Abstract
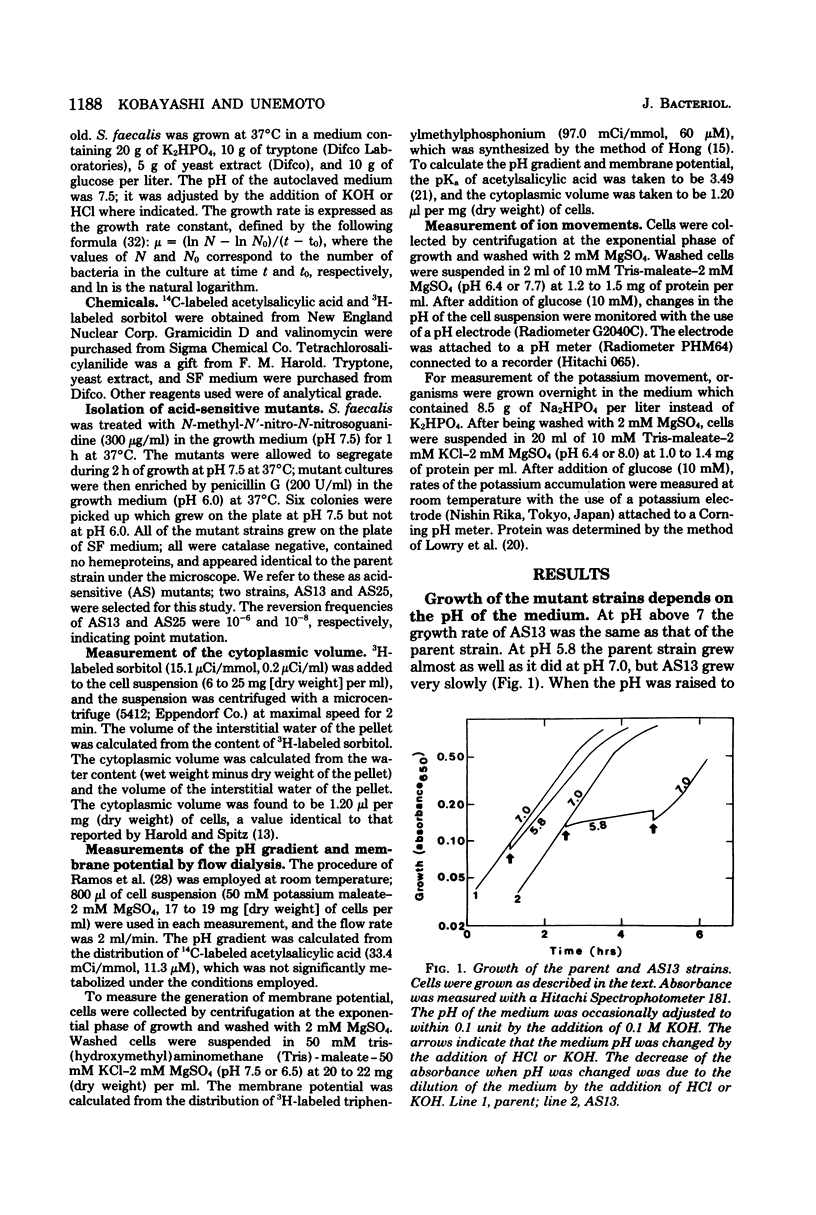
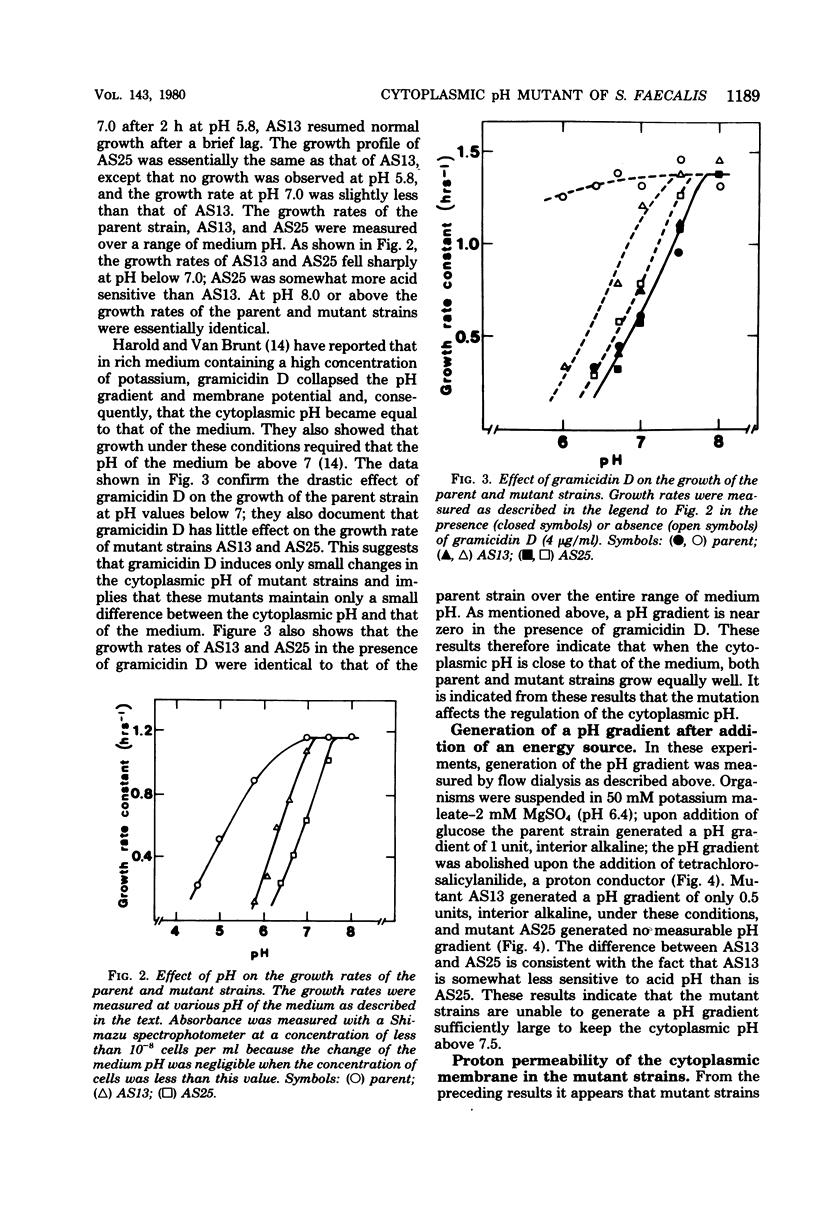
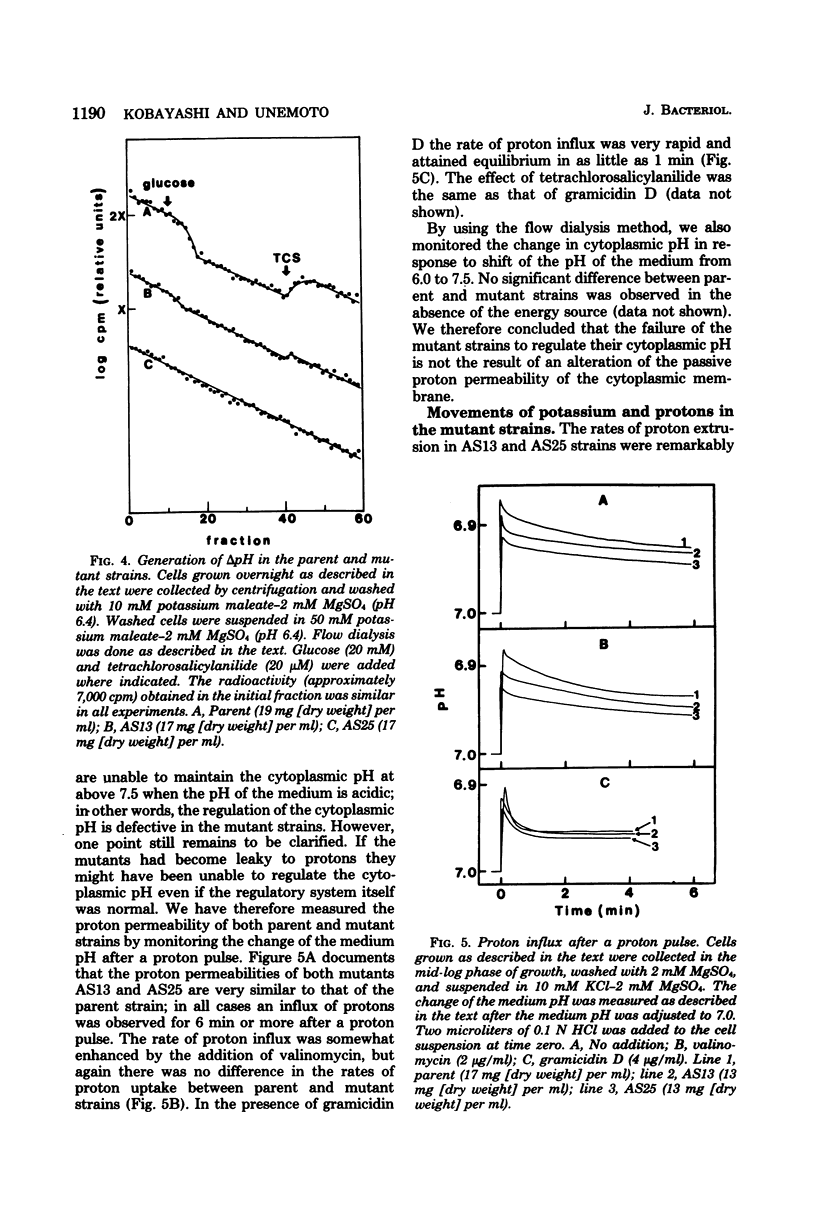
We have isolated two acid-sensitive mutants of Streptococcus faecalis (ATCC 9790), designated AS13 and AS25, which grew at pH 7.5 but not at pH below 6.0. The ionophore gramicidin D, which collapsed the pH gradient between the cytoplasm and the medium, had little effect on the growth of these mutants, indicating that growing cells maintain only a small pH gradient. In the presence of gramicidin D the growth rates of the parent and mutant strains were identical over a range of pH values. When glucose was added to a cell suspension at pH 6.4, the parent strain generated a pH gradient of 1.0 unit, interior alkaline; AS13 generated a pH gradient of only 0.5 units, and AS25 generated no measurable pH gradient. The proton permeability of the mutant strains was the same as that of the parent strain. These results suggest that a cytoplasmic pH of around 7.5 is required for the growth of the cells and that the mutant strains are unable to establish a neutral cytoplasmic pH in acidic medium because of damage to the regulatory system of the cytoplasmic pH. Mutant strains also have a reduced capacity to extrude protons and take up potassium. Therefore, it is likely that these cation transport systems are involved in the regulation of cytoplasmic pH.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in escherichia coli: properties of the sodium/proton antiporter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colb M., Shapiro L. A pH-conditional mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5637–5641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Nicholls D. G., Ingledew W. J. Transmembrane electrical potential and transmembrane pH gradient in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferro-oxidans. