Abstract
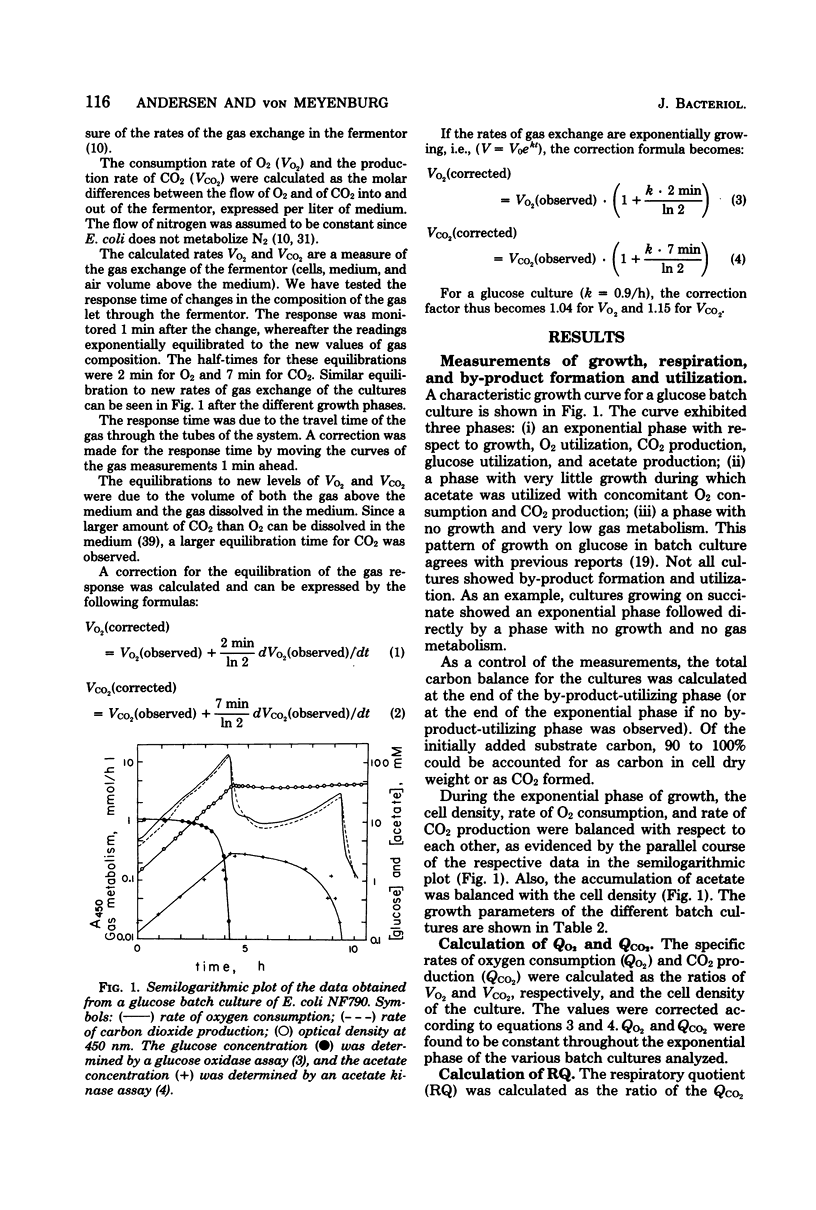
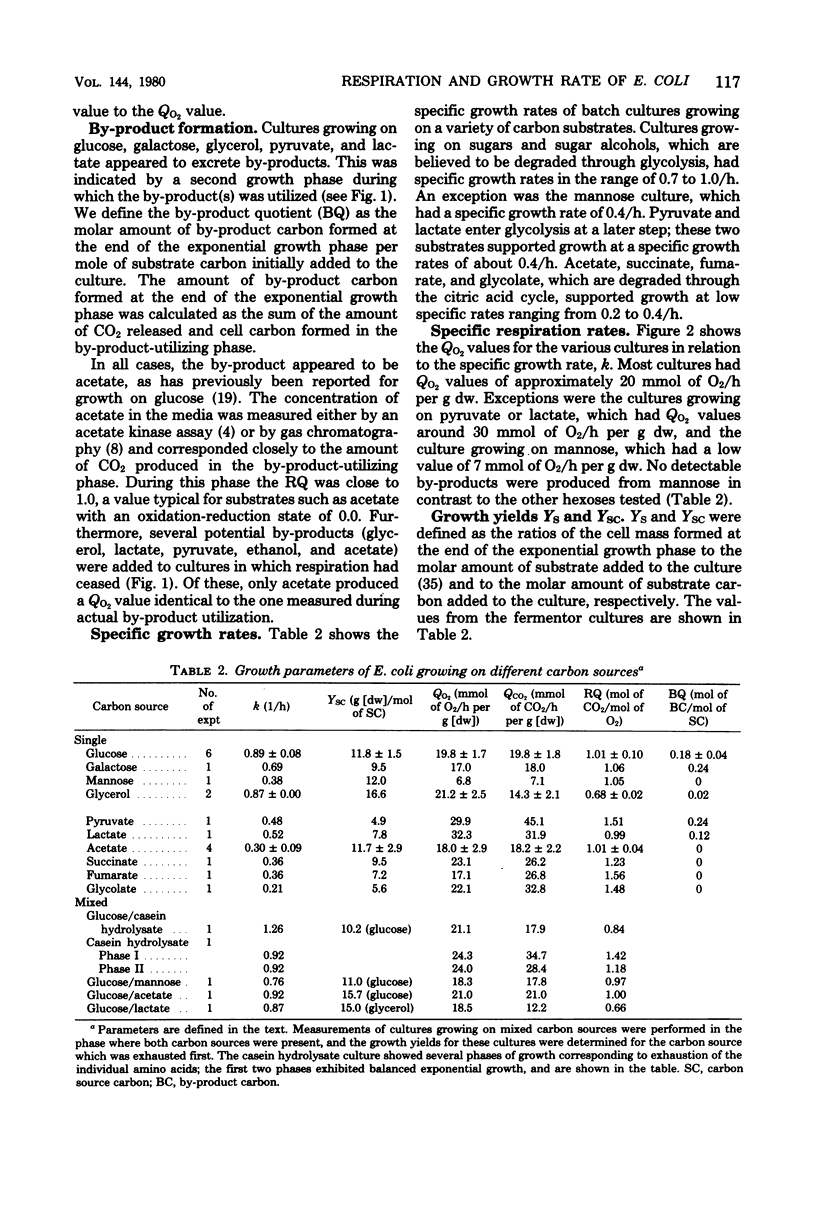
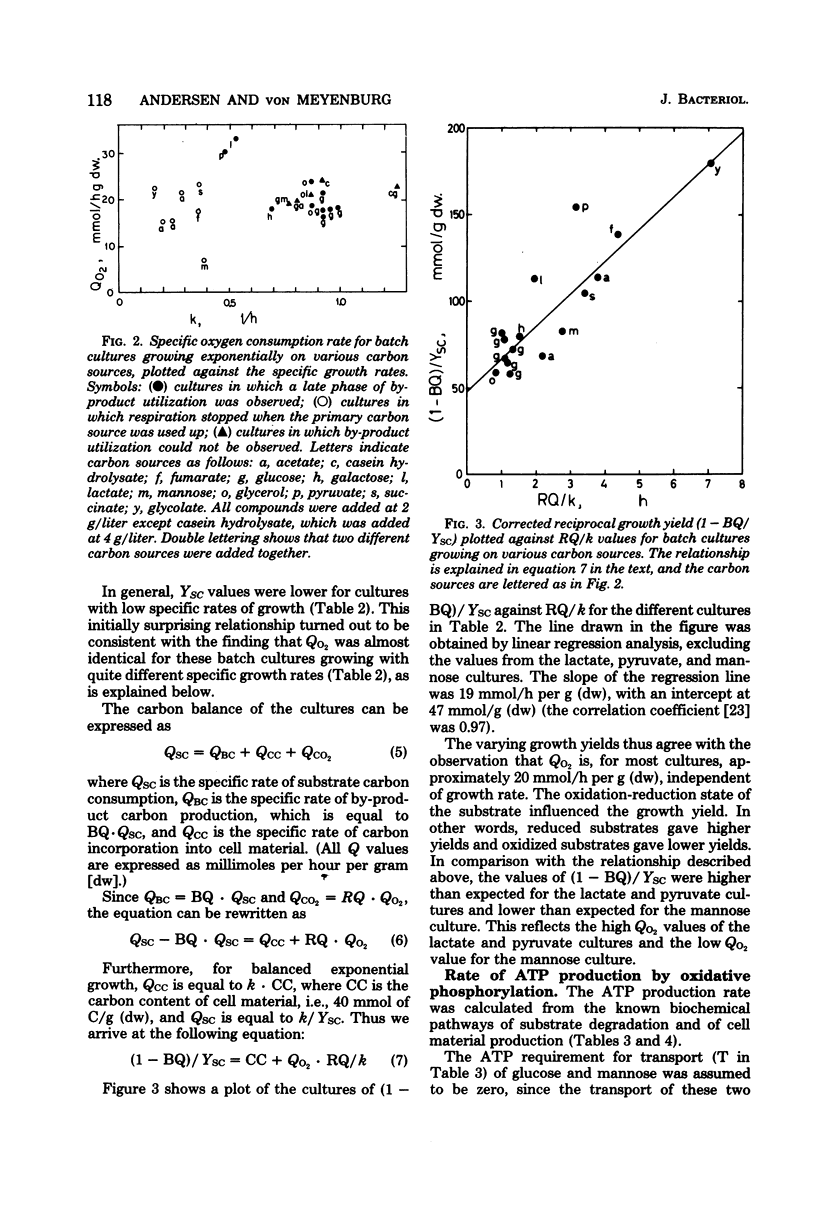
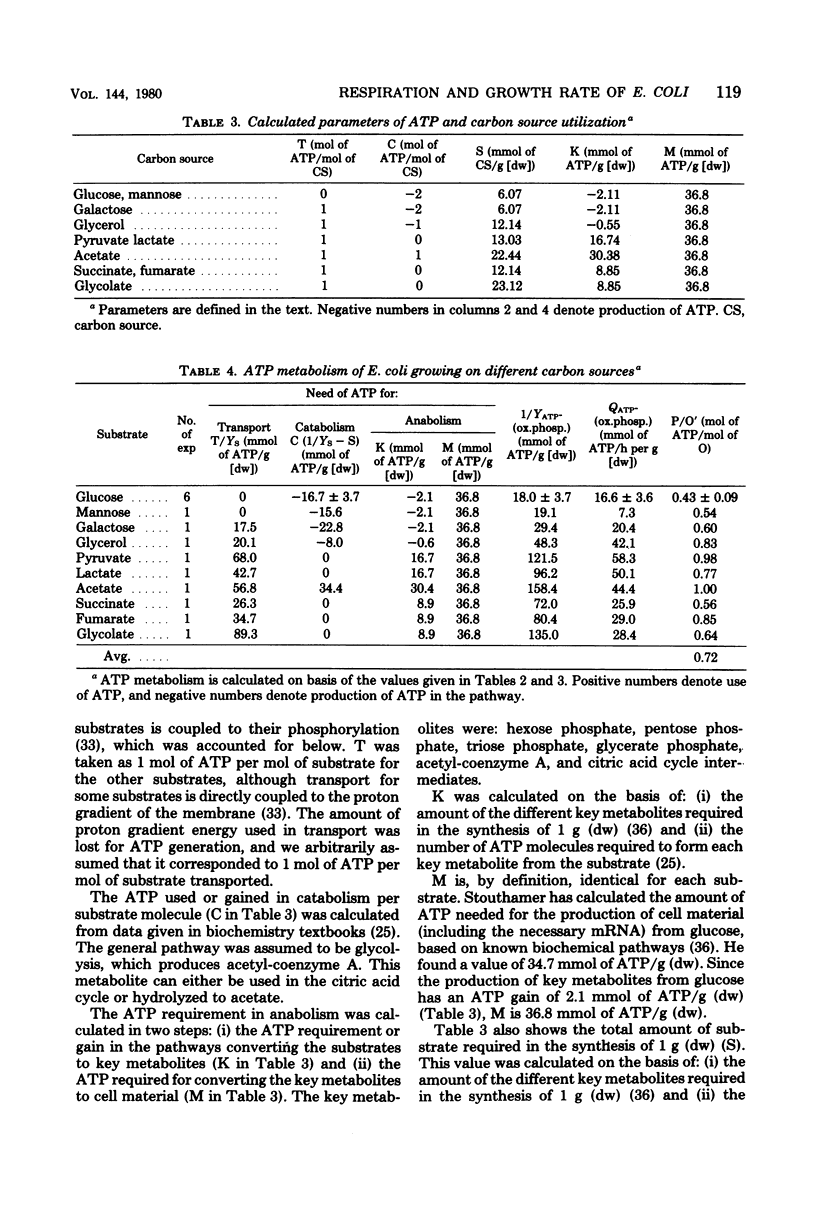
Batch cultures of Escherichia coli were grown in minimal media supplemented with various carbon sources which supported growth at specific growth rates from 0.2 to 1.3/h. The respiration rates of the cultures were measured continuously. With few exceptions, the specific rate of oxygen consumption was about 20 mmol of O2/h per g (dry weight), suggesting that the respiratory capacity was limited at this value. The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) required for the production of cell material from the different carbon sources was calculated on the basis of known ATP requirements in the biochemical pathways and routes of macromolecular synthesis. The calculated ATP requirements, together with the measured growth rates and growth yields on the different carbon sources, were used to calculate the rate of ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation. This rate was closely related to the respiration rate. We suggest that aerobic growth of E. coli in batch cultures is limited by the rate of respiration and the concomitant rate of ATP generation through oxidative phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen K. B., von Meyenburg K. Charges of nicotinamide adenine nucleotides and adenylate energy charge as regulatory parameters of the metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4151–4156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C., von Meyenburg H. K. Enzyme pattern and aerobic growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under various degrees of glucose limitation. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):479–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.479-486.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Preez J. C., Lategan P. M. Gas chromatographic determination of C2-C5 fatty acids in aqueous media with a Porapak N column. J Chromatogr. 