Abstract
Anti-tubular basement membrane disease (alpha TBM disease) produces T cell-mediated interstitial nephritis in SJL mice after immunization with renal tubular antigen. Initial mononuclear infiltrates appear in vivo after several weeks, with the subsequent progression to renal fibrosis and end stage renal disease over many months. We have analyzed the fine specificity of the autoreactive helper T cell repertoire in alpha TBM disease through the isolation and characterization of a panel of CD4+ Th1 clones harvested after 1-2 wk from animals immunized to produce disease. All clones capable of mediating alpha TBM disease are directed towards a 14-residue immunodominant epitope (STMSAEVPEAASEA) contained within the target antigen, 3M-1. Evaluation of the T cell receptor (TCR) V beta repertoire used by these autoreactive T cells reveals the use of several V beta genes, but with some preference for V beta 14. Sequencing across the putative CDR3 region of the TCR beta chains suggests that common amino acids at the V beta(N)D beta junction and the D beta(N)J beta junction may contribute to the specific ability of these cells to recognize the immunodominant epitope.
Full text
PDF


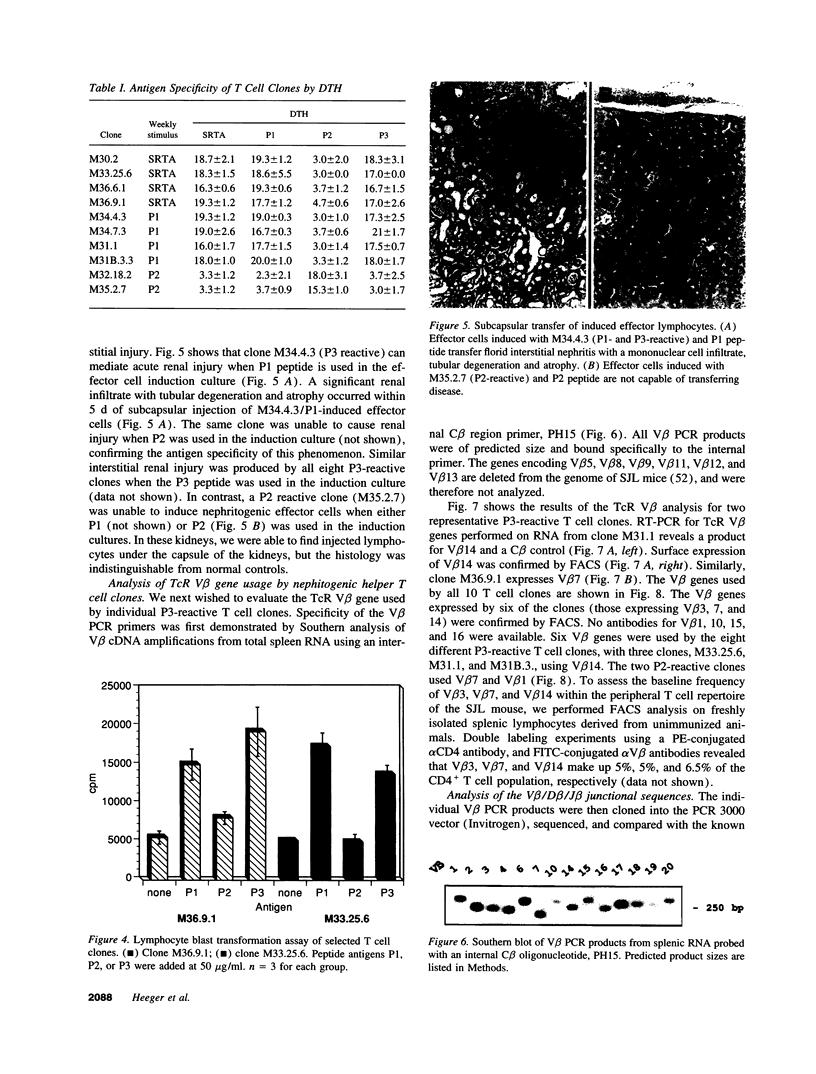
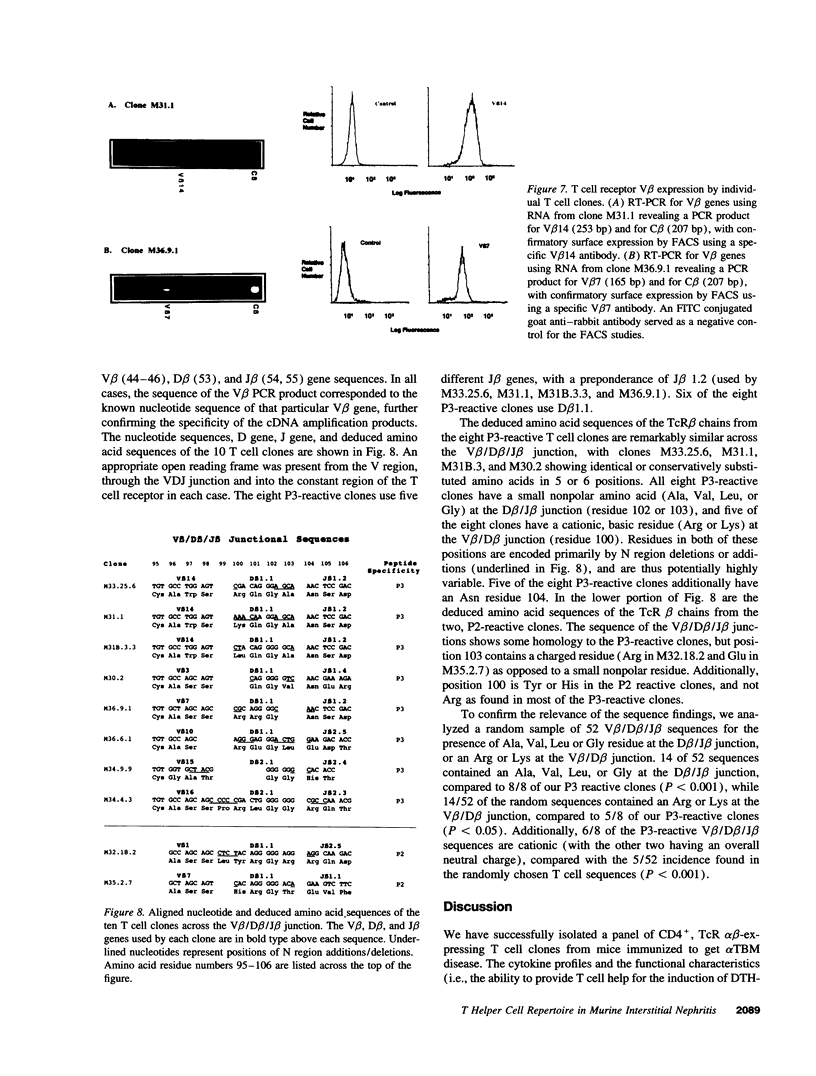



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. T cell receptors in murine autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:371–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S., Leblanc P., Datta S. K. Junctional region sequences of T-cell receptor beta-chain genes expressed by pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody-inducing helper T cells from lupus mice: possible selection by cationic autoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11271–11275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke M. A., Chou H. S., Huppi K., Loh D. Y. Murine T-cell receptor mutants with deletions of beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):767–771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke M. A., Loh D. Y. Alternative splicing of murine T-cell receptor beta-chain transcripts. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):379–382. doi: 10.1038/322379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke M. A., Spinella D. G., Chou H. S., Sha W., Hartl D. L., Loh D. Y. T-cell receptor beta-chain expression: dependence on relatively few variable region genes. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):566–570. doi: 10.1126/science.3875151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A., Michaud L., Alper R., Mann R., Kefalides N. A., Neilson E. G. Isolation and characterization of the nephritogenic antigen producing anti-tubular basement membrane disease. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):290–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton J. P., Gammon G. M., Ando D. G., Kono D. H., Hood L., Sercarz E. E. Peptide-specific prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neonatal tolerance induced to the dominant T cell determinant of myelin basic protein. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1681–1691. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danska J. S., Livingstone A. M., Paragas V., Ishihara T., Fathman C. G. The presumptive CDR3 regions of both T cell receptor alpha and beta chains determine T cell specificity for myoglobin peptides. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):27–33. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. F., Martin A., Concepcion E. S., Graves P., Cohen L., Ben-Nun A. Evidence of limited variability of antigen receptors on intrathyroidal T cells in autoimmune thyroid disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):238–244. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascoigne N. R., Chien Y., Becker D. M., Kavaler J., Davis M. M. Genomic organization and sequence of T-cell receptor beta-chain constant- and joining-region genes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):387–391. doi: 10.1038/310387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Bangs J., Maddock S., Springer T., Eardley D. D., Strom T. B. Characterization of a monoclonal rat anti-mouse interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor antibody and its use in the biochemical characterization of the murine IL-2 receptor. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jul;36(1):18–29. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam A. M., Pearson C. I., Smilek D. E., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. A polyalanine peptide with only five native myelin basic protein residues induces autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):605–609. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. P., Offner H., Sun D., Wiley S., Vandenbark A. A., Wilson D. B. Analysis of T cell receptor beta chains in Lewis rats with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: conserved complementarity determining region 3. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1467–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. P., Vainiene M., Celnik B., Wiley S., Gibbs C., Hashim G. A., Vandenbark A. A., Offner H. Characterization of the immune response to a secondary encephalitogenic epitope of basic protein in Lewis rats. II. Biased T cell receptor V beta expression predominates in spinal cord infiltrating T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1712–1717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goverman J., Minard K., Shastri N., Hunkapiller T., Hansburg D., Sercarz E., Hood L. Rearranged beta T cell receptor genes in a helper T cell clone specific for lysozyme: no correlation between V beta and MHC restriction. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haqqi T. M., Anderson G. D., Banerjee S., David C. S. Restricted heterogeneity in T-cell antigen receptor V beta gene usage in the lymph nodes and arthritic joints of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1253–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Amenta P. S., Watanabe M., Harper R. A., Kefalides N. A., Neilson E. G. Characterization of a renal tubular epithelial cell line which secretes the autologous target antigen of autoimmune experimental interstitial nephritis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1359–1368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Watanabe M., Neilson E. G., Kelly C. J. Protective modulation of class II MHC gene expression in tubular epithelium by target antigen-specific antibodies. Cell-surface directed down-regulation of transcription can influence susceptibility to murine tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1133–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeger P., Wolf G., Meyers C., Sun M. J., O'Farrell S. C., Krensky A. M., Neilson E. G. Isolation and characterization of cDNA from renal tubular epithelium encoding murine Rantes. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):220–225. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines W. H., Mann R. A., Kelly C. J., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IX. Induction of the nephritogenic effector T cell repertoire with an antigen-specific T cell cytokine. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. J., Levcovitz H., Gordon V., Wall K. A., Thompson P. A., Krolick K. A. Preferential use of a T cell receptor V beta gene by acetylcholine receptor reactive T cells from myasthenia gravis-susceptible mice. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3385–3390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jores R., Alzari P. M., Meo T. Resolution of hypervariable regions in T-cell receptor beta chains by a modified Wu-Kabat index of amino acid diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. L., Esser U., Fazekas de St Groth B., Reay P. A., Davis M. M. Mapping T-cell receptor-peptide contacts by variant peptide immunization of single-chain transgenics. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):224–230. doi: 10.1038/355224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. L., Reay P. A., Ehrich E. W., Davis M. M. Molecular components of T-cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:835–873. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp S. L., Kieber-Emmons T., Sun M. J., Wolf G., Neilson E. G. Molecular structure of a cross-reactive idiotype on autoantibodies recognizing parenchymal self. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):867–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo R. T., Born W., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pigeon M. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody which detects all murine alpha beta T cell receptors. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2736–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuncio G. S., Neilson E. G., Haverty T. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int. 1991 Mar;39(3):550–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao N. S., Maltzman J., Raulet D. H. Positive selection determines T cell receptor V beta 14 gene usage by CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):135–143. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Clayman M. D., Blanchard N., Sun M. J., Neilson E. G. Effector T cell differentiation in experimental interstitial nephritis. I. The development and modulation of effector lymphocyte maturation by I-J+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4200–4208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Zakheim B., Clayman M., McCafferty E., Michaud L., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IV. Long-term cultured L3T4+ T cell lines transfer delayed expression of disease as I-A-restricted inducers of the effector T cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers C. M., Kelly C. J. Effector mechanisms in organ-specific autoimmunity. I. Characterization of a CD8+ T cell line that mediates murine interstitial nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):408–416. doi: 10.1172/JCI115319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Clayman M. D., Haverty T., Kelly C. J., Mann R. Experimental strategies for the study of cellular immunity in renal disease. Kidney Int. 1986 Aug;30(2):264–279. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., McCafferty E., Phillips S. M., Clayman M. D., Kelly C. J. Antiidiotypic immunity in interstitial nephritis. II. Rats developing anti-tubular basement membrane disease fail to make an antiidiotypic regulatory response: the modulatory role of an RT7.1+, OX8- suppressor T cell mechanism. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1009–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G. Pathogenesis and therapy of interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 May;35(5):1257–1270. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Cell-mediated immunity in interstitial nephritis. I. T lymphocyte systems in nephritic guinea pigs: the natural history and diversity of the immune response. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Murine interstitial nephritis. I. Analysis of disease susceptibility and its relationship of pleiomorphic gene products defining both immune-response genes and a restrictive requirement for cytotoxic T cells at H-2K. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Sun M. J., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Haverty T. P., Clayman M. D., Cooke N. E. Molecular characterization of a major nephritogenic domain in the autoantigen of anti-tubular basement membrane disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2006–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Tonegawa S., Saito H., Kranz D. M., Eisen H. N. Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of T-cell-specific immunoglobulin-like polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offner H., Vainiene M., Gold D. P., Celnik B., Wang R., Hashim G. A., Vandenbark A. A. Characterization of the immune response to a secondary encephalitogenic epitope of basic protein in Lewis rats. I. T cell receptor peptide regulation of T cell clones expressing cross-reactive V beta genes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1706–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada C. Y., Holzmann B., Guidos C., Palmer E., Weissman I. L. Characterization of a rat monoclonal antibody specific for a determinant encoded by the V beta 7 gene segment. Depletion of V beta 7+ T cells in mice with Mls-1a haplotype. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3473–3477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., West S. G., Lafferty J. A., Clements J. R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Kotzin B. L. Evidence for the effects of a superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):325–329. doi: 10.1126/science.1857971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The T-cell repertoire is heavily influenced by tolerance to polymorphic self-antigens. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):796–801. doi: 10.1038/335796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. M., Golub E. E. A computer graphics program system for protein structure representation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1801–1812. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., al-Ramadi B. K., Rothbard J., Janeway C. A., Jr Truncation variants of peptides isolated from MHC class II molecules suggest sequence motifs. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):429–431. doi: 10.1038/359429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sercarz E. E., Lehmann P. V., Ametani A., Benichou G., Miller A., Moudgil K. Dominance and crypticity of T cell antigenic determinants. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:729–766. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Lopez M. T., McDevitt H. O. Autoimmune diseases: the failure of self tolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1380–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.1972595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six A., Jouvin-Marche E., Loh D. Y., Cazenave P. A., Marche P. N. Identification of a T cell receptor beta chain variable region, V beta 20, that is differentially expressed in various strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1263–1266. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilek D. E., Wraith D. C., Hodgkinson S., Dwivedy S., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. A single amino acid change in a myelin basic protein peptide confers the capacity to prevent rather than induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9633–9637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumida T., Yonaha F., Maeda T., Tanabe E., Koike T., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. T cell receptor repertoire of infiltrating T cells in lips of Sjögren's syndrome patients. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):681–685. doi: 10.1172/JCI115635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Cease K. B., Berzofsky J. A. Identification of proteases that process distinct epitopes on the same protein. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2221–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Kumar V., Kono D. H., Gomez C., Horvath S. J., Clayton J., Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hood L. Restricted use of T cell receptor V genes in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis raises possibilities for antibody therapy. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):577–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Pullen A., Choi K., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Antigen recognition properties of mutant V beta 3+ T cell receptors are consistent with an immunoglobulin-like structure for the receptor. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):119–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Acha-Orbea H. T cell recognition as the target for immune intervention in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90786-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim B., McCafferty E., Phillips S. M., Clayman M., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. II. The adoptive transfer of disease with immune T lymphocytes produces a phenotypically complex interstitial lesion. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ewijk W., van Soest P. L., van den Engh G. J. Fluorescence analysis and anatomic distribution of mouse T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies to the antigens Thy-1, Lyt-1, Lyt-2, and T-200. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2594–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]