Metabolic regulation of Drosophila apoptosis through inhibitory phosphorylation of Dronc
Sally Kornbluth and her co-workers establish Drosophila as a model system to study metabolic control of apoptosis in vivo. A novel DIAP1-independent regulatory pathway is revealed in Drosophila that involves NADPH- and CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of the caspase Dronc and inhibition of Dronc-mediated apoptosis.
Keywords: Dronc, Drosophila apoptosis, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, malic enzyme, NADPH metabolism
Abstract
Apoptosis ensures tissue homeostasis in response to developmental cues or cellular damage. Recently reported genome-wide RNAi screens have suggested that several metabolic regulators can modulate caspase activation in Drosophila. Here, we establish a previously unrecognized link between metabolism and Drosophila apoptosis by showing that cellular NADPH levels modulate the initiator caspase Dronc through its phosphorylation at S130. Depletion of NADPH removed this inhibitory phosphorylation, resulting in the activation of Dronc and subsequent cell death. Conversely, upregulation of NADPH prevented Dronc-mediated apoptosis upon DIAP1 RNAi or cycloheximide treatment. Furthermore, this CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of Dronc hindered Dronc activation, but not its catalytic activity. Blockade of NADPH production aggravated the death-inducing activity of Dronc in specific neurons, but not in the photoreceptor cells of the eyes of transgenic flies; similarly, non-phosphorylatable Dronc was more potent than wild type in triggering specific neuronal apoptosis. Our observations reveal a novel regulatory circuitry in Drosophila apoptosis, and, as NADPH levels are elevated in cancer cells, also provide a genetic model to understand aberrations in cancer cell apoptosis resulting from metabolic alterations.
Introduction
Accumulating evidence suggests that cellular metabolism impinges directly upon the decision to initiate cell death (Rathmell et al, 2003; Nutt et al, 2005; Yi et al, 2007; Yuneva et al, 2007; Zhao et al, 2008). In vertebrate cells, glucose metabolism and apoptosis are mutually regulated, at least in part, through the Bcl-2 family proteins, which control mitochondrial cytochrome c release, an important process in vertebrate intrinsic apoptosis (Liu et al, 1996; Kluck et al, 1997; Rathmell et al, 2003; Zhao et al, 2008). An additional paradigm for metabolic regulation of apoptosis is exemplified by caspase 2, which can be activated upon NADPH deprivation in Xenopus oocytes and is suppressed through phosphorylation in nutrient replete oocytes (Nutt et al, 2005). When activated, caspase 2 cleaves and activates the Bcl-2 family member Bid, to promote cytochrome c release from mitochondria and subsequent cell death (Bonzon et al, 2006).
Drosophila apoptosis is, instead, regulated by the balance between the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) and a group of pro-apoptotic regulators known as the Reaper, Hid and Grim (RHG) proteins (Kornbluth and White, 2005). The Drosophila initiator caspase Dronc is believed to be constitutively activated through autoprocessing by its activating protein, the Drosophila Apaf-1 homologue Dark (Igaki et al, 2002; Muro et al, 2002; Rodriguez et al, 2002). However, this continuous apoptotic signalling is largely antagonized in healthy cells by DIAP1, which suppresses the catalytic activity of Dronc and meditates its degradation through ubiquitination to prevent unnecessary cell death (Meier et al, 2000; Muro et al, 2002; Wilson et al, 2002; Yoo et al, 2002). The RHG proteins, transcriptionally upregulated following receipt of apoptotic stimuli, compete with DIAP1 for its binding site on caspases and decrease DIAP1 levels by stimulating its autoubiquitination, allowing the apoptotic signalling to propagate throughout the caspase cascade and initiate cell death (Wang et al, 1999; Goyal et al, 2000; Yoo et al, 2002; Kornbluth and White, 2005).
Recent RNAi-based screens have revealed that several metabolic regulators are involved in control of caspase activation (Yi et al, 2007), suggesting that fly apoptosis may be subject to metabolic control. Although mitochondrial release of cytochrome c does not appear to be required for caspase-dependent cell death in most Drosophila cells tested (Dorstyn et al, 2002; Abdelwahid et al, 2007; Dorstyn and Kumar, 2008), the regulation of vertebrate caspase 2 by NADPH levels raised the interesting possibility that Drosophila caspases might also be directly controlled by NADPH metabolism. We show here that the Drosophila initiator caspase Dronc is inhibited by phosphorylation at S130 in response to abundant NADPH and that abrogation of this phosphorylation by a point mutation renders this caspase refractory to metabolic control. These observations identify cellular NADPH levels as a novel gatekeeper that sets the threshold for Drosophila apoptosis through modulating Dronc activation, and suggest that such regulatory mechanisms are evolutionarily conserved and operate in somatic cells as well as in germ cells.
Results
Inhibition of NADPH production through the pentose phosphate pathway triggers apoptosis in Drosophila S2 cells
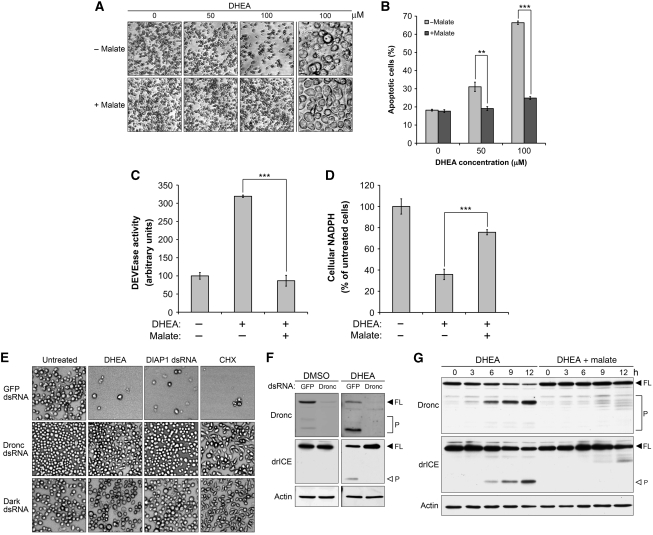
To elucidate a potential regulatory function for cellular NADPH levels in controlling Drosophila apoptosis, we treated Drosophila Schneider's S2 (S2) cells with varying concentrations of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), an allosteric inhibitor of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), to inhibit NADPH production through the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). DHEA treatment induced dosage-dependent cell death as evidenced by a decrease in cell density and an increase in the percentage of propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells, both of which were significantly suppressed by the addition of dimethyl L-malate (hereafter referred to as malate), a cell permeable malate analogue that elevates NADPH levels in conjunction with malic enzyme (Men) (Figure 1A and B). These results suggest that NADPH could modulate cell death in Drosophila cells. Notably, malate also blocked DHEA-induced membrane blebbing, a typical characteristic of apoptotic cell death, as cells treated with malate maintained a healthy morphology, even when exposed to 100 μM DHEA for 24 h (Figure 1A, right panel). To confirm that DHEA-induced cell death was occurring by apoptosis, we examined DEVDase (effector caspase-like) activity in lysates from DHEA-treated cells. As shown in Figure 1C, DHEA treatment stimulated DEVDase activity in S2 cells, whereas this increase was largely suppressed by malate, indicating that malate alleviates DHEA-induced caspase activation and consequent apoptosis.
Figure 1.
