Abstract
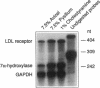
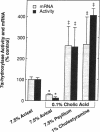
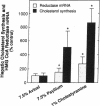
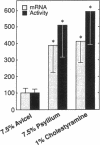
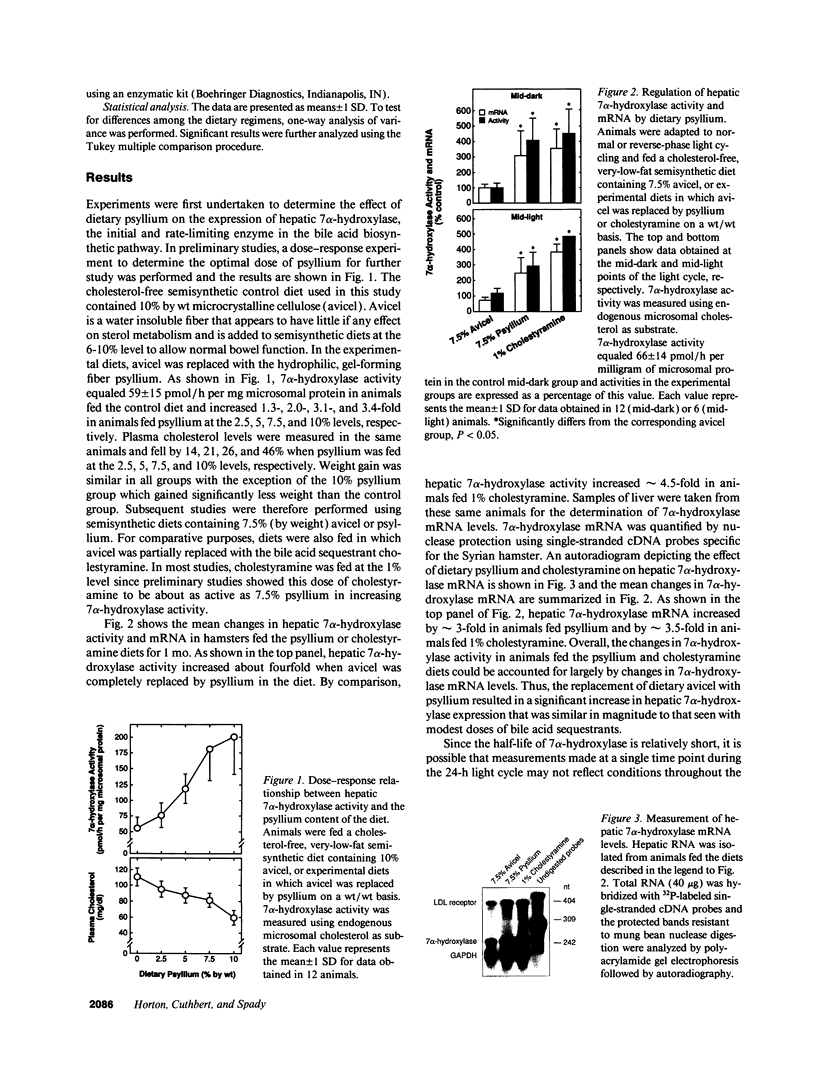
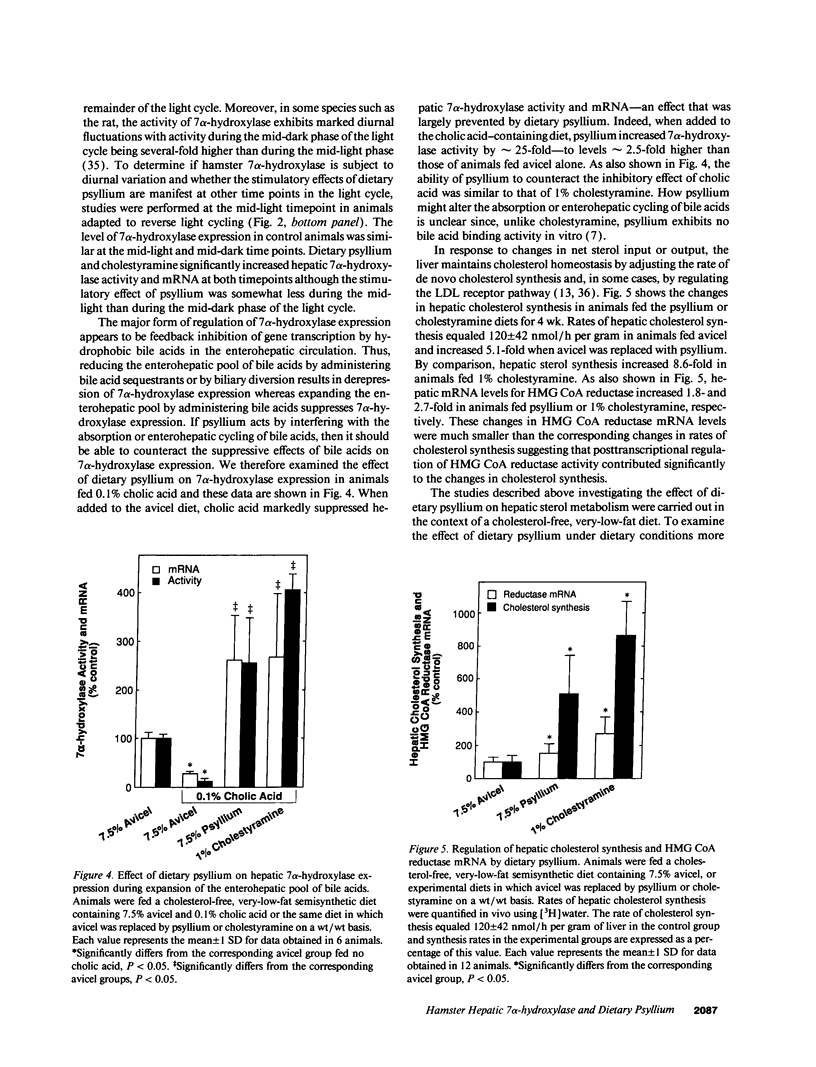
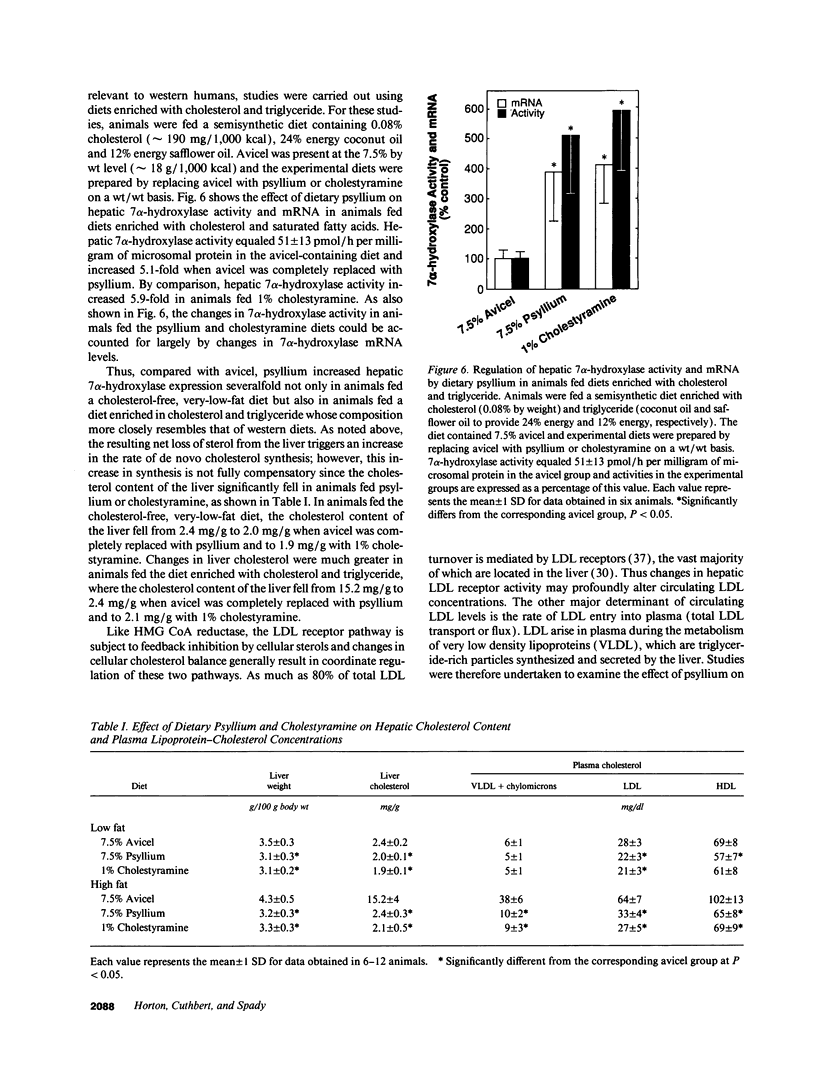
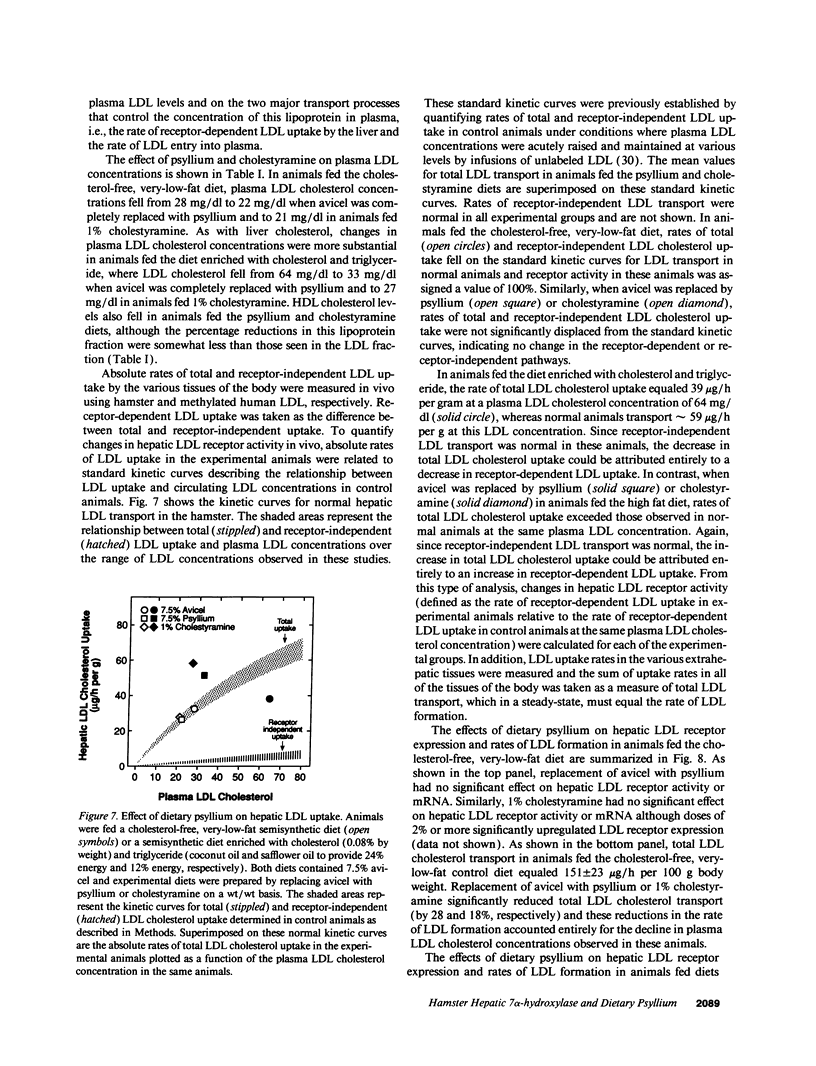
Soluble fiber consistently lowers plasma total and low density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol concentrations in humans and various animal models including the hamster; however, the mechanism of this effect remains incompletely defined. We performed studies to determine the activity of dietary psyllium on hepatic 7 alpha-hydroxylase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase and LDL receptor expression in the hamster. In animals fed a cholesterol-free semisynthetic diet containing 7.5% cellulose (avicel) as a fiber source, substitution of psyllium for avicel increased hepatic 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA levels by 3-4-fold. Comparable effects on 7 alpha-hydroxylase expression were observed with 1% cholestyramine. Psyllium also increased hepatic 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA in animals fed a diet enriched with cholesterol and triglyceride. Activation of 7 alpha-hydroxylase was associated with an increase in hepatic cholesterol synthesis that was apparently not fully compensatory since the cholesterol content of the liver declined. Although dietary psyllium did not increase hepatic LDL receptor expression in animals fed the cholesterol-free, very-low-fat diet, it did increase (or at least restore) receptor expression that had been downregulated by dietary cholesterol and triglyceride. Thus, 7.5% dietary psyllium produced effects on hepatic 7 alpha-hydroxylase and LDL metabolism that were similar to those of 1% cholestyramine. Induction of hepatic 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity by dietary psyllium may account, in large part, for the hypocholesterolemic effect of this soluble fiber.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham Z. D., Mehta T. Three-week psyllium-husk supplementation: effect on plasma cholesterol concentrations, fecal steroid excretion, and carbohydrate absorption in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Jan;47(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. W., Deakins D. A., Floore T. L., Smith B. M., Whitis S. E. Dietary fiber and coronary heart disease. