Abstract
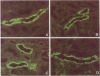
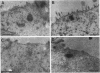
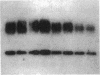
To examine whether expression and distribution of aquaporin of collecting duct (AQP-CD) are regulated by vasopressin V2 receptor (V2R), we performed immunohistochemical studies with specific antibody against AQP-CD. Normal Wistar rats were divided into four groups and treated for 3 d; control, dehydration, vasopressin V1 receptor (V1R) antagonist (OPC-21268 120 mg/kg), V2R antagonist (OPC-31260 30 mg/kg). At time of death, urine osmolality (Uosm) in the dehydration group (1884 +/- 245 mOsm/kg) was significantly higher than that in the control (938 +/- 91). In the V2R antagonist group, Uosm was significantly decreased to 249 +/- 29, whereas V1R antagonist showed no effect on Uosm. In the control and V1R antagonist groups, immunofluorescence studies showed the AQP-CD staining of both apical membrane and subapical cytoplasm of CD cells of the cortex and the inner medulla. Dehydration increased the immunostaining of both apical membrane and subapical cytoplasm of CD cells of the inner medulla, and the degree of increase was dominant in apical membrane. In the V2R antagonist group, only faint staining of apical membrane and weak labeling of cytoplasm of CD cells of the inner medulla were observed. These changes in the localization and protein amount of AQP-CD by dehydration and V2R antagonist were quantitatively confirmed by immunogold studies and immunoblot analysis of the inner medulla. The present results indicate that the distribution and amount of AQP-CD in the CD cells are regulated by vasopressin V2 receptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourguet J., Chevalier J., Hugon J. S. Alterations in membrane-associated particle distribution during antidiuretic challenge in frog urinary bladder epithelium. Biophys J. 1976 Jun;16(6):627–639. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85717-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnatowska-Hledin M. A., Spielman W. S. Vasopressin V1 receptors on the principal cells of the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Stimulation of cytosolic free calcium and inositol phosphate production via coupling to a pertussis toxin substrate. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):84–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI113888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion B., Spring K. R. Water permeability of apical and basolateral cell membranes of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F986–F999. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmanci M. C., Stern P., Kachadorian W. A., Valtin H., DiScala V. A. Vasopressin and collecting duct intramembranous particle clusters: a dose-response relationship. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):F560–F564. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.6.F560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankford S. P., Chou C. L., Terada Y., Wall S. M., Wade J. B., Knepper M. A. Regulation of collecting duct water permeability independent of cAMP-mediated AVP response. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F554–F566. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolait S. J., O'Carroll A. M., McBride O. W., Konig M., Morel A., Brownstein M. J. Cloning and characterization of a vasopressin V2 receptor and possible link to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):336–339. doi: 10.1038/357336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., DiGiovanni S. R., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Harris H. W. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11663–11667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Muller J., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin- and cAMP-induced changes in ultrastructure of isolated perfused inner medullary collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 2):F225–F238. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.2.F225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski N. L., Young W. S., 3rd, Knepper M. A., Lolait S. J. Expression of vasopressin V1a and V2 receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in the liver and kidney of embryonic, developing, and adult rats. Endocrinology. 1993 Oct;133(4):1849–1859. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.4.8404628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Wuarin F., Shi L. B., Verkman A. S., Ausiello D. A., Gluck S., Brown D. Apical endosomes isolated from kidney collecting duct principal cells lack subunits of the proton pumping ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):111–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Fushimi K., Saito H., Saito F., Uchida S., Ishibashi K., Kuwahara M., Ikeuchi T., Inui K., Nakajima K. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal mapping of human aquaporin of collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI117079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y., Ogawa H., Chihara T., Kondo K., Onogawa T., Nakamura S., Mori T., Tominaga M., Yabuuchi Y. OPC-21268, an orally effective, nonpeptide vasopressin V1 receptor antagonist. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):572–574. doi: 10.1126/science.1850553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y., Ogawa H., Yamashita H., Chihara T., Miyamoto H., Nakamura S., Onogawa T., Yamashita T., Hosokawa T., Mori T. Characterization of a novel aquaretic agent, OPC-31260, as an orally effective, nonpeptide vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):787–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]