Abstract
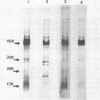
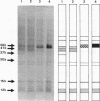
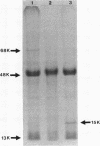
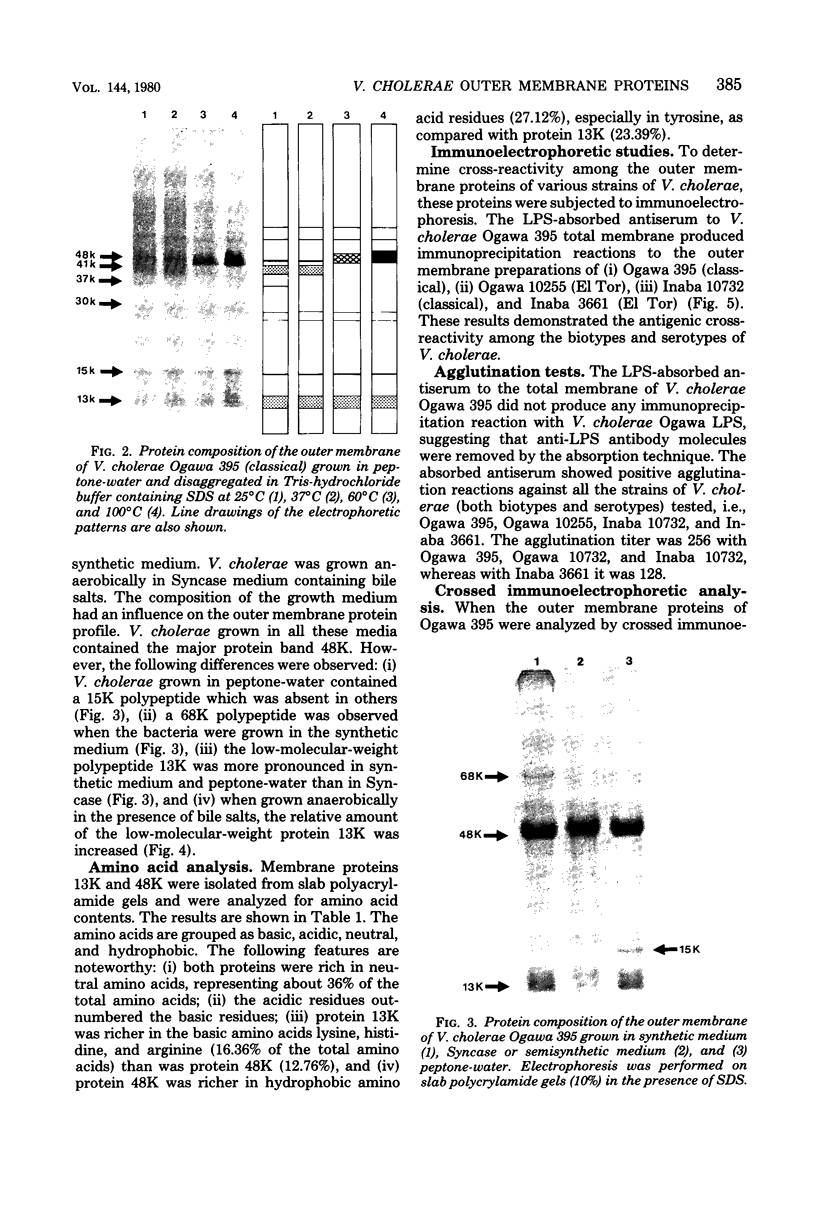
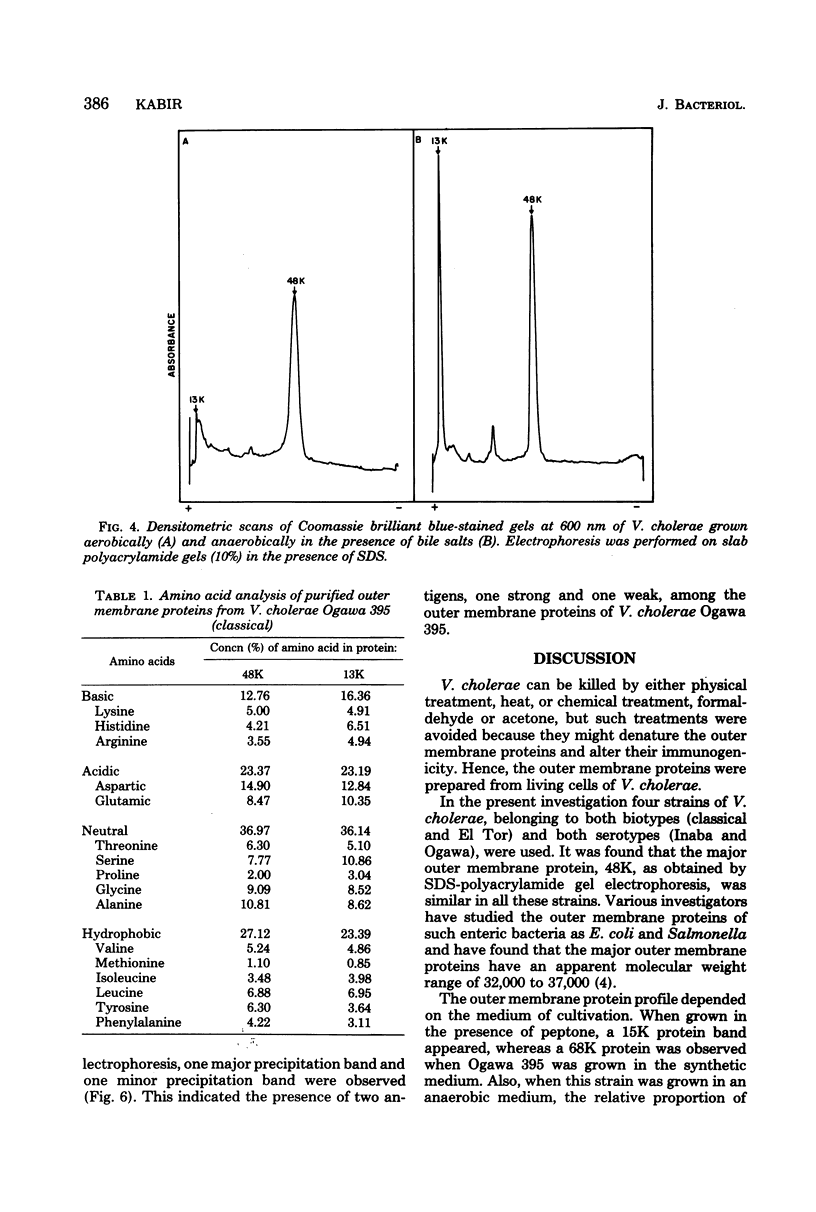
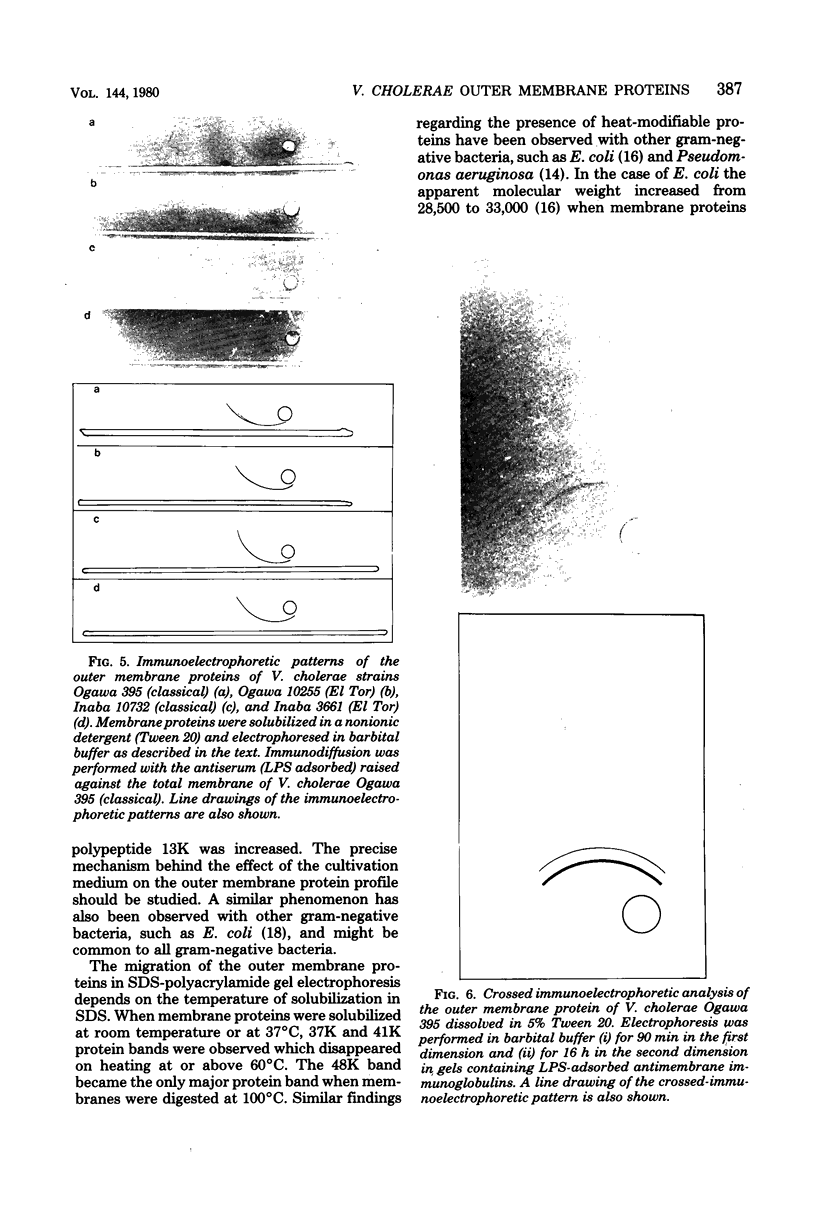
The protein compositions of the outer membranes of various Vibrio cholerae strains, belonging to both biotypes (El Tor and classical) and both serotypes (Ogawa and Inaba), were analyzed by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide slab gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. All these strains contained a major protein band of molecular weight 48,000. But they differed in the composition and proportions of minor proteins. The outer membrane protein profile was influenced by the growth medium. A protein band of molecular weight 15,000 was observed in the outer membrane when V. cholerae Ogawa 395 (classical) was grown in peptone-water, whereas a protein of molecular weight 68,000 appeared when it was grown in the synthetic medium. Under anaerobic growth conditions the proportion of the 13,000-molecular-weight protein was greatly enhanced. The outer membrane contained heat-modifiable proteins, as the protein bands with molecular weights 41,000 and 37,000 