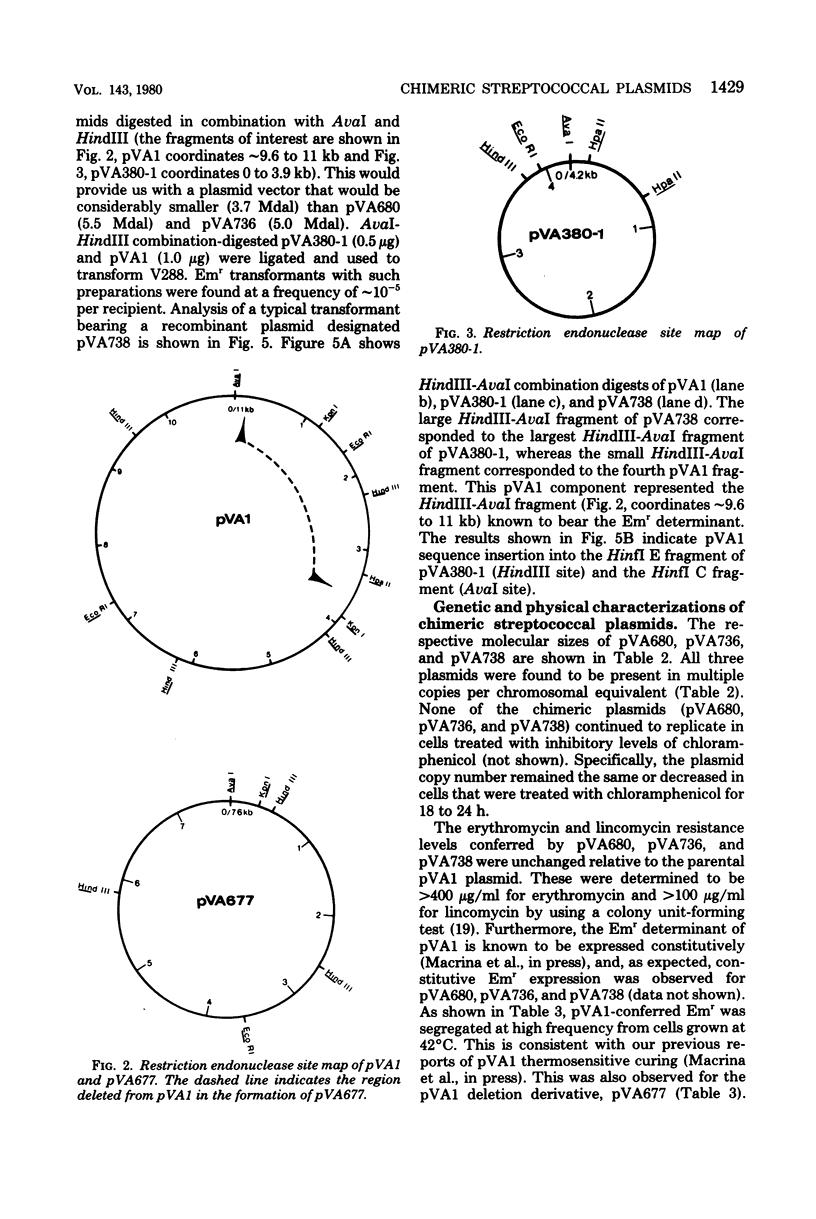
Abstract
Chimeric plasmids, which were useful as cloning vehicles in a Streptococcus sanguis (Challis) host vector system, have been constructed. By using three different strategies of restriction endonuclease digestion and ligation, a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment bearing an erythromycin resistance determinant was ligated in vitro to a phenotypially cryptic plasmid from Streptococcus ferus. Recombinant plasmids could be recovered after transformation of S. sanguis (Challis) with these preparations. Three useful chimeras were constructed. pVA680, 5.5 megadaltons in size, contained a single KpnI site into which passenger DNA may be spliced. pVA736, 5.0 megadaltons in size, contained single EcoRI, HindIII, and KpnI sites into which passenger DNA may be spliced. The EcoRI and KpnI sites of pVA736 may be used in combination with one another when ligating DNA into this plasmid. pVA738, 3.7 megadaltons in size, contained single HindIII and AvaI sites into which passenger DNA may be spliced. pVA680, pVA736, and pVA738 were stably maintained as multicopy plasmids in S. sanguis (Challis). None of them continued to replicate (amplify) in chloramphenicol-treated cells. By using pVA736 as a vector, we have cloned a chloramphenicol resistance determinant obtained from a large, conjugative streptococcal R plasmid. In addition, chromosomal DNA sequences from Streptococcus mutans have been inserted into pVA736 by using the KpnI-EcoRI site combination.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen W. H. The induction of rampant dental caries in monkeys (Macaca irus). Caries Res. 1969;3(3):227–237. doi: 10.1159/000259597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Specht P. A., Samol H. H. Streptococcus mutans in a wild, sucrose-eating rat population. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.216-219.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., JORDAN H. V., STANLEY H. R. Experimental caries and gingival pathologic changes in the gnotobiotic rat. J Dent Res. 1960 Sep-Oct;39:923–935. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390052701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M. Dissociation of plaque formation from glucan-induced agglutination in mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.189-196.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V. Plasmids mediating multiple drug resistance in group B streptococcus: transferability and molecular properties. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Araya S., Higuchi M. Plasmid DNA satellite bands seen in lysates of Streptococcus mutans that form insoluble extracellular polysaccharides. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):266–271. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bouanchaud D. H., Bieth G., Chabbert Y. A. R plasmids in Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):795–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Otake S., Hirasawa M., Williams K., Kiyoyono H., McGhee J. R., Shiota T. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: revertants of mutant C4. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.25-31.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama A., Ishikawa E., Ando T., Arai T. Isolation of plasmid DNA from naturally-occurring strains of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(12):1099–1103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson J. W., Gooder H. Growth and development of competence in the group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):820–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.820-825.