Programmed cell death is metabolically regulated in Drosophila S2 cells. (A–C) Malate overrides DHEA-induced apoptosis. (A, B) S2 cells were treated with different concentrations of DHEA±5 mM malate in glucose-free medium for 24 h. After 24 h treatment, (A) photomicrographs were taken with a confocal microscope. (B) Treated cells were also incubated in 0.5 μg/ml PI staining solution for 5 min and then the percentage of PI-positive cells was read by flow cytometry. Malate significantly suppressed DHEA-induced cell death in cells receiving 50 μM (**P<0.01) or 100 μM DHEA (***P<0.001). (C) Lysates from untreated S2 cells and cells treated with 100 μM DHEA±5 mM malate were analysed for effector caspase-like activity using the caspase substrate Ac-DEVD-pNA. The addition of malate significantly reduced DHEA-induced caspase activity (***P<0.001). (D) DHEA and malate modulates cellular NADPH levels. Lysates from cells receiving the same treatment as described above were analysed for NADPH content as described in Materials and methods. The DHEA-induced decrease in NADPH levels was significantly rectified by malate (***P<0.001). (E) Apoptosis induced by DHEA, DIAP1 dsRNA and CHX requires Dronc and Dark. S2 cells after 2 days pretreatment of 80 nM Dronc or Dark dsRNA were treated with 100 μM DHEA, 40 nM DIAP1 dsRNA or 40 μM CHX. Photomicrographs were taken 12 h (DIAP1 dsRNA and CHX) or 24 h (DHEA) post-treatment. (F) DHEA requires Dronc to initiate the caspase cascade. The processing of endogenous Dronc and drICE in Dronc-deficient cells treated with 100 μM DHEA was examined by immunoblotting. Full-length and processed caspases are indicated by FL and P, respectively. (G) Malate blocks DHEA-induced Dronc activation. Lysates were collected at the indicated time points from S2 cells treated with 100 μM DHEA±5 mM malate in glucose-free medium, and then analysed for the cleavage of caspases by immunoblotting. The autoprocessing of Dronc and Dronc-mediated cleavage of drICE were used as readouts to monitor Dronc activation (FL, full-length; P, processed). Each bar in (B–D) represents the mean±s.d. from three independent experiments, and the P-values were calculated according to two-tailed Student's t-test.
To further elucidate how DHEA and malate regulate apoptosis, NADPH levels in lysates from treated cells were measured. Strikingly, DHEA treatment decreased cellular NADPH levels by 60%, whereas the addition of malate significantly restored this reduction (Figure 1D), consistent with the idea that these two reagents control apoptosis through modulating cellular NADPH levels. Indeed, abrogation of malate-induced NADPH production by downregulation of Men demolished the protective effects of malate (Supplementary Figure 1; Figure 3; see below).
Drosophila initiator caspase Dronc mediates apoptosis induced by NADPH deprivation
Among seven identified caspases in Drosophila melanogaster, Dronc, Dredd and Strica (Dream) are categorized as initiator caspases because of their long prodomains (Hay and Guo, 2006). Moreover, Dronc, with the aid of Dark, has been shown to mediate most developmental and stress-induced apoptosis in Drosophila, including spontaneous caspase activation induced by the loss of DIAP1 (Kanuka et al, 1999; Rodriguez et al, 1999, 2002; Zhou et al, 1999; Chew et al, 2004; Daish et al, 2004; Waldhuber et al, 2005; Xu et al, 2005). Therefore, we first examined whether NADPH deprivation induces apoptosis through Dronc and Dark.
Upon DHEA treatment, S2 cells pretreated with control (GFP) double-stranded (ds)RNA underwent apoptotic cell death, whereas this cell death was completely abrogated in cells pretreated with either Dronc or Dark dsRNA, as shown by a constant cell density over 24 h of DHEA treatment in Dronc or Dark-deficient cells (Figure 1E). Immunoblotting also confirmed that both Dronc and Dark dsRNA molecules were able to downregulate their targets (Supplementary Figure 2). Consistent with the previous reports, silencing of Dronc or Dark also blocked apoptosis induced by DIAP1 dsRNA or cycloheximide (CHX), indicating that DHEA, as well as these two apoptosis-inducing reagents, uses the same signal transduction pathway to mediate cell death (Figure 1E). The processing of caspases in DHEA-treated cells was also analysed by immunoblotting. As shown in Figure 1F, DHEA treatment resulted in the cleavage of Dronc and its downstream effector caspase, drICE, in cells treated with control (GFP) dsRNA, whereas the activation of drICE was totally blocked in Dronc-deficient cells (Figure 1F), supporting the necessity of Dronc for DHEA-induced apoptosis. Interestingly, DHEA-induced cleavage of Dronc and drICE was greatly suppressed by the addition of malate (Figure 1G), suggesting that metabolic control targets either Dronc or an upstream regulator of Dronc. Taken together, these data strongly suggest that metabolic deficiencies can induce apoptosis through the canonical cell death pathway mediated by Dark, Dronc and its downstream effector caspase, drICE.
Malate protects S2 cells from CHX and DIAP1 dsRNA-induced apoptosis
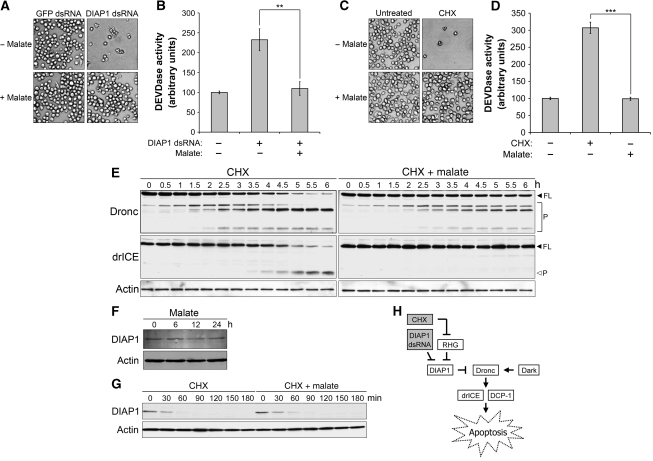
The results presented in Figure 1 showed that malate blocked DHEA-induced apoptosis. As DIAP1 dsRNA, CHX and DHEA all appeared to promote death through Dark and Dronc, we hypothesized that malate might also suppress apoptosis induced by DIAP1 dsRNA and CHX. Surprisingly, malate significantly protected S2 cells from apoptosis resulting from the loss of DIAP1. As shown in Figure 2A and B, malate alleviated the decrease in cell density and the upsurge in caspase activity induced by DIAP1 dsRNA. Interestingly, immunoblotting using DIAP1 antibody revealed that malate neither interfered with DIAP1 degradation nor increased DIAP1 protein levels (Supplementary Figure 3), suggesting that a novel metabolically regulated cell death checkpoint lies downstream of DIAP1.
Figure 2.
Metabolic status modulates Dronc activation. (A–D) Malate inhibits spontaneous caspase activation induced by the loss of DIAP1. (A, B) Malate blocks spontaneous caspase activation induced by DIAP1 dsRNA. S2 cells were treated with 40 nM GFP or DIAP1 dsRNA±5 mM malate in serum-free Schneider's medium for 12 h before (A) pictures were taken and (B) lysates were collected for caspase assay. The addition of malate greatly suppressed an increase in caspase activity resulting from the loss of DIAP1 (**P<0.01). (C, D) Malate suppresses CHX-induced apoptosis. S2 cells were treated with 40 μM CHX±5 mM malate in standard Schneider's medium. (C) Pictures were taken 12 h post-treatment. (D) Lysates from treated cells were also analysed by caspase assay. CHX-induced caspase activation was significantly alleviated by the addition of malate (***P<0.001). (E) Malate delays Dronc activation in CHX-treated cells. Lysates were collected at the indicated time points from S2 cells treated with 40 μM CHX±5 mM malate in standard Schneider's medium, and then analysed by immunoblotting. Spontaneous caspase activation was monitored by the autoprocessing of Dronc and Dronc-mediated cleavage of drICE (FL, full-length; P, processed). (F, G) Malate affects neither the expression levels nor the degradation of DIAP1. Lysates from S2 cells treated as indicated were analysed by immunoblotting to determine (F) the expression levels or (G) the half-life of DIAP1. Actin blotting was used as loading control. (H) The Drosophila apoptotic pathway. Shaded boxes represent apoptotic inducers used in this study. Values represented in (B) and (D) are the mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. The P-values were calculated according to two-tailed Student's t-test.
In addition, we examined malate's effects on CHX-induced apoptosis. Owing to the short in vivo half-life of DIAP1 (∼30 min), blockade of de novo protein synthesis with CHX causes a decrease in endogenous DIAP1 pools, resulting in the accumulation of processed Dronc and subsequent cell death (Igaki et al, 2002; Muro et al, 2002; Rodriguez et al, 2002; Wilson et al, 2002). Similarly to DIAP1 dsRNA, CHX-induced apoptosis was also significantly suppressed by the addition of malate, as evidenced by malate-mediated restoration of cell density and suppression of caspase activity (Figure 2C and D).
