Abstract
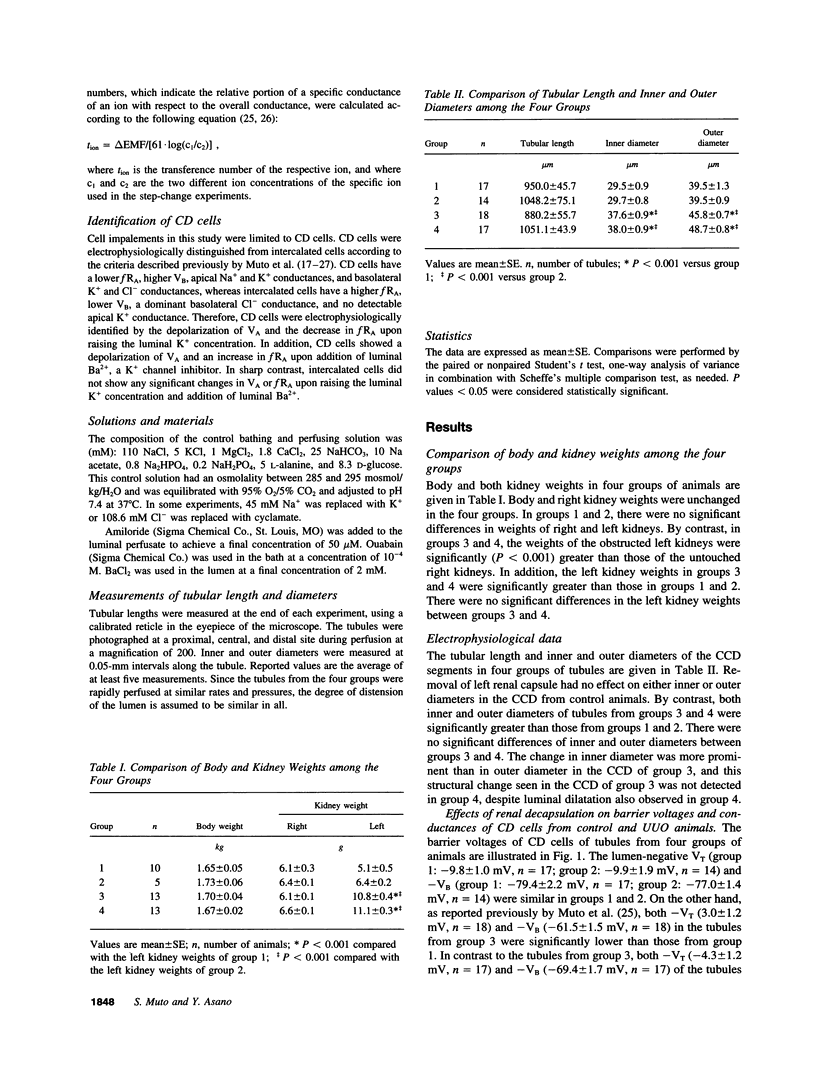
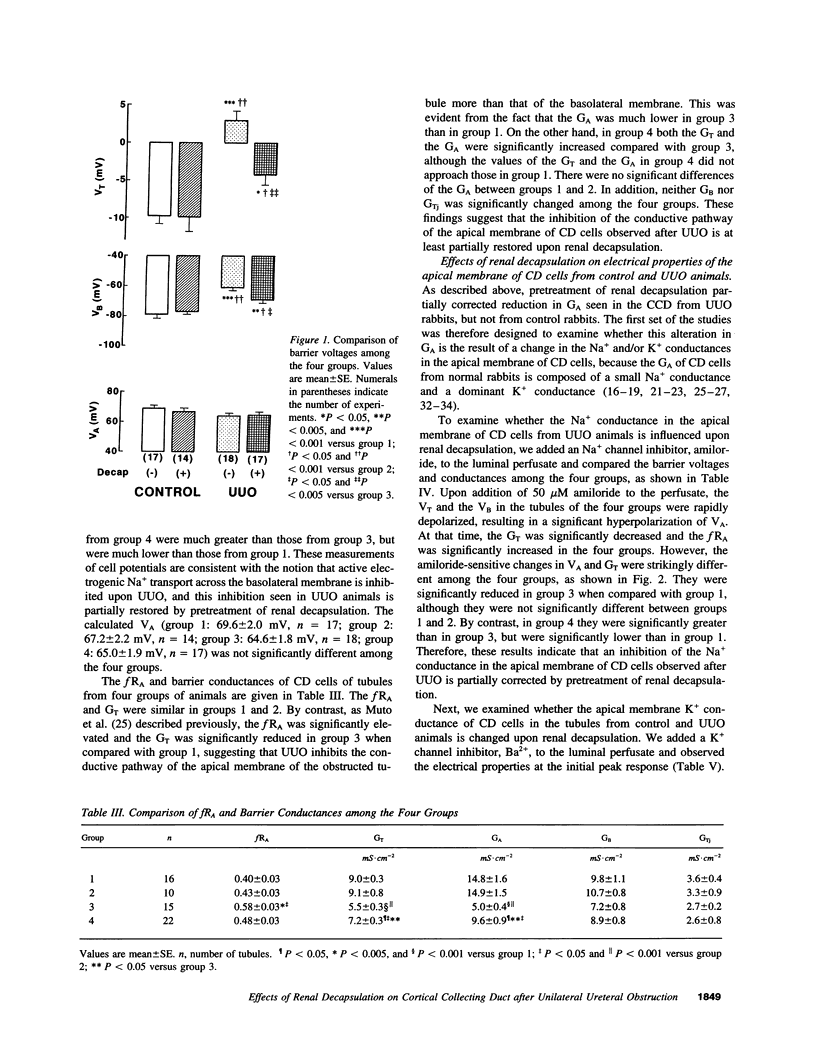
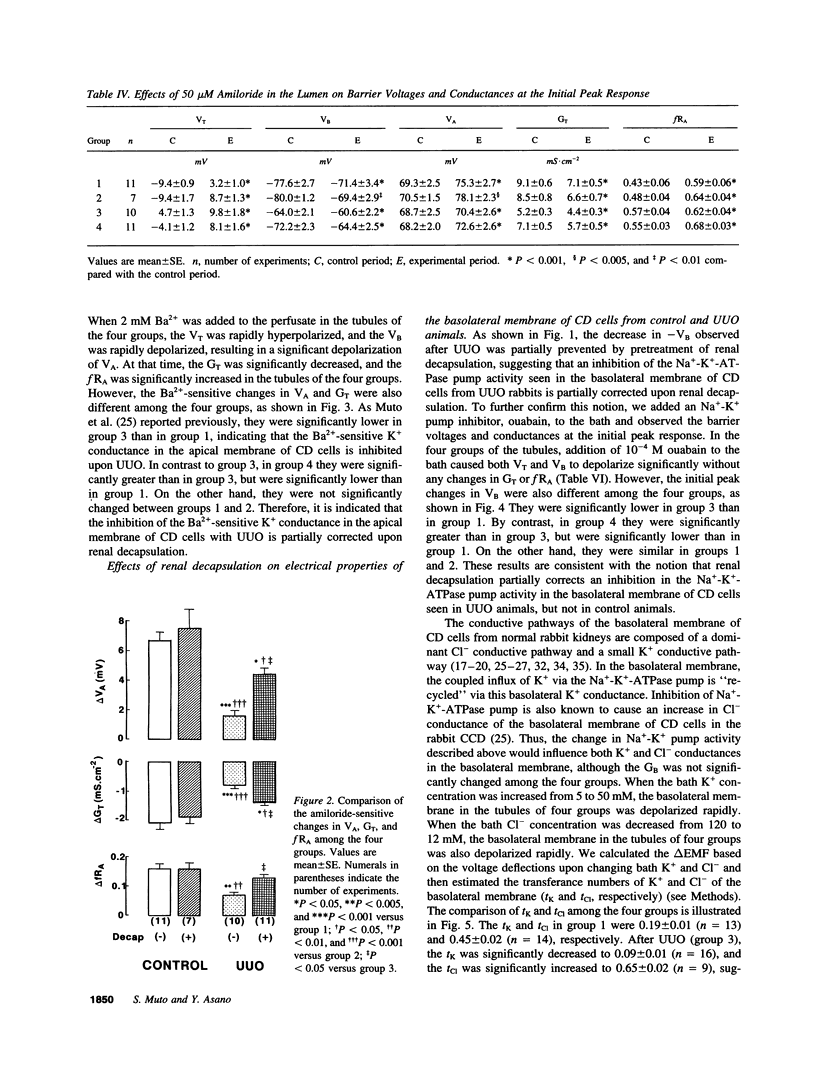
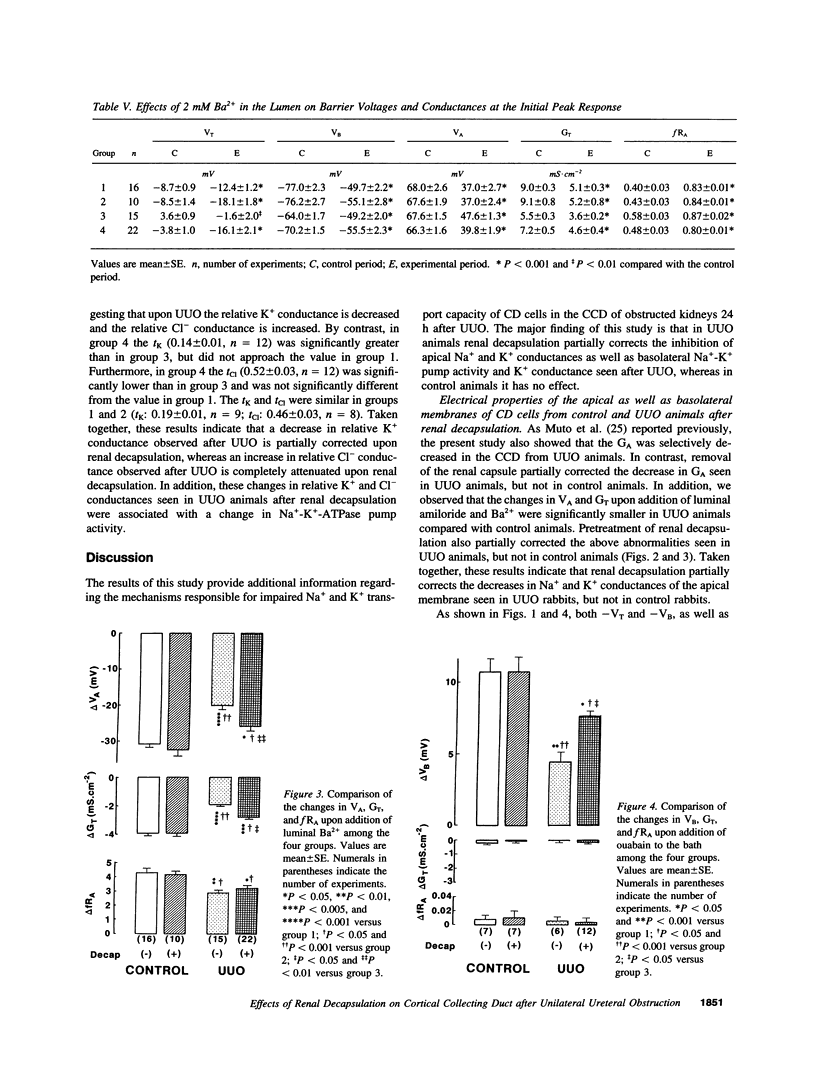
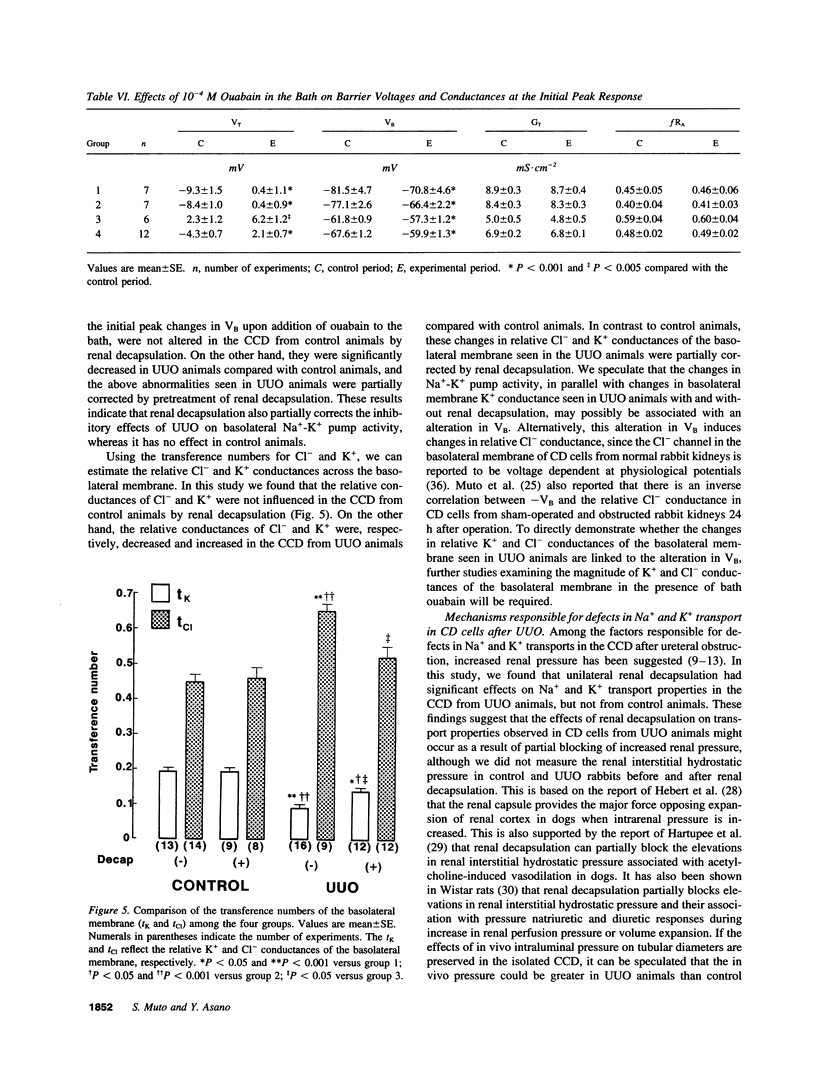
Ureteral obstruction causes impaired salt wastage and K+ secretion in the distal nephron segments, including the cortical collecting duct (CCD). Recently, we demonstrated that conductances of Na+ and K+ in the apical membrane, as well as the electrogenic Na(+)-K+ pump activity and the relative K+ conductance in the basolateral membrane of the collecting duct cell, were inhibited in the obstructed kidney after unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). To examine whether the increased intrarenal pressure might be causally related to these abnormalities in the CCD, the effects of unilateral renal decapsulation, a maneuver that partially blocks the increase in renal pressure, were evaluated with microelectrode techniques in isolated CCDs from UUO and sham-operated (control) rabbits 24 h after operation. Renal decapsulation had no effects on barrier voltages and conductances in the CCD from control animals. The lumen-negative transepithelial (VT) and basolateral membrane (VB) voltages as well as the transepithelial (GT) and the apical membrane (GA) conductances were decreased in the CCD from UUO animals compared with control animals. Pretreatment of renal decapsulation partially corrected the decreases in VT, VB, GT, and GA seen in the CCD from UUO animals. The changes in apical membrane voltage and GT upon addition of luminal amiloride and Ba2+, and the changes in VB upon addition of bath ouabain, were also decreased in the CCD from UUO animals compared with control animals. Pretreatment of renal decapsulation also partially corrected the above abnormalities seen in UUO animals, whereas it had no effect in control animals. The transference numbers for Cl- (tCl) and K+ (tK) in the basolateral membrane were, respectively, increased and decreased in the CCD from UUO animals compared with control animals. Pretreatment of renal decapsulation also partially corrected the changes in tCl and tK seen in UUO animals, whereas it had no effect in control animals. We conclude that, in UUO animals, renal decapsulation partially corrects the inhibition of apical Na+ and K+ conductances as well as basolateral Na(+)-K+ pump activity and relative K+ conductance seen after UUO, whereas in control animals