disappeared when membrane proteins were disaggregated in sodium dodecyl sulfate at or above 60 degrees C. The antisera to the outer membrane proteins of V. cholerae Ogawa 395 (classical) produced immunoprecipitation to the outer membrane proteins of both biotypes and both serotypes. Also, the antisera agglutinated bacteria of both biotypes and both serotypes, suggesting the presence of a common protein antigen in the outer membrane of V. cholerae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber C., Eylan E. Cross-protection induced in mice by immunizations with proteins of related bacteria species. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Jan;234(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Hindennach I., Henning U. The major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Characterization of proteins II* and III, comparison of all proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer R., Galanos C., Westphal O., Golecki J. R. A lipopolysaccharide-binding cell-surface protein from Salmonella minnesota. Isolation, partial characterization and occurrence in different Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):27–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Antigenic cross-reactivity of major outer membrane proteins in enterobacteriaceae species. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Apr;111(2):293–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. R., Richardson S. H. Fine structure of Vibrio cholerae during toxin production. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1393–1401. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1393-1401.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Peters R., Bernheimer H., Berendsen W. Influence of cultural conditions and mutations on the composition of the outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00582876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kageyama M. Separation and characterization of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biochem. 1978 Jul;84(1):179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reithmeier R. A., Bragg P. D. Molecular characterization of a heat-modifiable protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. IV. Differences in outer membrane proteins due to strain and cultural differences. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):454–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.454-464.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]