Abstract
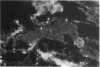
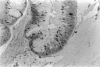
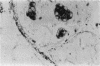
Human villous adenomas are thought to represent premalignancies that subsequently give rise to colorectal adenocarcinomas. Currently there is no in vivo model in which to study the dedifferentiation and malignant transformation of these tumors. We establish here that human villous adenomas can be successfully engrafted into severe combined immunodeficient (scid) mice. Furthermore, these xenografts remain viable for up to 18 mo after either a subcutaneous or intraperitoneal inoculation of the human tissue. Tumors grew slowly and secreted a clear mucinous fluid. Examination of the tumors histologically at 1, 4, and 12 mo after implantation revealed that the villous polypoid structure was maintained and islands of atypical cells were observed within pockets of mucin surrounding the adenomatous tissue. No gross or histologic evidence of malignancy was detected throughout the 20-mo observation period. The human identity of the cells in the graft was confirmed by DNA in situ hybridization with a human-specific probe. We conclude that the human-scid xenograft described here represents a viable animal model with which to study the potential malignant dedifferentiation of villous adenomas over a prolonged period of time and to evaluate the possible contribution of selected oncogenic vectors on the malignant transformation of these adenomas.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankert R. B., Umemoto T., Sugiyama Y., Chen F. A., Repasky E., Yokota S. Human lung tumors, patients' peripheral blood lymphocytes and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes propagated in scid mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;152:201–210. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74974-2_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérin-Reverchon I., Chardonnet Y., Chignol M. C., Thivolet J. A comparison of methods for the detection of human papillomavirus DNA by in situ hybridization with biotinylated probes on human carcinoma cell lines. Application to wart sections. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Oct 24;123(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Kaneshima H., Shultz L. D., Lieberman M., Weissman I. L. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1632–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller B. M., Reisfeld R. A. Potential of the scid mouse as a host for human tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1991 Oct;10(3):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00050791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeva C., Corfield A. P., Harper S., Hague A., Audcent K., Williams A. C. Colorectal carcinogenesis: sequential steps in the in vitro immortalization and transformation of human colonic epithelial cells (review). Anticancer Res. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5A):1189–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. C., Harper S. J., Paraskeva C. Neoplastic transformation of a human colonic epithelial cell line: in vitro evidence for the adenoma to carcinoma sequence. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4724–4730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. S., Alosco T. R., Croy B. A., Bankert R. B. The study of human neoplastic disease in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1993 Apr;43(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]