it has no effect. The increased renal pressure may partly contribute to the defects in Na+ and K+ transport in the CCD from obstructed kidneys. Renal decapsulation has protective effects on impaired Na+ and K+ transports in the CCD after ureteral obstruction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bander S. J., Buerkert J. E., Martin D., Klahr S. Long-term effects of 24-hr unilateral ureteral obstruction on renal function in the rat. Kidney Int. 1985 Oct;28(4):614–620. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle D. C., Arruda J. A., Kurtzman N. A. Hyperkalemic distal renal tubular acidosis associated with obstructive uropathy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):373–380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better O. S., Arieff A. I., Massry S. G., Kleeman C. R., Maxwell M. H. Studies on renal function after relief of complete unilateral ureteral obstruction of three months' duration in man. Am J Med. 1973 Feb;54(2):234–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell H. T., Bello-Reuss E., Klahr S. Hydraulic water permeability and transepithelial voltage in the isolated perfused rabbit cortical collecting tubule following acute unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):219–225. doi: 10.1172/JCI111677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Davis B. B., Needleman P. Localization of exaggerated prostaglandin synthesis associated with renal damage. Prostaglandins. 1981 Dec;22(6):933–944. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canton A., Corradi A., Stanziale R., Maruccio G., Migone L. Effects of 24-hour unilateral ureteral obstruction on glomerular hemodynamics in rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1979 May;15(5):457–462. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebata S., Muto S., Asano Y. Effects of uninephrectomy on electrical properties of the cortical collecting duct from rabbit remnant kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1547–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI116023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engbretson B. G., Stoner L. C. Flow-dependent potassium secretion by rabbit cortical collecting tubule in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F896–F903. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjeldborg O., Kim C. H. Spontaneous rupture of renal transplant. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1974;8(1):31–36. doi: 10.3109/00365597409132814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. J., Davidson K. Isolated nephron segments from rabbit models of obstructive nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):165–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI110427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. H., Yarger W. E. Renal function after release of unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):806–815. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartupee D. A., Burnett J. C., Jr, Mertz J. I., Knox F. G. Acetylcholine-induced vasodilation without natriuresis during control of interstitial pressure. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):F325–F329. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.4.F325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert L. A., Stuart K. A., Stemper J. A. Effect of renal decapsulation on renal function. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):632–639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert L. A., Stuart K. A., Stemper J. A. Whole kidney volume/pressure relationships. Kidney Int. 1975 Jan;7(1):45–54. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. J., Haas M., Harris H. W., Jr, Silva P., Yalla S., Sullivan M. R., Otuechere G., Kashgarian M., Zeidel M. L. Transport defects of rabbit medullary thick ascending limb cells in obstructive nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):21–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI116173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. J., Harris H. W., Jr, Otuechere G., Yalla S., Sullivan M. R., Kashgarian M., Benos D. J., Kleyman T. R., Zeidel M. L. Transport defects of rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells in obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 2):F808–F815. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.5.F808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAENIKE J. R., BRAY G. A. Effects of acute transitory urinary obstruction in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1960 Dec;199:1219–1222. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.6.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERR W. S., Jr Effects of complete ureteral obstruction in dogs on kidney function. Am J Physiol. 1956 Mar;184(3):521–526. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.184.