Abstract
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) have shown great potential as antioxidant and radioprotective agents for applications in cancer therapy. Recently, various polymer-coated nanoceria preparations have been developed to improve their aqueous solubility and allow for surface functionalization of these nanoparticles. However, the interaction of polymer-coated nanoceria with cells, their uptake mechanism and subcellular localization are poorly understood. Herein, we engineered polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface charge (positive, negative and neutral) and studied their internalization and toxicity in normal and cancer cell lines. Results showed that nanoceria with a positive or neutral charge enters most of the cell lines studied, while nanoceria with a negative charge internalizes mostly in the cancer cell lines. Moreover, upon entry into the cells, nanoceria is localized to different cell compartments (e.g. cytoplasm and lysosomes) depending on the nanoparticle's surface charge. The internalization and subcellular localization of nanoceria plays a key role in the nanoparticles’ cytotoxicity profile, exhibiting significant toxicity when they localize in the lysosomes of the cancer cells. In contrast, minimal toxicity is observed when they localize into the cytoplasm or do not enter the cells. Taken together, these results indicate that the differential surface-charge-dependent localization of nanoceria in normal and cancer cells plays a critical role in the nanoparticles’ toxicity profile.
Keywords: Polymer-coated nanoceria, nanoparticle cell uptake, cerium oxide, nanotoxicity, lysosomal uptake
Nanomaterials with unique magnetic, luminescent and catalytic properties are being engineered for numerous biomedical applications, ranging from imaging, diagnostics and therapy.1–7 However, nanomaterial’s greatest strength, which relies primarily on the enhanced physical and chemical characteristics that matter exhibits at this scale, has the potential to be its greatest liability. Potentially harmful interactions can occur between nanomaterials and living systems, including humans. For this reason, nanomaterials must be engineered using materials that are either non-toxic, biocompatible and biodegradable or that have minimal and in some cases beneficial properties. An inflammatory response is a parameter that is often investigated to assess the effect that nanomaterials have within an organism.8 For instance, recent studies have shown that titanium oxide nanoparticles, which are widely used in cosmetics and skin care products, can elicit an inflammatory response and generation of reactive oxygen species, causing DNA damage.9 Also, single-walled carbon nanotubes can cause lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and changes in cell morphology upon in vitro incubation with keratinocytes and bronchial epithelial cells. 10, 11 Furthermore, silver nanoparticles have been found to display size-dependent toxicity when exposed to alveolar macrophages via induction of oxidative stress,12,13 while quantum dots and fullerenes can also initiate an inflammatory response and generation of reactive oxygen species.14–16
Cerium oxide nanoparticle (nanoceria) is a unique nanomaterial, because it exhibits anti-inflammatory properties. Nanoceria has been found to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), possess superoxide-dismutase-like activity, prevent cardiovascular myopathy, and provide radioprotection to normal cells from radiation.17–21 We recently reported the synthesis of biocompatible polymer-coated nanoceria with enhanced aqueous stability and unique pH-dependent antioxidant activity.17 Particularly, we have found that nanoceria displays optimal antioxidant properties at physiological pH, whereas it behaves as an oxidase at acidic pH.22 Hence, this selective behavior may explain nanoceria’s selective cytoprotection to normal cells, but not to cancer cells during radiation treatment or oxidative stress.20 In addition, the nature of the polymeric coating surrounding the cerium oxide core could play a critical role in nanoceria’s beneficial (antioxidant) vs harmful (oxidant) properties. We also reasoned that the cytotoxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles could depend upon their subcellular localization. Once inside the cells, the nanoparticle’s toxicity could depend on whether they are localized in particular cellular organelles, such as the lysosomes (which are acidic), or distributed in the cytoplasm (which is at neutral pH in normal cells). In addition, since most tumors have an acidic microenvironment, this might switch off nanoceria’s antioxidant activity, turning on its oxidase activity and consequently sensitizing the tumor towards radiation therapy.
In this work, we report the polymer’s surface-charge-dependent cell internalization and cytotoxicity profile of cerium oxide nanoparticles in normal vs malignant cells. We selected various cell lines in order to assess the corresponding behavior of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Cardiac myocytes (H9c2) and human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells were selected as non-transformed (normal) cells, whereas lung (A549) and breast (MCF-7) carcinomas were selected as transformed (cancer) cell lines. Results showed that positively charged nanoceria internalized in all cells except for the breast carcinoma, localizing preferentially in the lysosomes and subsequently becoming toxic to these cells. In contrast, nanoceria with a negative charge was internalized only by lung carcinoma (A549) cells but not by the breast carcinoma cells (MCF-7), thus exhibiting toxicity only to the lung carcinoma cells. Notably, the negative charged nanoceria localized into the lysosomes of the A549 cells, while they were not internalized and therefore were not toxic to the normal cells (either cardiac myocytes or human embryonic kidney cells). Surprisingly, nanoceria with neutral charge was not toxic to normal cells or cancer cells, as these nanoparticles primarily localized in the cytoplasm of these cells. Taken together, our results suggest that the internalization and subcellular localization of polymer-coated nanoceria plays a critical role in the toxicity profile of this nanomaterial. Our results also suggest that the coating on nanoceria can be engineered in order to modulate its differential cytotoxicity behavior in cancer vs normal cells.