Dronc is a direct target subject to metabolic control
We also monitored the cleavage of different caspases along the Dronc signalling pathway. Notably, the addition of malate significantly delayed the activation of Dronc in CHX-treated cells. Most Dronc was processed after 6 h of CHX treatment, resulting in the cleavage of its downstream substrate, drICE (Figure 2E, left panel). In contrast, Dronc-mediated cleavage of drICE was completely blocked in cells co-treated with malate (Figure 2E, right panel), indicating that malate markedly suppresses CHX-induced increases in the proteolytic activity of Dronc. However, malate appeared to have no effect on the signalling pathways upstream of Dronc. The addition of malate affected neither the steady-state levels nor the half-life of DIAP1 (Figure 2F and G), indicating that metabolic control is not likely to act through the regulation of DIAP1. As shown in Figure 2H, CHX globally inhibits translation, including synthesis of the RHG proteins. Therefore, the RHG proteins are very unlikely to be involved in malate's protection, as they are largely controlled through transcriptional induction.
Taken together, these data strongly suggest that Dronc, rather than the upstream RHG proteins and DIAP1, is directly suppressed by metabolism. As factors involved in apoptotic control downstream of DIAP1 are largely unknown, we wished to decipher the signalling pathway underlying this novel regulation. Therefore, we used CHX as an apoptotic stimulus, bypassing control of RHG proteins and DIAP1 and focusing on downstream metabolic control of Dronc.
Malate's protection against CHX-induced apoptosis requires NADPH generation by malic enzyme
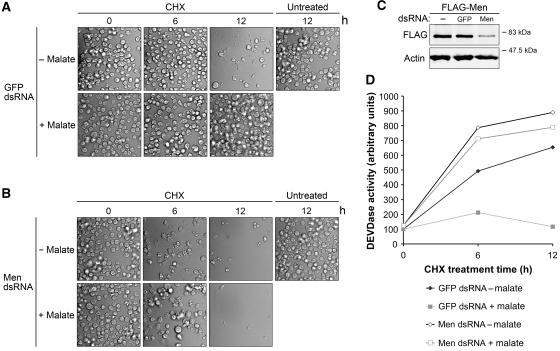
Intracellular malate can either enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in mitochondria or be metabolized by malic enzyme in the cytoplasm to produce NADPH. To confirm that malate's ability to protect cells from CHX-induced apoptosis required NADPH production, we knocked down Men using Men dsRNA. Interestingly, downregulation of Men sensitized S2 cells to CHX, as extensive membrane blebbing and decreased cell density were observed in Men-deficient cells after 6 h of CHX treatment, whereas most cells pretreated with control (GFP) dsRNA remained healthy at this time point (Figure 3A and B, 6 h). These data suggest that Men helps to set the threshold for apoptosis. More importantly, malate's anti-apoptotic ability was largely abrogated by the silencing of Men, indicating that apoptosis is not inhibited by malate per se but by downstream metabolic effects dependent upon Men (Figure 3A and B, 12 h). Similar results were obtained with dsRNA molecules directed against a different sequence of Men (Supplementary Figure 4). The efficacy of Men dsRNA was also assessed by immunoblotting (Figure 3C).
Figure 3.
Men RNAi abrogates malate's protection. (A, B) Malate's ability to inhibit CHX-induced apoptosis requires malic enzyme (Men). S2 cells pretreated with 80 nM (A) GFP or (B) Men dsRNA were then treated with 40 μM CHX±5 mM malate in standard Schneider's medium. Photomicrographs were taken at different time points to monitor membrane blebbing and decreased cell density. (C) S2 cells ectopically expressing FLAG-tagged Men were treated with Men dsRNA to access the efficacy of Men RNAi (as endogenous Drosophila Men antibody was not available). To avoid variation between transfections, S2 cells were transfected together, and then split into six-well plates for dsRNA treatments. Downregulation of FLAG-tagged Men was used as a proxy for the expression levels of endogenous Men. Actin blotting was used to ensure equal loading. (D) Men is required for malate's protection against CHX-induced increase in caspase activity. Lysates from cells treated as described above were analysed by caspase assay.
Malate's effects were also assessed by monitoring of caspase activity. As expected from the results above, the addition of malate suppressed CHX-induced caspase activation in cells pretreated with control dsRNA, but had very limited effects in Men-deficient cells (Figure 3D). Malate is metabolized by malic enzyme to produce NADPH and pyruvate (Frenkel, 1975); the latter enters the TCA cycle (Jeffrey et al, 1996). In Men-deficient cells, malate would still have been expected to enter the TCA cycle, yet its protective effects were largely abolished. Collectively, these data supported the notion that Drosophila apoptosis can be controlled by altering cellular NADPH levels.
Cellular NADPH levels modulate the phosphorylation at Dronc S130
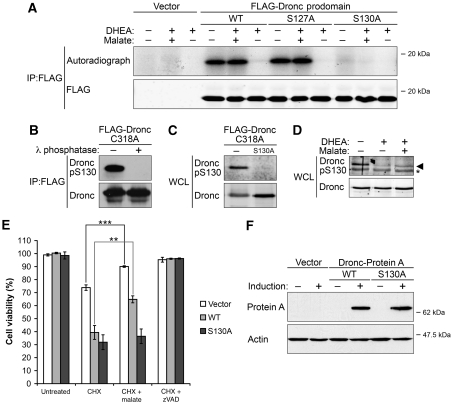
As our data suggested that Dronc could be directly modulated by cellular NADPH levels, we wished to elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying this metabolic control. Interestingly, when the peptide sequence of Dronc was compared with those of different vertebrate caspases, Dronc was found to be most similar to caspase 2 within its prodomain (Cooper et al, 2009). As metabolism regulates the activation of caspase 2 through phosphorylation in its prodomain, we first used metabolic phosphate labelling to determine how cellular NADPH levels might affect the phosphorylation of Dronc prodomain. As shown in Figure 4A, inhibition of the PPP by DHEA was accompanied by dephosphorylation of ectopically expressed Dronc prodomain, whereas the addition of malate overrode this decrease. DHEA-induced dephosphorylation of Dronc was not inhibited by the pan-caspase inhibitor, zVAD, suggesting that Dronc dephosphorylation is a caspase-independent event occurring before caspase activation. Experiments using a series of Dronc mutants further revealed that mutation at S130, but not the nearby S127, suppressed phosphorylation of the Dronc prodomain to a sub-detectable level. These data suggest that malate functions to maintain phosphorylation of the Dronc prodomain at S130.
Figure 4.
Dronc is metabolically regulated through the inhibitory phosphorylation at S130. (A) Metabolic status modulates S130 phosphorylation of ectopically expressed Dronc. S2 cells expressing FLAG-tagged Dronc prodomain were labelled as described in Materials and methods. Phosphorylation of WT and a panel of point-mutant Dronc prodomain were measured by autoradiography. Parallel immunoblotting was used to ensure equal loading. (B, C) Dronc pS130 antibody validation in S2 cells. Phospho-specific antibody targeted against Dronc S130 was generated as described in Materials and methods. (B) Dronc pS130 only recognized phosphorylated Dronc. FLAG-tagged full-length Dronc (C318A) was immunoprecipitated with FLAG beads, treated with λ-phosphatase and then analysed by immunoblotting using Dronc antibody and Dronc pS130 antibody. (C) Lysates from cells transfected with either Dronc C318A or Dronc C318A/S130A expression plasmids were examined by immunoblotting using Dronc antibody and Dronc pS130 antibody. (D) NADPH levels control the phosphorylation status of endogenous Dronc at S130. S2 cells were treated with 100 μM DHEA±5 mM malate in glucose-free medium supplemented with 50 μM zVAD for 6 h. Lysates from treated cells were collected for immunoblotting using Dronc antibody and Dronc pS130 antibody (Asterisk, non-specific band). (E) Mutation of Dronc S130 abolishes malate's inhibition of cell death. S2 cells expressing sub-lethal levels of full-length WT Dronc or S130A phosphomutant were treated with 40 μM CHX±5 mM malate in standard Schneider's medium for 8 h. The percentage of GFP-positive cells was examined by flow cytometry and used as an indicator of cell viability. Malate was able to rescue CHX-induced cell death in cells transfected with either empty vectors (***P<0.001) or WT Dronc expression vectors (**P<0.01), but did not protect cells expressing Dronc S130A phosphomutant (P=0.544). Data were collected from three independent experiments, and shown as mean±s.d. Two-tailed Student's t-tests were performed to determined P-values. (F) Expression levels of WT Dronc or S130A phosphomutant C-terminally tagged with protein A in stable lines were examined by immunoblotting using anti-protein A antibodies, and actin was used as a loading control.