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Mujais S. K. Cortical collecting duct Na-K pump in obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1320–F1327. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klahr S. Pathophysiology of obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1983 Feb;23(2):414–426. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Ebata S., Asano Y. Short-term effects of uninephrectomy on electrical properties of the cortical collecting duct from rabbit remnant kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):286–296. doi: 10.1172/JCI116958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Furuya H., Tabei K., Asano Y. Site and mechanism of action of epidermal growth factor in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):F163–F169. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.2.F163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Giebisch G., Sansom S. Effects of adrenalectomy on CCD: evidence for differential response of two cell types. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F742–F752. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Imai M., Asano Y. Effect of nafamostat mesilate on Na+ and K+ transport properties in the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Imai M., Asano Y. Further electrophysiological characterization of the alpha- and beta-intercalated cells along the rabbit distal nephron segments: effects of inhibitors. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Sep-Oct;1(5):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Imai M., Asano Y. Mechanisms of the hyperkalaemia caused by nafamostat mesilate: effects of its two metabolites on Na+ and K+ transport properties in the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):173–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Miyata Y., Asano Y. Electrical properties of the rabbit cortical collecting duct from obstructed and contralateral kidneys after unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):571–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI116624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Sansom S., Giebisch G. Effects of a high potassium diet on electrical properties of cortical collecting ducts from adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):376–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI113329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Yasoshima K., Yoshitomi K., Imai