Abstract
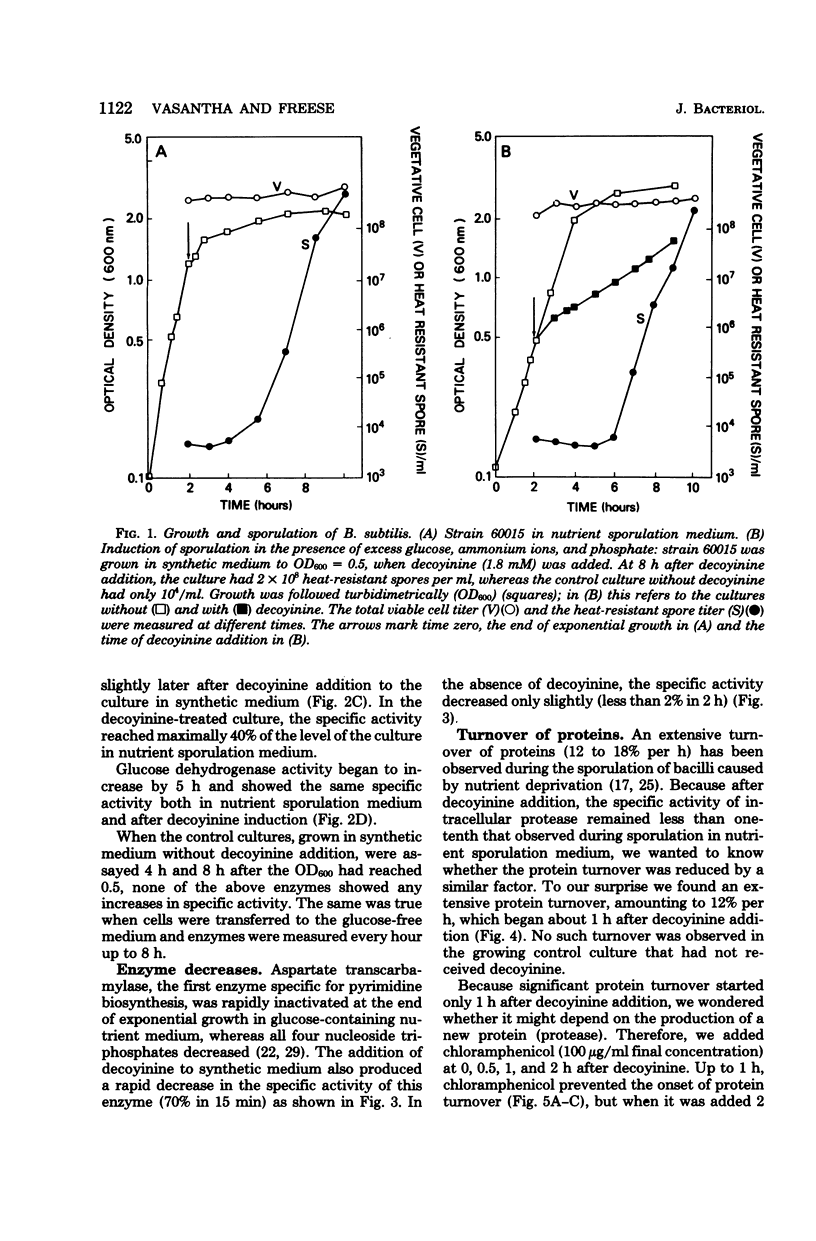
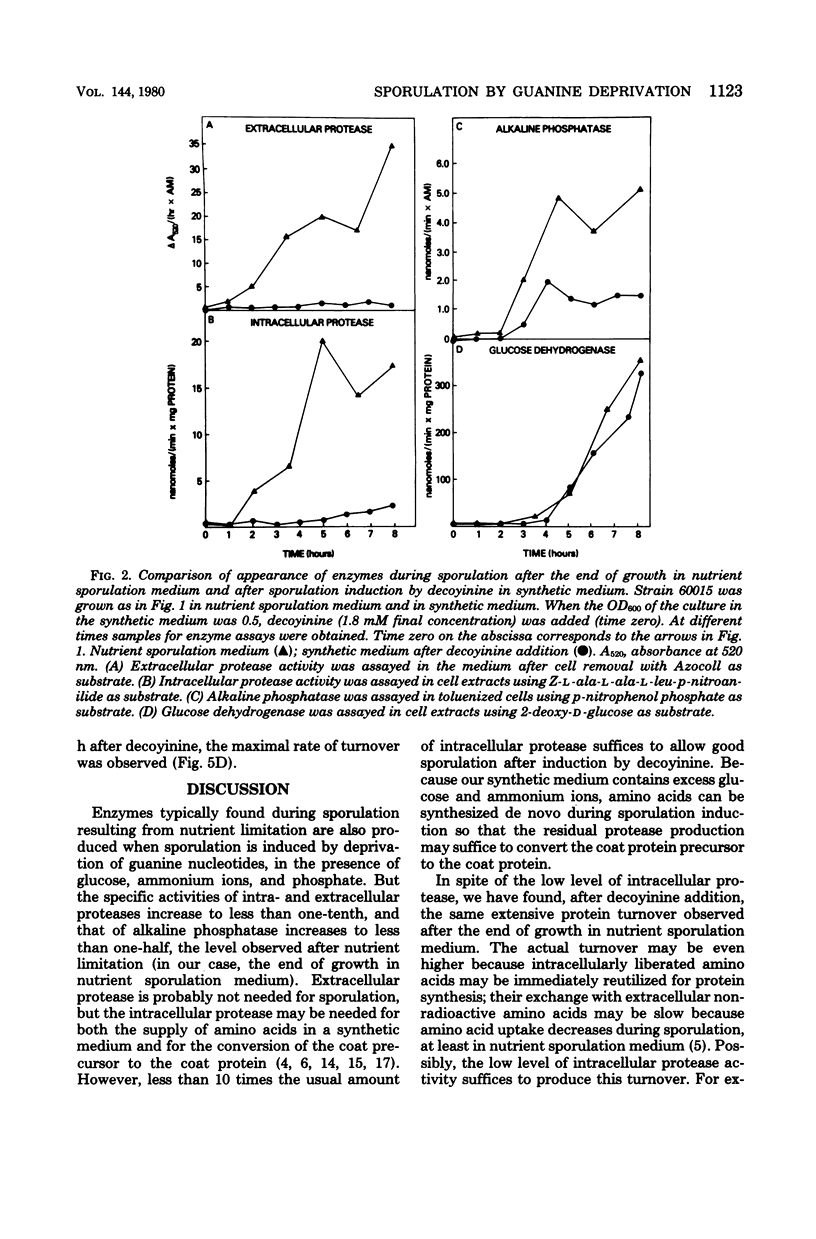
When sporulation is initiated by nutrient limitation, e.g., at the end of growth, certain biochemical processes occur in sequence. To determine which of these processes occur, even when the cells sporulate in the presence of a rapidly metabolizable carbon source, we induced sporulation of Bacillus subtilis by deprivation of guanine nucleotides, in a synthetic medium containing excess glucose, ammonium ions, and phosphate. The deprivation was produced either by decoyinine addition to a standard strain or by guanosin limitation of a guanine auxotroph. At 1 h after the onset of this deprivation, an extensive turnover of proteins began whose appearance was chloramphenicol sensitive. At least one enzyme (aspartate transcarbamylase) lost 70% of its activity within 15 min, indicating its rapid destruction. Whereas the magnitude of the above two changes was similar to that observed during sporulation at the end of growth in nutrient sporulation medium, protease (intracellular and extracellular) increased to less than one-tenth of the specific activity in nutrient sporulation medium, and alkaline phosphatase increased to less than one-half. However, glucose dehydrogenase, an enzyme made only in forespores, increased to the same specific activity under both conditions, presumably because the forespore compartment is protected from media (e.g., glucose) influences by the double membrane (two bilayers with opposite polarity).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernlohr R. W., Clark V. Characterization and regulation of protease synthesis and activity in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):276–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.276-283.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Aronson A. I. Alterations of spore coat processing and protein turnover in a Bacillus cereus mutant with a defective postexponential intracellular protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1254–1258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney P. H., Whiteman P. F., Freese E. Media dependence of commitment in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):901–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.901-907.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. B., Vasantha N., Freese E. Induction of sporulation in developmental mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 16;170(1):67–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00268581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Heinze J. E., Galliers E. M. Partial purine deprivation causes sporulation of Bacillus subtilis in the presence of excess ammonia, glucose and phosphate. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Nov;115(1):193–205. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. Sporulation of bacilli, a model of cellular differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:85–124. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Ramaley R., Freese E. Location and properties of glucose dehydrogenase in sporulating cells and spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):282–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.282-293.