Abstract
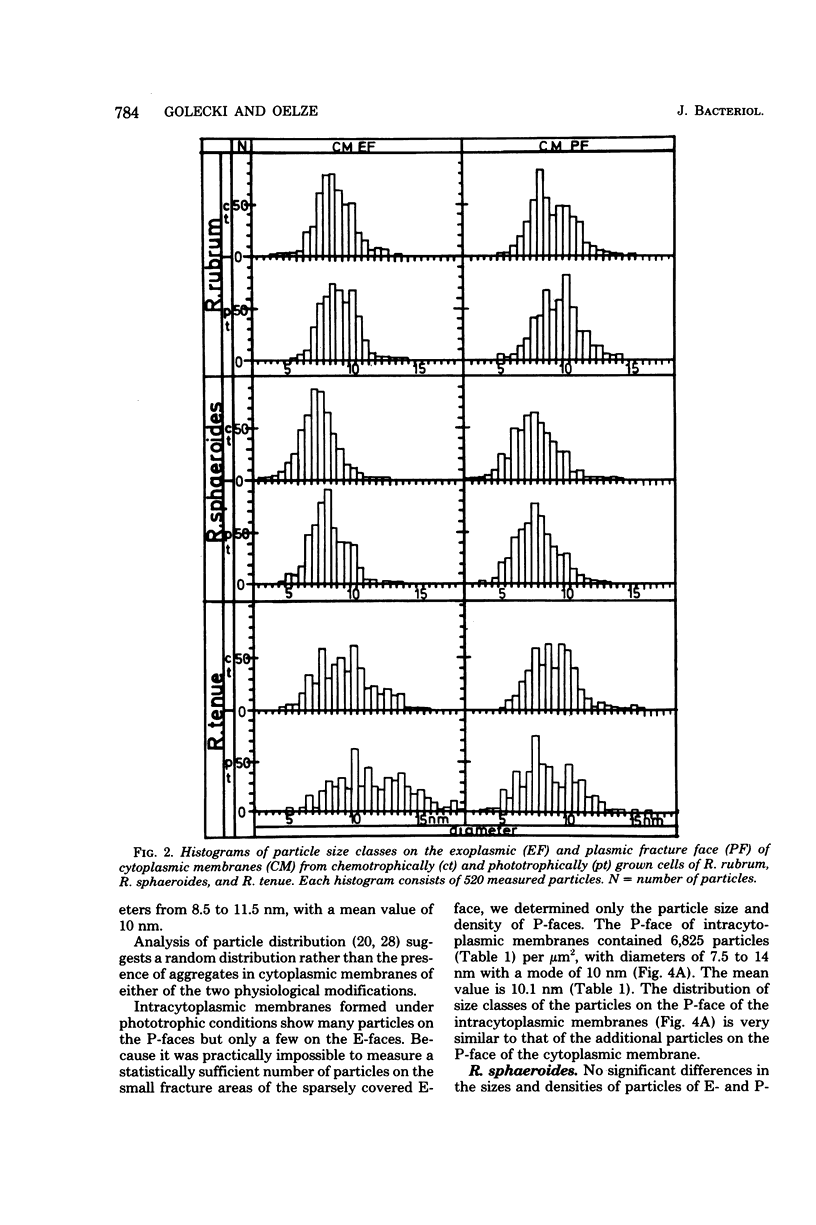
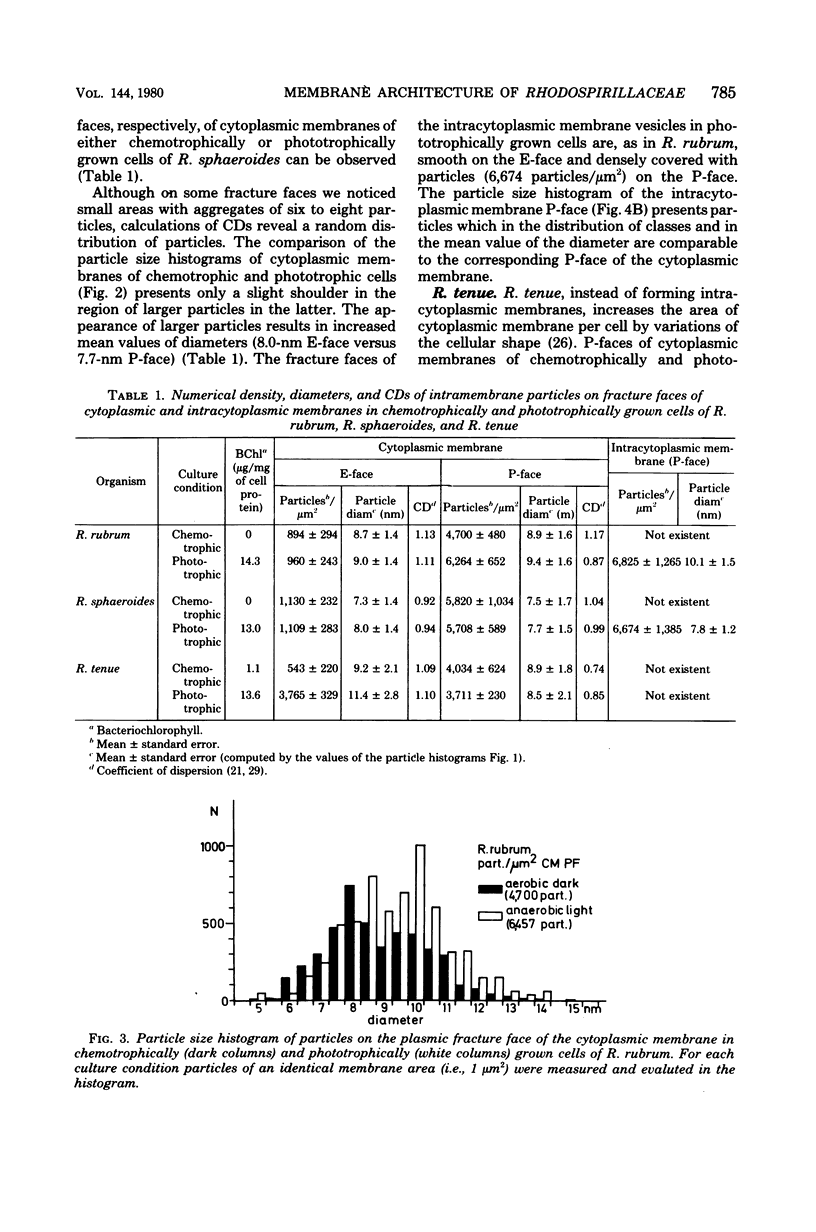
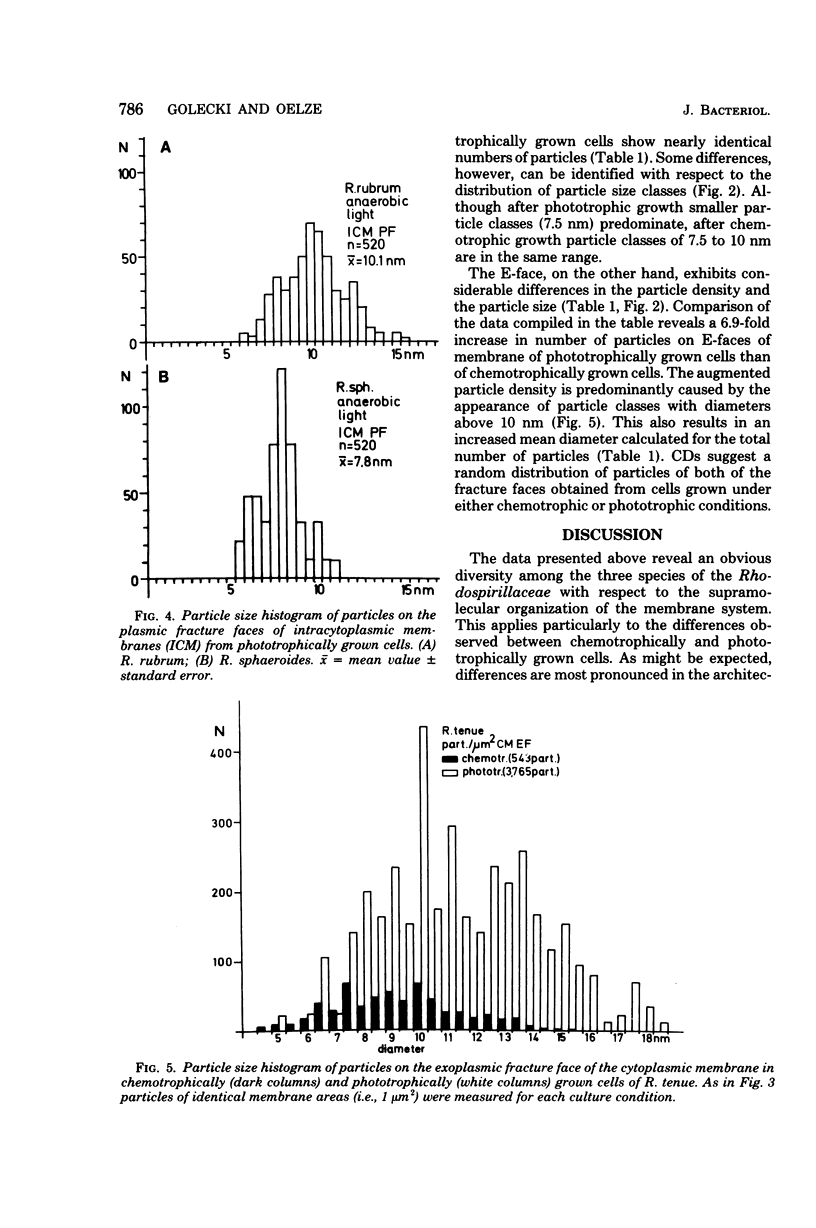
Freeze-fracture faces of membranes of either chemotrophically or phototrophically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, and Rhodospirillum tenue were analyzed. All three species differed from each other with respect to size as well as numerical density (number per square micrometer) of intramembrane particles. In R. rubrum the number of particles on exoplasmic fracture faces of the cytoplasmic membrane stayed nearly constant (about 900 particles per microns2), but on the plasmic fracture face there were 4,700 and 6,264 particles per microns2, respectively, under chemotrophic and phototrophic conditions. The increase in number was largely a result of an enhanced occurrence of particles 10 nm in diameter. This diameter corresponds to the mean diameter of the predominant class of particles visible on the plasmic fracture faces of intracytoplasmic membrane formed under phototrophic conditions. In R. sphaeroides the number of particles on both of the fracture faces of cytoplasmic membranes stayed nearly constant. The mean diameter of articles appeared to be slightly increased under phototrophic conditions. Particles of cytoplasmic and intracytoplasmic membranes of phototrophically grown cells were of similar diameter. The number of particles, however, on plasmic fracture faces of intracytoplasmic membranes (6,674/microns2) was significantly higher than that on cytoplasmic membranes (5,708/microns2). R. tenue, on the other hand, which does not produce intracytoplasmic membranes, showed on exoplasmic fracture faces 543 and 3,765 particles per micron2 under chemotrophic and phototrophic conditions, respectively, whereas the corresponding numerical densities of plasmic fracture faces were 4,043 and 3,711 particles per microns2. The increased number of articles on exoplasmic fracture faces was mainly the result of an increased occurrence of particles with