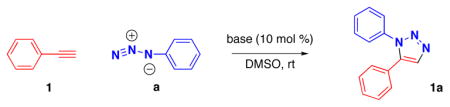
Abstract
1,5-Diarylsubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles are formed in high yield from aryl azides and terminal alkynes in DMSO in the presence of catalytic tetraalkyl ammonium hydroxide. The reaction is experimentally simple, does not require a transition-metal catalyst, and is not sensitive to atmospheric oxygen and moisture.
The copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) is a reliable means for the synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-1H-1,2,3-triazoles.1 The exceptional stability of 1,2,3-triazoles and the availability of a reliable synthesis leading to these heterocycles have enabled widespread applications of this previously underutilized class of azoles in medicinal chemistry, chemical biology and materials science.2
In contrast to the 1,4-disubstituted-1H-1,2,3-triazoles, general and regioselective routes leading to the 1,5-regioisomers are not as well developed.3–8 Although syntheses relying on the nucleophilic attack by the acetylide at the electrophilic terminal nitrogen of the azide are known,9 the requirement for the stoichiometric lithium or magnesium acetylide reagent imposes obvious limitations on the range of functional groups that are compatible with these processes. Reported here is a mild and experimentally simple catalytic method for the generation of the reactive acetylides which readily react with organic azides resulting in the exclusive formation of 1,5-disubstituted triazoles.
We envisioned that the high acidity of aryl acetylenes in dimethylsulfoxide10–12 should allow formation of the reactive acetylide species by treatment of the alkyne with a hydroxide or alkoxide base in this solvent. In fact, formation of acetylide intermediates has been proposed by Ishikawa and co-workers in their studies of the alkynylation of ketones.13 Screening of various hydroxides and alkoxides confirmed this hypothesis, revealing that anhydrous sodium, potassium, cesium hydroxides, and aqueous tetramethylammonium and benzyl-trimethylammonium hydroxides catalyze formation of 1,5-diarylsubstituted-1H-1,2,3-triazoles in DMSO at room temperature (Table 1).
Table 1.
Performance of selected hydroxide bases in catalytic synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles
base (0.42 mmol) was added to a solution of phenylacetylene (461 μL, 4.2 mmol) and azidobenzene (0.50 g, 4.2 mmol) in DMSO (16.8 mL) at room temperature and stirred under a CO2-free atmosphere. Product was isolated by vacuum filtration after addition of water;
reaction progress was monitored by LC-MS;
2.6M aqueous solution of KOH (160 μL, 0.42 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture.
Dry DMSO and less nucleophilic bases such as potassium tert-butoxide can also be used to minimize hydrolysis of substrates which contain base-sensitive functionalities. In many cases, the desired products precipitated upon addition of 5–20× volume of ice-cold water and were isolated by simple filtration. Reactions in DMSO afforded higher isolated yield than in DMF on larger scale and at higher concentration. Although tetraalkylammonium hydroxides resulted in the slightly diminished yield of the product compared to powdered KOH, the shorter reaction time and the experimental convenience of using aqueous base solutions make tetraalkylammonium hydroxides advantageous catalysts for practical reasons.
