Abstract
The swarmer cycle of Hyphomicrobium neptunium consists of a temporal sequence of discrete developmental events. To time morphogenesis and to investigate modulations in macromolecular synthesis, we attempted methods for synchronous culture. During synchrony, swarmer maturation occurred over 32%, hyphal growth occurred over 36%, and bud maturation occurred over 32% of the time required to complete the swarmer cycle. Daughter cells were released after 265 min. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication was discontinuous, having a G1 period of approximately 180 min. In addition, ribonucleic acid and protein syntheses were depressed during the earlier phases of development.
Full text
PDF
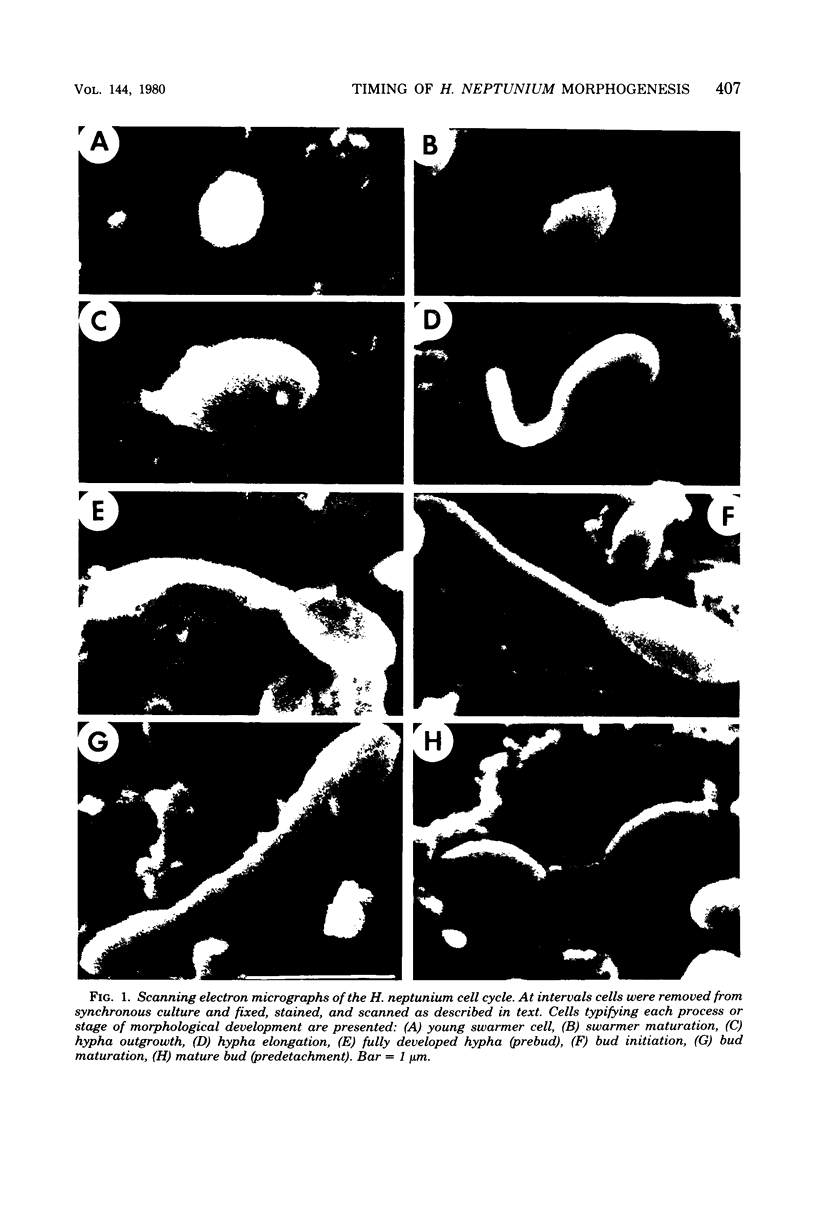
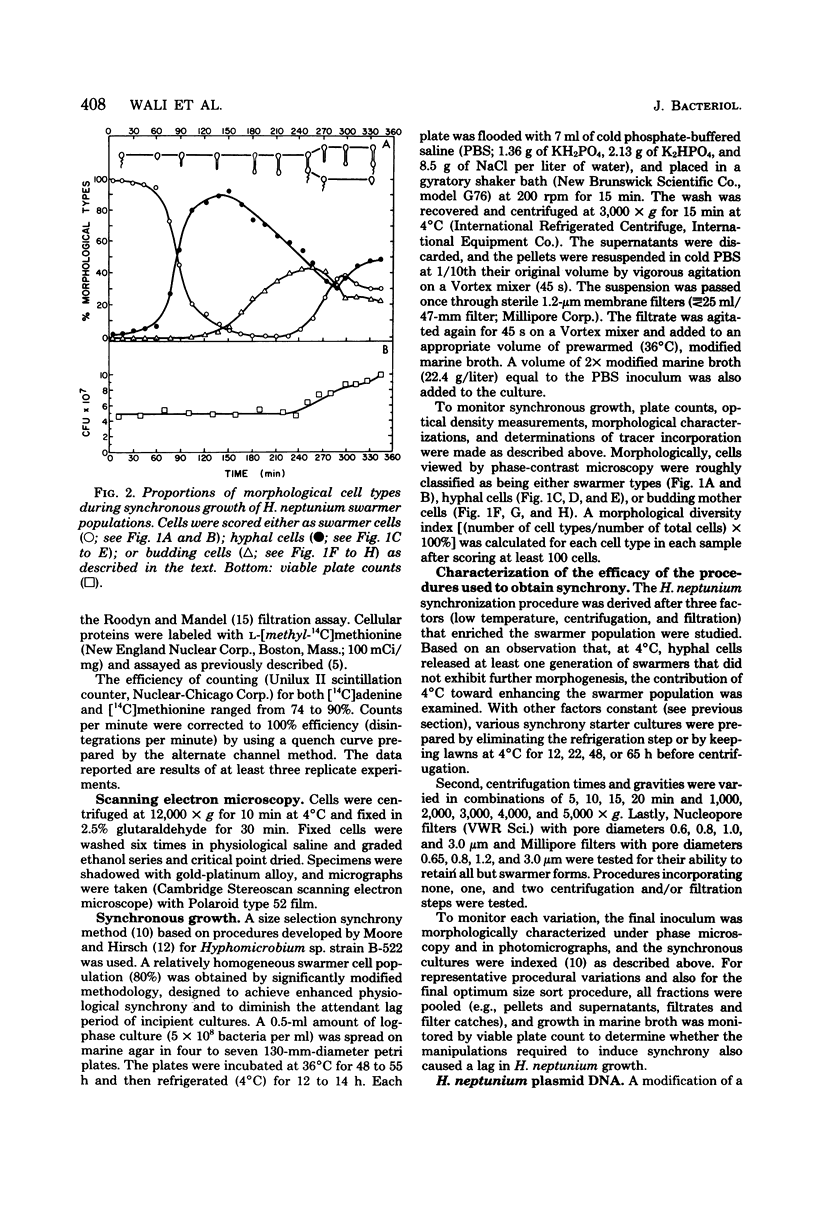

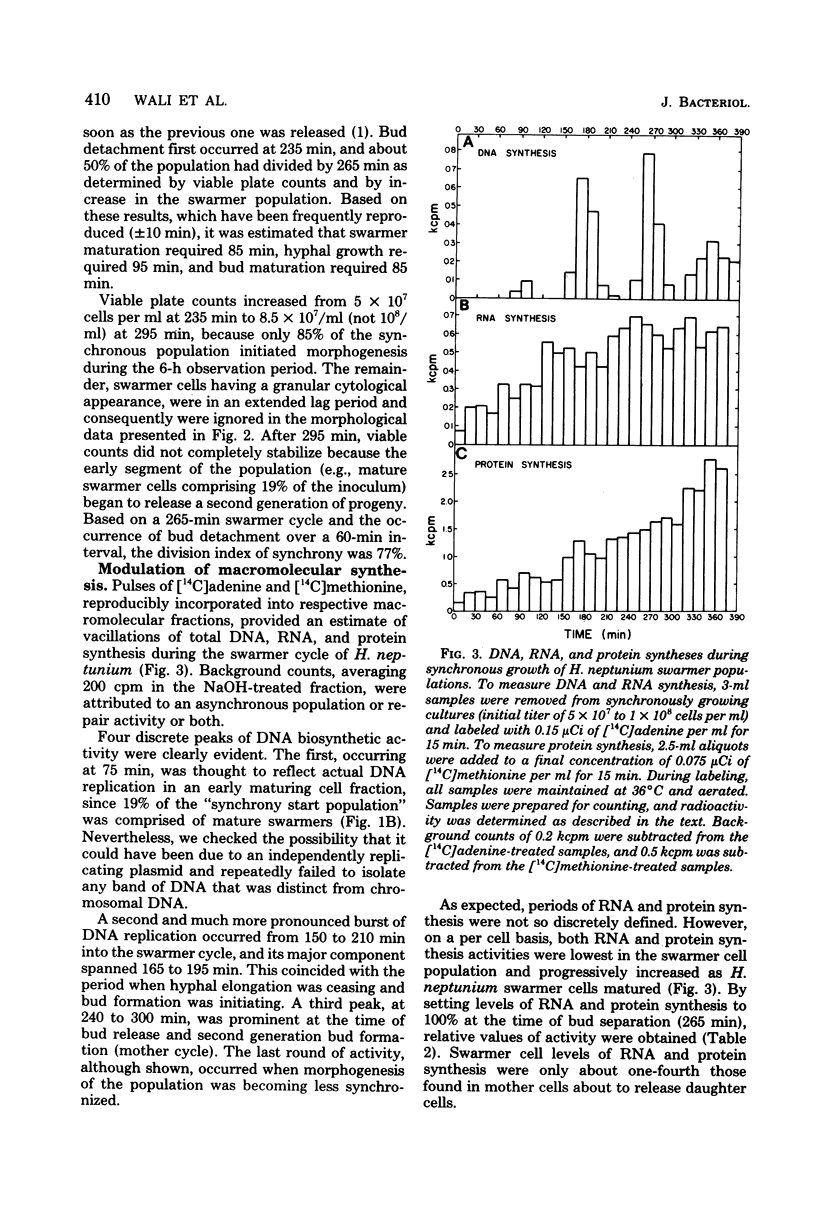


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. A., Weiner R. M. Photomicrography of nalidixic acid treated Hyphomicrobium neptunium: inhibition of bud formation and bud separation. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;21(2):226–230. doi: 10.1139/m75-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. A unifying model for the G1 period in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):17–19. doi: 10.1038/280017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W., Attwood M. M. Biology, physiology and biochemistry of hyphomicrobia. Adv Microb Physiol. 1978;17:303–359. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havenner J. A., McCardell B. A., Weiner R. M. Development of Defined, Minimal, and Complete Media for the Growth of Hyphomicrobium neptunium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):18–23. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.18-23.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch P. Budding bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):391–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. HYPHOMICROBIUM NEPTUNIUM SP. N. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:249–256. doi: 10.1007/BF02046730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Hirsch P. Deoxyribonucleic acid base sequence homologies of some budding and prosthecate bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):256–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.256-261.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Hirsch P. First generation synchrony of isolated Hyphomicrobium swarmer populations. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):418–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.418-423.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Hirsch P. Nuclear apparatus of Hyphomicrobium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1447–1455. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1447-1455.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. M., Roberson B. S., Weiner R. M. Serological relationships among budding, prosthecate bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):209–207. doi: 10.1139/m80-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN D. B., MANDEL H. G. A simple membrane fractionation method for determining the distribution of radioactivity in chemical fractions of Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:80–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. M., Blackman M. A. Inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and bud formation by nalidixic acid in Hyphomicrobium neptunium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1398–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1398-1404.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenbury R., Dow C. S. Morphogenesis and differentiation in Rhodomicrobium vannielii and other budding and prosthecate bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):754–808. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.754-808.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]