diameters greater than or equal to 10 nm. The results are interpreted to allow for the different modes of intractyoplasmic membrane development in Rhodospirillum rubrum and Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golecki J., Drews G., Bühler R. The size and number of intramembrane particles in cells of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata studied by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Cytobiologie. 1979 Feb;18(3):381–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. C., MARR A. G. EFFECT OF LIGHT INTENSITY ON THE FORMATION OF INTRACYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE IN RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1421–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1421-1429.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Kaplan S. Membrane proteins of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. IV. Characterization of chromatophore proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosakowski M. H., Kaplan S. Topology and growth of the intracytoplasmic membrane system of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: protein, chlorophyll, and phospholipid insertion into steady-state anaerobic cells. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1144–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1144-1157.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lommen M. A., Takemoto J. Comparison, by freeze-fracture electron microscopy, of chromatophores, spheroplast-derived membrane vesicles, and whole cells of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):730–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.730-741.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueking D. R., Fraley R. T., Kaplan S. Intracytoplasmic membrane synthesis in synchronous cell populations of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Fate of "old" and "new" membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):451–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Drews G. Membranes of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):209–239. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Golecki J. R., Kleinig H., Weckesser J. Characterization of two cell-envelope fractions from chemotrophically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(3):273–286. doi: 10.1007/BF02565063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota F., Fukui K., Morita J., Yoshida N., Kashiyama T. Ultrastructure of Rhodospirillum rubrum after freeze-etching. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;17(6):527–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks L. C., Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. V. Identification of bacteriochlorophyll alpha-depleted cytoplasmic membrane in phototrophically grown cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 20;511(1):70–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli B. U., Friedell G. H., Weinstein R. S. Topography and numerical densities of intramembrane particles in chemical carcinogen-induced urinary bladder carcinomas in Fischer rats. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):565–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Carter R. L., Kidwell W. R. Structural changes in memebranes of synchronized cells demonstrated by freeze-cleavage. Nature. 1971 Oct 13;233(5320):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Momvers C., Leunissen-Bijvelt J., Ververgaert P. H. Lipidic intramembranous particles. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):162–163. doi: 10.1038/279162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Ververgaert P. H. Freeze-fracture morphology of biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):303–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. S. Changes in plasma membrane structure associated with malignant transformation in human urinary bladder epithelium. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 2):2518–2524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