Results
Synthesis and characterization of polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles
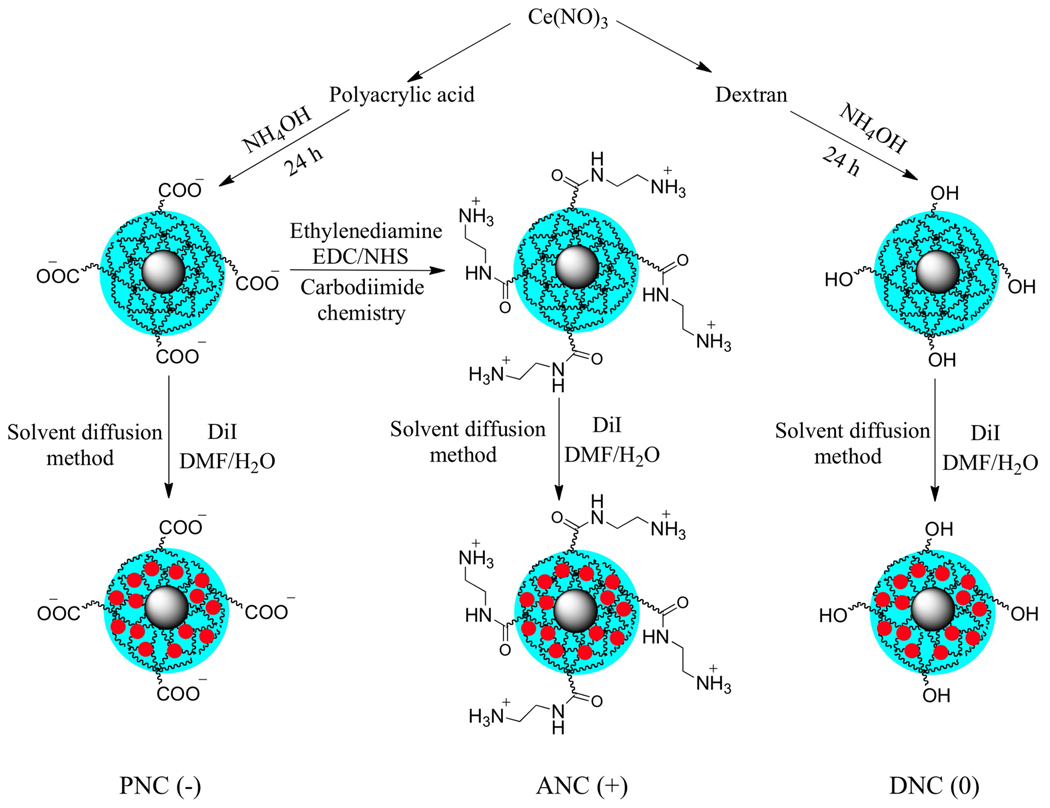
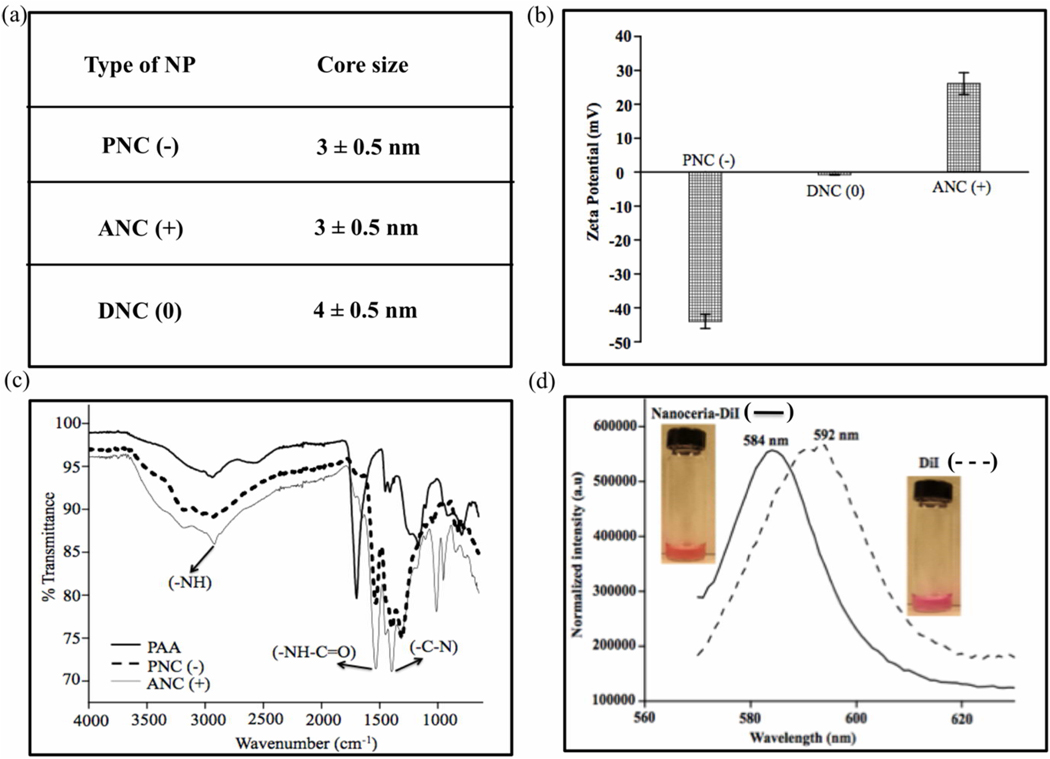
For our studies, we synthesized various nanoceria preparations coated with either polyacrylic acid (PNC), aminated polyacrylic acid (ANC), or dextran (DNC) (Scheme 1), endowing our nanoparticles with a negative (−), positive (+) or neutral (0) surface charge, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies showed the presence of nanoparticles of similar core size (3 to 4 nm) in all preparations as reported previously22 (Figure 1a). Dynamic light scattering experiments showed the presence of monodisperse nanoceria preparations with average hydrodynamic diameter of 14 nm for DNC(0) and 5 nm for both PNC(+) and ANC(−) (See Supporting Information, Figure S1). The presence of different surface charges in the various nanoceria preparations was assessed by zeta potential (Figure 1b), confirming the presence of a negative, neutral and positive charge for PNC, DNC and ANC, respectively. FT-IR analysis further confirmed the nanoparticle’s polymer surface coating and functionality (Figure 1c). During synthesis, we fluorescently labeled the nanoparticles, by encapsulating a dye (DiI) within the hydrophobic microdomains of the polymeric coatings of each nanoceria preparation, following a previously reported methodology.23 Therefore using this approach, we introduced fluorescent modality to the polymer-coated nanoceria, without compromising the solubility of the nanoparticles in aqueous media or reducing the number of available functional groups on the nanoparticle surface. Successful encapsulation of DiI into the nanoceria was confirmed via fluorescence spectroscopy, where a blue shift in the DiI-encapsulating ceria nanoparticles (584 nm) emission spectrum was observed as opposed to DiI alone (592 nm) (Figure 1d). The DiI-encapsulating polymer-coated-nanoceria displayed good aqueous stability over long periods of time without significant release of the dye, and can be used for the intracellular tracking of the nanoparticles.
Scheme 1.
Surface functionalization of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Cerium oxide nanoparticles with different polymer coatings and surface modifications were synthesized to yield nanoparticles with negative [PNC(−)], positive [ANC(+)] , and neutral [DNC(0)] charge. A fluorescent dye (DiI, red circle) was encapsulated using a modified solvent diffusion method.
Figure 1.
Characterization of cerium oxide nanoparticles. (a) Size of cerium oxide nanocrystal core by TEM. (b) Zeta potential of cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface functionalities (negative, neutral and positive). (c) FT-IR spectra of the carboxylated (negative) and aminated (positive) surface group on nanoceria. (d) Fluorescence emission spectra of the DiI-encapsulating nanoceria and free dye DiI.
Nanoceria’s surface-charge-dependent cellular interaction
Confocal microscopy experiments were performed in order to study the cellular uptake and intracellular localizaton of the DiI-labeled polymer-coated nanoceria. In these experiments, PNC(−), ANC(+) and DNC(0) (1.0 mM) were incubated with two transformed carcinoma cell lines (A549 lung and MCF-7 breast carcinomas), and two non-transformed (normal) cell lines (H9c2 cardiac myocytes and HEK293 human embryonic kidney cells). We selected these cell lines in order to investigate if they differently uptake the ANC(+), PNC(−) and DNC(0) nanoparticles, thus potentially displaying different toxicity profiles.
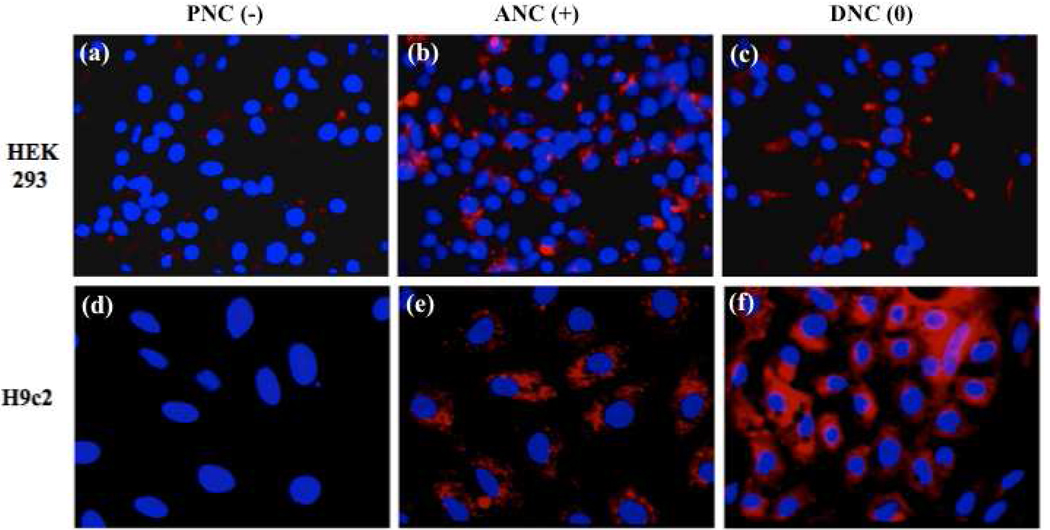
First, we studied the internalization pattern of ANC(+), PNC(−) and DNC(0) in the two normal cells [HEK293 and H9c2, (10,000 cells)] (Figure 2). After a 3 h incubation, results showed that the negatively charged carboxylated nanoparticles [PNC(−)] were minimally uptaken by the HEK293 cells and did not internalize in the H9c2 cell line. Meanwhile, the positively charged aminated nanoparticles [ANC(+)] were uptaken by both cells, with the H9c2 cardiac myocytes uptaking more nanoparticles than the HEK293 human embryonic kidney cells, as indicated by the elevated cell-associated fluorescence in the H9c2 cells. The neutral dextran-coated nanoparticle [DNC(0)] was internalized by both cell lines, although a higher degree of internalization was observed in the H9c2 as opposed to the HEK293. Interestingly, the DNC(0) intracellular fluorescence pattern (particularly in the H9c2 cells) was diffused, being different from the ANC(+) punctuated fluorescence pattern. This difference seems to indicate a unique nanoparticle surface-charge dependent internalization mechanism with different intracellular compartmentalization among the nanoparticles studied and these two non-transformed cell lines.
Figure 2.
Uptake of cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) by normal cells via confocal microscopy. PNC(−) is not being significantly uptaken by either cell line (a, d) whereas uptake is observed with the ANC(+) (b, e). DNC(0) exhibits diffused cytoplasmic localization (c, f) with greater internalization in H9c2.