1976 Sep 1;124(1):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)87838-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer I. S., Jones C. W. The energetics of Escherichia coli during aerobic growth in continuous culture. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):115–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest W. W., Walker D. J. The generation and utilization of energy during growth. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;5:213–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT D., ELSWORTH R., TELLING R. C. The continuous culture of bacteria; a theoretical and experimental study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):601–622. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. D., Holms W. H. Measurement of respiration of micro-organisms during batch culture. Lab Pract. 1970 Aug;19(8):795–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. T., Pato M. L., Molin S., Fill N. P., von Meyenburg K. Simple downshift and resulting lack of correlation between ppGpp pool size and ribonucleic acid accumulation. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):585–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.585-591.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E. The regulation of respiration rate in growing bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):243–313. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempfling W. P., Mainzer S. E. Effects of varying the carbon source limiting growth on yield and maintenance characteristics of Escherichia coli in continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1076–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1076-1087.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempfling W. P. Repression of oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli B by growth in glucose and other carbohydrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90461-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchener B. J., Egan A. F., Rogers P. J. Energetics of Microbacterium thermosphactum in glucose-limited continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1047–1052. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1047-1052.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holms W. H., Bennett P. M. Regulation of isocitrate dehydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli on adaptation to acetate. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jan;65(1):57–68. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JULIAN G. R. (14C)LYSINE PEPTIDES SYNTHESIZED IN AN IN VITRO ESCHERICHIA COLI SYSTEM IN THE PRESENCE OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER D. P., RICKENBERG H. V. The competitive inhibition of alpha-methylglucoside uptake in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Mar 25;10:482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainzer S. E., Hempfling W. P. Effects of growth temperature on yield and maintenance during glucose-limited continuous culture of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):251–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.251-256.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer E. M., van Verseveld H. W., van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Energy conservation during aerobic growth in Paracoccus denitrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00446650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neijssel O. M., Tempest D. W. Bioenergetic aspects of aerobic growth of Klebsiella aerogenes NCTC 418 in carbon-limited and carbon-sufficient chemostat culture. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Mar 19;107(2):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00446843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. A., Schrock H. L., Russell P., Blake R., 2nd, Gennis R. B. Preparation of Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase utilizing a thiamine pyrophosphate affinity column. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):13–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P. J., Stewart P. R. Energetic efficiency and maintenance. Energy characteristics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (wild type and petite) and Candida parapsilosis grown aerobically and micro-aerobically in continuous culture. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):25–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00696220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., MAALOE O., KJELDGAARD N. O. Dependency on medium and temperature of cell size and chemical composition during balanced grown of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):592–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase systems: structural, functional, and evolutionary interrelationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):856–871. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.856-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. A theoretical study on the amount of ATP required for synthesis of microbial cell material. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(3):545–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02578899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. W. Determination of the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation in continuous cultures of Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Mar 10;102(3):187–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00428367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W., Kapteijn W. M., van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Molar growth yields and fermentation balances of Lactobacillus casei L3 in batch cultures and in continuous cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):333–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Oxidative phosphorylation in intact bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):327–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00408900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