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1780195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. A requirement for ATP for beta-galactoside transport by Bacillus alcalophilus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1033–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Harold R. L., Baarda J. R., Abrams A. A genetic defect in retention of potassium by Streptococcus faecalis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1777–1784. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Ion currents and physiological functions in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:181–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. II. Proton and sodium extrusion. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):45–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01868094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Pavlasová E., Baarda J. R. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Spitz E. Accumulation of arsenate, phosphate, and aspartate by Sreptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):266–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.266-277.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Van Brunt J. Circulation of H+ and K+ across the plasma membrane is not obligatory for bacterial growth. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):372–373. doi: 10.1126/science.69317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S. An ecf mutation in Escherichia coli pleiotropically affecting energy coupling in active transport but not generation or maintenance of membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8582–8588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsung J. C., Haug A. Intracellular pH of Thermoplasma acidophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 21;389(3):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Davidson L. F., Filip S. J., Jr, Zuckerman R. S., Guffanti A. A. The protonmotive force and beta-galactoside transport in Bacillus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4599–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Mandel K. G., Bornstein R. F., Guffanti A. A. A non-alkalophilic mutant of Bacillus alcalophilus lacks the Na+/H+ antiporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Obligatory coupling between proton entry and the synthesis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.564-575.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Vectorial chemistry and the molecular mechanics of chemiosmotic coupling: power transmission by proticity. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(3):399–430. doi: 10.1042/bst0040399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Arakawa H., Baba M. Biochemical studies on an acidophilic, thermophilic bacterium, Bacillus acidocaldarius: isolation of bacteria, intracellular pH, and stabilities of biopolymers. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):1107–1113. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plack R. H., Jr, Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Absence of potassium/proton antiporter activity in a pH-sensitive mutant. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3824–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven J. A., Smith F. A. The evolution of chemiosmotic energy coupling. J Theor Biol. 1976 Apr;57(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of transmembrane electrochemical proton gradients. J Bioenerg. 1975 May;7(2):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01558427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy buffering as the biological function of Na+/K+ gradient. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