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J. H., Carlton B. C. Effects of mutational loss of specific intracellular proteases on the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.612-617.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjan P., Keryer E., Szulmajster J. Characterization of a thermosensitive sporulation mutant of Bacillus subtilis affected in the structural gene of an intracellular protease. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):353–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. M., Marks C. L., Freese E. The decrease of guanine nucleotides initiates sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 4;587(2):238–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. M., Uratani-Wong B., Freese E. Catabolite repression of enzyme synthesis does not prevent sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1447–1449. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1447-1449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Brabson J. S., Switzer R. L. Immunochemical studies of the inactivation of aspartate transcarbamylase by stationary phase Bacillus subtilis cells. Evidence for selective, energy-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5585–5593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Switzer R. L. Aspartate transcarbamylase synthesis ceases prior to inactivation of the enzyme in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):943–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.943-951.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani T., Heinze J. E., Freese E. Induction of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis by decoyinine or hadacidin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1118–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego C., Kerjan P., Manca de Nadra M. C., Szulmajster J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in a thermosensitive sporulation mutant (ts-4) of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):636–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.636-647.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germaination. VII. Protein turnover during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4600–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strongin A. Y., Izotova L. S., Abramov Z. T., Gorodetsky D. I., Ermakova L. M., Baratova L. A., Belyanova L. P., Stepanov V. M. Intracellular serine protease of Bacillus subtilis: sequence homology with extracellular subtilisins. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1401-1411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Freese E. The role of manganese in growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):329–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waindle L. M., Switzer R. L. Inactivation of aspartic transcarbamylase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis: demonstration of a requirement for metabolic energy. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):517–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.517-527.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Deans J. A., Ellar D. J. Biochemical evidence for the reversed polarity of the outer membrane of the bacterial forespore. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):561–569. doi: 10.1042/bj1520561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


