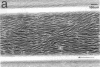
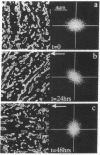
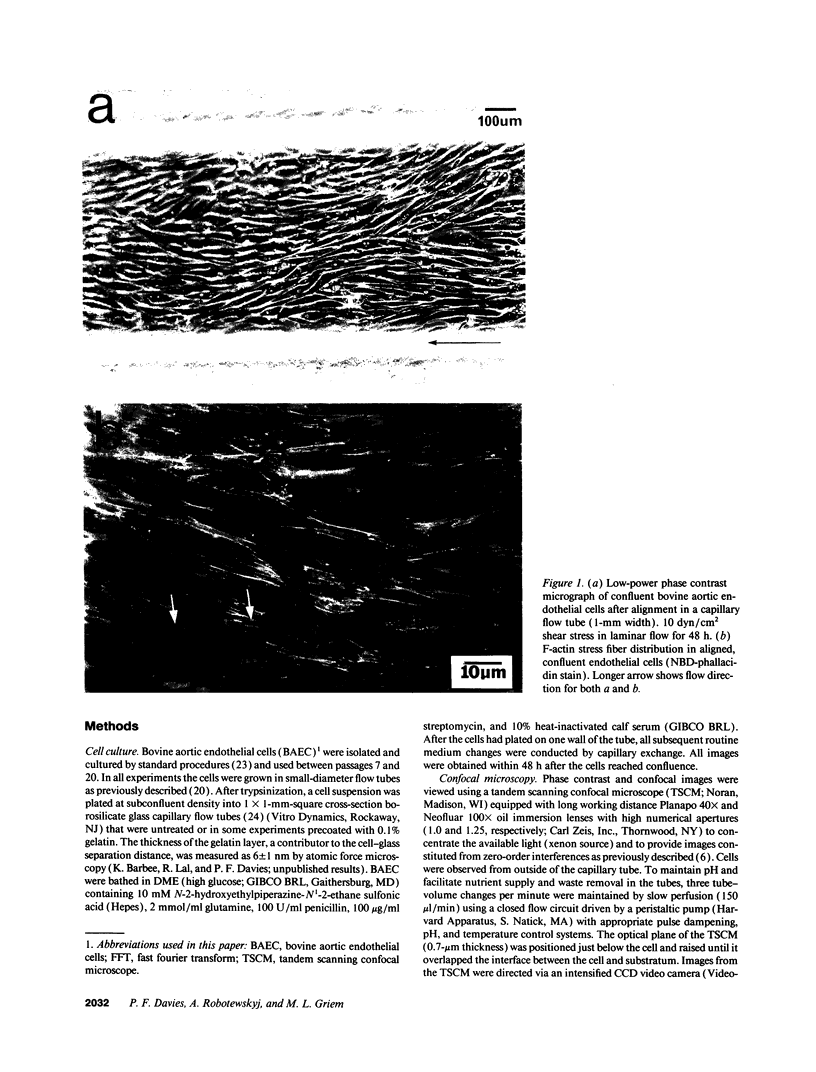
Abstract
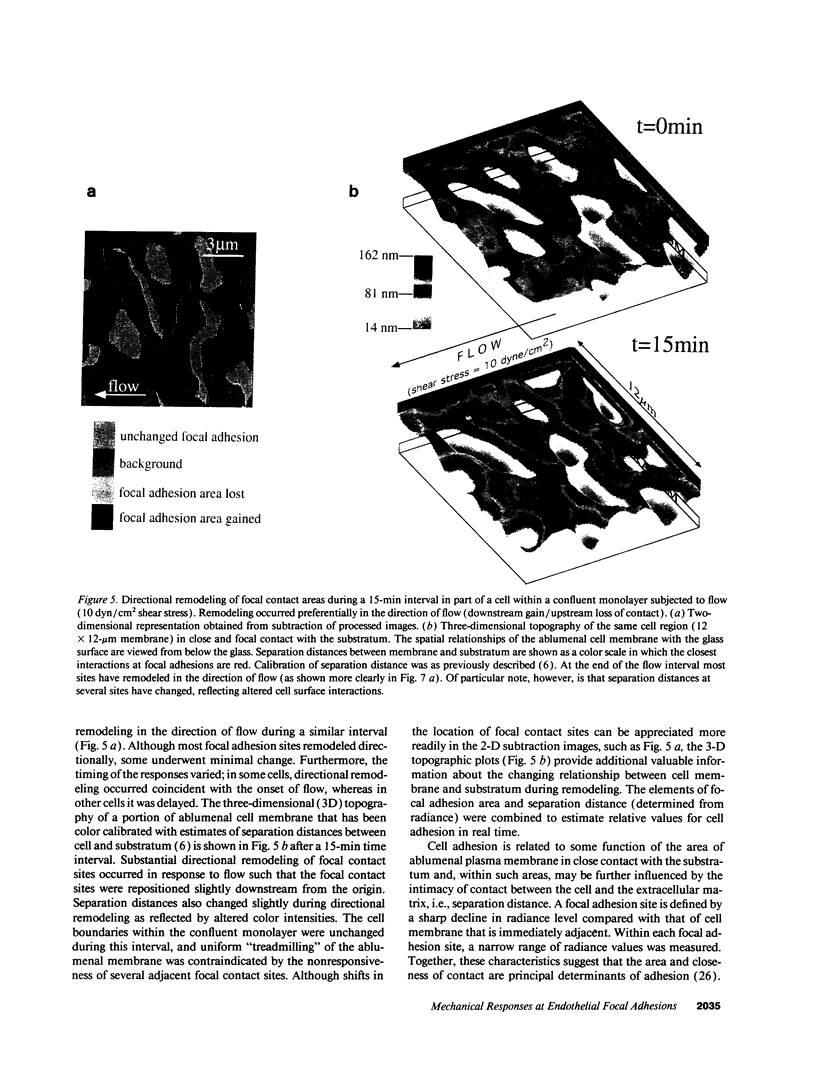
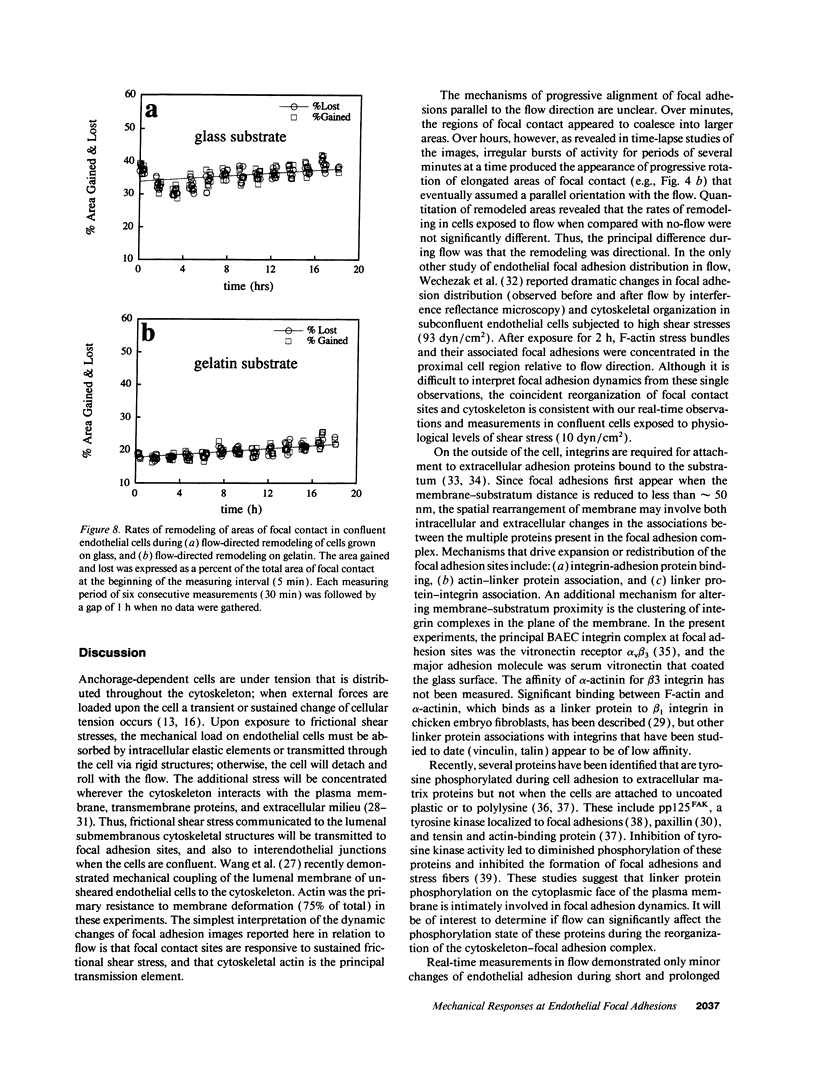
Focal adhesion sites were observed in cultured endothelial cells by tandem scanning confocal microscopy and digitized image analysis, techniques that provide real-time images of adhesion site area and topography in living cells. Image subtraction demonstrated that in the presence of unidirectional steady laminar flow (shear stress [tau] = 10 dyn/cm2) a substantial fraction of focal adhesion sites remodeled in the direction of flow. In contrast, focal adhesions of control (no flow) cells remodeled without preferred direction. In confluent monolayers subjected to shear stresses of 10 dyn/cm2, cells began to realign in the direction of flow after 7-9 h. This was accompanied by redistribution of intracellular stress fibers, alignment of individual focal adhesion sites, and the coalescence of smaller sites resulting in fewer, but larger, focal adhesions per cell. Cell adhesion, repeatedly calculated in the same cells as a function of the areas of focal contact and the separation distances between membrane and substratum, varied by < 10% during both short (30 min), or prolonged (< or = 24 h), periods of exposure to flow. Consistent with these measurements, the gains and losses of focal adhesion area as each site remodeled were approximately equivalent. When the glass substratum was coated with gelatin, rates of remodeling were inhibited by 47% during flow (tau = 10 dyn/cm2). These studies: (a) reveal the dynamic nature of focal adhesion; (b) demonstrate that these sites at the ablumenal endothelial membrane are both acutely and chronically responsive to frictional shear stress forces applied to the opposite (lumenal) cell surface; and (c) suggest that components of the focal adhesion complex may be mechanically responsive elements coupled to the cytoskeleton.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockholt S. M., Burridge K. Cell spreading on extracellular matrix proteins induces tyrosine phosphorylation of tensin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14565–14567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Turner C. E., Romer L. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):893–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Nannizzi L., Smith J. W., Cheresh D. A. The vitronectin receptor alpha v beta 3 binds fibronectin and acts in concert with alpha 5 beta 1 in promoting cellular attachment and spreading on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2795–2800. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F. Endothelium as a signal transduction interface for flow forces: cell surface dynamics. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Robotewskyj A., Griem M. L. Endothelial cell adhesion in real time. Measurements in vitro by tandem scanning confocal image analysis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2640–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI116503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Tripathi S. C. Mechanical stress mechanisms and the cell. An endothelial paradigm. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):239–245. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Conforti G., Abbadini M., Gaboli M., Marchisio P. C. Fibronectin and vitronectin regulate the organization of their respective Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1215–1223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennerll T. J., Joshi H. C., Steel V. L., Buxbaum R. E., Heidemann S. R. Tension and compression in the cytoskeleton of PC-12 neurites. II: Quantitative measurements. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):665–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dull R. O., Tarbell J. M., Davies P. F. Mechanisms of flow-mediated signal transduction in endothelial cells: kinetics of ATP surface concentrations. J Vasc Res. 1992 Nov-Dec;29(6):410–419. doi: 10.1159/000158959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Birdwell C. R. Determination of cellular shape by the extracellular matrix and its correlation with the control of cellular growth. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4155–4171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. D., Meier S. Stimulation of corneal differentiation by interaction between cell surface and extracellular matrix. II. Further studies on the nature and site of transfilter "induction". Dev Biol. 1976 Aug;52(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Buxbaum R. E. Tension as a regulator and integrator of axonal growth. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;17(1):6–10. doi: 10.1002/cm.970170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A. R., Kellie S. Regulation of integrin mobility and cytoskeletal association in normal and RSV-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1990 Oct;97(Pt 2):307–315. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. Mechanochemical switching between growth and differentiation during fibroblast growth factor-stimulated angiogenesis in vitro: role of extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):317–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. Integrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzard C. S., Lochner L. R. Formation of cell-to-substrate contacts during fibroblast motility: an interference-reflexion study. J Cell Sci. 1980 Apr;42:81–116. doi: 10.1242/jcs.42.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Pasquale E. B., Wang J. Y., Singer S. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins are concentrated in focal adhesions and intercellular junctions in normal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6576–6580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Hök M. Thrombospondin modulates focal adhesions in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1309–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen S. P., Clapham D. E., Davies P. F. Haemodynamic shear stress activates a K+ current in vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):168–170. doi: 10.1038/331168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otey C. A., Pavalko F. M., Burridge K. An interaction between alpha-actinin and the beta 1 integrin subunit in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):721–729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock S. W. Tandem scanning reflected-light microscopy of cell-substratum adhesions and stress fibres in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 May;93(Pt 1):143–146. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pienta K. J., Coffey D. S. Nuclear-cytoskeletal interactions: evidence for physical connections between the nucleus and cell periphery and their alteration by transformation. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Aug;49(4):357–365. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad A. R., Logan S. A., Nerem R. M., Schwartz C. J., Sprague E. A. Flow-related responses of intracellular inositol phosphate levels in cultured aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):827–836. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick N., Collins T., Atkinson W., Bonthron D. T., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M. D., Borgman C. A., Cobb B. S., Vines R. R., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. pp125FAK a structurally distinctive protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J. R., Karp S., Ingber D. E. Altering the cellular mechanical force balance results in integrated changes in cell, cytoskeletal and nuclear shape. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):1215–1222. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truskey G. A., Burmeister J. S., Grapa E., Reichert W. M. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM). II. Topographical mapping of relative cell/substratum separation distances. J Cell Sci. 1992 Oct;103(Pt 2):491–499. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner C. E., Burridge K. Transmembrane molecular assemblies in cell-extracellular matrix interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner C. E., Glenney J. R., Jr, Burridge K. Paxillin: a new vinculin-binding protein present in focal adhesions. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1059–1068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschueren H. Interference reflection microscopy in cell biology: methodology and applications. J Cell Sci. 1985 Apr;75:279–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.75.1.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk T., Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. A role for integrin in the formation of sarcomeric cytoarchitecture. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90449-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechezak A. R., Wight T. N., Viggers R. F., Sauvage L. R. Endothelial adherence under shear stress is dependent upon microfilament reorganization. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):136–146. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. P., Odland G. F., Clark R. A. Temporal relationships of F-actin bundle formation, collagen and fibronectin matrix assembly, and fibronectin receptor expression to wound contraction. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):133–145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zand M. S., Albrecht-Buehler G. Long-term observation of cultured cells by interference-reflection microscopy: near-infrared illumination and Y-contrast image processing. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;13(2):94–103. doi: 10.1002/cm.970130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]