Abstract
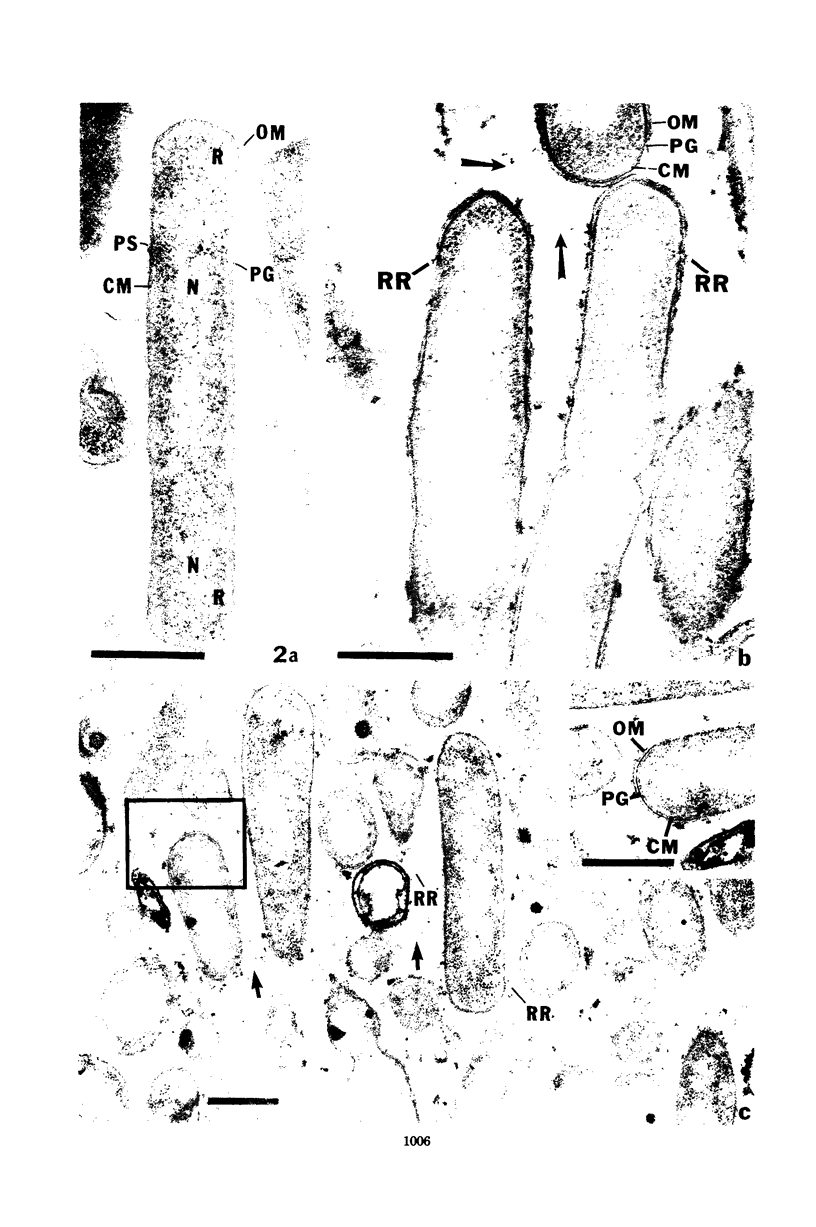
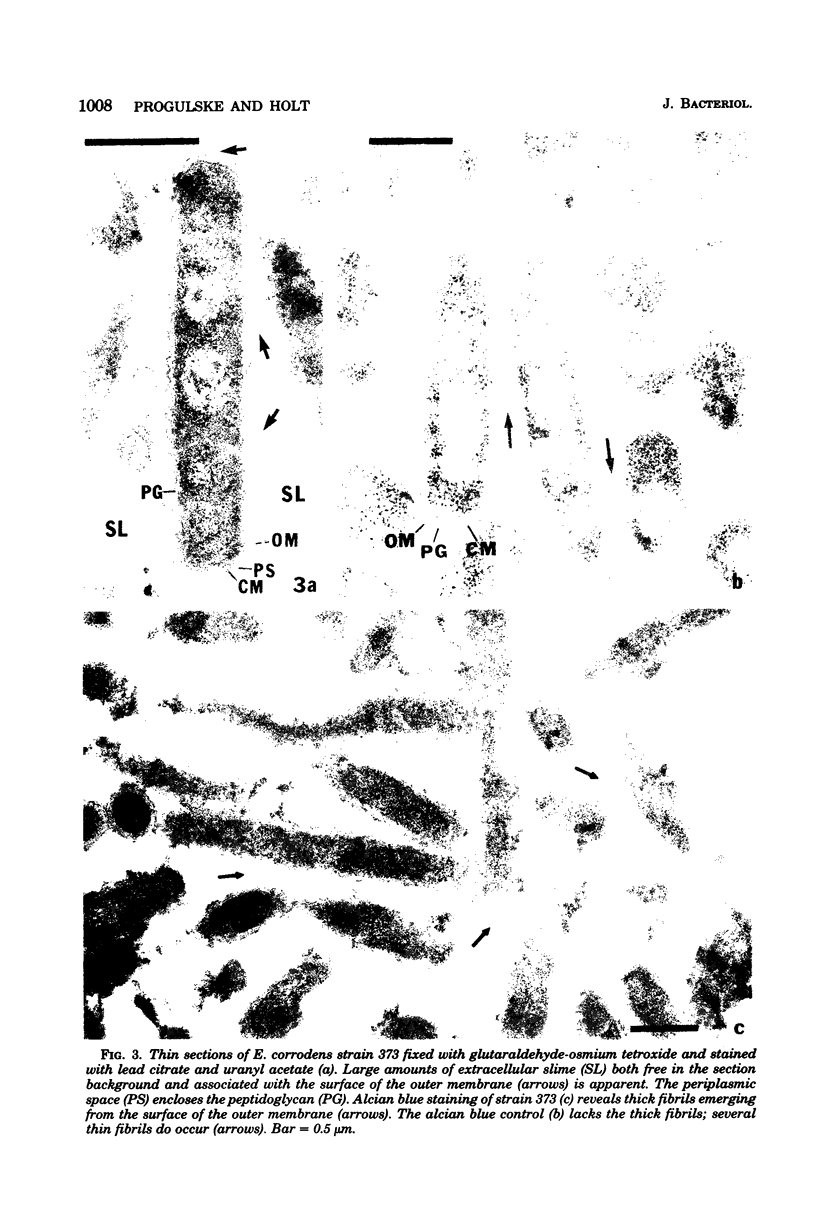
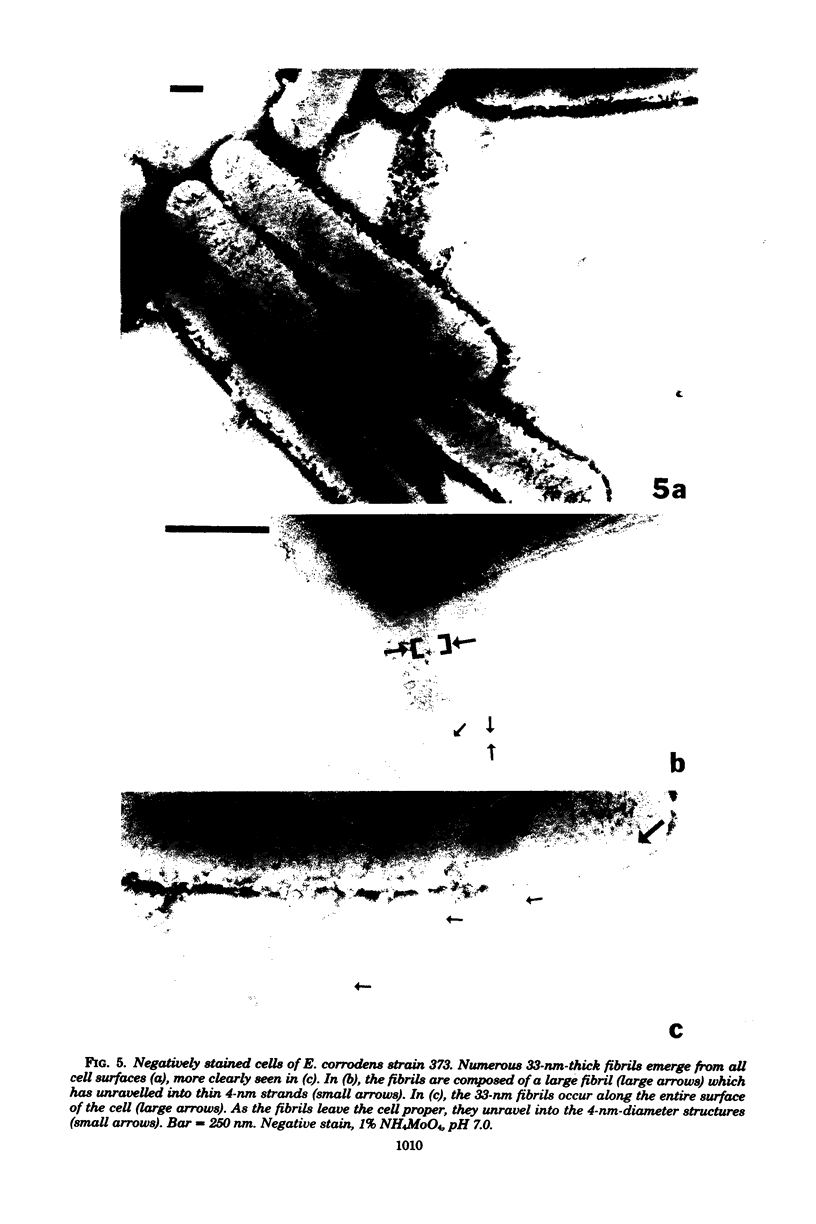
The morphology of Eikenella corrodens 333/54-55 (ATCC 23834) and two human periodontal lesion isolates, strains 470 and 373, was examined by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. All strains exhibited a cell envelope characteristic of gram-negative bacteria. Staining with ruthenium red and alcian blue revealed a loosely organized fibrous slime layer associated with the outer surface of the outer membrane. Slime "stabilization" was achieved by incubation of cells with antisera prepared against whole cells of the Eikenella strains. The stabilized slime appeared as a thick, electron-opaque layer juxtaposed to the outer membrane. Negative staining and heavy metal shadow-casting revealed an interwoven network of fibrils approximately 4 nm in diameter. These fibrils appeared to represent subunits of a larger fibril. Scanning electron microscopy after antibody slime stabilization confirmed the presence and location of the slime layer.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger S. J., Butler T., Kim C. K., Johnston K. H. Experimental Eikenella corrodens endocarditis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.751-757.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behling U. H., Pham P. H., Nowotny A. Biological activity of the slime and endotoxin of the periodontopathic organism Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):580–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.580-584.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., O'Donoghue J. M., Rissing J. P., Soapes K., Smith J. W. Eikenella corrodens, a recently recognized pathogen: infections in medical-surgical patients and in association with methylphenidate abuse. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Sep;53(5):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehmel F., Feige U., Niemann H., Stirm S. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. VII. Bacteriophage 29-host capsular polysaccharide interactions. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):591–601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.591-601.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer G., Helmke U., Christner A. Ultrahistochemical demonstration of alcian blue stained mucousubstances by the sulfide-silver reaction. Acta Histochem. 1971;40(1):80–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D. Corroding bacteria from the respiratory tract. 2. Bacteroides corrodens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R., Socransky S. S. Capnocytophaga: new genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. II. Morphology and ultrastructure. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):17–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00408041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. L., Goodman Y. E., Bel F. R., Wong P. C., Whitehouse R. L. Taxonomic status of facultative and strictly anaerobic "corroding bacilli" that have been classified as Bacteroides corrodens. J Med Microbiol. 1971 May;4(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. L., Romig D. A. Eikenella corrodens: a pathogen in head and neck infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1979 Dec;48(6):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(79)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. H., Listgarten M. A. Immune labeling of certain strains of Actinomyces naeslundii and Actinomyces viscosus by fluorescence and electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1016–1028. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1016-1028.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Thies E. S. Influence of encapsulation on phagocytosis of Pasteurella multocida by bovine neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):76–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.76-81.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. B., Hyde W. A. Isolation of Bacteroides corrodens from infections in children. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;24(2):117–119. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Preusser H. J., Verma J. P. Uber die Oberflächenstruktur von Myxobakterien. II. Anionische Heteropolysaccharide als Basustoffe der Schleimhülle von Cytophage hutchinsonii und Sporocytophaga myxococcoides. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;62(1):72–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L., Cisneros R. L., Bartlett J. G. The capsular polysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis as a virulence factor: comparison of the pathogenic potential of encapsulated and unencapsulated strains. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):82–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Quintarelli G., Dellovo M. C. The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. I. The mechanism of Alcian Blue staining. Histochemie. 1964 Jul 17;4(2):73–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00306149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Hausmann E. Longitudinal study of experimentally induced periodontal disease in Macaca arctoides: relationship between microflora and alveolar bone loss. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):260–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.260-269.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Lohmander S., Friberg U. Electron microscopic demonstration of proteoglycans in guinea pig epiphyseal cartilage. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Dec;45(5):407–427. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D. D., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Ultrastructure of Bacteroides species: Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies melaninogenicus, and B. melaninogenicus subspecies intermedius. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):534–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Palenstein Helderman W. H. Total viable count and differential count of vibrio (campylobacter) sputorum, fusobacterium nucleatum, selenomonas sputigena, bacteroides ochraceus and veillonella in the inflamed and non inflamed human gingival crevice. J Periodontal Res. 1975 Nov;10(5):294–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]