Abstract
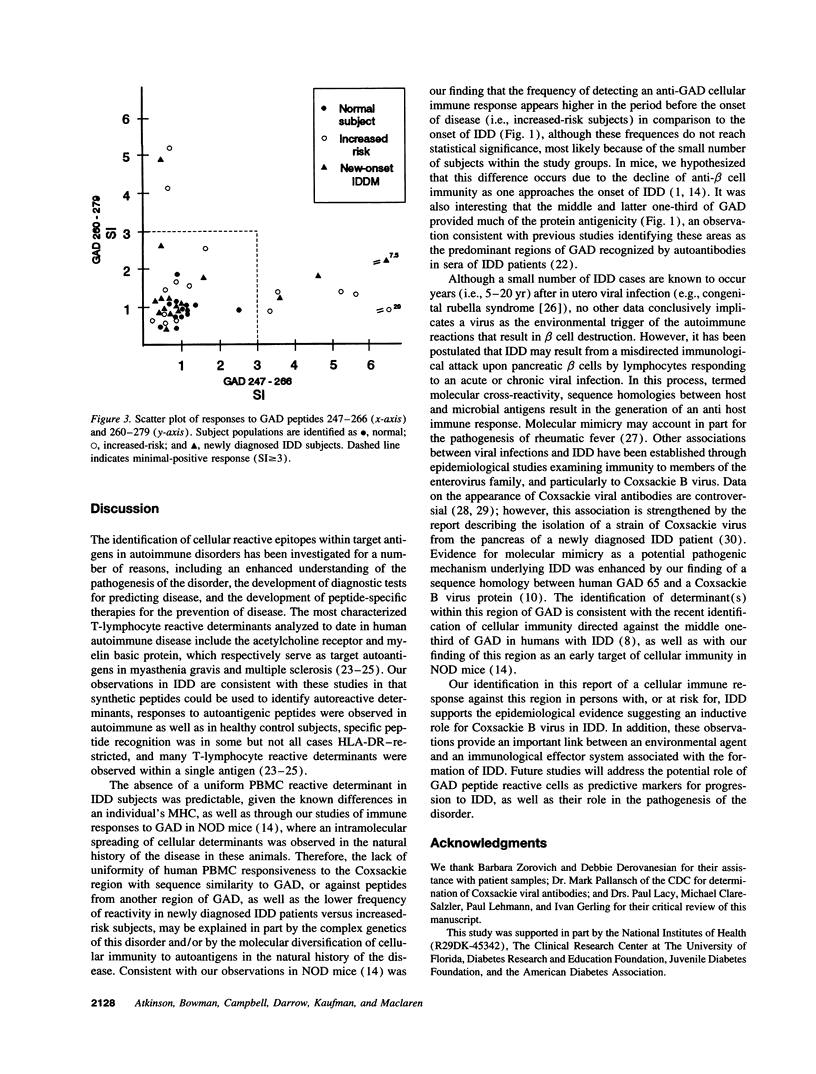
Insulin-dependent diabetes (IDD) results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells. Autoreactive T-lymphocytes are thought to play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of IDD; however, the target antigens of these cells, as well as the inductive events in the disease, are unclear. PBMC in persons with or at increased risk for IDD show elevated reactivity to the beta cell enzyme glutamate decarboxylase (GAD). To identify the T-lymphocyte-reactive determinants of GAD, an overlapping set of synthetic peptides was used to stimulate the PBMC from these individuals, PBMC responsiveness to GAD peptides was not restricted to those with IDD, and a number of peptides elicited responses in PBMC. However, the major determinant of GAD recognized by persons at increased risk for IDD was amino acids 247-279, a region which has significant sequence similarity to the P2-C protein of Coxsackie B virus (47% of 15 increased risk [islet cell autoantibody-positive relatives]; 25% of 16 newly diagnosed IDD patients; and 0% of 13 healthy control subjects). Responses to tetanus and insulin antigens were not different between the study groups. In addition, PBMC from individuals responding to GAD peptides within 247-279 also responded to a Coxsackie viral peptide (i.e., P2-C amino acids 32-47), an observation supporting potential molecular mimicry in this immune response. Although the role of environmental agents in the pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, these cellular immunological findings support the epidemiological evidence suggesting an inductive role for enteroviruses like Coxsackie B in the autoimmunity underlying IDD.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Kaufman D. L., Campbell L., Gibbs K. A., Shah S. C., Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J., Maclaren N. K. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):458–459. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K. What causes diabetes? Sci Am. 1990 Jul;263(1):62-3, 66-71. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0790-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E. Is insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus caused by coxsackievirus B infection? A review of the epidemiologic evidence. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):207–215. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. The resurgence of acute rheumatic fever in the United States. Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:319–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Lernmark A., Dawkins R. L. Serum exchange and use of dilutions have improved precision of measurement of islet cell antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruining G. J., Molenaar J. L., Grobbee D. E., Hofman A., Scheffer G. J., Bruining H. A., de Bruyn A. M., Valkenburg H. A. Ten-year follow-up study of islet-cell antibodies and childhood diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1989 May 20;1(8647):1100–1103. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño L., Eisenbarth G. S. Type-I diabetes: a chronic autoimmune disease of human, mouse, and rat. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:647–679. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Chu S. X., DeAizpurua H. J., Graham M., Honeyman M. C., Colman P. G. Islet-reactive T cells are a marker of preclinical insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1161–1165. doi: 10.1172/JCI115698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Honeyman M. C., DeAizpurua H. J., Schmidli R. S., Colman P. G., Tait B. D., Cram D. S. Inverse relation between humoral and cellular immunity to glutamic acid decarboxylase in subjects at risk of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1365–1369. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90940-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman M. C., Cram D. S., Harrison L. C. Glutamic acid decarboxylase 67-reactive T cells: a marker of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):535–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jingwu Z., Medaer R., Hashim G. A., Chin Y., van den Berg-Loonen E., Raus J. C. Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis and controls: precursor frequency, fine specificity, and cytotoxicity. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):330–338. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Grubin C. E., Dube S., Disteche C. M., Adler D. A., Bärmeier H., Mathewes S., Grant F. J., Foster D. Cloning and primary structure of a human islet isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase from chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8337–8341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Erlander M. G., Clare-Salzler M., Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Tobin A. J. Autoimmunity to two forms of glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):283–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI115573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Richter W., Aanstoot H. J., Shi Y., Fu Q., Rajotte R., Warnock G., Baekkeskov S. Differential expression of GAD65 and GAD67 in human, rat, and mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1993 Dec;42(12):1799–1808. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.12.1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi A. A., Protti M. P., Dalton M. W., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. T helper cell recognition of muscle acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. Epitopes on the gamma and delta subunits. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):1055–1067. doi: 10.1172/JCI116610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melms A., Chrestel S., Schalke B. C., Wekerle H., Mauron A., Ballivet M., Barkas T. Autoimmune T lymphocytes in myasthenia gravis. Determination of target epitopes using T lines and recombinant products of the mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):785–790. doi: 10.1172/JCI113958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menser M. A., Forrest J. M., Bransby R. D. Rubella infection and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 14;1(8055):57–60. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis D., Rjasanowski I., Hildmann W., Kohnert K. D., Richter K. V. Validity of WHO criteria for classification of newly diagnosed diabetics. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;85(1):61–69. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1210420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen B. K., Petersen J. S., Boel E., Møldrup A., Dyrberg T., Madsen O. D. Cloning, characterization, and autoimmune recognition of rat islet glutamic acid decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W., Endl J., Eiermann T. H., Brandt M., Kientsch-Engel R., Thivolet C., Jungfer H., Scherbaum W. A. Human monoclonal islet cell antibodies from a patient with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus reveal glutamate decarboxylase as the target antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Krischer J., Spillar R. P., Silverstein J. H., Schatz D. A., Schwartz S., Malone J., Shah S., Vadheim C. A prospective study of the development of diabetes in relatives of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 25;323(17):1167–1172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010253231704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O., Arden S. D., de Vries R. R., Hutton J. C. T-cell clones from a type-1 diabetes patient respond to insulin secretory granule proteins. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):632–634. doi: 10.1038/345632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O., Kallan A. A., Hazenbos W. L., Bruining G. J., Bailyes E. M., Arden S. D., Hutton J. C., de Vries R. R. T-cell reactivity to 38 kD insulin-secretory-granule protein in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 1991 Jun 15;337(8755):1439–1441. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93127-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szopa T. M., Titchener P. A., Portwood N. D., Taylor K. W. Diabetes mellitus due to viruses--some recent developments. Diabetologia. 1993 Aug;36(8):687–695. doi: 10.1007/BF00401138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Austin M., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 24;300(21):1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905243002102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