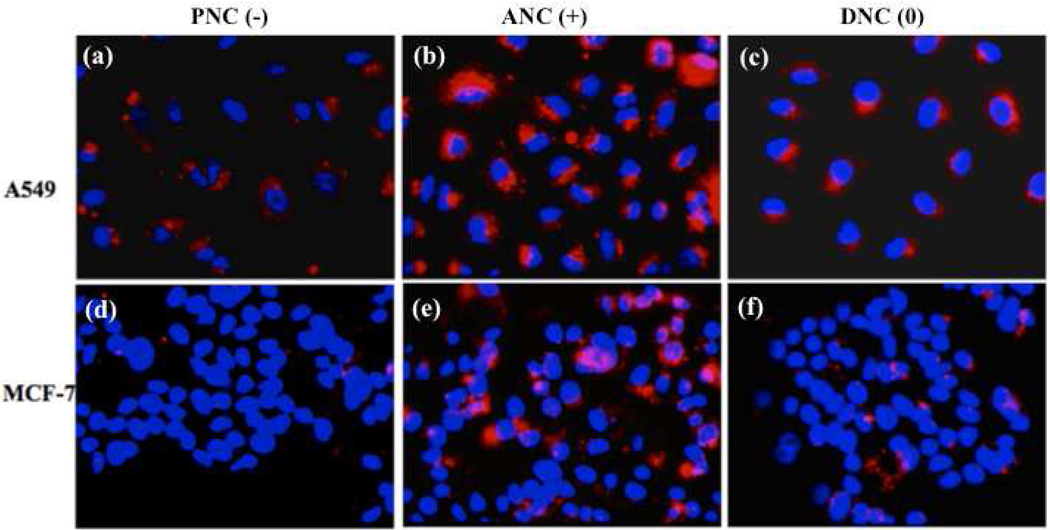
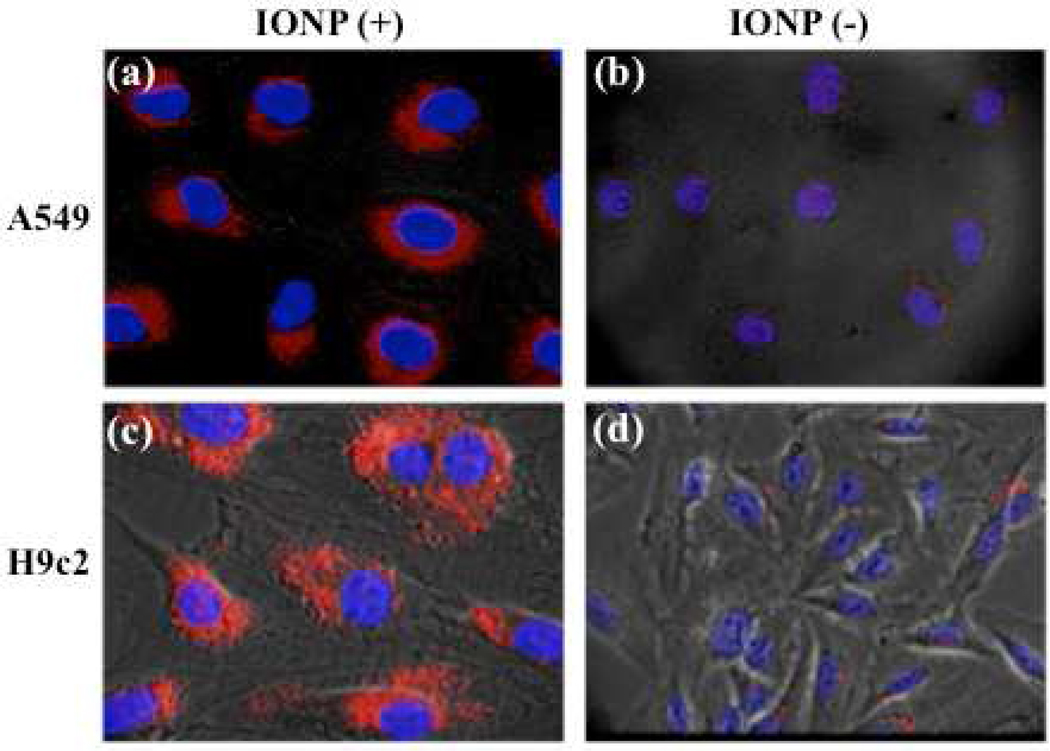
Internalization experiments preformed with cancer cells (10,000 cells) derived from lung (A549) and breast (MCF-7) carcinomas revealed PNC(−) uptake by the A549 cells, but no uptake by the MCF-7 cells (Figure 3). In contrast, both cell lines were able to uptake ANC(+). Interestingly, a higher degree of internalization and pronounced punctuated fluorescence was observed with the ANC(+) in the A549 cells. This might indicate that in these cells the majority of the ANC(+) localized into endosomal compartments. In contrast, minimal and diffused intracellular fluorescence was observed with the DNC(0) in both the A549 and MCF-7 cells, suggesting that these nanoparticles are mostly localized in the cytosol with a small fraction confined within the endosomal compartments. Taken together, the above results suggest that the surface charge on polymer-coated nanoceria dictates their differential internalization and localization in normal vs cancer cells (Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively).
Figure 3.
Uptake of cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) by cancer cells. Confocal images of A549 and MCF-7 carcinoma cells after treatment with PNC(−), ANC(+) and DNC(0) for 3 h. PNC(−) (a,d) are being uptaken by A549 and not by MCF-7 cells, while ANC(+) (b,e) are being uptaken by both cell lines. Meanwhile, DNC(0) internalized in the A549 (c), while they were minimally internalized by MCF-7 (f).
Cellular mechanism of nanoparticle uptake
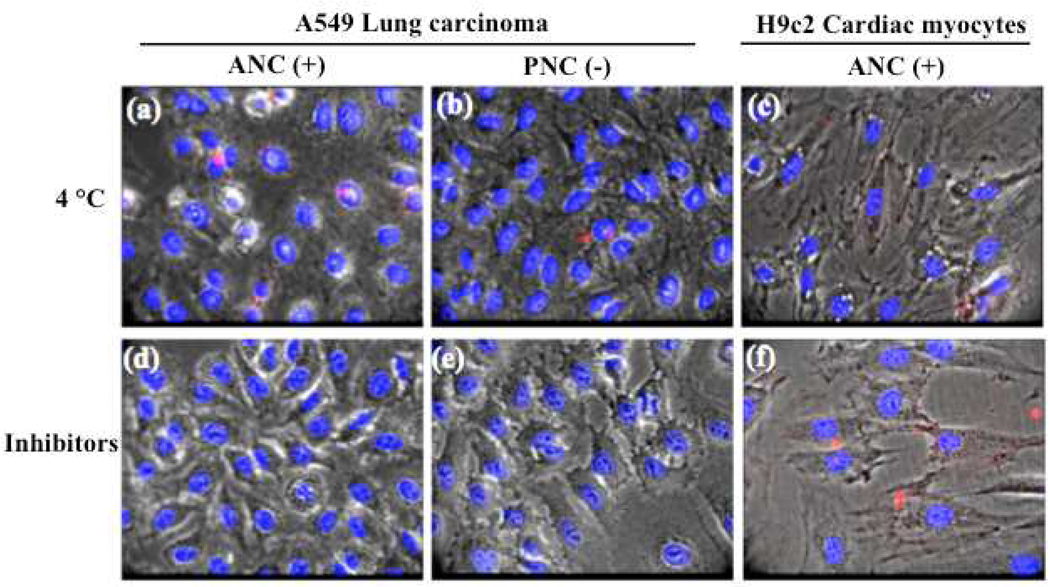
To further investigate the mechanism of cellular uptake and verify if the endocytic pathway is responsible for the internalization of polymer-coated nanoceria, we performed a series of experiments at 4 °C and with endocytic inhibitors [2-deoxyglucose (50 mM) and sodium azide (10 mM)]. For instance, at 4 °C the endocytic/pinocytic mechanism is arrested.24–26 Thus, after incubating cells (10,000 cells) with the various DiI-labeled nanoceria preparations (1.0 mM) at 4 °C, we observed negligible nanoparticle internalization (Figure 4a, 4b and 4c). Since none of the polymer-coated nanoceria entered the A549 lung carcinoma or H9c2 cardiac myocytes cells, it was suggested that endocytosis is a possible mechanism of internalization in all cases. Experiments performed at 37 °C in the presence of 2-deoxyglucose and sodium azide confirmed our results (Figure 4d, 4e and 4f). Specifically, both A549 and H9c2 cells did not uptake the DiI-labeled nanoceria [PNC(−), ANC(+) or DNC(0)] in the presence of these inhibitors as expected. These results confirm that these nanoparticles were actively uptaken by an endocytic process. Since PNC(−) were not significantly uptaken by the H9c2 cells, experiments using these cells at 4 °C or in the presence of inhibitors were not performed.
Figure 4.
Inhibition of endocytic pathways prevents nanoceria uptake. No internalization of ANC(+) and PNC(−) is seen in both cell lines at 4 °C (a, b, c). Similarly, internalization of the nanoparticles is abrogated in the presence of inhibitors (2-deoxyglucose and sodium azide), which collectively block active endocytosis (d, e, f).