To monitor the phosphorylation status of endogenous Dronc in response to cellular NADPH levels, we generated an affinity-purified phospho-specific antibody (Dronc pS130) directed against this phosphosite. To validate the antibody, FLAG-tagged full-length Dronc carrying a mutation (C318A) to prevent autoprocessing was immunoprecipitated and treated with λ-phosphatase. As shown in Figure 4B, Dronc pS130 antibody only recognized phosphorylated Dronc, in that λ-phosphatase treatment abolished recognition by this antibody (Figure 4B). More importantly, the phospho-antibody was unable to recognize Dronc (S130A/C318A) that had been mutated at S130 to render it non-phosphorylatable, indicating that this antibody specifically detects Dronc phosphorylated at S130 (Figure 4C). Notably, malate treatment reversed the DHEA-induced decrease in signal detected by the phospho-specific (Dronc pS130) antibody, revealing that phosphorylation of endogenous Dronc at S130 is indeed controlled by NADPH levels in S2 cells (Figure 4D).
Phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 suppresses its death-inducing activity
Given that an increase in NADPH levels resulted in phosphorylation of Dronc at S130, we wished to characterize the physiological significance of this phosphorylation. Towards this end, sub-lethal levels of full-length wild-type (WT) Dronc or Dronc S130A phosphomutant were induced in stably transfected S2 cells constitutively expressing GFP. We then examined the responsiveness of these cells to malate upon CHX treatment by monitoring the loss of GFP by flow cytometry. Similar assays have been used in other systems to assess cell viability (Zimmermann et al, 2002). To validate this assay in our system, CHX-treated cells collected at various time points were used to assess the percentage of GFP-positive cells by flow cytometry and then lysed to measure cellular DEVDase activity by caspase assay (Supplementary Figure 5). We found that the percentage of GFP-positive cells decreased as caspase activity increased. Moreover, blocking CHX-induced caspase activity with zVAD inhibited the accompanying loss of GFP signal, indicating that the loss of GFP was due to caspase-dependent cell death. Thus, this measure was used as a proxy to assess cell viability in the following experiments.
Notably, cells transfected with either empty vector or WT Dronc expression plasmids remained sensitive to malate, as cell viability was partially restored by malate treatment (Figure 4E, white and grey bar). In contrast, malate was unable to protect cells expressing Dronc S130A from CHX-induced apoptosis. These data indicate a vital function for phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 in metabolic control of apoptosis (Figure 4E, black bar). Note that WT Dronc and Dronc S130A proteins were expressed at comparable levels as assessed by immunoblotting (Figure 4F).
NADPH-mediated phosphorylation of Dronc prevents its activation by Dark
We reasoned that this metabolically regulated phosphorylation might either directly suppress Dronc's catalytic activity or interfere with its activation. To distinguish these two levels of regulation, we needed an in vitro system in which Dronc's catalytic activity should not be dependent on Dark-dependent activation. Moreover, we needed to identify a relevant kinase in order to phosphorylate Dronc at S130 in vitro.
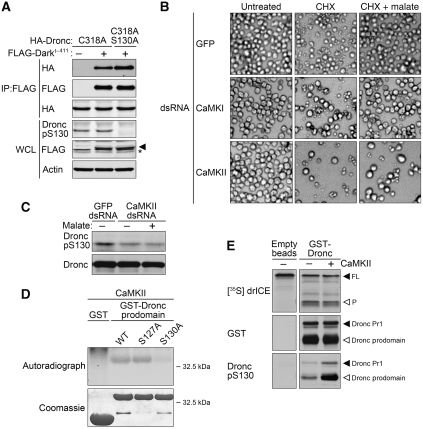
We first tested the effect of S130 phosphorylation on Dronc activation. The interactions between Dronc and its activating protein, Dark, or its inhibitory protein, DIAP1, were examined by co-immunoprecipitiation. Both catalytically inactive Dronc (C318A) and phosphomutant (C318A/S130A) were specifically precipitated in association with the Dark CARD domain (Dark1−411) in transfected S2 cells. Notably, Dronc phosphomutant (C318A/S130A) displayed a stronger interaction with Dark, suggesting that phosphorylation of the Dronc prodomain could hamper the formation of the Drosophila apoptosome by decreasing the interaction between Dronc and Dark (Figure 5A). In contrast, we observed no change in the interaction between Dronc and DIAP1, regardless of the phosphorylation status of Dronc S130 (Supplementary Figure 6).
Figure 5.
CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 prevents its interaction with Dark, but has no effect on its catalytic activity. (A) Phosphorylation at Dronc S130 dampens the interaction between Dark and Dronc. Lysates containing HA-tagged Dronc molecules and FLAG-tagged Dark's CARD domain (Dark1−411) were incubated with FLAG beads. Precipitates were analysed by immunoblotting with FLAG antibodies to show that the same amount of Dark was precipitated, and with HA antibodies for Dronc molecules interacting with Dark's CARD. Expression levels and phosphorylation status of ectopically expressed proteins in lysates were also assessed by immunoblotting, in which an actin blotting was used to verify equal loading. Shown are representative data from three independent experiments (asterisk, non-specific band). (B) CaMKII RNAi abrogates malate's inhibition. S2 cells pretreated with GFP, CaMKI or CaMKII dsRNA were then treated with CHX 40 μM CHX±5 mM malate in standard Schneider's medium. Cell death and membrane blebbing were recorded 12 h post-CHX treatment. (C) CaMKII is required for phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 in vivo. CaMKII-deficient cells were generated as described in Materials and methods and then treated with 5 mM malate in glucose-free medium as indicated. Lysates were examined by immunoblotting for the phosphorylation status of endogenous Dronc at S130. (D) CaMKII phosphorylates the Dronc prodomain at S130 in vitro. GST-tagged recombinant Dronc prodomain (WT, S127A and S130A) and GST were incubated with CaMKII and 32P-ATP in kinase buffer as described in Materials and methods. Sample amounts and phosphorylation status were examined by coomassie blue and autoradiography, respectively. (E) Phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 does not affect its catalytic activity. In vitro translated drICE was incubated with mock-treated or CaMKII-treated recombinant Dronc at 25°C with occasional shaking for 2 h. Dronc-mediated processing of drICE was monitored by autoradiography. Protein levels and phosphorylation status of Dronc were examined by immunoblotting using the antibodies indicated.
CaMKII phosphorylates Dronc at S130 and is essential for NADPH-mediated survival
We next attempted to identify the kinase responsible for phosphorylation at Dronc S130 in vivo. PKA, CK1 and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase (CaMK) were predicted to phosphorylate Dronc at S130 based on the known consensus sequences of these kinases and the peptide sequences flanking this site. PKA and CK1, however, appeared not to be involved in this metabolic control of Dronc, as neither chemical inhibitors (H-89 for PKA and IC261 for CK1) at concentrations known to inhibit the Drosophila kinases (Zhao et al, 2007; Mennella et al, 2009) nor dsRNA targeted against these two kinases blocked malate's ability to protect from CHX-induced apoptosis (Supplementary Figure 7).
