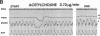Abstract
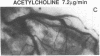
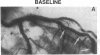
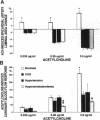
The effects of age, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia on vascular function of the coronary circulation were studied by subselective intracoronary infusions of acetylcholine, which releases endothelium-derived relaxing factor, and papaverine, which directly relaxes vascular smooth muscle, in normal patients (n = 18; no risk factors for coronary artery disease), in patients with evidence of early atherosclerosis but normal cholesterol levels and normal blood pressure (n = 12), in patients with hypertension without left ventricular hypertrophy (n = 12), and in patients with hypercholesterolemia (n = 20). Papaverine-induced maximal increases in coronary blood flow were significantly greater in normals, but no differences were noted between the groups of patients with early atherosclerosis, with hypertension, and with hypercholesterolemia. The capacity of the coronary system to increase blood flow in response to acetylcholine was similar in normal and normocholesterolemic patients with epicardial atherosclerosis and/or hypertension but was significantly impaired in patients with hypercholesterolemia, irrespective of evidence of epicardial atherosclerotic lesions. Age (r = -0.62, P < 0.0001) and total serum cholesterol levels (r = -0.70; P < 0.0001) were the only significant independent predictors of a blunted coronary blood flow response to acetylcholine. Thus, hypercholesterolemia and advanced age selectively impair endothelium-mediated relaxation of the coronary microvasculature in response to acetylcholine, whereas endothelial dysfunction is restricted to epicardial arteries in age-matched normocholesterolemic patients with evidence of coronary atherosclerosis and/or hypertension.
Full text
PDF



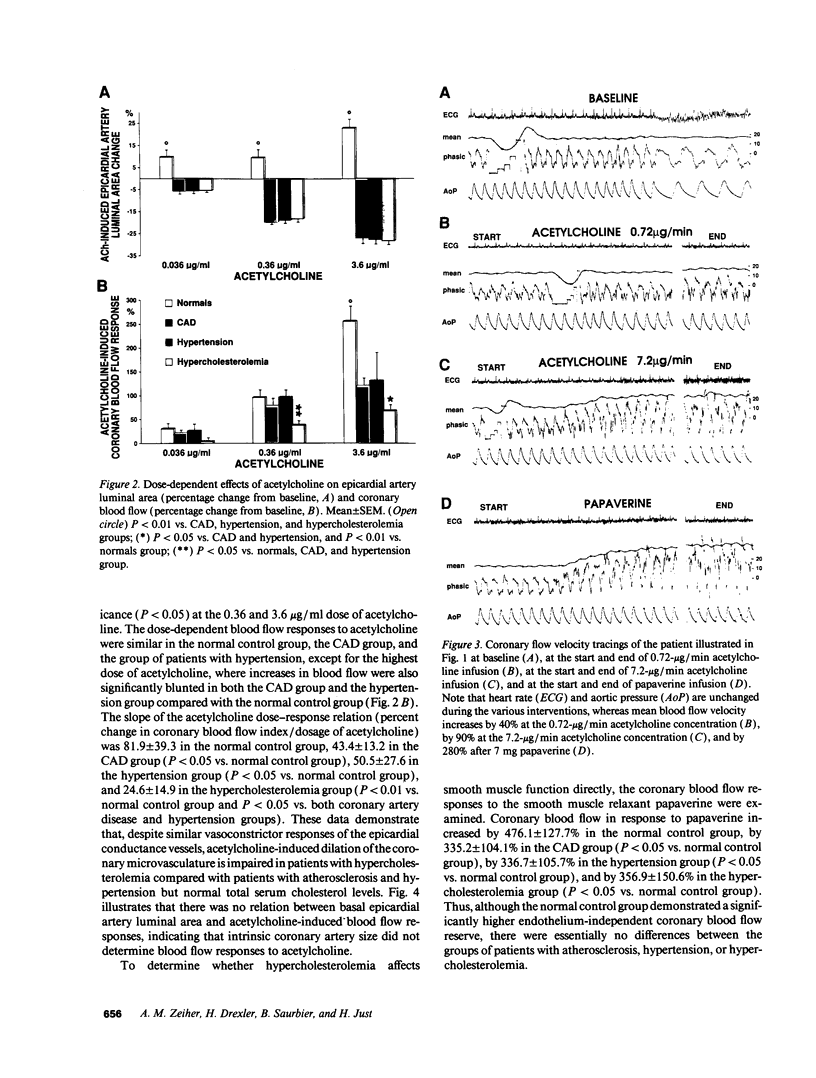
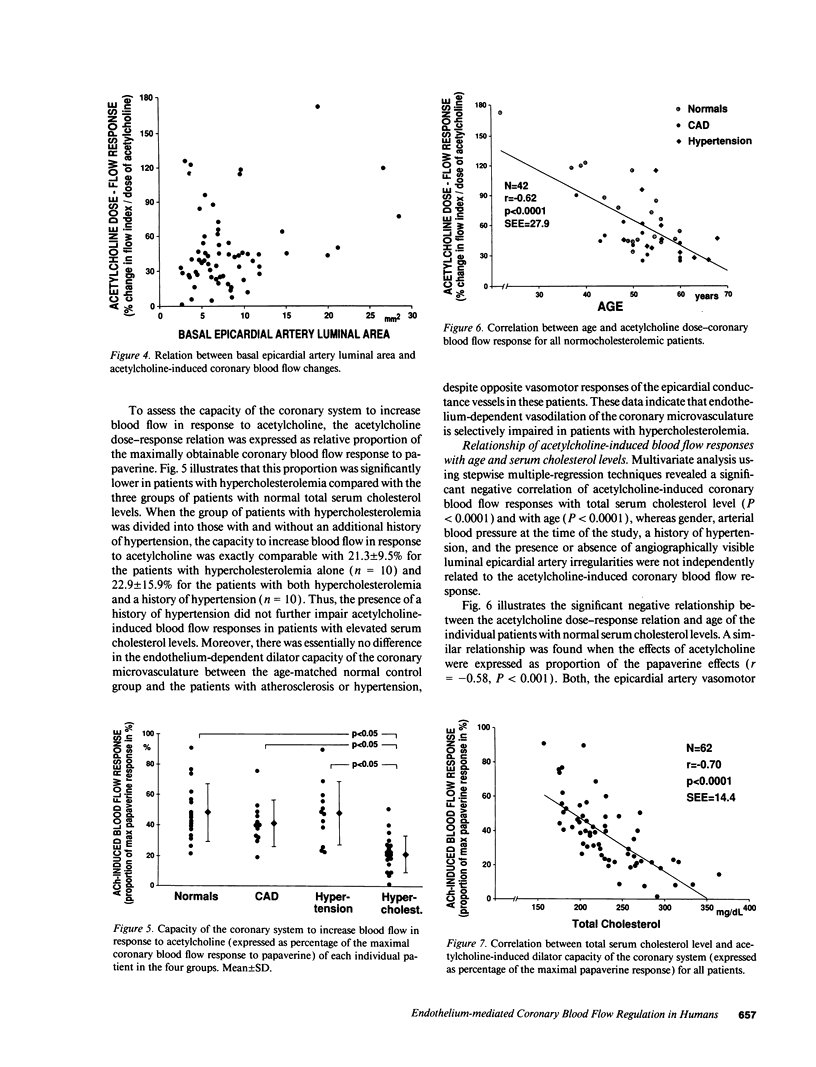





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassenge E., Busse R. Endothelial modulation of coronary tone. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;30(5):349–380. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(88)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C. The microcirculation in coronary ischemia. Are native anticoagulant mechanisms a path to new therapies? Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):439–441. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossaller C., Habib G. B., Yamamoto H., Williams C., Wells S., Henry P. D. Impaired muscarinic endothelium-dependent relaxation and cyclic guanosine 5'-monophosphate formation in atherosclerotic human coronary artery and rabbit aorta. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):170–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI112779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Advanced glycosylation products quench nitric oxide and mediate defective endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):432–438. doi: 10.1172/JCI115014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. O., 3rd, Schenke W. H., Leon M. B., Rosing D. R., Urqhart J., Epstein S. E. Limited coronary flow reserve after dipyridamole in patients with ergonovine-induced coronary vasoconstriction. Circulation. 1987 Jan;75(1):163–174. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester A. H., O'Neil G. S., Moncada S., Tadjkarimi S., Yacoub M. H. Low basal and stimulated release of nitric oxide in atherosclerotic epicardial coronary arteries. Lancet. 1990 Oct 13;336(8720):897–900. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92269-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilian W. M., Eastham C. L., Marcus M. L. Microvascular distribution of coronary vascular resistance in beating left ventricle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 2):H779–H788. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.4.H779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. P., Rossitch E., Jr, Andon N. A., Loscalzo J., Dzau V. J. Flow activates an endothelial potassium channel to release an endogenous nitrovasodilator. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1663–1671. doi: 10.1172/JCI115481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. P., Stamler J., Andon N., Davies P. F., McKinley G., Loscalzo J. Flow stimulates endothelial cells to release a nitrovasodilator that is potentiated by reduced thiol. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H804–H812. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creager M. A., Cooke J. P., Mendelsohn M. E., Gallagher S. J., Coleman S. M., Loscalzo J., Dzau V. J. Impaired vasodilation of forearm resistance vessels in hypercholesterolemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):228–234. doi: 10.1172/JCI114688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohi Y., Thiel M. A., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Activation of endothelial L-arginine pathway in resistance arteries. Effect of age and hypertension. Hypertension. 1990 Aug;16(2):170–179. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H., Zeiher A. M., Meinzer K., Just H. Correction of endothelial dysfunction in coronary microcirculation of hypercholesterolaemic patients by L-arginine. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1546–1550. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H., Zeiher A. M., Wollschläger H., Meinertz T., Just H., Bonzel T. Flow-dependent coronary artery dilatation in humans. Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):466–474. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Safar M. E. Large conduit arteries in hypertension: role of the vascular renin-angiotensin system. Circulation. 1988 May;77(5):947–954. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.5.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of canine coronary smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangos J. A., Eskin S. G., McIntire L. V., Ives C. L. Flow effects on prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1477–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.3883488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiman P. C., Mitchell G. G., Heistad D. D., Armstrong M. L., Harrison D. G. Atherosclerosis impairs endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation to acetylcholine and thrombin in primates. Circ Res. 1986 Jun;58(6):783–789. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girerd X. J., Hirsch A. T., Cooke J. P., Dzau V. J., Creager M. A. L-arginine augments endothelium-dependent vasodilation in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Circ Res. 1990 Dec;67(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.6.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golino P., Piscione F., Willerson J. T., Cappelli-Bigazzi M., Focaccio A., Villari B., Indolfi C., Russolillo E., Condorelli M., Chiariello M. Divergent effects of serotonin on coronary-artery dimensions and blood flow in patients with coronary atherosclerosis and control patients. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 7;324(10):641–648. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103073241001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib J. B., Bossaller C., Wells S., Williams C., Morrisett J. D., Henry P. D. Preservation of endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in cholesterol-fed rabbit by treatment with the calcium blocker PN 200110. Circ Res. 1986 Feb;58(2):305–309. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. M., Marshall J. J. Direct vasoconstriction and endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Mechanisms of acetylcholine effects on coronary flow and arterial diameter in patients with nonstenotic coronary arteries. Circulation. 1989 May;79(5):1043–1051. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.5.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Harbison R. G., Wood K. S., Kadowitz P. J. Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from intrapulmonary artery and vein: stimulation by acetylcholine, bradykinin and arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakody L., Senaratne M., Thomson A., Kappagoda T. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in experimental atherosclerosis in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1987 Feb;60(2):251–264. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz M. A., Lamping K. G., Bates J. N., Eastham C. L., Marcus M. L., Harrison D. G. Mechanisms responsible for the heterogeneous coronary microvascular response to nitroglycerin. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):847–855. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder L., Kiowski W., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Indirect evidence for release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in human forearm circulation in vivo. Blunted response in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1990 Jun;81(6):1762–1767. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.6.1762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludmer P. L., Selwyn A. P., Shook T. L., Wayne R. R., Mudge G. H., Alexander R. W., Ganz P. Paradoxical vasoconstriction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1046–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. L., Chilian W. M., Kanatsuka H., Dellsperger K. C., Eastham C. L., Lamping K. G. Understanding the coronary circulation through studies at the microvascular level. Circulation. 1990 Jul;82(1):1–7. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. P., Clarke J. G., Davies G. J., Kaski J. C., Haider A. W., Maseri A. Effect of intracoronary serotonin on coronary vessels in patients with stable angina and patients with variant angina. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 7;324(10):648–654. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103073241002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel L. A., Rivera L. M., Bilder G. E., Perrone M. H. Differential alteration of vascular reactivity in rabbit aorta with modest elevation of serum cholesterol. Circ Res. 1990 Sep;67(3):550–555. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Banitt P. F., Guerra R., Jr, Harrison D. G. Characteristics of canine coronary resistance arteries: importance of endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 2):H603–H610. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.2.H603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Osol G., Halpern W. Reactivity of isolated porcine coronary resistance arteries to cholinergic and adrenergic drugs and transmural pressure changes. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):741–748. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. A., Lento P. H., Siegfried M. R., Stahl G. L., Fusman B., Lefer A. M. Cardiovascular effects of acute hypercholesterolemia in rabbits. Reversal with lovastatin treatment. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):465–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI113905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. A., Siegman M. J., Sedar A. W., Mooers S. U., Lefer A. M. Lack of endothelium-dependent relaxation in coronary resistance arteries of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C591–C597. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panza J. A., Quyyumi A. A., Brush J. E., Jr, Epstein S. E. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):22–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossitch E., Jr, Alexander E., 3rd, Black P. M., Cooke J. P. L-arginine normalizes endothelial function in cerebral vessels from hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1295–1299. doi: 10.1172/JCI115132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto S., Kashiki M., Imai N., Liang C. S., Hood W. B., Jr Effects of short-term, diet-induced hypercholesterolemia on systemic hemodynamics, myocardial blood flow, and infarct size in awake dogs with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):378–386. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnider S. L., Kohn R. R. Glucosylation of human collagen in aging and diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1179–1181. doi: 10.1172/JCI109950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellke F. W., Armstrong M. L., Harrison D. G. Endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation is abnormal in the coronary microcirculation of atherosclerotic primates. Circulation. 1990 May;81(5):1586–1593. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.5.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Münzel T., Bassenge E. Reversal of acetylcholine-induced coronary resistance vessel dilation by hemoglobin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. A., Magliocco M., Hayakawa K., Farrell C. L., Del Maestro R. F., Girvin J., Kaufmann J. C., Vinters H. V., Gilbert J. A quantitative analysis of blood-brain barrier ultrastructure in the aging human. Microvasc Res. 1987 Mar;33(2):270–282. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner F. C., Noll G., Boulanger C. M., Lüscher T. F. Oxidized low density lipoproteins inhibit relaxations of porcine coronary arteries. Role of scavenger receptor and endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Circulation. 1991 Jun;83(6):2012–2020. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.6.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. G., Cole P. A., Zions J. D., Daugherty A., Larson K. B., Sutera S. P., Kilo C., Williamson J. R. Increased ischemia-reperfusion injury to the heart associated with short-term, diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rabbits. Circ Res. 1987 Apr;60(4):551–559. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treasure C. B., Vita J. A., Cox D. A., Fish R. D., Gordon J. B., Mudge G. H., Colucci W. S., Sutton M. G., Selwyn A. P., Alexander R. W. Endothelium-dependent dilation of the coronary microvasculature is impaired in dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1990 Mar;81(3):772–779. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.3.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi M., Richard V., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Importance of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in porcine coronary resistance arteries. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 2):H13–H20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.1.H13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Collier J., Moncada S. Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral arteriolar tone in man. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):997–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Anggård E. E., Botting R. M. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Rubanyi G. M., Miller V. M., Houston D. S. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle contraction by the endothelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:307–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita J. A., Treasure C. B., Nabel E. G., McLenachan J. M., Fish R. D., Yeung A. C., Vekshtein V. I., Selwyn A. P., Ganz P. Coronary vasomotor response to acetylcholine relates to risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):491–497. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werns S. W., Walton J. A., Hsia H. H., Nabel E. G., Sanz M. L., Pitt B. Evidence of endothelial dysfunction in angiographically normal coronary arteries of patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1989 Feb;79(2):287–291. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Bossaller C., Cartwright J., Jr, Henry P. D. Videomicroscopic demonstration of defective cholinergic arteriolar vasodilation in atherosclerotic rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1752–1758. doi: 10.1172/JCI113516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue H., Matsuyama K., Matsuyama K., Okumura K., Morikami Y., Ogawa H. Responses of angiographically normal human coronary arteries to intracoronary injection of acetylcholine by age and segment. Possible role of early coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):482–490. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Drexler H. Coronary hemodynamic determinants of epicardial artery vasomotor responses during sympathetic stimulation in humans. Basic Res Cardiol. 1991;86 (Suppl 2):203–213. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72461-9_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Drexler H., Wollschlaeger H., Saurbier B., Just H. Coronary vasomotion in response to sympathetic stimulation in humans: importance of the functional integrity of the endothelium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Nov 1;14(5):1181–1190. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Drexler H., Wollschläger H., Just H. Endothelial dysfunction of the coronary microvasculature is associated with coronary blood flow regulation in patients with early atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1991 Nov;84(5):1984–1992. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.5.1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Drexler H., Wollschläger H., Just H. Modulation of coronary vasomotor tone in humans. Progressive endothelial dysfunction with different early stages of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1991 Feb;83(2):391–401. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Schächinger V., Weitzel S. H., Wollschläger H., Just H. Intracoronary thrombus formation causes focal vasoconstriction of epicardial arteries in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1991 May;83(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.5.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]