Intracellular distribution of polymeric cerium oxide nanoparticles
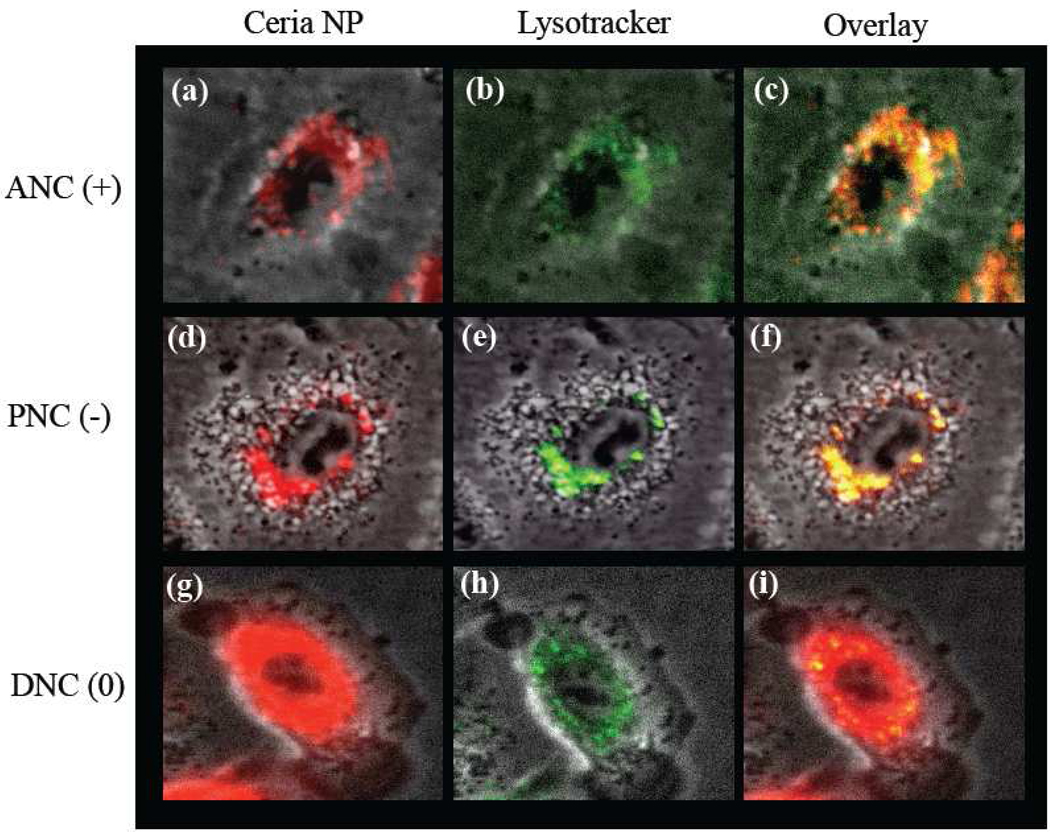
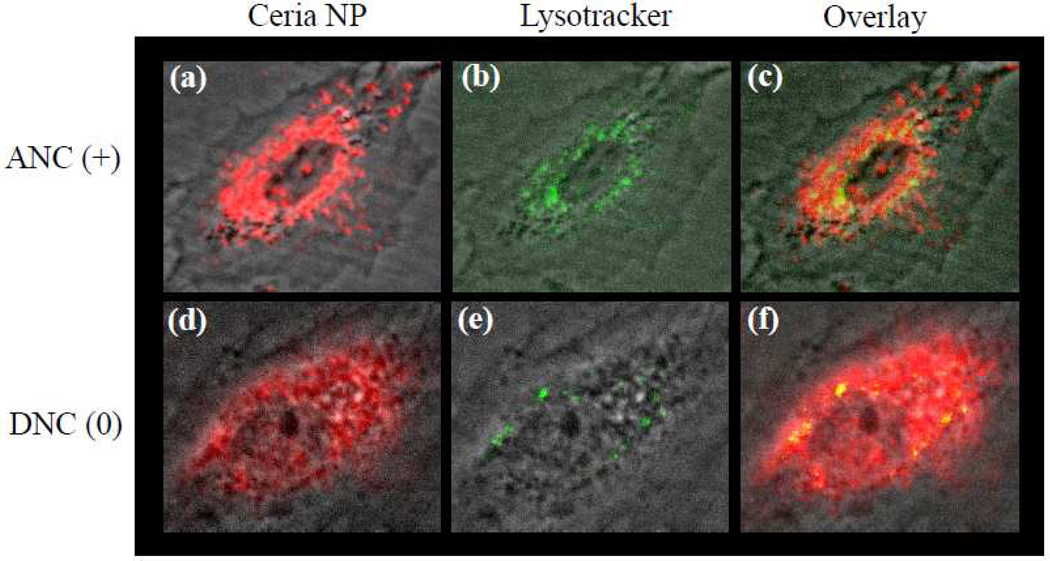
To corroborate that after internalization some of the polymer-coated nanoceria localized in endosomal compartments, we first treated the cells (10,000 cells) for 3 h with the PNC(−), ANC(+) and DNC(0) (1.0 mM) followed by a 20 minutes treatment with Lysotracker (35 nM), a lysosome-specific dye. Lysotracker is a green fluorescent dye that stains the acidic lysosomes, hence the potential co-localization between DiI-labeled-nanoceria (red) and lysosomes (green) should yield a yellow/orange overlap when the images are merged. Experiments were carried out with A549 lung carcinoma cells and H9c2 cardiac myocytes. Results showed that DiI-labeled-ANC(+) and DiI-labeled-PNC(−) colocalized with Lysotracker in the A549 lung cancer cells, as determined by confocal microscopy (Figure 5a–5f and See Supporting Information Figure S2). Even though less internalization of DiI-labeled-PNC(−) is observed in these cells, the internalized nanoparticles predominantely co-localized mostly with the Lysotracker dye indicating lysosomal localization. In contrast, DiI-labeled-DNC(0) showed a diffused distribution with minimal localization in the lysosomes of A549 cells (Figure 5g – 5i and See Supporting Information, Figure S3)). Interestingly, in the case of H9c2 cardiac myocytes, the distribution of DiI-labeled-ANC(+) inside the cell co-localized mostly with the Lysotracker marker (Figure 6a–6c and See Supporting Information Figure 3). Meanwhile, when the DiI-labeled-DNC(0) was used, a diffused distribution of internalized nanoparticles (DiI signal) was observed with minimal co-localization with the lysosomes (Figure 6d–6f and See Supporting Information, Figure S3). This indicates that in H9c2 cardiac myocytes, the neutral DiI-labeled-DNC(0) primarily localizes to the cytosol while the DiI-labeled-ANC(+) localized to the lysosome. Lysosomal co-localization experiments were not done using H9c2 and DiI-labeled-PNC(−) since these nanoparticles are not uptaken by these cells (Figure 2). These results demonstrate that the surface charge on the ceria nanoparticles dictates the nanoparticles’ subcellular localization in cancer and normal cells.
Figure 5.
Polymer-coated nanoceria’s intracellular localization in lung carcinoma cells (A549). Upon internalization, both the positively charged [ANC(+), a-c] and negatively charged [PNC(−), d-f] nanoceria co-localized with the lysosome. In contrast, neutral nanoceria [DNC(0), g-i] localized mostly in the cytoplasm.
Figure 6.
Polymer-coated nanoceria’s intracellular localization in cardiac myocytes (H9c2). Upon internalization, the positively charged [ANC(+), a-c] nanoceria is found in both the cytoplasm and lysosomes. In contrast, neutral nanoceria [DNC(0), d-f] does not significantly co-localized to the lysosomes with most of the nanoparticles found in the cytoplasm.
Determination of the oxidase-like activity of lysosome-residing nanoceria
Nanoceria has been reported to possess unique oxidase-like activity at acidic pH, oxidizing various colorimetric substrates, such as 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzydine (TMB) and 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothizoline-6-sulfonic acid (AzBTS).22 This activity can be employed to assess the localization of nanoceria in various cell organelles, particularly lysosomes, via the nanoparticle’s oxidase activity, using TMB as the colorimetric substrate. Hence to further confirm that some of the polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles localized into the lysosomes, cells were incubated with the different nanoceria preparations for 3 h, followed by lysosomal isolation. Then, the oxidase activity of the isolated lysosomes was determined spectrophotometrically via TMB oxidation. As expected and in agreement with the microscopy and lysosomal co-localization experiments, we found that ANC(+) were mostly entrapped within the lysosome of the H9c2, HEK293 and A549 cell lines, as the lysosomes isolated from these cells exhibited significant levels of oxidase activity (Figure 7a, 7b and 7c). In MCF-7 breast carcinoma cell line, no localization to the lysosomes was observed as these cells do not uptake any of the nanoparticles (Figure 7d). Interestingly, when cells were incubated with PNC(−), only the lysosomes isolated from A549 lung carcinoma cells exhibited oxidase activity as expected based on the lysosomal co-localization experiments. Meanwhile, the lysosomes from cells incubated with the DNC(0) exhibit minimal oxidase activity, corroborating the confocal microscopy studies. Lysosomes isolated from untreated cells (H9c2, HEK293, A549 and MCF-7) did not possess any oxidase activity (control), as indicated by the absence of TMB oxidation (Figure 7) and confirming the absence of endogenous oxidase activity in these organelles.
Figure 7.
Lysosomal isolation and determination of the oxidase-like activity of the entrapped nanoceria. In H9c2 and HEK293 cell lines, the ANC(+) nanoparticles are mostly localized into lysosomes, judged by the presence of significant oxidase activity in the lysosomes isolated from these cell lines after incubation with ANC(+) (a and b). PNC(−) and DNC(0) treated H9c2 and HEK293 cells showed minimal oxidase activity in their lysosomes. In the A549 cell lines, oxidase activity was detected in cells treated with ANC(+) and PNC(−), while minimal activity was present in the DNC(0) treated cells (c). The lysomes isolated from MCF-7 cells did not show significant oxidase activity as the nanoceria did not internalized in these cells (d). Lysosomes isolated from non-treated cells do not show any oxidase activity as expected.
