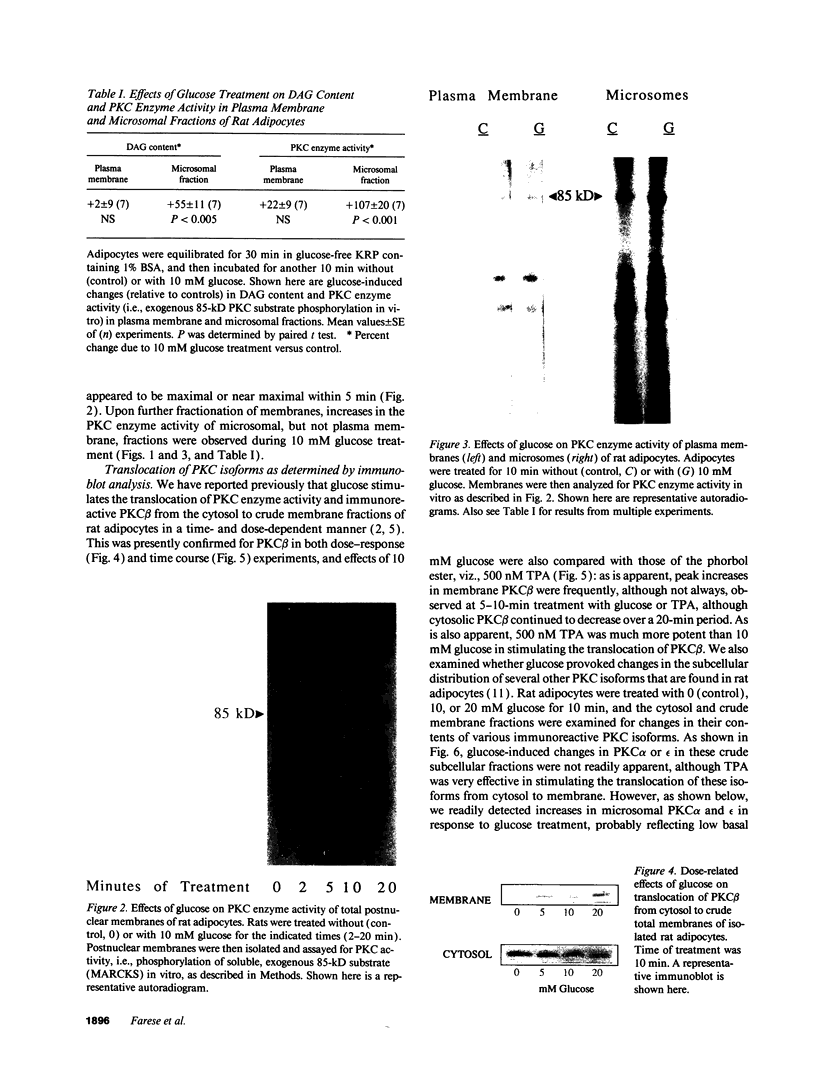
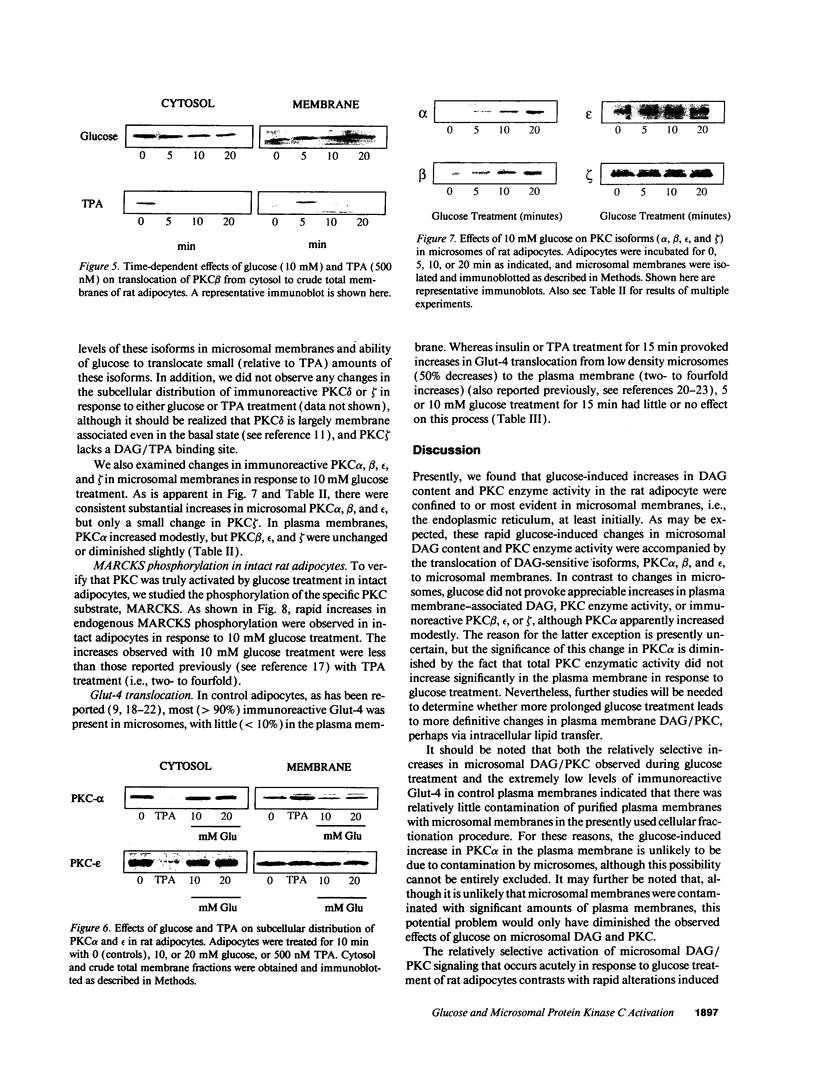
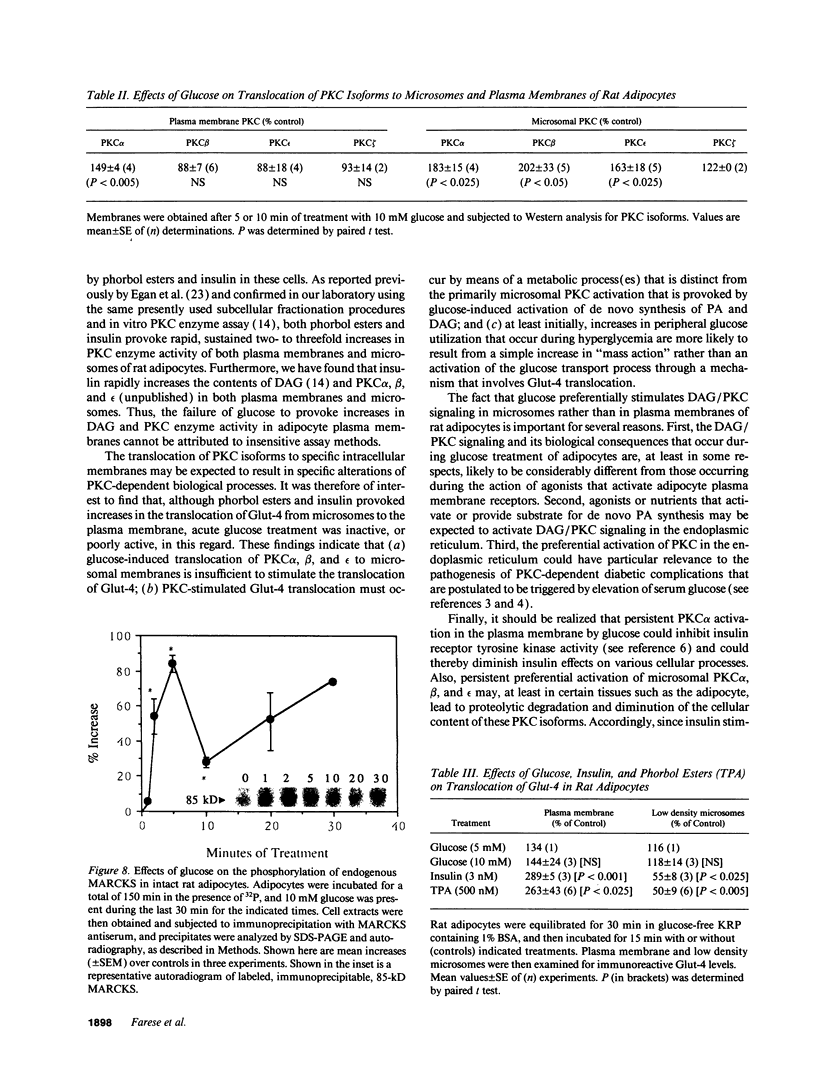
Glucose has been reported to increase the de novo synthesis of diacylglycerol (DAG) and translocate and activate protein kinase C (PKC) in rat adipocytes. Presently, we examined the major subcellular site of PKC translocation/activation in response to glucose-induced DAG. Glucose rapidly increased DAG content and PKC enzyme activity in microsomes, but not in plasma membranes or other membranes, during a 30-min treatment of rat adipocytes. This glucose-induced increase in microsomal DAG was attended by increases in immunoreactive PKC alpha, beta, and epsilon. Glucose-induced activation of DAG/PKC signaling in microsomes was not associated with a change in the translocation of Glut-4 transporters from microsomes to the plasma membrane, a biological response that is known to be stimulated by agonists, e.g., phorbol esters, which increase DAG/PKC signaling in plasma membranes, as well as in microsomes. In conclusion, an increase in de novo phospholipid synthesis, as occurs during glucose treatment of rat adipocytes, primarily activates DAG/PKC signaling in microsomes; moreover, this signaling response and biological consequences thereof may differ from those of agonists that primarily stimulate DAG/PKC signaling in the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold T. P., Standaert M. L., Hernandez H., Watson J., Mischak H., Kazanietz M. G., Zhao L., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate) phosphorylation (and other parameters of protein kinase C activation) in rat adipocytes, rat soleus muscle and BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):155–164. doi: 10.1042/bj2950155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Coleman R. A. Enzymes of glycerolipid synthesis in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:459–487. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarthy B. R., Franks D. J., Whitfield J. F., Durkin J. P. A novel method for measuring protein kinase C activity in a native membrane-associated state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91661-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Heydrick S., Kurowski T., Ruderman N. B. Diacylglycerol-protein kinase C signalling in skeletal muscle: a possible link to insulin resistance. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1991;104:206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Jaspers S., Pasceri M. Acute inhibition of insulin-stimulated glucose transport by the phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9271–9275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Davidson C. M., DeRubertis F. R. Increase in diacylglycerol mass in isolated glomeruli by glucose from de novo synthesis of glycerolipids. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):667–674. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Leitner J. W., Sussman K. E., Sherman N. A. Insulin and glucose modulate protein kinase C activity in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):570–575. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. J., Saltis J., Wek S. A., Simpson I. A., Londos C. Insulin, oxytocin, and vasopressin stimulate protein kinase C activity in adipocyte plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Francois A. J., Ways K., Arnold T. P., Hernandez H., Cooper D. R. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on subcellular distribution of protein kinase C isoforms in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):319–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2880319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M., Yu B., Hernandez H., Cooper D. R. 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin enhances phorbol ester effects on glucose transport and/or protein kinase C-beta translocation to the plasma membrane in rat adipocytes and soleus muscles. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):19949–19955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. M., Ishizuka T., Farese R. V. Interrelated effects of insulin and glucose on diacylglycerol-protein kinase-C signalling in rat adipocytes and solei muscle in vitro and in vivo in diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):2937–2948. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-2937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Cooper D. R., Arnold T., Hernandez H., Farese R. V. Downregulation of protein kinase C and insulin-stimulated 2-deoxyglucose uptake in rat adipocytes by phorbol esters, glucose, and insulin. Diabetes. 1991 Oct;40(10):1274–1281. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.10.