Interestingly, downregulation of CaMKII, but not CaMKI, by dsRNA was able to abolish malate's protective effect; cells pretreated with CaMKII dsRNA underwent apoptosis upon CHX treatment even in the presence of malate, whereas this apoptotic cell death was greatly suppressed by malate in cells pretreated with GFP or CaMKI dsRNA (Figure 5B). Cell lysates from CaMKII-deficient cells were also analysed for phosphorylation at S130 by immunoblotting. As shown in Figure 5C, malate was unable to restore phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 in cells pretreated with CaMKII dsRNA, consistent with the idea that CaMKII is the relevant kinase in intact cells (Figure 5C). In vitro kinase assays also revealed that CaMKII could directly phosphorylate the Dronc prodomain at S130, as a mutation at S130 abrogated CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of the recombinant GST-tagged Dronc prodomain, whereas both recombinant WT and S127A Dronc prodomain, but not GST, were susceptible to CaMKII (Figure 5D). These data are of particular interest in that we have reported previously that CaMKII is responsible for caspase 2 phosphorylation in response to changes in NADPH levels in Xenopus oocytes. Thus, our data suggest that a similar regulatory circuit linking metabolism and apoptosis is evolutionarily conserved in vertebrates and Drosophila.
Phosphorylation at S130 does not affect Dronc's catalytic activity
As recombinant CaMKII could phosphorylate Dronc at S130 in vitro, this allowed us to determine whether phosphorylation of Dronc could alter its catalytic activity. Recombinant Dronc was purified from bacteria in which high concentrations of Dronc could trigger its Dark-independent dimerization and autoprocessing, activating its proteolytic activity as previously described (Muro et al, 2004; Dorstyn and Kumar, 2008). Immunoblotting indicated the presence of two processed Dronc species in our preparation: Pr1 resulted from a cleavage between the small and large subunit, which allows Dronc to form a stable homodimer with greatly enhanced catalytic activity and the prodomain released upon full processing of Dronc (Figure 5E, middle panel) (Muro et al, 2002, 2004; Yan et al, 2006; Dorstyn and Kumar, 2008). 35S-labelled full-length drICE was then used as a substrate for Dronc that had been either mock-treated or pre-phosphorylated with CaMKII. As shown in Figure 5E, recombinant CaMKII phosphorylated bacterially expressed Dronc at S130 (Figure 5E, lower panel), yet it had no effect on Dronc's proteolytic activity towards its apoptosis-relevant substrate, drICE (Figure 5E, upper panel). These data indicate that phosphorylation of Dronc at S130 has no effect on its proteolytic activity once it is dimerized and activated, and support the notion that NADPH suppresses Dronc by inhibiting its activation rather than its catalytic activity.
The elav-driven overexpression of UAS-Dronc results in caspase-dependent cell death in neuronal tissues
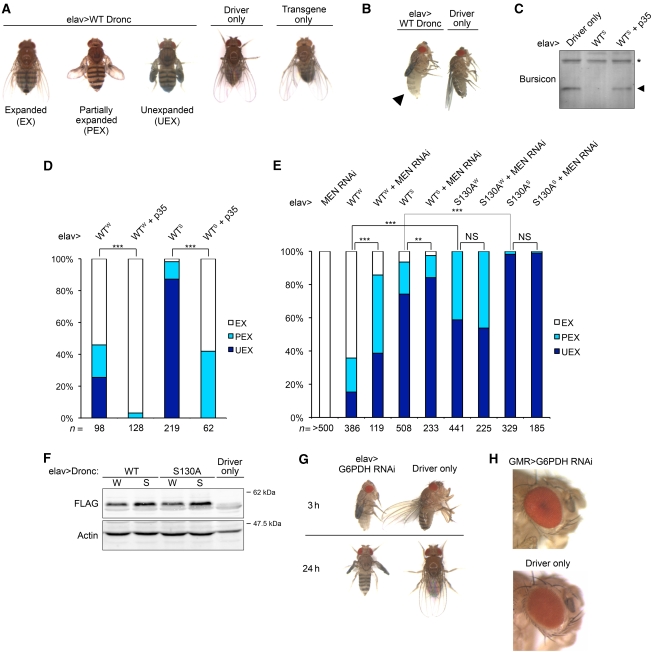
As S2 cells are an embryonic haemocyte-like cell line (Abrams et al, 1992), our observations imply that metabolic regulation of apoptosis likely functions in somatic cells as well as in oocytes. To examine this hypothesis in a whole organism, we first induced apoptosis by expressing UAS-WT Dronc constructs using different tissue-specific Gal4 drivers. Interestingly, when we used the eye-specific driver, GMR-Gal4, only homozygous animals (2 × UAS-Dronc) exhibited eye ablation, the mosaic phenotype resulting from the death of eye pigment cells (Supplementary Figure 8; see further on Dronc and apoptosis in the eye, below). In contrast, overexpression of the UAS-Dronc constructs with the pan-neuronal driver, elav-Gal4, was able to cause inadequate wing expansion even in heterozygous animals (1 × UAS-Dronc) (see below). Progeny exhibiting wing expansion defects could be categorized into three groups based on the severity of the phenotype, whereas their siblings carrying only the transgene or driver showed no morphological abnormalities (Figure 6A; see Materials and methods). Moreover, newly eclosed flies overexpressing WT Dronc (elav-Gal4>WT Dronc) remained untanned in their abdomen after incubation at 25°C for 3 h, whereas their siblings (driver only) exhibited normal maturation as evidenced by their darkened abdomen, indicating a delayed maturation (Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
NADPH metabolism regulates Dronc-mediated apoptosis in transgenic flies. (A) Overexpression of WT Dronc in neuronal tissues through elav-Gal4 induces wing expansion defects. Flies expressing WT Dronc were categorized into three groups (elav-Gal4/+; +; UAS-Dronc/+). Same-sex siblings carrying driver or transgene only were also shown as control (elav-Gal4/+; +; +; + and +; +; UAS-Dronc/+; +). Progeny from different crosses were categorized and scored based on their phenotypes as described in Materials and methods. (B) Photograph taken 3 h after eclosion of female age-matched elav-Gal4>UAS-WT Dronc (left) or sibling carrying driver only (right) shows the inhibition of cuticle tanning in animals ectopically expressing WT Dronc in neuronal tissues. (C, D) Co-expression of p35 suppresses Dronc-induced bursicon deficiency in haemolymph and the consequent wing expansion defects, where W (Weak) and S (Strong) indicate the expression levels of Dronc. (C) Immunoblot analysis shows bursicon levels in haemolymph extracted from age and sex-matched newly eclosed progeny. (D) Bar graph shows the frequency of wing expansion deficits in the progeny. The χ2 analysis shows that defects induced by WT Dronc were significantly suppressed by p35 (***P<0.001). Genotype: elav-Gal4/+; +; UAS-p35/UAS-WT Dronc. (E) Cell-killing activity of Dronc is metabolically suppressed in transgenic flies through phosphorylation of Dronc at S130. Indicated lines were crossed with elav-Gal4. Data were analysed by χ2 test (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, NS, not significant). Genotype: elav-Gal4/+; +; UAS-Dronc/+ and elav-Gal4/+; UAS-Men RNAi hairpins +; UAS-Dronc/+. (F) Expression levels of Dronc. Lysates from 10 newly eclosed progeny with desired genotype were analysed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibodies for FLAG-tagged WT Dronc or S130A phosphomutant. (G) Downregulation of NADPH-generating enzyme, G6PDH, in neuronal tissues causes delay in maturation and wing expansion defects. Pictures were taken 3 h (upper panel) or 24 h (lower panel) post-eclosure. Genotype: elav-Gal4/+; UAS-G6PDH RNAi hairpins/+; +; + and elav-Gal4/+; +; +; +. Crosses were set up at 23°C. (H) Downregulation of G6PDH does not cause defects in the eye. Genotype: +; UAS-G6PDH RNAi hairpins/GMR-Gal4; +; + and +; GMR-Gal4/+; +; +. Shown are male age-matched progeny from crosses set up at 23°C.
After eclosion, Drosophila wing expansion and sclerotization are known to be controlled by the neuropeptide hormone bursicon, which is produced by a subset of neurons named CCAP (Fraenkel and Hsiao, 1962; Luan et al, 2006). Overexpression of Reaper, a member of the RHG proteins, in CCAP neurons has also been shown to lead to defects in wing expansion and cuticle tanning (Park et al, 2003; Dewey et al, 2004), similar to the defects we have observed. To further characterize the defects that resulted from elav-driven overexpression of our UAS-Dronc constructs, another UAS construct encoding p35, a viral anti-apoptotic protein, was co-expressed in the flies. Notably, co-expression of p35 not only significantly restored bursicon levels in haemolymph, but also reduced the wing expansion defects regardless of the expression levels of Dronc (Figure 6C and D). These observations strongly suggest that the pathological phenotypes we observed are attributable to caspase-dependent bursicon deficiency, and thereby could be used as readout for Dronc's activity in transgenic flies.