Intracellular-distribution-dependent cytotoxicity of polymeric cerium oxide nanoparticles
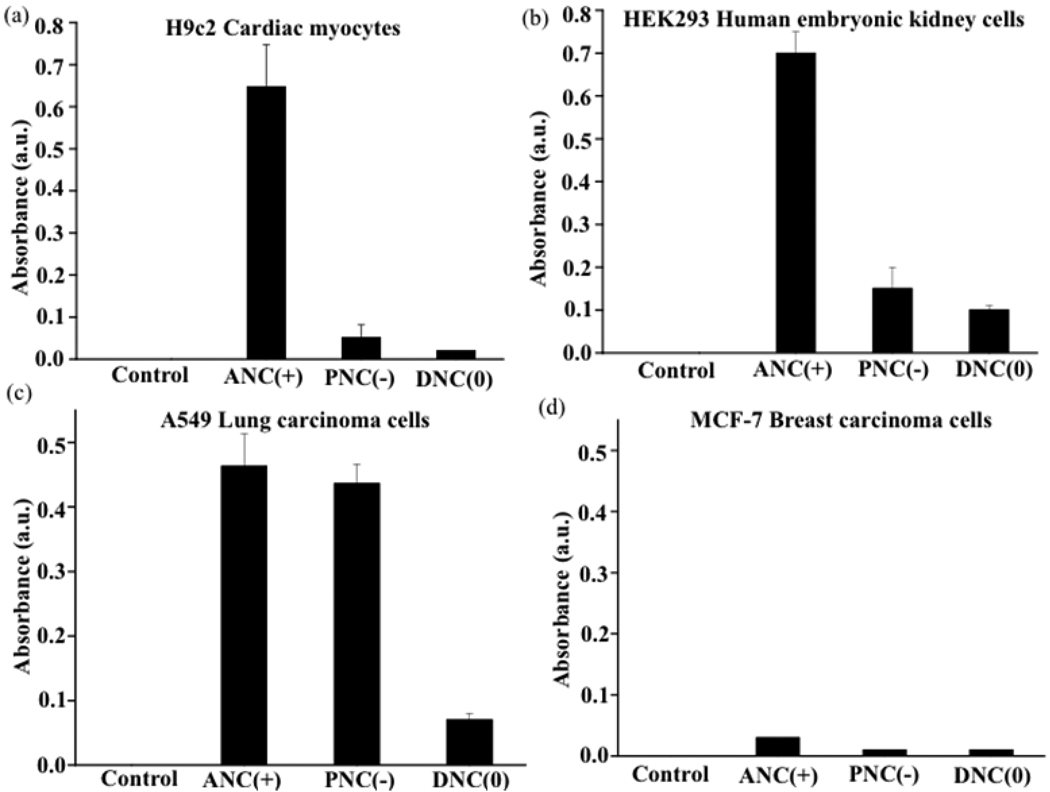
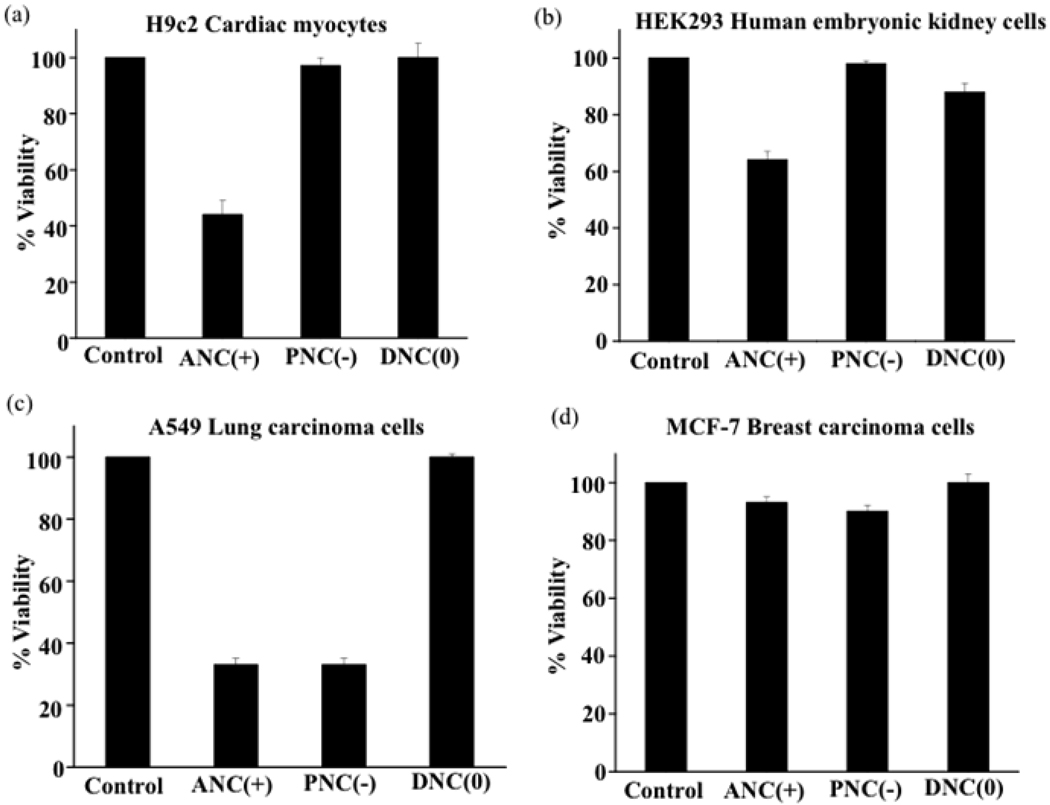
In order to determine if the surface-charge-dependent internalization and intracellular (lysosomal vs cytoplasmic) localization of the polymeric nanoceria plays a role in the nanoparticle’s cytotoxicity, cell viability (MTT) assays were performed. Interestingly, we found that DNC(0) did not exhibit any toxicity to the cell lines studied (Figure 8), as most of these nanoparticles localized to the cytoplasm. Furthermore, prolonged incubation of these cell lines with the dextran-coated-nanoceria did not affect cell morphology and proliferation ability as previously reported.17 In contrast, ANC(+) and PNC(−) had different degrees of toxicity, depending on the nanoparticle’s localization inside the cell. For instance, the PNC(−) nanoparticles were not toxic to the H9c2 cardiac myocytes or the HEK293 kidney cells (Figure 8a and 8b), whereas they were toxic to the A549 lung carcinoma cells (Figure 8c). This can be explained by the minimal uptake of PNC(−) by normal cells, as opposed to the A549 cancer cells that exhibited enhanced nanoparticle uptake and localization to the lysosomes (Figure 5d–5f and Figure 7c). ANC(+) also exhibited various degrees of toxicity. Notably, these nanoparticles were more toxic to H9c2, A549 and HEK 293 cells, since these cells exhibited increased nanoparticle internalization and lysosomal localization. Interesitingly the breast cancer cells (MCF-7) did not show any toxicity after treatment with any of the nanoparticles studied, since these cells did not show any significant nanoparticle uptake. Incubation of the H9c2 and A549 cells with ANC(+) in the presence of inhibitors of endocytic pathway (2-deoxyglucose and sodium azide) abrogated the nanoparticle’s cytotoxicity (Figure 9a and 9b), confirming that an endocytic uptake of these nanoparticles and eventual localization to lysosomes was responsible for their cellular toxicity. Taken together, these results demonstrate that localization of nanoceria into lysosomes (an acidic cell compartment), as opposed to localization into the cytoplasm, leads to cytotoxicity by activating the oxidase activity of nanoceria within these organelles.
Figure 8.
Cytotoxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. MTT assays show that the ANC(+) is cytotoxic to all cell lines except for the breast carcinoma cells. PNC(−) is only cytotoxic to A549 lung cancer cells as they internalize and localize into the lysosomes of these cells. DNC(0) does not show any toxicity to any of the cell lines.
Figure 9.
Cytotoxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in the presence of endocytosis inhibitors. Nanoparticles are not cytotoxic to either lung carcinoma or cardiac myocytes in presence of 2-deoxyglucose and sodium azide.