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton N. W., Kakehashi S., Fitzgerald R. J. Recovery of specific "caries-inducing" streptococci from carious lesions in the teeth of children. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 May;15(5):461–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Rowan J., Straffon L. H., Loos P. J. Association of Streptococcus mutants with human dental decay. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1252–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1252-1260.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Reider J. L., Virgili S. S., Kopecko D. J. Survey of the extrachromosomal gene pool of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):215–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.215-226.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Scott C. L. Evidence for a disseminated plasmid in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):296–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.296-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Virgili S. S., Scott C. L. Extrachromosomal gene systems in Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:859–868. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Wood P. H., Jones K. R. Genetic transformation of Streptococcus sanguis (Challis) with cryptic plasmids from Streptococcus ferus. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):692–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.692-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Wood P. H., Jones K. R. Simple method for demonstrating small plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in oral streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1070–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1070-1073.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Shiota T., Ikeda T., Navia J. M., McGhee J. R. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: biochemical and pathogenic characteristics of mutant isolates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Nov;150(2):498–502. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake S., McGhee J. R., Hirasawa M., Williams K., Arnold R. R., Babb J. L., Kiyono H., Cox C., Michalek S. M., Shiota T. Use of mutants in the elucidation of virulence of Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:673–683. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B., Schnös M., Inman R. Construction and characterization of a chimeric plasmid composed of DNA Pfrom Escherichia coli and Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2064–2072. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L. Genetic alterations of Streptococcus mutans' virulence. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:661–672. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., McLellan T. S., Frez W. A., Clewell D. B. Characterization of a small plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain of Streptococcus sanguis isolated from dental plaque. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):884–887. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Stoppelaar J. D., König K. G., Plasschaert A. J., van der Hoeven J. S. Decreased cariogenicity of a mutant of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Aug;16(8):971–975. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]