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1990;29(2):95–147. doi: 10.1080/10408399009527518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. W., Garrity T. F., Wood C. L., Whitis S. E., Smith B. M., Oeltgen P. R. Prospective, randomized, controlled comparison of the effects of low-fat and low-fat plus high-fiber diets on serum lipid concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Nov;56(5):887–894. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/56.5.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. W., Zettwoch N., Feldman T., Tietyen-Clark J., Oeltgen P., Bishop C. W. Cholesterol-lowering effects of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid for hypercholesterolemic men. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Feb;148(2):292–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. P., Hectorne K., Reynolds H., Balm T. K., Hunninghake D. B. Cholesterol-lowering effects of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid. Adjunct therapy to a prudent diet for patients with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia. JAMA. 1989 Jun 16;261(23):3419–3423. doi: 10.1001/jama.261.23.3419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang J. Y. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography assay of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:483–491. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06117-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Einarsson K., Johansson G. Effect of biliary drainage on individual reactions in the conversion of cholesterol to taurochlic acid. Bile acids and steroids 180. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jul;2(1):44–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., Daggy B. P., McKinley C., Story J. A. Effects of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid on LDL-cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in hypercholesterolemic men. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1183–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Pittman R. C., Keller G. A., Steinberg D. Tissue sites of degradation of apoprotein A-I in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7161–7167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. J., Drummond J. L. Circadian rhythm of biliary excretion and its control mechanisms in rats with chronic biliary drainage. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1427–1437. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. D., Cuthbert J. A., Spady D. K. Dietary fatty acids regulate hepatic low density lipoprotein (LDL) transport by altering LDL receptor protein and mRNA levels. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):743–749. doi: 10.1172/JCI116645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Andersson S., Slaughter C. A., Russell D. W. Cloning and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8190–8197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. J., Wolever T. M., Rao A. V., Hegele R. A., Mitchell S. J., Ransom T. P., Boctor D. L., Spadafora P. J., Jenkins A. L., Mehling C. Effect on blood lipids of very high intakes of fiber in diets low in saturated fat and cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 1;329(1):21–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307013290104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. M. Dietary fiber. J Lipid Res. 1982 Feb;23(2):221–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesaniemi Y. A., Witztum J. L., Steinbrecher U. P. Receptor-mediated catabolism of low density lipoprotein in man. Quantitation using glucosylated low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):950–959. doi: 10.1172/JCI110849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesäniemi Y. A., Tarpila S., Miettinen T. A. Low vs high dietary fiber and serum, biliary, and fecal lipids in middle-aged men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990 Jun;51(6):1007–1012. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/51.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaw K. T., Barrett-Connor E. Dietary fiber and reduced ischemic heart disease mortality rates in men and women: a 12-year prospective study. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Dec;126(6):1093–1102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromhout D., Bosschieter E. B., de Lezenne Coulander C. Dietary fibre and 10-year mortality from coronary heart disease, cancer, and all causes. The Zutphen study. Lancet. 