Comparison of the toxicity of surface-charge-engineered nanoceria and iron oxide nanoparticles
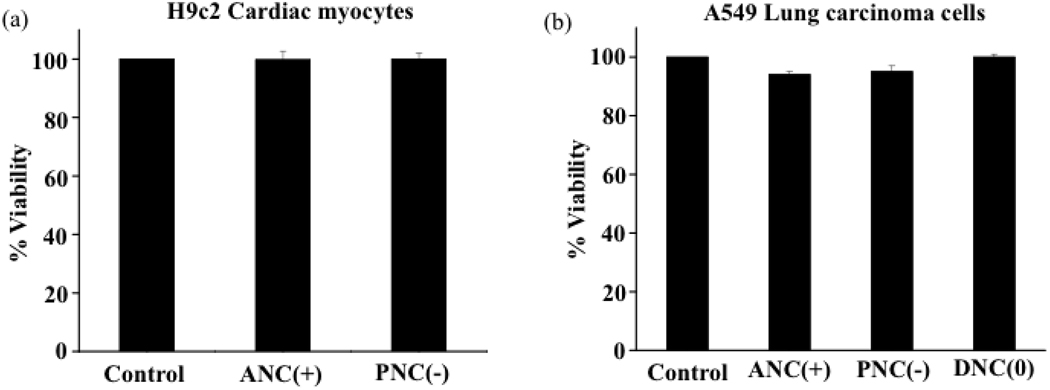
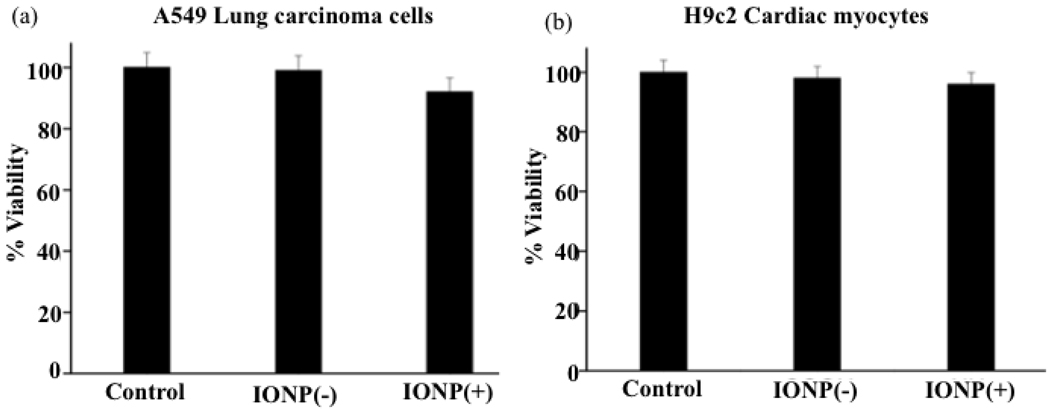
To demonstrate that the observed cytotoxicity of nanoceria is attributed to the cerium oxide core (oxidase activity) and not to the nature of the polymeric coating, we performed experiments with DiI-labeled-aminated polyacrylic acid [IONP(+)] and DiI-labeled carboxylated polyacrylic acid [IONP(−)] coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles have been widely used in various applications, particularly in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with minimal toxicity. For instance, various preparations of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles are used in the clinic for liver and lymph node metastasis imaging.27–29 Confocal microscopy studies of A549 and H9c2 cells incubated with these nanoparticles showed that IONP(+) were uptaken by the A549 lung carcinoma cells and H9c2 cardiac myocytes (Figure 10a and 10c), with a more punctuated internalization in the H9c2 cells, indicating lysosomal localization. In contrast, IONP(−) were not internalized by both cells (Figure 10b and 10d). As expected, the polymeric iron oxide nanoparticles [IONP(+) and IONP(−)] were not toxic to either the non-transformed H9c2 cell line or the transformed A549 carcinoma cell line (Figure 11a and 11b). The fact that more of the IONP(+) nanoparticles were localized into the lysosomes upon internalization in H9c2 did not seem to significantly alter the toxicity profile of the polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. These results are not surprising, as iron oxide nanoparticles do not possess oxidase activity, particularly at the low pH of the lysosomes. Therefore, we can conclude that the intrinsic oxidase behavior of cerium oxide nanoparticles is responsible for the nanoparticle’s cytotoxicity, particularly when they localize into acidic cell compartments such as lysosomes. Cytotoxicity experiments with the neutral dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles were not performed since it is well established that these nanoparticles are non-toxic.27–29
Figure 10.
Uptake of polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles [IONP(−)] and aminated polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles [IONP(+)] by A549 and H9c2 cells. Confocal images of A549 and H9c2 cells after treatment with positively charged IONP(+) for 3 h show significant uptake of the nanoparticles (a and c). Meanwhile, no uptake of the negatively charged IONP(−) was observed in either A549 or H9c2 cells (b and d).
Figure 11.
Cytotoxicity of polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles [IONP(−)] and aminated polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles [IONP(+)] by A549 and H9c2 cells.
Discussion
The toxicity of nanomaterials depends on various factors, including the nature and chemical composition of the nanoparticle's core, mode of synthesis, size, shape and crystallinity, surface reactivity, solubility in aqueous media and degree of aggregation.8,24 Although efforts have been made to study the effect of the polymeric surface coating and surface charge on the uptake, localization and toxicity of nanomaterials, the mechanistic implications are still not completely understood. This is highly important as some nanomaterials, such as cerium oxide, may display either a beneficial (antioxidant) or toxic (oxidant) effect, depending on the pH of the compartment where they localize inside the cell. Here, we have shown that polymer-coated nanoceria displays different levels of toxicity, depending upon cellular uptake and subsequent subcellular localization. We have found that when polymer-coated nanoceria internalize and localize in the lysosomes, it becomes toxic due to the acidic microenvironment of these organelles, which activates the oxidase activity of nanoceria (Scheme 2). However, lower toxicity is observed when polymer-coated nanoceria localize into the cytoplasm of cells and when is not internalized by the cells. Our results also show that the internalization, eventual localization and cytotoxicity of polymer-coated nanoceria within the cell greatly depend on the surface charge of the polymeric coating and the type of cell (cancerous vs normal). For instance, we have found that the aminated nanoceria [ANC(+)] were toxic to most of the cancer and normal cell lines studied, as these nanoparticles were uptaken and localized mostly into the lysosomes. This might indicate that nanoceria’s intrinsic oxidant behaviour at acidic pH is responsible for the observed cytotoxic of the cationic polymer-coated nanoparticles [ANC(+)]. Meanwhile, PNC(−) internalized mostly into the A549 lung carcinoma cells but not significantly into any of the other cell lines studied. This observation is corroborated by the fact that no lysosomal localization and therefore no toxicity is observed in MCF-7, H9c2 or HEK293 cells treated with PNC(−). In contrast, significant lysosomal localization and cytotoxicity is observed in the A549 cells treated with PNC(−). Surprisingly, distinct changes in cellular uptake were observed with the dextran-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles [DNC(0)]. A very disperse and diffused intracellular distribution was seen in all cell lines (cancer and normal) exposed to DNC(0), with very few of the DNC(0) localizing into the lysosomes. Therefore, the neutral DNC (0) nanoparticles were found to be non toxic to any of the cell lines studied as they localize primarily in the cytoplasm. This suggests that the observed non-toxic behavior of DNC(0) might be attributed to its significantly low entrapment into lysosomes, contrary to ANC(+). Based on these results, DNC(0) would be a great platform for further development of therapeutic antioxidant nanoagents, as they exhibit minimal toxicity. In addtion, they can be effectively used in radiation therapy, since they are not toxic to normal cells. Also, as other dextran-coated nanoparticles have been found to have long circulation time, 27–29 similarly dextran-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles can be employed as long circulating antioxidant nanoagents.
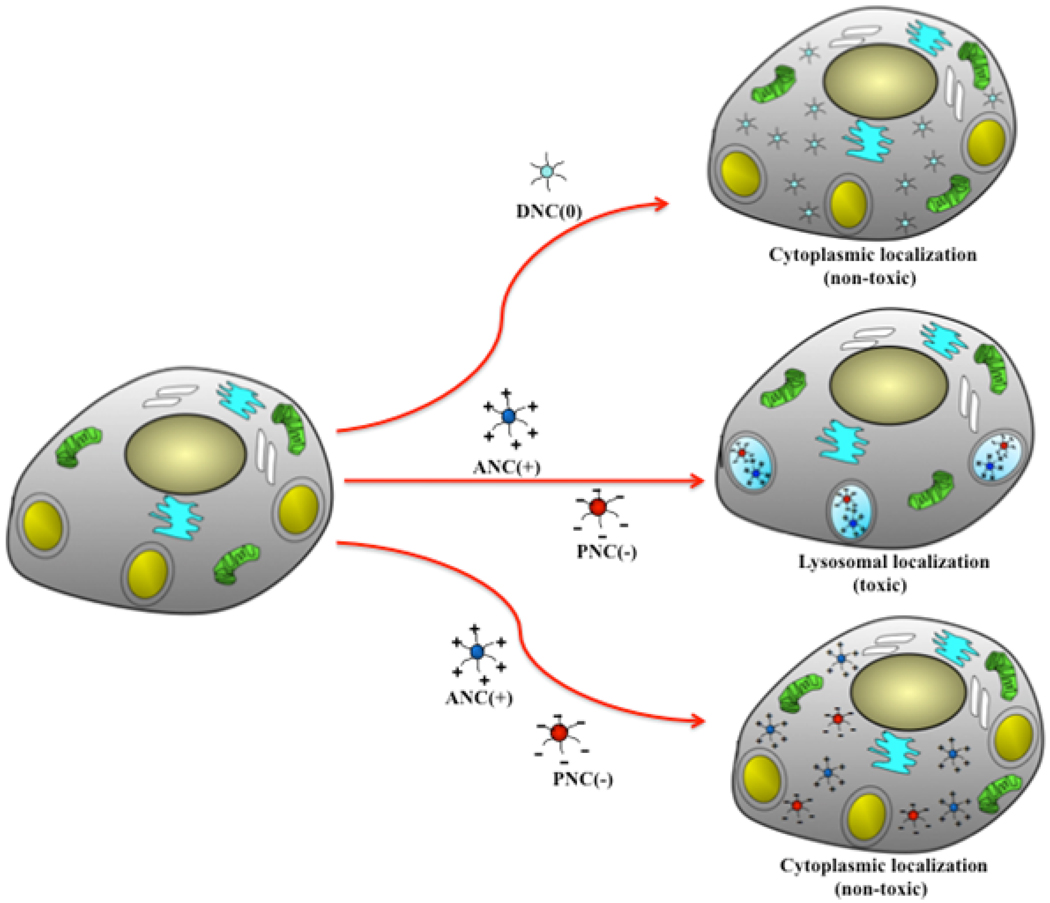
Scheme 2.
