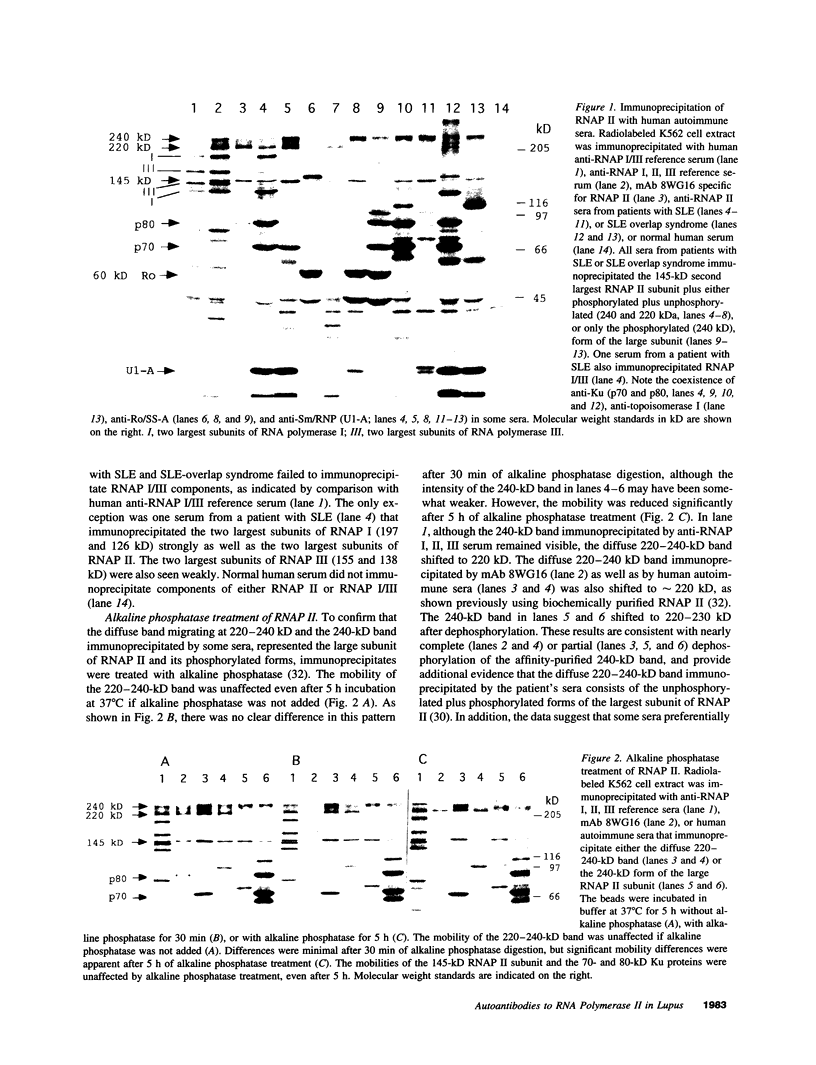
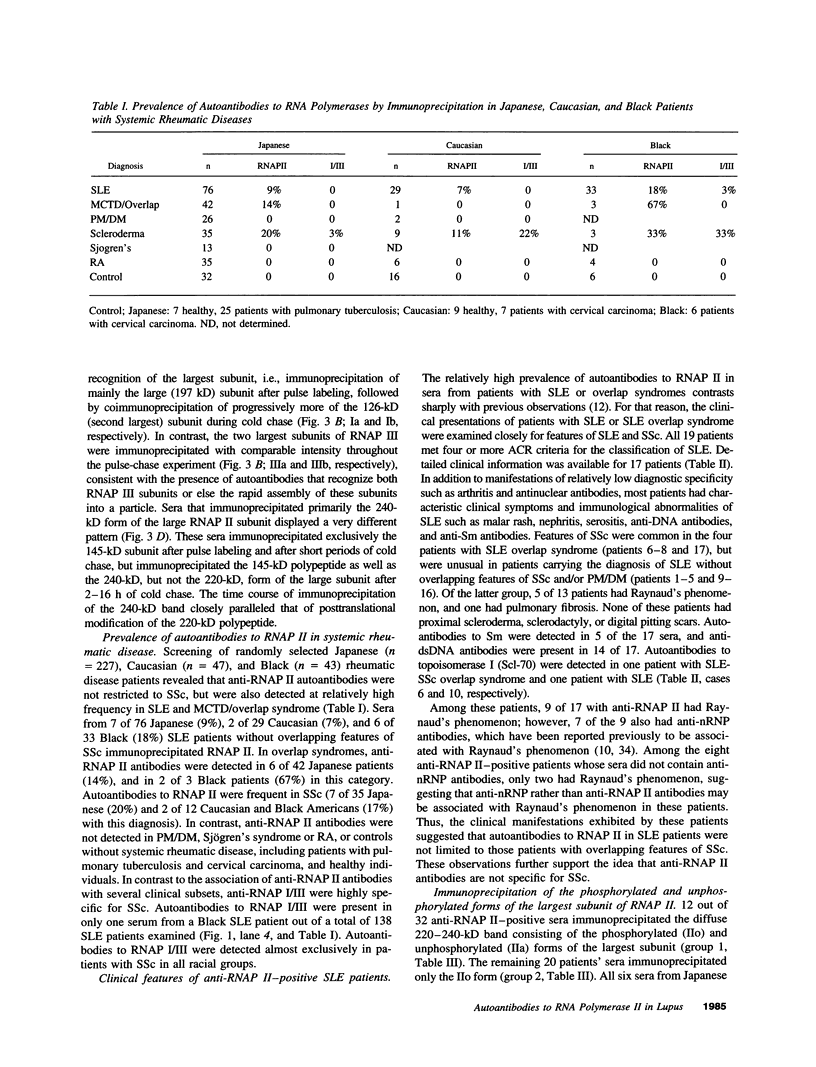
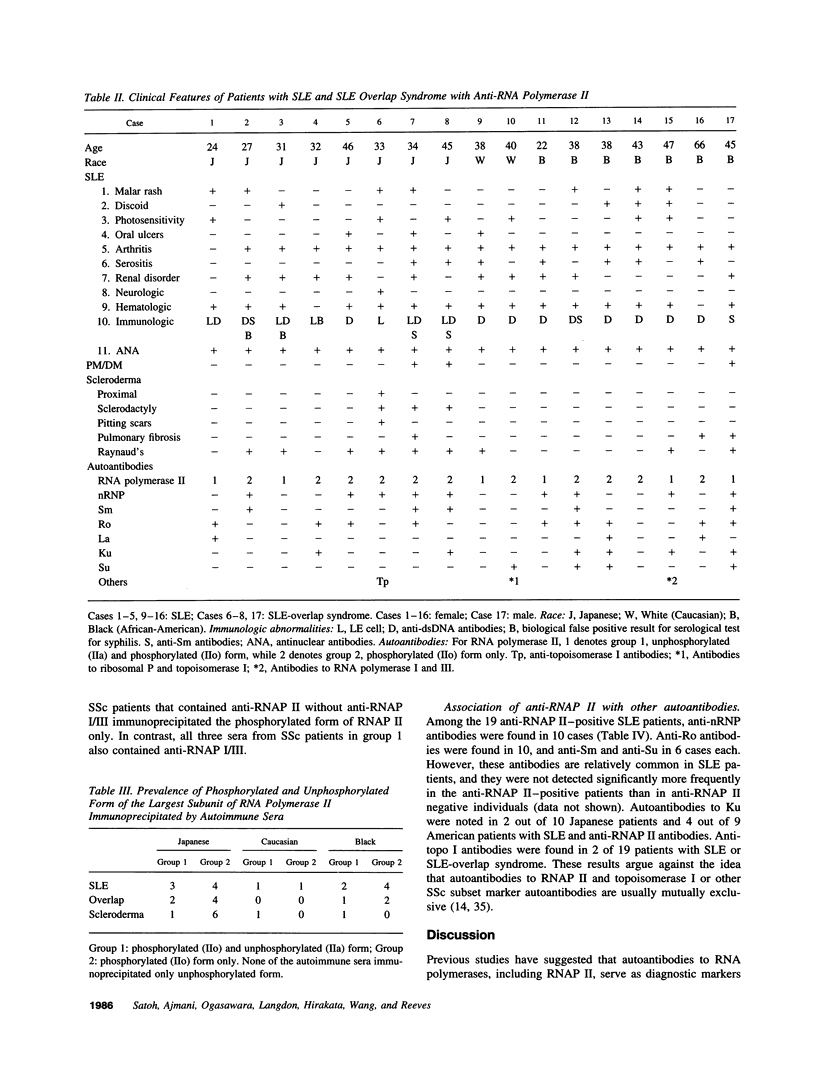
Abstract
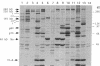
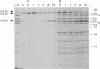
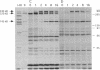
Autoantibodies to RNA polymerases (RNAP) I, II, and III are reported to be highly specific for the diagnosis of scleroderma (systemic sclerosis, SSc). In the present study, the specificity of autoantibodies to RNAP I and III for SSc was confirmed by immunoprecipitation of 35S-labeled proteins. However, we report here the previously unrecognized production of anti-RNAP II autoantibodies by 9-14% of patients with SLE and mixed connective tissue disease/overlap syndrome. 12 out of 32 anti-RNAP II positive sera (group 1) immunoprecipitated a diffuse 220-240-kD band identified as the largest subunit of RNAP II whereas the remaining 20 (group 2) immunoprecipitated preferentially the 240-kD phosphorylated (IIo) form of the large subunit. After pulse labeling, group 1 sera immunoprecipitated only the 220-kD (IIa) RNAP II subunit, whereas the diffuse IIa/IIo band plus the 145-kD second largest RNAP II subunit (IIc) were immunoprecipitated after several hours of cold chase, suggesting that these sera recognized primarily the largest subunit of RNAP II. Group 2 sera recognized the IIc subunit after pulse labeling, and immunoprecipitated the IIc and IIo, but not the IIa, subunits after cold chase. Although it has been suggested that autoantibodies to RNAP II are usually accompanied by anti-RNAP I/III in SSc, all but one of the anti-RNAP II positive sera from SLE or mixed connective tissue disease/overlap syndrome patients, as well as most of the SSc sera, were negative for anti-RNAP I/III. Moreover, in contrast to previous reports suggesting that anti-RNAP antibodies rarely coexist with other SSc subset marker antibodies, anti-RNAP II antibodies were often accompanied by anti-Ku, anti-nRNP, or anti-topoisomerase I autoantibodies in the present study. We conclude that autoantibodies to RNAP II are not a specific marker for SSc, whereas autoantibodies to RNAP I/III are associated primarily with SSc. In addition, we have identified two distinctive patterns of RNAP II antigen recognition by autoantibodies, one of them characterized by specific recognition of the transcriptionally active (phosphorylated) form of RNAP II. The clinical significance of these different patterns remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker J., Wintzerith M., Vigneron M., Kédinger C. Primary structure of the second largest subunit of human RNA polymerase II (or B). J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1295–1299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91071-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alspaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Antibodies to cellular antigens in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1067–1073. doi: 10.1172/JCI108007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boire G., Craft J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of the Ro ribonucleoprotein particles. Analysis with sera specific for the RohY5 particle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):270–279. doi: 10.1172/JCI114150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L. Drug-induced anti-histone autoantibodies display two patterns of reactivity with substructures of chromatin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):680–690. doi: 10.1172/JCI115353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Tan E. M. Human autoantibody-reactive epitopes of SS-B/La are highly conserved in comparison with epitopes recognized by murine monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1627–1640. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G., Reichlin M., Tomasi T. B., Jr Characterization of a soluble cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythmatosus. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvir A., Peterson S. R., Knuth M. W., Lu H., Dynan W. S. Ku autoantigen is the regulatory component of a template-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11920–11924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Rothfield N. Identification of a family of human centromere proteins using autoimmune sera from patients with scleroderma. Chromosoma. 1985;91(3-4):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00328227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A. The lupus autoantigens and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):457–460. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata M., Okano Y., Pati U., Suwa A., Medsger T. A., Jr, Hardin J. A., Craft J. Identification of autoantibodies to RNA polymerase II. Occurrence in systemic sclerosis and association with autoantibodies to RNA polymerases I and III. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2665–2672. doi: 10.1172/JCI116505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Mimori T., Takeda Y., Akama H., Yoshida T., Ogasawara T., Akizuki M. Autoantibodies to the Sm antigen: immunological approach to clinical aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):188–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tojo T., Akizuki M., Yamagata H. Criteria for Sjögren's syndrome in Japan. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1986;61:26–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Dahmus M. E. Purification of RNA polymerase IIO from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18880–18885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar M., Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Identification of human DNA topoisomerase I as a cofactor for activator-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11508–11512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Kaburaki J., Mimori T., Tojo T., Homma M. Autoantibody reactive with three classes of RNA polymerases in sera from patients with systemic sclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1399–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI116343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Kaburaki J., Okano Y., Tojo T., Homma M. Clinical and prognostic associations based on serum antinuclear antibodies in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jan;37(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M. Myositis autoantibody inhibits histidyl-tRNA synthetase: a model for autoimmunity. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):177–179. doi: 10.1038/304177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Reichlin M., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R. M. Anti-threonyl-tRNA synthetase, a second myositis-related autoantibody. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):420–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):421–429. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Madden K. R., Lane W. S., Champoux J. J., Reinberg D. DNA topoisomerase I is involved in both repression and activation of transcription. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):227–232. doi: 10.1038/365227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Steen V. D., Medsger T. A., Jr Autoantibody reactive with RNA polymerase III in systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Nov 15;119(10):1005–1013. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-10-199311150-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. The transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation is associated with phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19621–19629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):581–590. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Fisher D. E., Wisniewolski R., Gottlieb A. B., Chiorazzi N. Psoriasis and Raynaud's phenomenon associated with autoantibodies to U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 10;315(2):105–111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607103150207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Satoh M., Wang J., Chou C. H., Ajmani A. K. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Antibodies to DNA, DNA-binding proteins, and histones. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994 Feb;20(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the characterization of novel DNA-binding proteins recognized by human autoimmune sera. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):18–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Rose K. M., Scheer U., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to RNA polymerase I in scleroderma sera. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):65–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI112809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Bordwell B., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. High titers of autoantibodies to topoisomerase I (Scl-70) in sera from scleroderma patients. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.3003910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Purification of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II by immunoaffinity chromatography. Elution of active enzyme with protein stabilizing agents from a polyol-responsive monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7069–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Maldonado E., Goldring A., Lu H., Houbavi C., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Specific interaction between the nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II and the TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):871–881. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90297-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintzerith M., Acker J., Vicaire S., Vigneron M., Kedinger C. Complete sequence of the human RNA polymerase II largest subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):910–910. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka H., Willis E. H., Carson D. A. Human autoantibodies to poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase recognize cross-reactive epitopes associated with the catalytic site of the enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):180–186. doi: 10.1172/JCI113856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation causes a conformational change in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the mouse RNA polymerase II largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2297–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]