M., Asano Y. Electrophysiological identification of alpha- and beta-intercalated cells and their distribution along the rabbit distal nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1829–1839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Sansom S. C. Electrophysiological properties of cellular and paracellular conductive pathways of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(3):281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF01871637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini S., Kurtzman N. A. Enzyme activity in obstructive uropathy: basis for salt wastage and the acidification defect. Kidney Int. 1990 Jan;37(1):79–84. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Agulian S., Muto S., Illig V., Giebisch G. K activity of CCD principal cells from normal and DOCA-treated rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F136–F142. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., La B. Q., Carosi S. L. Double-barreled chloride channels of collecting duct basolateral membrane. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):F46–F52. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.1.F46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., O'Neil R. G. Effects of mineralocorticoids on transport properties of cortical collecting duct basolateral membrane. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 2):F743–F757. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.4.F743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., O'Neil R. G. Mineralocorticoid regulation of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ transport of the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F858–F868. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Weinman E. J., O'Neil R. G. Microelectrode assessment of chloride-conductive properties of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F291–F302. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirakomen K., Kozlov N., Arruda J. A., Kurtzman N. A. Renal hydrogen ion secretion after release of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1233–1239. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whinnery M. A., Shaw J. O., Beck N. Thromboxane B2 and prostaglandin E2 in the rat kidney with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):F220–F225. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.3.F220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