Polymer-coated nanoceria’s cell internalization, localization and proposed toxicity mechanism. Neutral DNC(0) internalized and localized mostly into the cytoplasm of cells and hence it is not cytotoxic. ANC(+) and PNC(−) can localize either into the cytoplasm or the lysosomes, depending on the type of cells. When the nanoceria localized to the lysosome, the low pH of this organelle activates the nanoparticle’s oxidase-like activity, exhibiting toxicity. ANC(−) or PNC(+) that localized into the cytoplasm displayed no cytotoxicity.
Another factor, which may contribute to the cytotoxic behavior of polymer-coated nanoceria is the type of cell line used and pH of the cell’s microenvironment.30–33 This is particularly relevant as tumor progression, increased invasion, metastasis and acidic tumor environment have been found to be interrelated.34–36 Differences between normal and tumor tissue and tumor-to-tumor variation may play a key role in dictating the antioxidant vs oxidase behavior of the polymer-coated nanoceria. Previously, we have reported that polymer-coated nanoceria displays unique oxidase-like behavior at slightly acidic pH.22 Therefore, in view of this oxidase-like property at acidic pH, intracellular distribution of the polymer-coated nanoceria into the lung carcinoma’s lysosomes may be the reason for these nanoparticles’ cytotoxicity. In addition, as A549 lung carcinoma cells and most tumors have been found to have upregulated glycolysis and increased lactic acid production,30–33 this effect might further contribute towards the built up of an acidic microenvironment, favoring nanoceria’s oxidase activity and therefore sensitizing tumors towards radiation therapy. In summary, we believe that understanding the role of the polymer-coated nanoceria’s surface charge and the influence that it has in the cell internalization, subcellular distribution and differential antioxidant/oxidant activity will shed new light in delineating the mechanisms that lead to nanoceria’s toxicity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Synthesis of polymer-coated nanoceria preparations [DNC(0), PNC(−) and ANC(+)]
The polymer coated nanoceria preparations, DNC(0) and PNC(−) were synthesized using the methodology described previously.22 Briefly, a solution of cerium (III) nitrate (2.17 g, 1.0 M, Aldrich, 99%) in water (5.0 mL) was mixed separately with an aqueous solution of either polyacrylic acid (PAA, 0.5 M, Sigma) or dextran (1.0 M, Sigma) and mixed it thoroughly using a vortex mixer. The resulting mixture was then added to an ammonium hydroxide solution (30.0 mL, 30%, Sigma Aldrich) under continuous stirring for 24 h at room temperature. The preparation was then centrifuged at 4000 rpm for two 30-minutes cycles to settle down any debris and large agglomerates. The supernatant solution was then purified from free polymers and other reagents and then concentrated using a 30K Amicon cell (Millipore Inc.). ANC(+) was synthesized directly from PNC(−). In this method, PNC(−) (5.0 mL, 1.5 mg/mL) was treated with EDC [1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide] solution (28.0 mg, 30 mmol) in MES buffer (500 µL, 0.1 M, pH 6.0) followed by the drop-wise addition of N-Hydroxy succinamide (NHS) solution (22.0 mg, 30 mmol) in MES buffer (500 µL, 0.1 M, pH 6.0) and incubated for 3 minutes at room temperature. Ethylenediamine (EDA, 10 mg, 25 mmol) in DMSO (100 µL) was then added drop-wise to the final reaction mixture and stirred for an additional 3 h at room temperature. The resulting solution was purified to remove excess EDA and other reagents using an Amicon dialysis membrane (MWCO 30K) from Millipore. The final ANC(+) preparation (1.5 mg/mL) in DI water was stored in the refrigerator for further characterization.
DiI encapsulation in polymer-coated nanoceria [DNC(0), PNC(−) and ANC(+)]
In order to encapsulate the DiI dye (Invitrogen) into the polymeric matrix of the various polymer-coated nanoceria, we have used a modified solvent diffusion method, as reported previously.23 Briefly, to 4.0 mL of the nanoparticle solution [1.5 mg/mL, DNC(0), PNC(−) or, ANC(+)], 200.0 µL of DiI solution [6.0 µL of DiI (10 mg/mL) in 194 µL of DMSO] was added drop-wise while mixing (1000 rpm) at room temperature. Afterwards, the preparation was dialyzed (MWCO: 30K) against deionized water to remove any free DiI, and finally was dialyzed overnight in phosphate-buffered saline (1X PBS) to reconstitute the final preparation in PBS.
Characterization
The various polymer-coated nanoceria preparations were charecterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to confirm the size of the nanocrystal core. TEM was performed by mounting a drop of nanoparticles on a holey carbon-coated copper 400-mesh grid (2SPI, USA) and images were taken on a FEI TECNAI F30 microscope operating at 300 kV. Surface charge on the nanoparticle was confirmed by zeta potential measurements (Malvern Zetasizer and disposable zeta cells). FT-IR experiments were performed on vacuum-dried samples to verify the surface functionalities on the nanoparticles (Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100 FT-IR spectrometer). Fluorescence spectroscopy studies were done on DiI-labeled nanoceria using a Nanolog HORIBA JOBIN YVON Spectrometer to confirm the DiI dye encapsulation in the nanoparticles.
Cell culture
All cell lines in this study [lung carcinoma (A549), cardiac myocytes (H9c2), human embryonic kidney (HEK293) and breast carcinoma (MCF-7)] were obtained from ATCC. The cardiomyocytes were grown in Eagle’s Minimal Essential medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10%), sodium pyruvate, L-glutamine, penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin B and non-essential amino acids. HEK293 cells were grown in Eagle’s Minimal Essential medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10%) and 1% penicillin. The lung cancer cells were grown in Kaighn’s modification of Ham’s F12 medium (F12K) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum, L-glutamine, streptomycin, amphotericin B and sodium bicarbonate. All cell lines were maintained at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. MCF-7 cells were grown in Eagle’s Minimal Essential medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10%) with 0.01 mg/mL bovine insulin and 1% penicillin.
Cellular uptake of polymer-coated nanoceria [DNC(0), PNC(−) and ANC(+)]
10,000 cells (cardiomyocytes, human embryonic kidney cells, lung carcinoma cells and breast carcinoma cells) were seeded in petri dishes and incubated with DiI-labeled-DNC(0), DiI-labeled-PNC(−) and DiI-labeled-ANC(+) (1.0 mM), for 3 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. Then, the cells were washed with 1X PBS and fixed with 10% formalin in 1X PBS. Afterwards, the cells were incubated with DAPI (1 mg/mL, Molecular Probes) for 10 minutes. Then the cells were washed and visualized with a confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 510).
Inhibition of cellular uptake of the polymer-coated nanoceria
For these studies, 10,000 cells (H9c2 and A549) were treated with the inhibitors sodium azide (10 mM) and 2-deoxyglucose (50 mM) for 30 minutes. Then, the cells were incubated with DiI-labeled PNC(−) and DiI-labeled ANC(+) preparations (1.0 mM) for 3 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. Fixation and subsequent staining with DAPI were performed as described above. Experiments were done at 4 °C incubating the cells with the DiI-labeled PNC(−) and DiI-labeled ANC(+) prepartions (1.0 mM) for 3 h.
Lysosomal staining
After treatment of the corresponding cell lines with DiI-labeled-DNC(0), DiI-labeled-PNC(−) and DiI-labeled-ANC(+) for 3 h, cells were washed and incubated for 20 minutes with Lysotracker (Invitrogen) (35 nM) at 37°C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. Fixation procedures were performed as stated before.
Lysosomal isolation and oxidase-activity determination of entrapped nanoceria
Lysosome were isolated using a previously reported procedure described by Schroter et al.37 10,000 cells (cardiomyocytes, human embryonic kidney cells, lung carcinoma cells and breast carcinoma cells) were seeded in petri dishes and incubated with ANC(+), PNC(−) and DNC(0) (1.0 mM) for 3 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. Then, the cells were washed with 1X PBS, trypsinized and centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 8 minutes. In order to isolate the lysosomes, cells were resuspended in an isotonic sucrose solution (1.0 mL, 0.08 M CaCl2, 0.25 M sucrose, 10 mM Tris-HCl) to lyse the cells into cytosolic and organelles fractions and centrifuged at 25,000g for 15 minutes. Subsequently, the supernatant was carefully removed, and the pellet was resuspended in 1.0 mL 150 mM KCl (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4) followed by centrifugation at 25,000g for 15 minutes to sediment the lysosomes. The pellet containing the lysosomes was resuspended in 200 µL of TMB (1.0 mg/mL) and incubated overnight at room temperature. After the incubation period, the absorbance at 652 nm of the lysosome suspension was recorded.