1982 Sep 4;2(8297):518–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90600-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Miller V. T., Muesing R. A., Stoy D. B., Balm T. K., LaRosa J. C. Comparison of psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid and cellulose as adjuncts to a prudent diet in the treatment of mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Sep;150(9):1822–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Melchior G. W., Innerarity T. L., Holcombe K. S. Inhibition of receptor-mediated clearance of lysine and arginine-modified lipoproteins from the plasma of rats and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M. R., Mehta T., Leathers C. W., Foster D. M. Psyllium husk. I: Effect on plasma lipoproteins, cholesterol metabolism, and atherosclerosis in African green monkeys. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Aug;56(2):376–384. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/56.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Effects of neomycin alone and in combination with cholestyramine on serum cholesterol and fecal steroids in hypercholesterolemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1485–1493. doi: 10.1172/JCI109607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Tarpila S. Serum lipids and cholesterol metabolism during guar gum, plantago ovata and high fibre treatments. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Aug 31;183(3):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myant N. B., Mitropoulos K. A. Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):135–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Okuda K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80992-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Bennett M., Rhee K. Red 25, a protein that binds specifically to the sterol regulatory region in the promoter for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18973–18982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reihnér E., Angelin B., Rudling M., Ewerth S., Björkhem I., Einarsson K. Regulation of hepatic cholesterol metabolism in humans: stimulatory effects of cholestyramine on HMG-CoA reductase activity and low density lipoprotein receptor expression in gallstone patients. J Lipid Res. 1990 Dec;31(12):2219–2226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Setchell K. D. Bile acid biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4737–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Biochemical site of regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Sterol synthesis in vivo in 18 tissues of the squirrel monkey, guinea pig, rabbit, hamster, and rat. J Lipid Res. 1983 Mar;24(3):303–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K. Hepatic clearance of plasma low density lipoproteins. Semin Liver Dis. 1992 Nov;12(4):373–385. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Meddings J. B., Dietschy J. M. Kinetic constants for receptor-dependent and receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the tissues of the rat and hamster. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1474–1481. doi: 10.1172/JCI112460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Stange E. F., Bilhartz L. E., Dietschy J. M. Bile acids regulate hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor activity in the hamster by altering cholesterol flux across the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1916–1920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Rates of low density lipoprotein uptake and cholesterol synthesis are regulated independently in the liver. J Lipid Res. 1985 Apr;26(4):465–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprecher D. L., Harris B. V., Goldberg A. C., Anderson E. C., Bayuk L. M., Russell B. S., Crone D. S., Quinn C., Bateman J., Kuzmak B. R. Efficacy of psyllium in reducing serum cholesterol levels in hypercholesterolemic patients on high- or low-fat diets. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Oct 1;119(7 Pt 1):545–554. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-7_part_1-199310010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley M. M., Paul D., Gacke D., Murphy J. Effects of cholestyramine, metamucil, and cellulose on fecal bile salt excretion in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Dec;65(6):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling K. E., Benson G. M., Bond B., Gee A., Glen A., Haynes C., Jackson B. Cholesterol lowering and bile acid excretion in the hamster with cholestyramine treatment. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Aug;89(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90059-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Herndon M. W., Dietschy J. M. Reevaluation and application of the dual-isotope plasma ratio method for the measurement of intestinal cholesterol absorption in the hamster. J Lipid Res. 1994 Feb;35(2):328–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama C., Wang X., Briggs M. R., Admon A., Wu J., Hua X., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):187–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]