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Hoffman J., Cooper D. R., Watson J. E., Pushkin D. B., Farese R. V. Glucose-induced synthesis of diacylglycerol de novo is associated with translocation (activation) of protein kinase C in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):234–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80630-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. S., Saltsman K. A., Ohashi H., King G. L. Activation of protein kinase C by elevation of glucose concentration: proposal for a mechanism in the development of diabetic vascular complications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5141–5145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Research Misconduct Found]
- Müller H. K., Kellerer M., Ermel B., Mühlhöfer A., Obermaier-Kusser B., Vogt B., Häring H. U. Prevention by protein kinase C inhibitors of glucose-induced insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase resistance in rat fat cells. Diabetes. 1991 Nov;40(11):1440–1448. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.11.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Wang J. K., Walaas S. I., Albert K. A., Greengard P. Localization of the MARCKS (87 kDa) protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C, in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1683–1698. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01683.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth B. L., Mehegan J. P., Jacobowitz D. M., Robey F., Iadarola M. J. Rat brain protein kinase C: purification, antibody production, and quantification in discrete regions of hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1989 Jan;52(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb10919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Egan J. J., Londos C., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of glucose transport in the rat adipose cell. Translocation of glucose transporters without stimulation of glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):261–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt B., Mushack J., Seffer E., Häring H. U. The translocation of the glucose transporter sub-types GLUT1 and GLUT4 in isolated fat cells is differently regulated by phorbol esters. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj2750597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]