Abstract
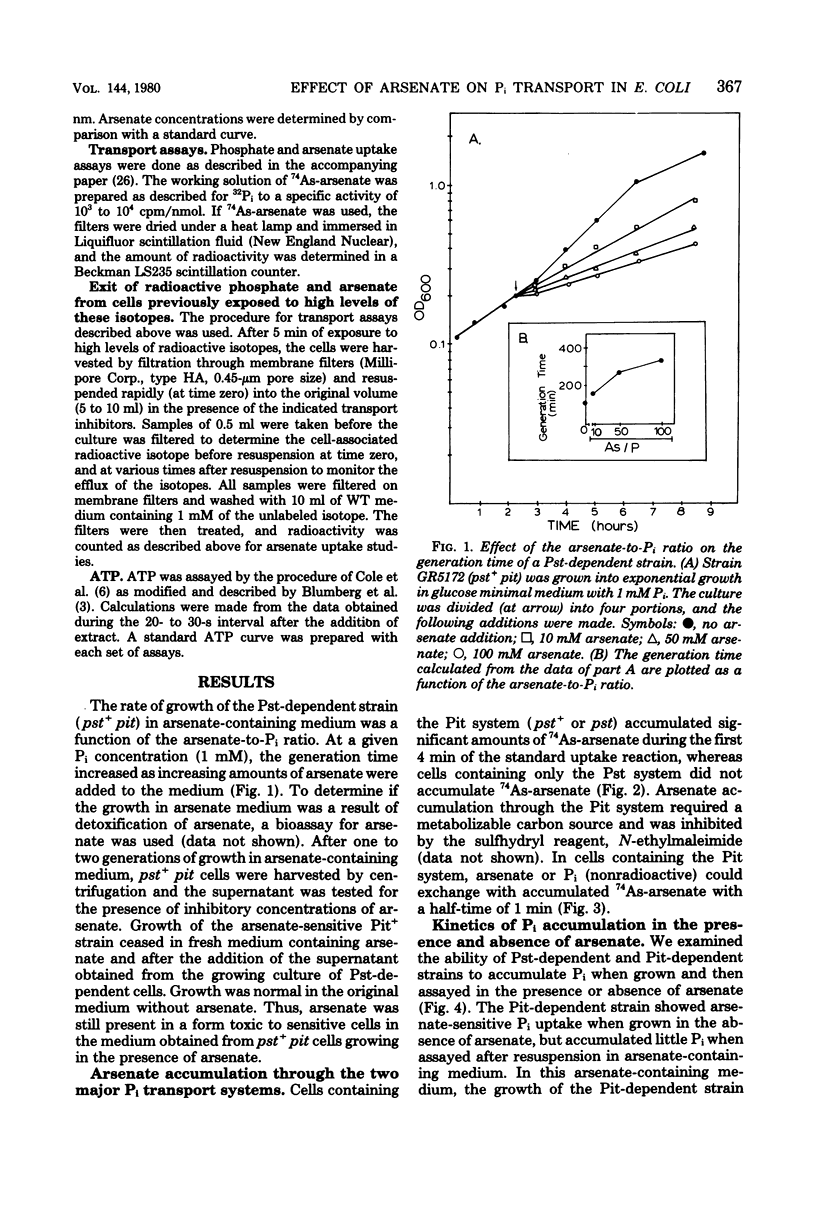
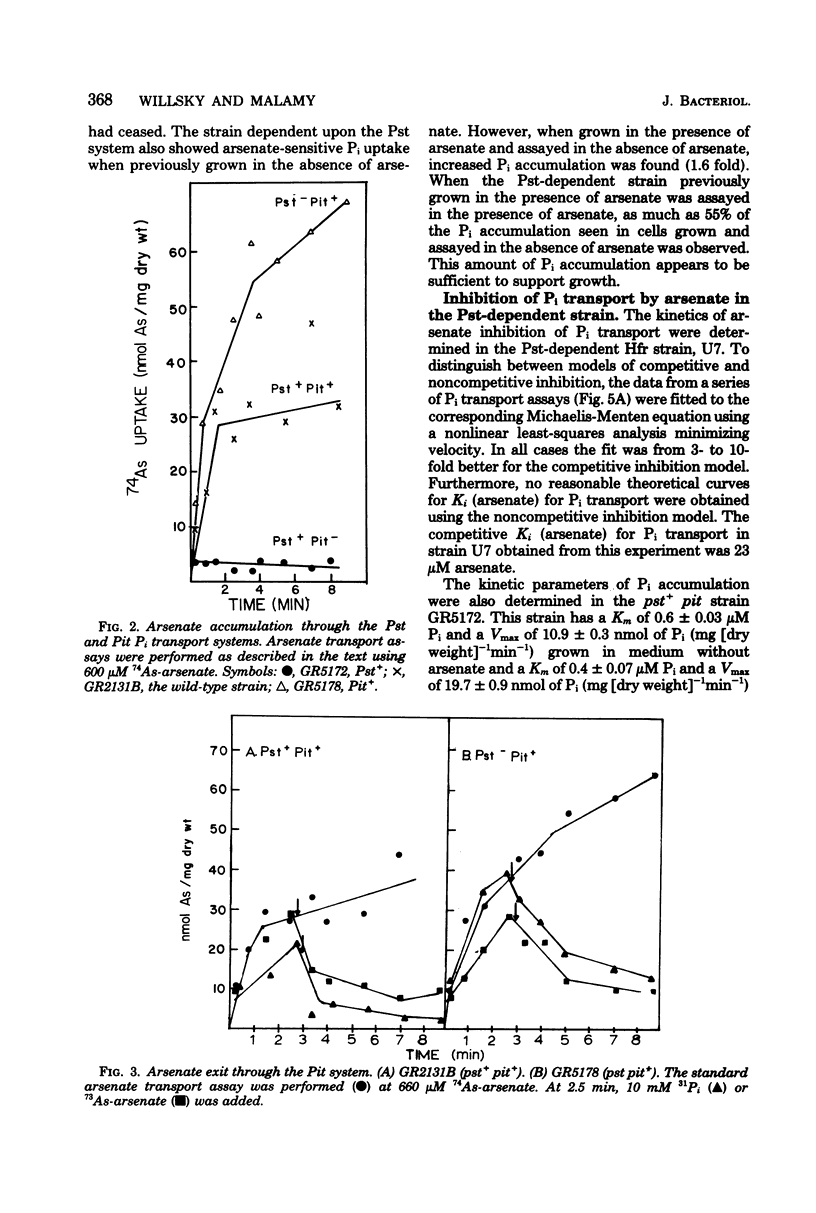
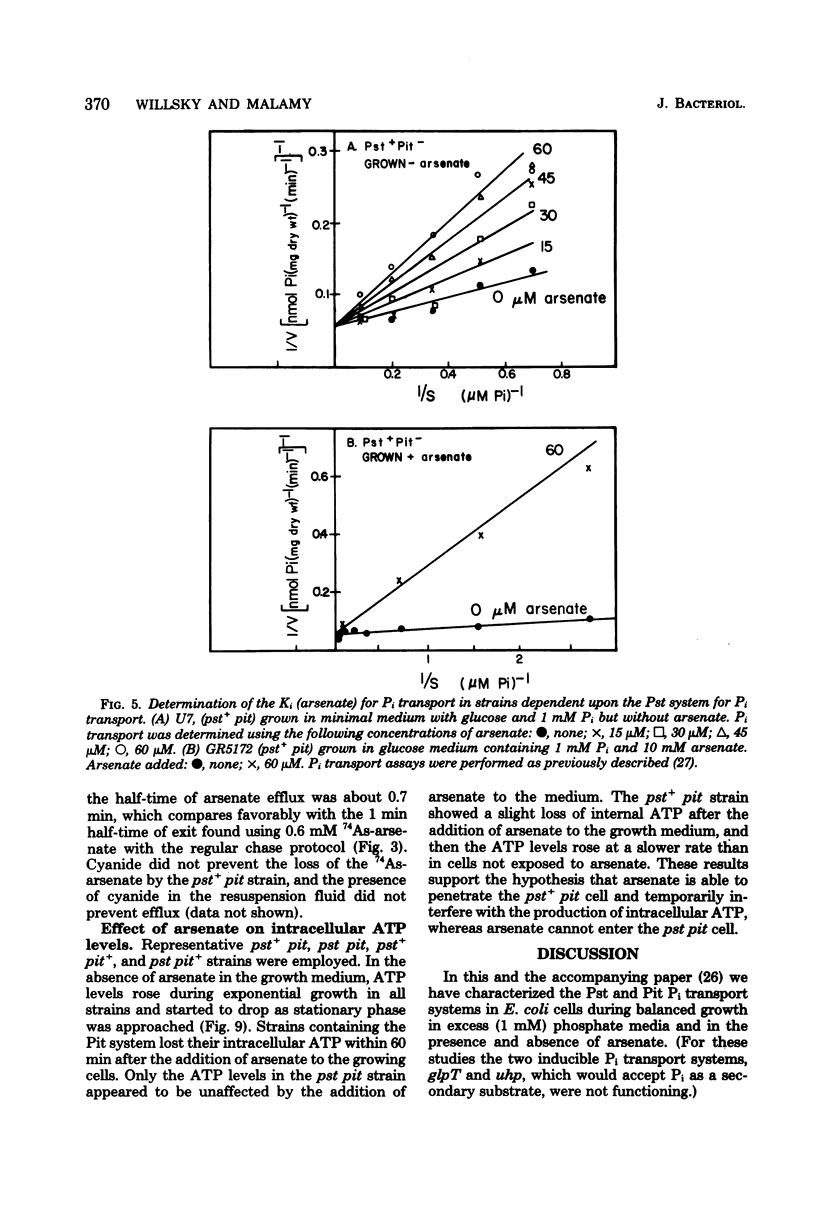
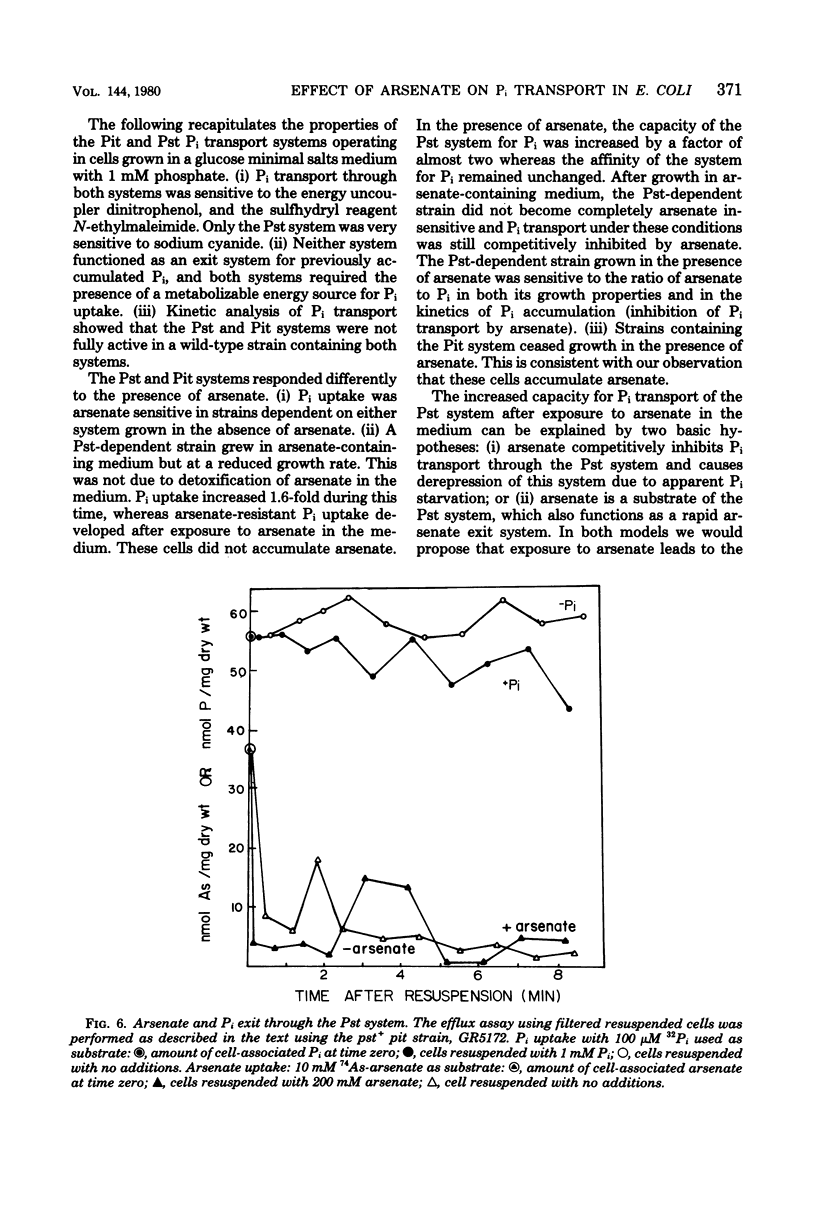
The effect of arsenate on strains dependent on the two major inorganic phosphate (Pi) transport systems in Escherichia coli was examined in cells grown in 1 mM phosphate medium. The development of arsenate-resistant Pi uptake in a strain dependent upon the Pst (phosphate specific transport) system was examined. The growth rate of Pst-dependent cells in arsenate-containing medium was a function of the arsenate-to-Pi ratio. Growth in arsenate-containing medium was not due to detoxification of the arsenate. Kinetic studies revealed that cells grown with a 10-fold excess of arsenate to Pi have almost a twofold increase in capacity (Vmax) for Pi, but maintained the same affinity (Km). Pi accumulation in the Pst-dependent strain was still sensitive to changes in the arsenate-to-Pi ratio, and a Ki (arsenate) for Pi transport of 39 microM arsenate was determined. The Pst-dependent strain did not accumulate radioactive arsenate, and showed only a transient decrease in intracellular adenosine triphosphate levels after arsenate was added to the medium. The Pi transport-dependent strain ceased growth in arsenate-containing media. This strain accumulated 74As-arsenate, and intracellular adenosine triphosphate pools were almost completely depleted after the addition of arsenate to the medium. Arsenate accumulation required a metabolizable energy source and was inhibited by N-ethylmaleimide. Previously accumulated arsenate could exchange with arsenate or Pi in the medium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett R. L., Malamy M. H. Arsenate resistant mutants of Escherichia coli and phosphate transport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D., Mabie C. T., Malamy M. H. T7 protein synthesis in F-factor-containing cells: evidence for an episomally induced impairment of translation and relation to an alteration in membrane permeability. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.94-105.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha M., Yagil E. A ne type of alkaline phosphatase-negative mutants in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 27;122(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00337973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Beckwith J. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E. The ATP pool in Escherichia coli. I. Measurement of the pool using modified luciferase assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECHOLS H., GAREN A., GAREN S., TORRIANI A. Genetic control of repression of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:425–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., OTSUJI N. ISOLATION OF A PROTEIN SPECIFIED BY A REGULATOR GENE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:841–852. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes R. G., Rosenberg H. The relationship between the phosphate-binding protein and a regulator gene product from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 10;351(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes R. G., Strickland K. P., Rosenberg H. Restoration of phosphate transport by the phosphate-binding protein in spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.512-518.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Transport of phosphate across the osmotic barrier of Micrococcus pyogenes; specificity and kinetics. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):73–82. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medveczky N., Rosenberg H. Phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):494–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H., Schlesinger M. J., Bracha M., Yagil E. Pleiotropic effects of mutations involved in the regulation of Escherichia coli K-12 alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):583–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.583-592.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae A. S., Strickland K. P., Medveczky N., Rosenberg H. Studies of phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. I. Reexamination of the effect of osmotic and cold shock on phosphate uptake and some attempts to restore uptake with phosphate binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae A. S., Strickland K. P. Studies on phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. II. Effects of metabolic inhibitors and divalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):564–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae A. S., Strickland K. P. Uncoupler and anaerobic resistant transport of phosphate in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Cox G. B., Butlin J. D., Gutowski S. J. Metabolite transport in mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in electron transport and coupled phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):417–423. doi: 10.1042/bj1460417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Gerdes R. G., Chegwidden K. Two systems for the uptake of phosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.505-511.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Gerdes R. G., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to the transport of inorganic phosphate in Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):133–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1780133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. M., Rosenberg H. Linked transport of phosphate, potassium ions and protons in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):13–21. doi: 10.1042/bj1840013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Bell R. M., Cronan J. E., Jr A mutant of Escherichia coli auxotrophic for organic phosphates: evidence for two defects in inorganic phosphate transport. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;143(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00269422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins A. S. Physiological factors in the regulation of alkaline phosphatase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):616–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.616-623.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Bennett R. L., Malamy M. H. Inorganic phosphate transport in Escherichia coli: involvement of two genes which play a role in alkaline phosphatase regulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):529–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.529-539.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. Characterization of two genetically separable inorganic phosphate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):356–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.356-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. Control of the synthesis of alkaline phosphatase and the phosphate-binding protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):595–609. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.595-609.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. The loss of the phoS periplasmic protein leads to a change in the specificity of a constitutive inorganic phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):226–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