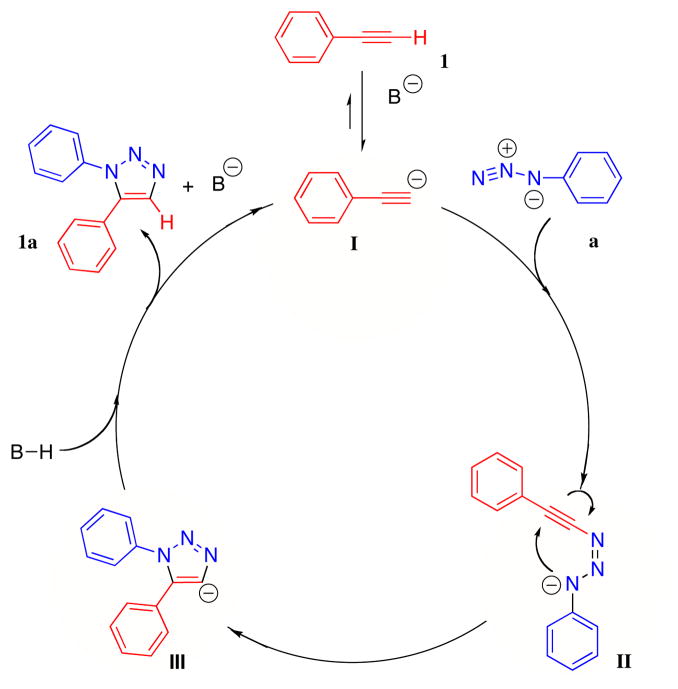
While our mechanistic studies of this hydroxide-catalyzed synthesis of triazoles in DMSO are not complete, we offer in Scheme 1 a general proposal for 1,5-triazole formation from acetylides and organic azides. Reversible deprotonation of the terminal alkyne 1 generates an aryl acetylide I, which acts as a nucleophile to attack the terminal nitrogen of aryl azide a. The triazenide intermediate II then undergoes either 6π-electrocyclization or 5-endo-dig cyclization to form 1,5-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazolyl anion III which completes the catalytic cycle by deprotonation of a molecule of DMSO, terminal alkyne, or water. That DMSO is likely deprotonated under the reaction conditions is evidenced by the incorporation of deuterium into the product when the reaction is performed in d6-DMSO with potassium tert-butoxide (0.2 equiv). This finding suggests that in addition to stabilizing the anionic intermediates (II and III), DMSO participates in the various necessary proton-relay events. Observation of trace amount of 4-triazenyl triazole byproduct, the formation of which can be rationalized by the nucleophilic attack of triazolyl anion III on another molecule of aryl azide, lends further support to the involvement of triazolyl anion III.
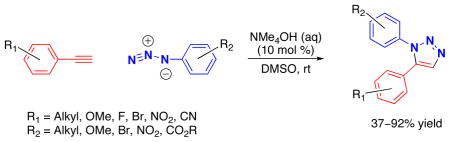
The scope of this process was examined as illustrated by the examples in Table 2. Most aryl and heteroaryl azides and terminal alkynes readily participate in this 1,5-diarylsubstituted-1,2,3-triazole synthesis. It is noteworthy that base-labile functionalities (entries 6, 9, 14) were tolerated. Aryl azides with sterically demanding ortho-substituents gave slightly lower yields, possibly due to interference with the ring closure of the triazenide intermediate (Table 2, entries 2, 4, 15). Electronic properties of both reactants significantly influence the outcome of the reaction. For example, very electron-deficient 4-nitrophenyl azide produced the triazole in moderate 62% yield (entry 3), likely due to the less efficient triazenide cyclization step. Similarly, 4-nitrophenyl acetylene produced the desired triazole product in only 37% yield (entry 12), which could be a consequence of the reduced nucleophilicity of the acetylide anion. Alkyl acetylenes failed to react under the current conditions, probably due to their lower acidity.14
Table 2.
Scope of the base-catalyzed synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles
| entry | product | yielda (%) | mp (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
1a | 86 | 113–114 |
| 2 |  |
1b | 60c | 100–102 |
| 3 | 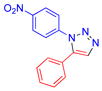 |
1c | 62c | 164.5–165.5 |
| 4 | 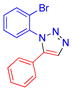 |
1d | 64c | 95–97 |
| 5 | 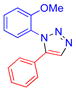 |
1e | 79c | 105–107 |
| 6 | 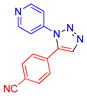 |
2f | 70b,c | 170–171 |
| 7 | 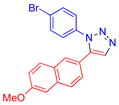 |
3g | 56c | 152–153 |
| 8 | 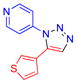 |
4f | 69b | 184–185 |
| 9 | 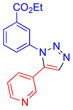 |
5h | 79b,c | 75.5–77.5 |
| 10 | 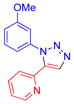 |
6i | 92c | oil |
| 11 |  |
7g | 83 | 120–122 |
| 12 | 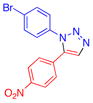 |
8g | 37c | 172–173 |
| 13 | 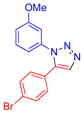 |
9i | 92c | 148–149 |
| 14 | 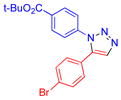 |
9j | 76b | 153–156 |
| 15 | 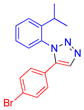 |
9k | 70c | Oil |
| 16 | 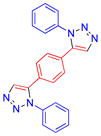 |
10a | 85 | 267–269 |
Unless stated otherwise, method A (base = aq NMe4OH) was used and the product was isolated by filtration;
method B (base = t-BuOK) was used;
isolated yield after flash column chromatography.
