Abstract
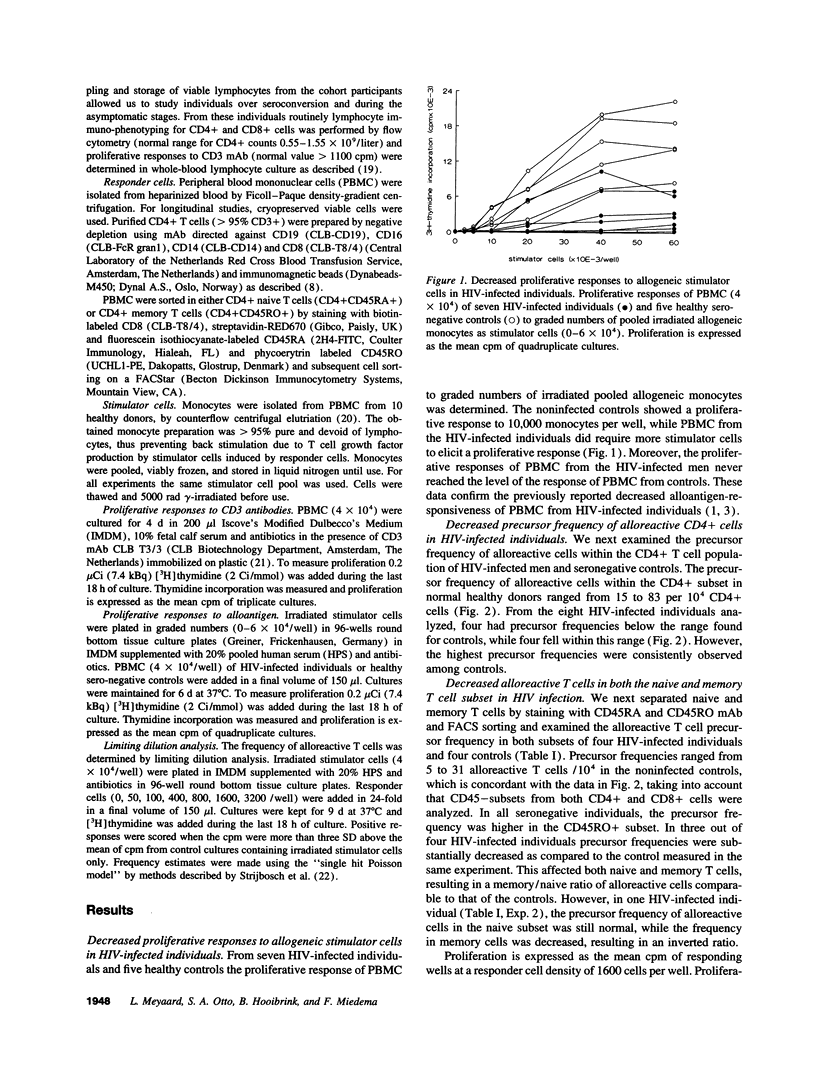
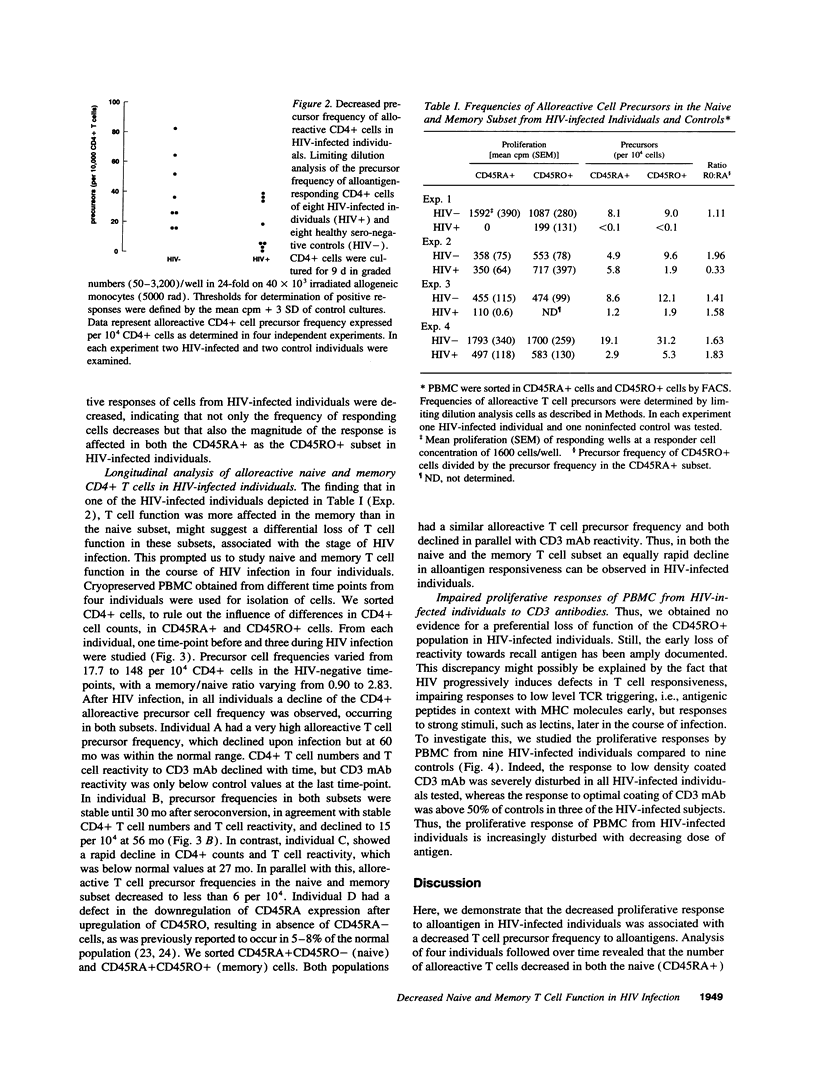
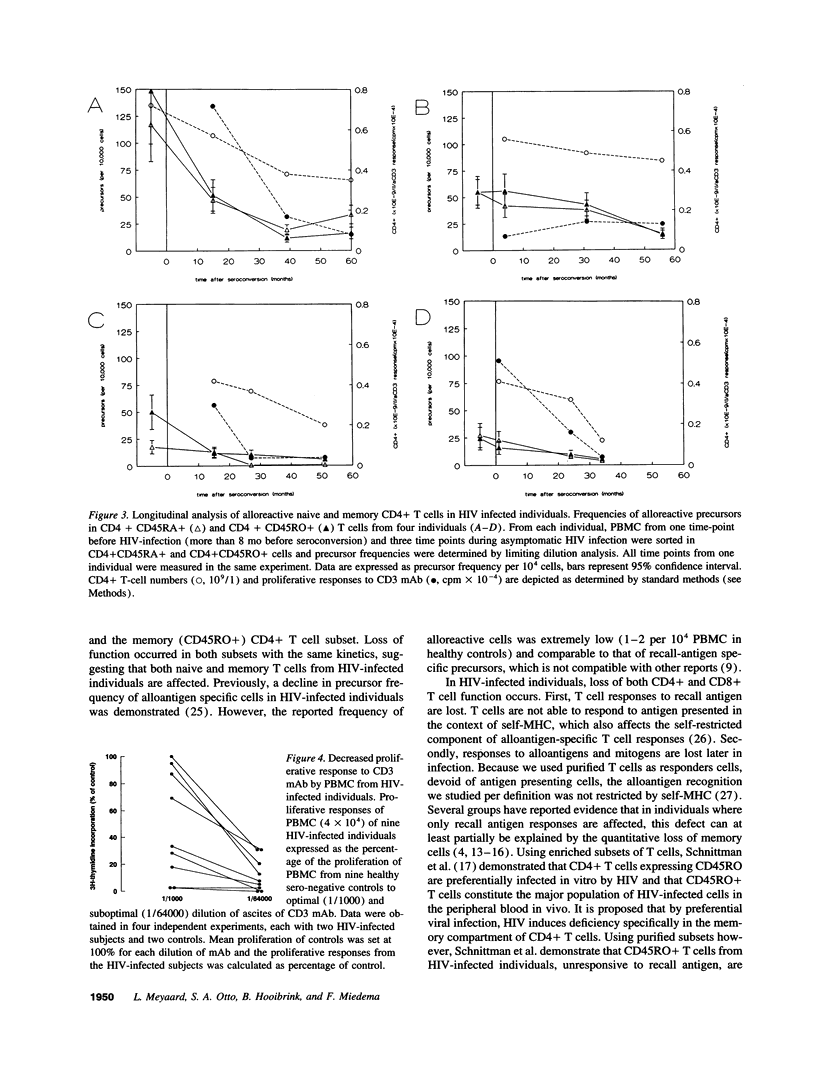
Early in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are qualitatively affected. Loss of responses to recall antigen precedes impaired responses to allogeneic MHC and mitogens. The selective quantitative loss of memory T cells in early infection, only partially explains the observed defects. We investigated whether functional loss of T cells is preferentially observed for memory T cells or whether both naive and memory T cell subsets are affected in the course of HIV infection. We studied the proliferative response of CD4+ T cells from HIV-infected individuals to alloantigens, to which normally both naive and memory T cells respond, by limiting dilution analysis. The decreased proliferative response to alloantigens in HIV-infected individuals was associated with a decreased precursor frequency of alloreactive cells. The frequency was decreased in both the CD45RA+ (naive) and the CD45RO+ (memory) subset of CD4+ T cells. Analysis of four individuals in the course of HIV infection revealed similar kinetics of the decline in function in both subsets. Although initially T cell defects may be accounted for by the selective quantitative loss of memory cells, in later stages of HIV infection the function of both CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ cells is affected.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M. Interconversion of CD45R subsets of CD4 T cells in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):163–166. doi: 10.1038/348163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayota A., Vuillier F., Scott-Algara D., Feuillie V., Dighiero G. Impaired proliferative capacity and abnormal cytokine profile of naive and memory CD4 T cells from HIV-seropositive patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):478–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehimi J., Starr S. E., Frank I., D'Andrea A., Ma X., MacGregor R. R., Sennelier J., Trinchieri G. Impaired interleukin 12 production in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1361–1366. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirmule N., Kalyanaraman V. S., Oyaizu N., Slade H. B., Pahwa S. Inhibition of functional properties of tetanus antigen-specific T-cell clones by envelope glycoprotein GP120 of human immunodeficiency virus. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Stocks N. I., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Lucey D. R., Via C. S., Shearer G. M. Detection of three distinct patterns of T helper cell dysfunction in asymptomatic, human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive patients. Independence of CD4+ cell numbers and clinical staging. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1892–1899. doi: 10.1172/JCI114376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Via C. S., Lucey D. R., Roilides E., Pizzo P. A., Shearer G. M. Functional dichotomy of CD4+ T helper lymphocytes in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):665–670. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Battistin S., Crovatto M., Modolo M. L., Carbone A., Tirelli U., Santini G. Immunologic abnormalities related to antigenaemia during HIV-1 infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):317–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Eck H. P., Mihm S. HIV-induced cysteine deficiency and T-cell dysfunction--a rationale for treatment with N-acetylcysteine. Immunol Today. 1992 Jun;13(6):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figdor C. G., Bont W. S., Touw I., de Roos J., Roosnek E. E., de Vries J. E. Isolation of functionally different human monocytes by counterflow centrifugation elutriation. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):46–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. A., Azen S. P., Adelsberg B., Gjerset G., Hassett J., Kaplan J., Niland J. C., Odom-Maryon T., Parker J. W., Stites D. P. Immunophenotyping in a multicenter study: the Transfusion Safety Study experience. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jul;52(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Terpstra F. G., De Goede R. E., Mulder J. W., De Wolf F., Schellekens P. T., Van Lier R. A., Tersmette M., Miedema F. Immunological and virological markers in individuals progressing from seroconversion to AIDS. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):837–844. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Terpstra F. G., De Jong R., Van Noesel C. J., Van Lier R. A., Miedema F. Selective loss of T cell functions in different stages of HIV infection. Early loss of anti-CD3-induced T cell proliferation followed by decreased anti-CD3-induced cytotoxic T lymphocyte generation in AIDS-related complex and AIDS. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1039–1044. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekow J., Wachsman W., McCutchan J. A., Cronin M., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Transforming growth factor beta and noncytopathic mechanisms of immunodeficiency in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8321–8325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yamada A., Rothstein D. M., Anderson K. C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD45 isoforms associated with distinct functions of CD4 cells derived from unusual healthy donors lacking CD45RA- T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;137(2):406–419. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90089-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkenschlager M., Terry L., Edwards R., Beverley P. C. Limiting dilution analysis of proliferative responses in human lymphocyte populations defined by the monoclonal antibody UCHL1: implications for differential CD45 expression in T cell memory formation. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1653–1661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyaard L., Schuitemaker H., Miedema F. T-cell dysfunction in HIV infection: anergy due to defective antigen-presenting cell function? Immunol Today. 1993 Apr;14(4):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90279-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie C. A., McLean A., Alcock C., Beverley P. C. Lifespan of human lymphocyte subsets defined by CD45 isoforms. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):264–265. doi: 10.1038/360264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miedema F., Tersmette M., van Lier R. A. AIDS pathogenesis: a dynamic interaction between HIV and the immune system. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90116-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens P. T., Roos M. T., De Wolf F., Lange J. M., Miedema F. Low T-cell responsiveness to activation via CD3/TCR is a prognostic marker for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) in human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1)-infected men. J Clin Immunol. 1990 Mar;10(2):121–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00918194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Greenhouse J., Justement J. S., Baseler M., Fauci A. S. Preferential infection of CD4+ memory T cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: evidence for a role in the selective T-cell functional defects observed in infected individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6058–6062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulick R. D., Clerici M., Dolan M. J., Shearer G. M. Limiting dilution analysis of interleukin-2-producing T cells responsive to recall and alloantigens in human immunodeficiency virus-infected and uninfected individuals. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Feb;23(2):412–417. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinzer R., Wonigeit K. Genetically determined lack of CD45R- T cells in healthy individuals. Evidence for a regulatory polymorphism of CD45R antigen expression. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1803–1808. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Bernstein D. C., Tung K. S., Via C. S., Redfield R., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C. A model for the selective loss of major histocompatibility complex self-restricted T cell immune responses during the development of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2514–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Ela S. W., Roederer M., Anderson M. T., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Glutathione deficiency and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet. 1992 Apr 11;339(8798):909–912. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90939-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff M. C., Auerbach B. S., Nelson K. E., Vlahov D., Becker R. L., Graham N. M., Schwartz D. H., Lucas A. H., Chaisson R. E. Antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccines in men with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 26;325(26):1837–1842. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112263252603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strijbosch L. W., Does R. J., Buurman W. A. Computer aided design and evaluation of limiting and serial dilution experiments. Int J Biomed Comput. 1988 Dec;23(3-4):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tough D. F., Sprent J. Turnover of naive- and memory-phenotype T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1127–1135. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Via C. S., Tsokos G. C., Stocks N. I., Clerici M., Shearer G. M. Human in vitro allogeneic responses. Demonstration of three pathways of T helper cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2524–2528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong R., Brouwer M., Miedema F., van Lier R. A. Human CD8+ T lymphocytes can be divided into CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ cells with different requirements for activation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2088–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martini R. M., Turner R. R., Formenti S. C., Boone D. C., Bishop P. C., Levine A. M., Parker J. W. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell abnormalities and their relationship to clinical course in homosexual men with HIV infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Feb;46(2):258–271. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wolf F., Lange J. M., Houweling J. T., Coutinho R. A., Schellekens P. T., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Numbers of CD4+ cells and the levels of core antigens of and antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus as predictors of AIDS among seropositive homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):615–622. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lier R. A., Brouwer M., Rebel V. I., van Noesel C. J., Aarden L. A. Immobilized anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies induce accessory cell-independent lymphokine production, proliferation and helper activity in human T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):45–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Noesel C. J., Gruters R. A., Terpstra F. G., Schellekens P. T., van Lier R. A., Miedema F. Functional and phenotypic evidence for a selective loss of memory T cells in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-infected men. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):293–299. doi: 10.1172/JCI114698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



