Abstract
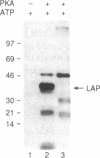
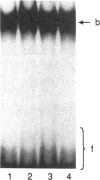
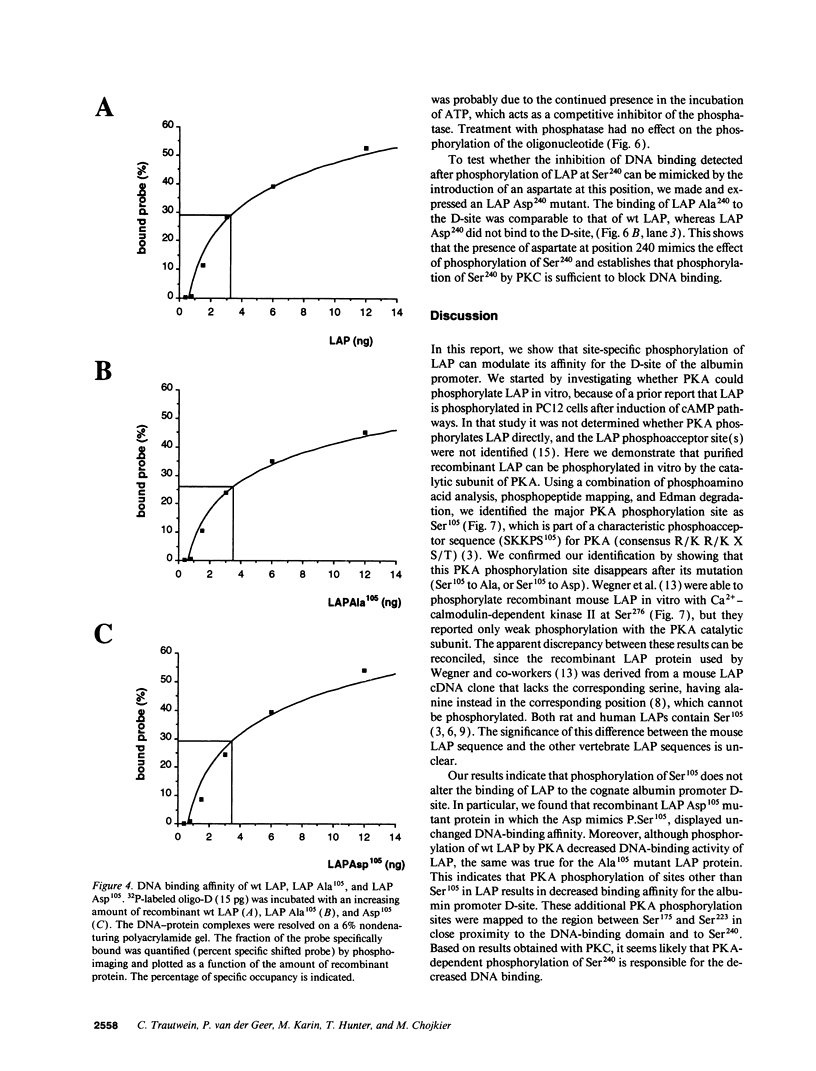
LAP (NF-IL6 or C/EBP beta), is a liver transcriptional activator protein that confers liver-specific gene expression. Because LAP has a characteristic phosphoacceptor sequence for cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), we tested if in vitro phosphorylation of LAP by PKA modulates its interaction with specific DNA sequences. The major PKA phosphorylation site of LAP was identified as Ser105, which is a predicted PKA site. As expected, this PKA phosphorylation site disappears after mutation of Ser105 to Ala. Kinetic studies with LAP and LAP Asp105 (which mimics a phosphoserine residue) demonstrated that phosphorylation of Ser105 itself has no effect on DNA binding. Phosphorylation of other sites by PKA, identified in the region between Ser173 and Ser223 and at Ser240, by analysis of truncated and mutated LAP peptides, resulted in an inhibition of DNA binding. LAP was also phosphorylated by purified protein kinase C in vitro, and the major phosphoacceptor was shown to be Ser240 within the DNA-binding domain of LAP. Phosphorylation of LAP at this residue or introduction of a Ser240 to Asp mutation resulted in marked decrease in its binding to DNA. These results suggest that site-specific phosphorylations of LAP modulate transactivation of its target genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weih F., Nichols M., Schütz G. The tissue-specific extinguisher locus TSE1 encodes a regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Hall Z. W. How many agrins does it take to make a synapse? Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90525-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Zhou J., James G., Heller-Harrison R., Czech M. P., Olson E. N. FGF inactivates myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins through phosphorylation of a conserved protein kinase C site in their DNA-binding domains. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1181–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Weinberg R. A. G1/S phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein is associated with an altered affinity for the nuclear compartment. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panduro A., Shalaby F., Shafritz D. A. Changing patterns of transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of liver-specific gene expression during rat development. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Caelles C., van der Geer P., Hunter T., Karin M., Chojkier M. Transactivation by NF-IL6/LAP is enhanced by phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):544–547. doi: 10.1038/364544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Bertics P. J., Hudson L. G., Vedvick T. S., Gill G. N. A three-step purification procedure for protein kinase C: characterization of the purified enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90471-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Cao Z., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcium-regulated phosphorylation within the leucine zipper of C/EBP beta. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):370–373. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Rivier J., Montminy M. R. Characterization of a bipartite activator domain in transcription factor CREB. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90664-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]