The results described above demonstrate that sufficiently nucleophilic and reactive acetylides can be prepared from terminal alkynes without involving aggressive lithium or magnesium reagents. Such acetylides react selectively with even modestly electrophilic organic azides, producing 1,5-disubstituted triazoles under mild, transition metal-free conditions. Experimental simplicity, ease of product isolation, low cost, and ready availability of reagents should make this method immediately useful for the synthesis of these heterocycles.
Supplementary Material
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanism of the 1,5-triazole formation
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, National Institutes of Health (GM087620), the Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology, and Pfizer, Inc. is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank Profs. M. G. Finn and K. B. Sharpless (The Scripps Research Institute) for helpful discussions.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available. Experimental procedures, characterization data, copies of 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra. This material is available free of charge on the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.(a) Tornøe CW, Christensen C, Meldal M. J Org Chem. 2002;67:3057. doi: 10.1021/jo011148j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rostovtsev VV, Green LG, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2002;41:2596. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020715)41:14<2596::AID-ANIE2596>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.For recent reviews see Wu P, Fokin VV. Aldrichimica Acta. 2007;40:7.Fournier D, Hoogenboom R, Schubert US. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36:1369. doi: 10.1039/b700809k.Moses JE, Moorhouse AD. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36:1249. doi: 10.1039/b613014n.Johnson JA, Koberstein JT, Finn MG, Turro NJ. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2008;29:1052.
- 3.Brunner M, Maas G, Klaerner FG. Helv Chim Acta. 2005;88:1813. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coats SJ, Link JS, Gauthier D, Hlasta DJ. Org Lett. 2005;7:1469. doi: 10.1021/ol047637y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Holzer W, Ruso K. J Heterocycl Chem. 1992;29:1203. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Uhlmann P, Felding J, Vedso P, Begtrup M. J Org Chem. 1997;62:9177. [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Zhang L, Chen X, Xue P, Sun HHY, Williams ID, Sharpless KB, Fokin VV, Jia G. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:15998. doi: 10.1021/ja054114s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rasmuseen LK, Boren BC, Fokin VV. Org Lett. 2007;9:5337. doi: 10.1021/ol701912s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Boren BC, Narayan S, Rasmuseen LK, Zhang L, Zhao H, Lin Z, Jia G, Fokin VV. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:8923. doi: 10.1021/ja0749993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Krasinski A, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB. Org Lett. 2004;6:1237. doi: 10.1021/ol0499203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Akimova GS, Chistokletov VN, Petrov AA. Zh Obsh Khim. 1965;1:2077. [Google Scholar]; (b) Akimova GS, Chistokletov VN, Petrov AA. Zh Org Khim. 1967;3:2241. [Google Scholar]; (c) Akimova GS, Chistokletov VN, Petrov AA. Zh Org Khim. 1967;3:968. [Google Scholar]; (d) Akimova GS, Chistokletov VN, Petrov AA. Zh Org Khim. 1968;4:389. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Matthews WS, Bares JE, Bartmess JE, Bordwell FG, Cornforth FJ, Drucker GE, Margolin Z, McCallum RJ, McCollum GJ, Vanier NR. J Am Chem Soc. 1975;97:7006. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Olmstead WN, Margolin Z, Bordwell FG. J Org Chem. 1980;45:3295. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bordwell FG, Algrim D, Fried HE. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans. 1979;2:726. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ishikawa T, Mizuta T, Hagiwara K, Aikawa T, Kudo T, Saito S. J Org Chem. 2003;68:3702. doi: 10.1021/jo026592g. and the references cited herein. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chrisment J, Delpuech JJ. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans. 1977;2:407. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.