Metabolism suppresses death-inducing activity of Dronc in specific neuronal tissues, but not in the photoreceptor cells of the eyes
To further examine how NADPH levels control apoptosis in a whole organism, we artificially generated an energy crisis by expressing UAS-RNAi hairpins targeted against NADPH-generating enzymes. We then assessed how NADPH deficiency affected phenotypes resulting from overexpression of UAS-Dronc. As shown in Figure 6E, downregulation of malic enzyme (Men) aggravated wing expansion defects induced by the elav-driven overexpression of WT Dronc, indicating that NADPH deficiency could enhance the death-inducing ability of WT Dronc in transgenic flies. This implied that the activity of WT Dronc might be suppressed by physiological levels of NADPH. In contrast, phosphomutant Dronc (S130A) appeared not to be sensitive to cellular NADPH levels, as co-expression of Men RNAi had no effect on the phenotype induced by overexpression of Dronc S130A, suggesting that NADPH suppressed Dronc in certain neuronal cells through metabolically mediated phosphorylation of Dronc at S130. Indeed, when transgenic strains expressing similar levels of WT or non-phosphorylatable Dronc were compared, flies expressing the Dronc S130A phosphomutant exhibited far more severe wing expansion defects than those expressing WT Dronc, indicating that preventing the metabolically induced inhibitory phosphorylation of Dronc could enhance its cell-killing activity in transgenic flies (Figure 6E and F). In contrast, GMR-driven overexpression of either WT or phosphomutant Dronc (S130A) caused similar eye phenotypes, suggesting that Dronc might not be regulated by NADPH in eye tissues (Supplementary Figure 8). Taken together, these data show that Dronc is metabolically suppressed in specific neuronal tissues in vivo.
NADPH prevents unnecessary death during neuronal development in Drosophila through modulating Dronc
As Dronc is required for the development of several neuronal tissues in Drosophila (Waldhuber et al, 2005; Choi et al, 2006; Kuo et al, 2006; Koto et al, 2009), we then tested whether NADPH metabolism affected cell fate determination in these tissues. Surprisingly, downregulation of G6PDH, which has been shown to be responsible for ∼40% of NADPH production in Drosophila larvae (Geer et al, 1979; Merritt et al, 2009), through elav-driven expression of UAS-G6PDH RNAi resulted in severe wing expansion defects and delayed maturation in all progeny (Figure 6G), phenocoyping elav-driven neuronal overexpression of UAS-Dronc (Figure 6A and B). This suggests that NADPH deficiency during development can trigger apoptosis in specific neurons, possibly through activating Dronc. In contrast, in eye tissues, in which Dronc appeared not to be susceptible to metabolic control, GMR-driven expression of UAS-G6PDH RNAi did not result in detectable eye ablation. Thus, G6PDH deficiency did not activate Dronc to induce phenotypic abnormalities, consistent with the notion that metabolic control of Dronc is more significant in neuronal tissues than in the eye (Figure 6H).
Discussion
NADPH levels set a threshold for Drosophila apoptosis
DIAP1's central function in regulating Drosophila apoptosis is well recognized (reviewed by Hay and Guo, 2006; Kumar, 2007); signals regulating apoptosis in flies are known to target either DIAP1 itself or its antagonists, the RHG proteins, which induce apoptosis by neutralizing DIAP1's inhibition (Wang et al, 1999; Goyal et al, 2000; Meier et al, 2000; Muro et al, 2002; Wilson et al, 2002; Yoo et al, 2002; Hay and Guo, 2006; Kumar, 2007). In this study, using cultured S2 cells and transgenic animals, we revealed a novel regulatory circuit in Drosophila apoptosis wherein cellular metabolic status controls Dronc through CaMKII-mediated inhibitory phosphorylation of Dronc at S130, and thereby suppresses Dronc-mediated Drosophila apoptosis without directly modulating DIAP1.
Interestingly, endogenous Dronc appears to be subject to extensive post-translational modifications in S2 cells, as assessed by 2D-immunoblotting. Our Dronc pS130 antibody recognizes several species of endogenous Dronc, suggesting that a considerable portion of endogenous Dronc is phosphorylated at S130 in healthy cells (data not shown). On the basis of our data, we suggest that when cell metabolism is compromised, NADPH deficits decrease the proportion of phosphorylated Dronc, facilitating the interaction between Dronc and Dark. Therefore, the threshold for apoptosis is lowered and cells are sensitized to apoptotic stimuli.
Notably, Dronc has been shown to function in a non-apoptotic context, mediating morphogenesis in Drosophila neuronal tissues (Kuo et al, 2006; Koto et al, 2009). However, little is known about how active caspases exert their non-apoptotic functions without triggering cell death. Current evidence suggests that limited activities of caspases may be sufficient to mediate cell fate decisions during neuronal differentiation without inducing cell death (Kanuka et al, 2005; Kuranaga et al, 2006; Koto et al, 2009). In support of this hypothesis, our results suggest that the cell-killing activity of Dronc can be modulated by cellular NADPH in vivo through its phosphorylation at S130, even in the absence of DIAP1. As DIAP1 is cleared from the cells during a particular developmental stage in neuronal tissues, such regulation would allow active Dronc to mediate neuronal differentiation without inducing unnecessary cell death.
Metabolic regulators are involved in caspase activation
Two studies using RNAi-based genome-wide silencing in Drosophila have been conducted by Yi et al, 2007 and Chew et al, 2009 to identify novel regulators of Drosophila apoptosis. As we showed that dsRNA directed against malic enzyme (Men) and CaMKII regulates apoptosis, one may wonder why those factors were not identified in previous studies. This may be simply explained by the fact that both published reports identify factors protecting cells from apoptosis after their knockdown, whereas depletion of either Men or CaMKII would accelerate apoptosis. Blocking enzymes consuming NADPH, conversely, would be predicted to artificially increase cellular NADPH levels, resulting in protective effects on apoptosis. However, NADPH is used by multiple biological processes, so inhibition of a single pathway may not raise NADPH sufficiently to sustain a detectable protection upon prolonged apoptotic stimulation. Therefore, a genome-wide RNAi screen to identify genes required for malate's protection from apoptosis could be fruitful in identifying novel apoptotic modulators.
Drosophila somatic cells are subject to metabolic control of cell death
Our data also show that NADPH-mediated control of caspase activity applies to not only germ cells, as might be concluded based on the regulation of caspase 2 in oocytes (Nutt et al, 2005), but also to somatic cells as both haemocyte-like S2 and elav-expressing neuronal cells are subject to this metabolic control. These findings suggest that initiator caspases such as caspase 2 in vertebrates and Dronc in flies may be suppressed by nutrients in most tissues through constitutive phosphorylation. Conversely, nutrient depletion (or other metabolic aberrations) could induce pathological apoptosis by triggering caspase dephosphorylation and activation, leading to cellular loss and degenerative disorders.
Of note, most cancer cells exhibit altered metabolism, in which NADPH is robustly produced as a ‘by-product'(Vander Heiden et al, 2009). On the basis of our observations, abnormally sustained levels of cellular NADPH may allow cancer cells to escape from apoptosis by suppressing caspase activation. The Drosophila system should now provide a genetically tractable model by which to identify novel therapeutic targets for these disorders through further elucidation of the upstream circuitry linking metabolism and caspase activation.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Drosophila Schneider's S2 cells were maintained in standard Schneider's medium (Schneider's medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated foetal bovine serum (Invitrogen)). For RNAi, cells were treated with three successive 2-day treatments of 80 nM dsRNA in standard Schneider's medium unless otherwise specified in the figure legends. Subpassage was performed every 2 days. Medium was supplemented with 50 μM zVAD as needed. Primers used to generate RNAi templates can be found in Supplementary Table S1. Samples for immunoblotting were lysed in 2 × SDS sample buffer, followed by sonication. To measure caspase activity, treated cells were lysed in hypotonic buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.7, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM EGTA, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 10 μM cytochalasin B, 1 × Roche complete protease inhibitor, 10 mM Na4P2O7). Lysates were incubated with 90 μl DEVDase buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.1% CHAPS, 10 mM DTT, 1 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol) and the substrate Ac-DEVD-pNA (200 μM, Enzo) at 37°C. Absorbance was measured at 405 nm and normalized to the amount of protein input. Cellular NADPH levels were measured by NADP/NADPH quantification kit (BioVision) according to the manual.
