Abstract
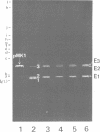
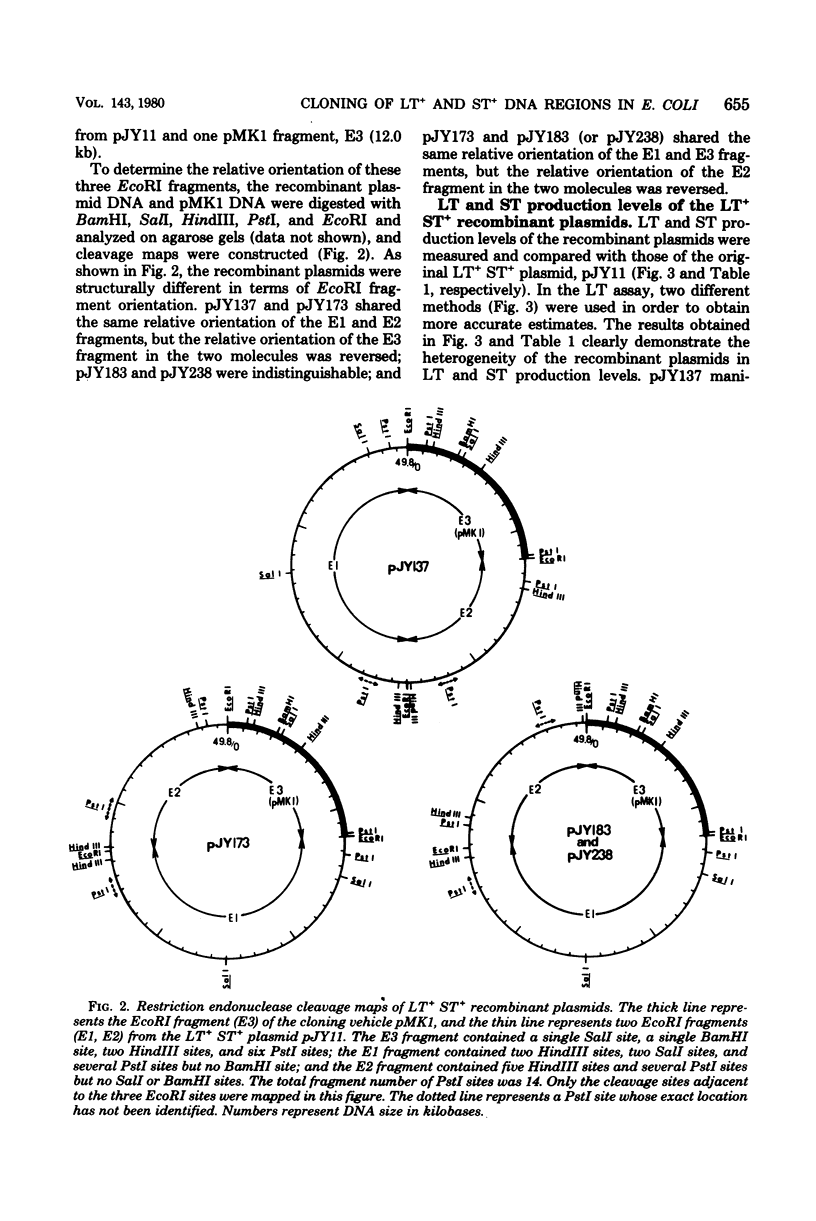
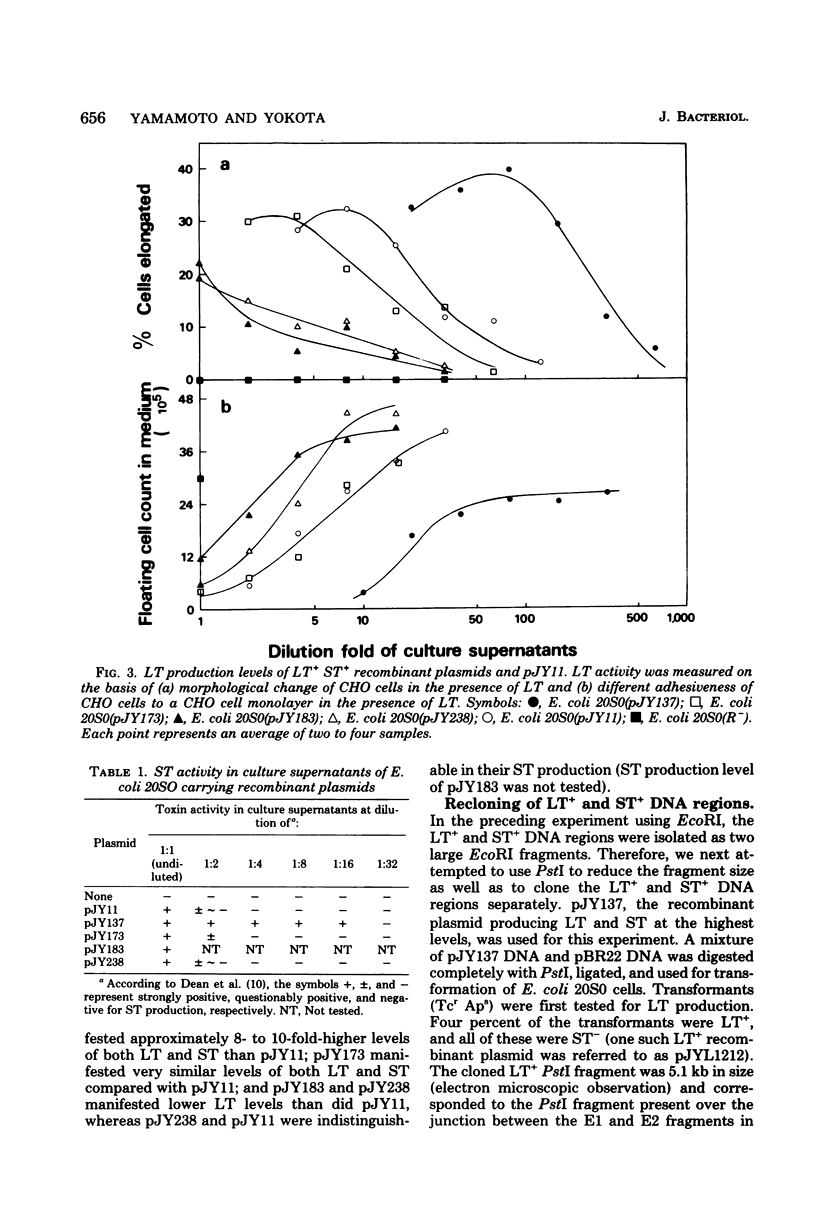
A heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxin (LT+ ST+) plasmic (62.7 kilobases in size) was isolated from an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli human strain, H10407, and used for analysis of the LT+ and ST+ deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) regions. A DNA segment containing the LT+ and ST+ DNA regions, which consisted of two restriction endonuclease EcoRI fragments (E1 and E2), was inserted into the cloning vehicle ColE1::Tn5 by EcoRI digestion and subsequent ligation. Further cloning experiments localized the LT+ DNA region on a 5.1-kilobase restriction endonuclease PstI fragment present over the junction between the E1 and E2 fragments, as seen in the original LT+ ST+ plasmid, and the ST+ DNA region on a 1.5-kilobase PstI fragment present in either the E1 or E2 fragment. A change in the relative orientation of the E1 and E2 fragments resulted in altered levels of LT production. The relative orientation of the ColE1::Tn5 fragment to the E1 and E2 fragments also markedly influenced both LT and ST production levels. The LT+ ST+ E1-E2 region contained two unique DNA sequences consisting of a DNA segment flanked by inverted repeats which were readily distinguished from each other by size. The cloned ST+ PstI fragment was structurally very similar to one of these unique DNA sequences present in the LT+ ST+ E1-E2 region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Davies J., Allet B., Rochaix J. D. Transposition of R factor genes to bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. The molecular nature of heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) of escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):406–407. doi: 10.1038/277406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner F., Hughes C., Nahler G., Högenauer G. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: DNA-directed in vitro synthesis and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4832–4836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W. Effect of purified Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on intestinal cyclic nucleotide metabolism and fluid secretion. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):19–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.19-23.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., So M., Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):40–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Translocatable elements in procaryotes. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome P. M., Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A. Effect of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on cyclic GMP levels in mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):290–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.290-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa R. T., Yokota T., Kuwahara S. Assay method for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by automated counting of floating chinese hamster ovary cells in culture medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):479–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.479-485.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Boyer H. W., Betlach M., Falkow S. Molecular cloning of an Escherichia coli plasmid determinant than encodes for the production of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):463–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.463-472.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Characterization of an Escherichia coli plasmid encoding for synthesis of heat-labile toxin: molecular cloning of the toxin determinant. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.405-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Murphy J. R. Bacteriophage conversion of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):172–177. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.172-177.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Sakakibara Y., Kakefuda T. Replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA in cell extracts. Origin and direction of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2260–2264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K., Wells J., Shipley P., Ryder R. Heat-labile enterotoxin production in isolates from a shipboard outbreak of human diarrheal illness. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):793–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.793-797.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi H., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H. Excision and duplication of su3+-transducing fragments carried by bacteriophage phi 80. I. Novel structure of phi 80sus2psu3+ DNA molecule. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1016-1023.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Host-dependent, thermosensitive replication of an R plasmid, pJY5, isolated from Enterobacter cloacae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):923–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.923-930.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]