Cell viability assays
Cells (cardiomyocytes, human embryonic kidney cells, lung carcinoma cells and breast carcinoma cells) were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 3,000 cells per well and incubated with ANC(+), PNC(−) and DNC(0) (1.0 mM) for 3 h. Then, 0.5 mM of MTT [3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] (Sigma) was added, followed by incubation for 24 h. After 24 h, the resulting crystals were dissolved in 40 µL of acidified isopropanol and the absorbance at 570 nm was recorded using a plate reader (Bio-TEK, Synergy HT Multidetection Microplate reader).
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (CA10178) and UCF-NSTC Start Up Fund, all to J. M. P. The HEK293 cells and MCF-7 were generous gifts from Dr. Antonis Zervos and Dr. James Turkson, respectively (UCF School of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine).
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available:
Dynamic light scattering measurements of DNC(0), PNC(−) and ANC(+) (Figure S1). DiI-labeled cerium oxide nanoparticles colocalization studies with the lysotracker green dye (Figure S2 and Figure S3). This materials is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
REFERENCES
- 1.Weissleder R. Molecular Imaging in Cancer. Science. 2006;312:1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.1125949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rosi NL, Giljohann DA, Thaxton CS, Lytton-Jean AKR, Han MS, Mirkin CA. Oligonucleotide-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for Intracellular Gene Regulation. Science. 2006;312:1027–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.1125559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lewin M, Carlesso N, Tung CH, Tang XW, Cory D, Scadden DT, Weissleder R. Tat peptide-derivatized Magnetic Nanoparticles allow In vivo Tracking and Recovery of Progenitor Cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:410–414. doi: 10.1038/74464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.George S, Pokhrel S, Xia T, Gilbert B, Ji ZX, Schowalter M, Rosenauer A, Damoiseaux R, Bradley KA, Nel AE et al. Use of a Rapid Cytotoxicity Screening Approach To Engineer a Safer Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle through Iron Doping. ACS Nano. 2010;4:15–29. doi: 10.1021/nn901503q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xia TA, Kovochich M, Liong M, Meng H, Kabehie S, George S, Zink JI, Nel AE. Polyethyleneimine Coating Enhances the Cellular Uptake of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Allows Safe Delivery of siRNA and DNA Constructs. ACS Nano. 2009;3:3273–3286. doi: 10.1021/nn900918w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roiter Y, Ornatska M, Rammohan AR, Balakrishnan J, Heine DR, Minko S. Interaction of Nanoparticles with Lipid Memberane. Nano Lett. 2008;8:941–944. doi: 10.1021/nl080080l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vallhov H, Gabrielsson S, Stromme M, Scheynius A, Garcia-Bennett AE. Mesoporous Silica Particles Induce Size Dependent Effects on Human Dendritic Cells. Nano Lett. 2007;7:3576–3582. doi: 10.1021/nl0714785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nel AE, Madler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EM, Somasundaran P, Klaessig F, Castranova V, Thompson M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat Mater. 2009;8:543–557. doi: 10.1038/nmat2442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schanen BC, Karakoti AS, Seal S, Drake DR, 3rd, Warren WL, Self WT. Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials Provokes Inflammation of an In vitro Human Immune Construct. ACS Nano. 2009;3:2523–2532. doi: 10.1021/nn900403h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shvedova AA, Castranova V, Kisin ER, Schwegler-Berry D, Murray AR, Gandelsman VZ, Maynard A, Baron P. Exposure to Carbon Nanotube Material: Assessment of Nanotube Cytotoxicity using Human Keratinocyte Cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2003;66:1909–1926. doi: 10.1080/713853956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lam CW, James JT, McCluskey R, Hunter RL. Pulmonary Toxicity of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in Mice 7 and 90 Days After Intratracheal Instillation. Toxicol Sci. 2004;77:126–134. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfg243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ. Unique Cellular Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles: Size-dependent Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112:13608–13619. doi: 10.1021/jp712087m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hussain SM, Schlager JJ. Safety Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles: Inhalation Model for Chronic Exposure. Toxicol Sci. 2009;108:223–224. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen HHC, Yu C, Ueng TH, Chen SD, Chen BJ, Huang KJ, Chiang LY. Acute and Subacute Toxicity Study of Water-Soluble Polyalkylsulfonated C60 in Rats. Toxicol Path. 1998;26:143–151. doi: 10.1177/019262339802600117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen HHC, Yu C, Ueng TH, Liang CT, Chen BJ, Hong CC, Chiang LY. Renal Effects of Water-soluble Polyarylsulfonated C60 in Rats with an Acute Toxicity Study. Fullerene Sci Techn. 1997;5:1387–1396. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N. Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel. Science. 2006;311:622–627. doi: 10.1126/science.1114397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Perez JM, Asati A, Nath S, Kaittanis C. Synthesis of Biocompatible Dextran-coated Nanoceria with pH-dependent Antioxidant Properties. Small. 2008;4:552–556. doi: 10.1002/smll.200700824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen JP, Patil S, Seal S, McGinnis JF. Rare Earth Nanoparticles Prevent Retinal Degeneration Induced by Intracellular Peroxides. Nat Nanotecnol. 2006;1:142–150. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2006.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Niu J, Azfer A, Rogers LM, Wang X, Kolattukudy PE. Cardioprotective Effects of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in a Transgenic Murine Model of Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73:549–559. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tarnuzzer RW, Colon J, Patil S, Seal S. Vacancy Engineered Ceria Nanostructures for Protection from Radiation-induced Cellular Damage. Nano Lett. 2005;5:2573–2577. doi: 10.1021/nl052024f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Korsvik C, Patil S, Seal S, Self WT. Vacancy Engineered Ceria oxide Nanoparticles Catalyze Superoxide Dismutase Activity. Chem Commun. 2007:1056–1058. doi: 10.1039/b615134e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Asati A, Santra S, Kaittanis C, Nath S, Perez JM. Oxidase-Like Activity of Polymer-Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:2308–2312. doi: 10.1002/anie.200805279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Santra S, Kaittanis C, Grimm J, Perez JM. Drug/dye-loaded, Multifunctional Iron oxide Nanoparticles for Combined Targeted Cancer Therapy and Dual Optical/Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Small. 2009;5:1862–1868. doi: 10.1002/smll.200900389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Verma A, Stellacci F. Effect of Surface Properties on Nanoparticle-Cell Interactions. Small. 2010;6:12–21. doi: 10.1002/smll.200901158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verma A, Uzun O, Hu Y, Hu Y, Han HS, Watson N, Chen S, Irvine DJ, Stellacci F. Surface-structure-regulated Cell-membrane Penetration by Monolayer-protected Nanoparticles. Nat Mater. 2008;7:588–595. doi: 10.1038/nmat2202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hu Y, Litwin T, Nagaraja AR, Kwong B, Katz J, Watson N, Irvine DJ. Cytosolic Delivery of Membrane-impermeable Molecules in Dendritic Cells Using pH-responsive Core-shell Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2007;7:3056–3064. doi: 10.1021/nl071542i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Weissleder R. Liver MR Imaging with Iron Oxides: Toward Consensus and Clinical Practice. Radiology. 1994;193:593–595. doi: 10.1148/radiology.193.3.7972790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Harisinghani MG, Barentsz J, Hahn PF, Deserno WM, Tabatabaei S, van de Kaa CH, de la Rosette J, Weissleder R. Noninvasive Detection of Clinically Occult Lymph-Node Metastases in Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2491–2499. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Harisinghani MG, Saksena MA, Hahn PF, King B, Kim J, Torabi MT, Weissleder R. Ferumoxtran-10-enhanced MR Lymphangiography: Does Contrast-enhanced Imaging Alone Suffice for Accurate Lymph Node Characterization? Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:144–148. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouyssegur J. Hypoxia Signalling Controls Metabolic Demand. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:223–229. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim JW, Dang CV. Cancer's Molecular Sweet Tooth and the Warburg Effect. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8927–8930. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Smith-Jones PM, Solit D, Afroze F, Rosen N, Larson SM. Early Tumor Response to Hsp90 Therapy Using HER2 PET: Comparison with 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:793–796. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wu M, Neilson A, Swift AL, Moran R, Tamagnine J, Parslow D, Armistead S, Lemire K, Orrell J, Teich J, et al. A. Multiparameter Metabolic Analysis Reveals a Close Link Between Attenuated Mitochondrial Bioenergetic Function and Enhanced Glycolysis Dependency in Human Tumor Cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C125–C136. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00247.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Raghunand N, Mahoney B, van Sluis R, Baggett B, Gillies RJ. Acute Metabolic Alkalosis Enhances Response of C3H Mouse Mammary Tumors to the Weak Base Mitoxantrone. Neoplasia. 2001;3:227–235. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rofstad EK, Mathiesen B, Kindem K, Galappathi K. Acidic Extracellular pH Promotes Experimental Metastasis of Human Melanoma Cells in Athymic Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6699–6707. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stubbs M, McSheehy PM, Griffiths JR. Causes and Consequences of Acidic pH in Tumors: A Magnetic Resonance Study. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1999;39:13–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(98)00018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schroter CJ, Braun M, Englert J, Beck H, Schmid H, Kalbacher H. A Rapid Method to Separate Endosomes from Lysosomal Contents Using Differential Centrifugation and Hypotonic Lysis of Lysosomes. J Immunol Methods. 1999;227:161–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(99)00079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.