Transient and stable transfections
S2 cells were transfected by Effectene (QIAGEN) according to the manual. For transient expression, cells were transfected with 0.4–0.8 μg of DNA. For stable transfections, cells were cotransfected with 0.05 μg of GFP expression plasmids and 0.5 μg of plasmids containing a hygromycin B resistant gene and the copper-inducible gene of interest. Transfected cells were selected in standard Schneider's medium supplemented with 125 μg/ml hygromycin B for >3 weeks.
Cell viability assay
Apoptosis was triggered with 40 μM CHX in S2 cells cultured in standard Schneider's medium, 40 nM DIAP1 dsRNA in serum-free Schneider's medium or indicated concentrations of DHEA in glucose-free medium (HBSS supplemented with 1 × essential and non-essential amino-acid mixture (Invitrogen), pH 7.0 by NaOH) in the presence or absence of 5 mM dimethyl L-malate (Sigma). Cell viability was analysed by flow cytometry for PI-positive cells in PBS with 0.5 μg/ml PI or pictures taken under microscopes. To test malate's protection in S2 stable lines, cells were induced for 8 h with 150 μM CuSO4 in standard Schneider's medium in the presence or absence of 5 mM malate or 50 μM zVAD, followed by the addition of 40 μM CHX for another 8 h. Flow cytometry was used to score GFP-positive cells. Mean±s.d. from three independent experiments are shown.
Metabolic labelling of phosphoproteins in S2 cells
S2 cells expressing FLAG-Dronc prodomain were pretreated with 100 μM DHEA±5 mM malate for 2 h in glucose-free medium supplemented with 50 μM zVAD. After pretreatment, cells in each well were labelled with 1 mCi 32P-orthophosphate (PerkinElmer) for 4 h in the same medium. Treated cells were then lysed in lysis buffer (40 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol, 4 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM Na4P2O7, 10 mM NaF, 2 mM Na3VO4 and 1 × Roche complete protease inhibitor). Dronc prodomain were immunoprecipitated with FLAG beads (Sigma), and analysed by immunoblotting and autoradiography.
Co-immunoprecipitation
Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed as previously described (Quinn et al, 2000; Yang et al, 2005). In brief, lysates from transfected cells were incubated with FLAG beads at 4°C for 2 h. Precipitates and whole cell lysates were then analysed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
In vitro kinase assay
Bacterially expressed GST fusion Dronc prodomain (WT, S127A and S130A) bound to Glutathione-Sepharose beads was incubated in kinase buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl at pH 7.2, 0.1 mM ATP, 2 μCi 32P-ATP, 10 mM MgCl2 and 1 mM DTT at pH 7.2) with CaMKII (CalBiochem) for 1 h at room temperature followed by SDS–PAGE, coomassie blue stain and autoradiography.
Antibodies
Rabbit anti-DIAP1 serum (1:500) and Dronc pS130 phospho-specific antibody (1:1000) were raised against synthetic peptides, and the latter was then purified as previously described (Nutt et al, 2009). Anti-Dronc (1:1000) antibody was raised in rabbit against purified recombinant Dronc large domain (p20). Anti-FLAG (Sigma, 1:3000) and anti-actin (Santa Cruz, 1:2000) antibodies were used. Purified anti-DIAP1 (1:1000), anti-drICE (1:3000) and anti-bursiconα (1:1000) antibodies were generous gifts from Masayuki Miura (University of Tokyo), Paul Friesen (University of Wisconsin-Madison) and Benjamin H White (NIH), respectively.
Purification of recombinant Dronc
pDEST15 plasmids (Invitrogen) encoding N-terminally GST-tagged Dronc were transformed into Escherichia coli strain BL21-AI (Invitrogen). Overnight cultures were grown at 37°C and then diluted 1:10 in LB broth. Expression of protein was induced at 30°C with L-arabinose (2 g/l) for 1 h when the OD (600 nm) of the diluted cultures reached 0.7. After harvesting, bacteria were sonicated in lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.7, 100 mM NaCl, 1 × Roche complete protease inhibitors). Recombinant proteins were then purified from the lysates using Glutathione-Sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Transgenic flies and phenotyping
Genotypes of lines used in crosses are available in the Supplementary data. UAS-Dronc transgenic flies were generated according to standard protocols. The integration sites in different lines were mapped to individual chromosomes. Expression of FLAG-tagged Dronc in different lines was driven by indicted Gal4 drivers. UAS-p35 flies were obtained from John York (Duke). Progeny from the indicated crosses was categorized into unexpanded, partially expanded and totally expanded based on criteria previously described (Luan et al, 2006). Individual lines and all crosses were maintained at 18°C, unless otherwise specified. To score wing expansion defects, newly eclosed progeny were transferred into clean vials within 3 h after eclosion and then incubated at 18°C overnight. To examine the darkening process in the fly abdomen, flies were transferred within 1 h after eclosion and then incubated at 25°C for 3 h. Haemolymph was extracted and analysed as previously described (Luan et al, 2006).
Statistical test
Data from flow cytometry-based experiments were analysed by unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. Nominal data were analysed by χ2 analysis.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Eric Spana and Carrie Marean-Reardon for invaluable help with fly experiments, Macro Tsui for advice on experimental design, John York for UAS-p35 flies, Masayuki Miura, Paul Friesen and Benjamin H White for antibodies, David MacAlpine and Heather MacAlpine for constructs used in S2 stable transfections and members of the laboratory for discussions. This study was supported by a National Institutes of Health grant RO1 GM 080333 to SK. CSY was supported in part by the Taiwanese Merit Scholarship NSC-095-SAF-I-564-016-TMS.
Footnotes
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Abdelwahid E, Yokokura T, Krieser RJ, Balasundaram S, Fowle WH, White K (2007) Mitochondrial disruption in Drosophila apoptosis. Dev Cell 12: 793–806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams JM, Lux A, Steller H, Krieger M (1992) Macrophages in Drosophila embryos and L2 cells exhibit scavenger receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10375–10379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonzon C, Bouchier-Hayes L, Pagliari LJ, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (2006) Caspase-2-induced apoptosis requires bid cleavage: a physiological role for bid in heat shock-induced death. Mol Biol Cell 17: 2150–2157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew SK, Akdemir F, Chen P, Lu WJ, Mills K, Daish T, Kumar S, Rodriguez A, Abrams JM (2004) The apical caspase dronc governs programmed and unprogrammed cell death in Drosophila. Dev Cell 7: 897–907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew SK, Chen P, Link N, Galindo KA, Pogue K, Abrams JM (2009) Genome-wide silencing in Drosophila captures conserved apoptotic effectors. Nature 460: 123–127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi YJ, Lee G, Park JH (2006) Programmed cell death mechanisms of identifiable peptidergic neurons in Drosophila melanogaster. Development 133: 2223–2232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper DM, Granville DJ, Lowenberger C (2009) The insect caspases. Apoptosis 14: 247–256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daish TJ, Mills K, Kumar S (2004) Drosophila caspase DRONC is required for specific developmental cell death pathways and stress-induced apoptosis. Dev Cell 7: 909–915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey EM, McNabb SL, Ewer J, Kuo GR, Takanishi CL, Truman JW, Honegger HW (2004) Identification of the gene encoding bursicon, an insect neuropeptide responsible for cuticle sclerotization and wing spreading. Curr Biol 14: 1208–1213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorstyn L, Kumar S (2008) A biochemical analysis of the activation of the Drosophila caspase DRONC. Cell Death Differ 15: 461–470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorstyn L, Read S, Cakouros D, Huh JR, Hay BA, Kumar S (2002) The role of cytochrome c in caspase activation in Drosophila melanogaster cells. J Cell Biol 156: 1089–1098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel G, Hsiao C (1962) Hormonal and nervous control of tanning in the fly. Science 138: 27–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel R (1975) Regulation and physiological functions of malic enzymes. Curr Top Cell Regul 9: 157–181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geer BW, Lindel DL, Lindel DM (1979) Relationship of the oxidative pentose shunt pathway to lipid synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet 17: 881–895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal L, McCall K, Agapite J, Hartwieg E, Steller H (2000) Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J 19: 589–597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay BA, Guo M (2006) Caspase-dependent cell death in Drosophila. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22: 623–650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igaki T, Yamamoto-Goto Y, Tokushige N, Kanda H, Miura M (2002) Down-regulation of DIAP1 triggers a novel Drosophila cell death pathway mediated by Dark and DRONC. J Biol Chem 277: 23103–23106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey FM, Storey CJ, Sherry AD, Malloy CR (1996) 13C isotopomer model for estimation of anaplerotic substrate oxidation via acetyl-CoA. Am J Physiol 271: E788–E799 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanuka H, Kuranaga E, Takemoto K, Hiratou T, Okano H, Miura M (2005) Drosophila caspase transduces Shaggy/GSK-3beta kinase activity in neural precursor development. EMBO J 24: 3793–3806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanuka H, Sawamoto K, Inohara N, Matsuno K, Okano H, Miura M (1999) Control of the cell death pathway by Dapaf-1, a Drosophila Apaf-1/CED-4-related caspase activator. Mol Cell 4: 757–769 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (1997) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 275: 1132–1136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S, White K (2005) Apoptosis in Drosophila: neither fish nor fowl (nor man, nor worm). J Cell Sci 118: 1779–1787 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koto A, Kuranaga E, Miura M (2009) Temporal regulation of Drosophila IAP1 determines caspase functions in sensory organ development. J Cell Biol 187: 219–231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S (2007) Caspase function in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 14: 32–43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo CT, Zhu S, Younger S, Jan LY, Jan YN (2006) Identification of E2/E3 ubiquitinating enzymes and caspase activity regulating Drosophila sensory neuron dendrite pruning. Neuron 51: 283–290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Tonoki A, Takemoto K, Tomioka T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi S, Miura M (2006) Drosophila IKK-related kinase regulates nonapoptotic function of caspases via degradation of IAPs. Cell 126: 583–596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X (1996) Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 86: 147–157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luan H, Lemon WC, Peabody NC, Pohl JB, Zelensky PK, Wang D, Nitabach MN, Holmes TC, White BH (2006) Functional dissection of a neuronal network required for cuticle tanning and wing expansion in Drosophila. J Neurosci 26: 573–584 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P, Silke J, Leevers SJ, Evan GI (2000) The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1. EMBO J 19: 598–611 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennella V, Tan DY, Buster DW, Asenjo AB, Rath U, Ma A, Sosa HJ, Sharp DJ (2009) Motor domain phosphorylation and regulation of the Drosophila kinesin 13, KLP10A. J Cell Biol 186: 481–490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt TJ, Kuczynski C, Sezgin E, Zhu CT, Kumagai S, Eanes WF (2009) Quantifying interactions within the NADP(H) enzyme network in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 182: 565–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro I, Hay BA, Clem RJ (2002) The Drosophila DIAP1 protein is required to prevent accumulation of a continuously generated, processed form of the apical caspase DRONC. J Biol Chem 277: 49644–49650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro I, Monser K, Clem RJ (2004) Mechanism of Dronc activation in Drosophila cells. J Cell Sci 117: 5035–5041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt LK, Buchakjian MR, Gan E, Darbandi R, Yoon SY, Wu JQ, Miyamoto YJ, Gibbons JA, Andersen JL, Freel CD, Tang W, He C, Kurokawa M, Wang Y, Margolis SS, Fissore RA, Kornbluth S (2009) Metabolic control of oocyte apoptosis mediated by 14-3-3zeta-regulated dephosphorylation of caspase-2. Dev Cell 16: 856–866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt LK, Margolis SS, Jensen M, Herman CE, Dunphy WG, Rathmell JC, Kornbluth S (2005) Metabolic regulation of oocyte cell death through the CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of caspase-2. Cell 123: 89–103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park JH, Schroeder AJ, Helfrich-Forster C, Jackson FR, Ewer J (2003) Targeted ablation of CCAP neuropeptide-containing neurons of Drosophila causes specific defects in execution and circadian timing of ecdysis behavior. Development 130: 2645–2656 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn LM, Dorstyn L, Mills K, Colussi PA, Chen P, Coombe M, Abrams J, Kumar S, Richardson H (2000) An essential role for the caspase dronc in developmentally programmed cell death in Drosophila. J Biol Chem 275: 40416–40424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathmell JC, Fox CJ, Plas DR, Hammerman PS, Cinalli RM, Thompson CB (2003) Akt-directed glucose metabolism can prevent Bax conformation change and promote growth factor-independent survival. Mol Cell Biol 23: 7315–7328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez A, Chen P, Oliver H, Abrams JM (2002) Unrestrained caspase-dependent cell death caused by loss of Diap1 function requires the Drosophila Apaf-1 homolog, Dark. EMBO J 21: 2189–2197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez A, Oliver H, Zou H, Chen P, Wang X, Abrams JM (1999) Dark is a Drosophila homologue of Apaf-1/CED-4 and functions in an evolutionarily conserved death pathway. Nat Cell Biol 1: 272–279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324: 1029–1033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhuber M, Emoto K, Petritsch C (2005) The Drosophila caspase DRONC is required for metamorphosis and cell death in response to irradiation and developmental signals. Mech Dev 122: 914–927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang SL, Hawkins CJ, Yoo SJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (1999) The Drosophila caspase inhibitor DIAP1 is essential for cell survival and is negatively regulated by HID. Cell 98: 453–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R, Goyal L, Ditzel M, Zachariou A, Baker DA, Agapite J, Steller H, Meier P (2002) The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensable for regulating apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4: 445–450 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu D, Li Y, Arcaro M, Lackey M, Bergmann A (2005) The CARD-carrying caspase Dronc is essential for most, but not all, developmental cell death in Drosophila. Development (Cambridge, England) 132: 2125–2134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan N, Huh JR, Schirf V, Demeler B, Hay BA, Shi Y (2006) Structure and activation mechanism of the Drosophila initiator caspase Dronc. J Biol Chem 281: 8667–8674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang CS, Yu C, Chuang HC, Chang CW, Chang GD, Yao TP, Chen H (2005) FBW2 targets GCMa to the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation system. J Biol Chem 280: 10083–10090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi CH, Sogah DK, Boyce M, Degterev A, Christofferson DE, Yuan J (2007) A genome-wide RNAi screen reveals multiple regulators of caspase activation. J Cell Biol 179: 619–626 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo SJ, Huh JR, Muro I, Yu H, Wang L, Wang SL, Feldman RM, Clem RJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (2002) Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 4: 416–424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuneva M, Zamboni N, Oefner P, Sachidanandam R, Lazebnik Y (2007) Deficiency in glutamine but not glucose induces MYC-dependent apoptosis in human cells. J Cell Biol 178: 93–105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y, Coloff JL, Ferguson EC, Jacobs SR, Cui K, Rathmell JC (2008) Glucose metabolism attenuates p53 and Puma-dependent cell death upon growth factor deprivation. J Biol Chem 283: 36344–36353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y, Tong C, Jiang J (2007) Hedgehog regulates smoothened activity by inducing a conformational switch. Nature 450: 252–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L, Song Z, Tittel J, Steller H (1999) HAC-1, a Drosophila homolog of APAF-1 and CED-4 functions in developmental and radiation-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell 4: 745–755 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann KC, Ricci JE, Droin NM, Green DR (2002) The role of ARK in stress-induced apoptosis in Drosophila cells. J Cell Biol 156: 1077–1087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.