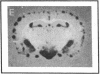
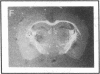
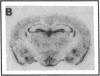
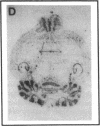
Abstract
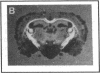
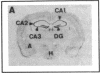
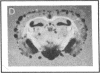
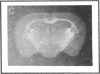
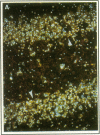
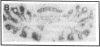
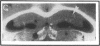
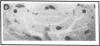
Plasminogen activators are important mediators of extracellular metabolism. In the nervous system, plasminogen activators are thought to be involved in the remodeling events required for cell migration during development and regeneration. We have now explored the expression of the plasminogen activator/plasmin system in the adult murine central nervous system. Tissue-type plasminogen activator is synthesized by neurons of most brain regions, while prominent tissue-type plasminogen activator-catalyzed proteolysis is restricted to discrete areas, in particular within the hippocampus and hypothalamus. Our observations indicate that tissue-type plasminogen activator-catalyzed proteolysis in neural tissues is not limited to ontogeny, but may also contribute to adult central nervous system physiology, for instance by influencing neuronal plasticity and synaptic reorganization. The identification of an extracellular proteolytic system active in the adult central nervous system may also help gain insights into the pathogeny of neurodegenerative disorders associated with extracellular protein deposition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Leprince P., Rogister B., Lefebvre P. P., Delree P., Selak I., Moonen G. Plasminogen activators in developing peripheral nervous system, cellular origin and mitogenic effect. Brain Res. 1987 Nov;433(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Combépine C., Godeau F., Nagamine Y., Reich E., Kocher H. P., Duvoisin R. M. Cloning, nucleotide sequencing and expression of cDNAs encoding mouse urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. G., Novak J. F., Yanosick T. B., McMaster J. H. Involvement of the plasmin system in dissociation of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Endocrinology. 1992 Mar;130(3):1401–1412. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.3.1371448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., Bell S. M., Schaefer L. A., Elliott R. W. Characterization of the cDNA coding for mouse plasminogen and localization of the gene to mouse chromosome 17. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90225-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes triggers the translation and polyadenylation of dormant tissue-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1201–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator in mouse and rat oocytes: induction during meiotic maturation. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S. Alzheimer's disease: a cell biological perspective. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):780–783. doi: 10.1126/science.1589757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Seeds N. W. Plasminogen activator release at the neuronal growth cone. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.7197054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire P. G., Seeds N. W. Degradation of underlying extracellular matrix by sensory neurons during neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90121-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D. Cell-derived proteases and protease inhibitors as regulators of neurite outgrowth. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonen G., Grau-Wagemans M. P., Selak I. Plasminogen activator-plasmin system and neuronal migration. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):753–755. doi: 10.1038/298753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Tsuzaki N., Nagata K., Takemoto N., Kohsaka S. Production and secretion of plasminogen in cultured rat brain microglia. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 17;308(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81270-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Tamagnone L., Vigna E., Sachs M., Hartmann G., Birchmeier W., Daikuhara Y., Tsubouchi H., Blasi F., Comoglio P. M. Extracellular proteolytic cleavage by urokinase is required for activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4825–4833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecorino L. T., Darrow A. L., Strickland S. In vitro analysis of the tissue plasminogen activator promoter reveals a GC box-binding activity present in murine brain but undetectable in kidney and liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3139–3147. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N. Release of plasminogen activator and a calcium-dependent metalloprotease from cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Gilbert M. E., Colicos M. A., Kandel E. R., Kuhl D. Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):453–457. doi: 10.1038/361453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quon D., Wang Y., Catalano R., Scardina J. M., Murakami K., Cordell B. Formation of beta-amyloid protein deposits in brains of transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):239–241. doi: 10.1038/352239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Darrow A. L., Strickland S. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA to mouse tissue plasminogen activator mRNA and its expression during F9 teratocarcinoma cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1563–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D., Bizik J., Quarto N., Blei F., Dennis P., Flaumenhaft R., Mignatti P. Growth factor control of extracellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston M. C., Rothwell N. J., Roberts G. W. Alzheimer's disease: pathology to potential treatments? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Apr;13(4):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90047-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Busso N., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4043–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea T. B., Beermann M. L. Regulation of neuronal migration and neuritogenesis by distinct surface proteases. Relative contribution of plasmin and a thrombin-like protease. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80765-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R. Learning-related synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;1(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Miskin R. Plasminogen activator in the developing rat cerebellum: biosynthesis and localization in granular neurons. Brain Res. 1983 Dec;313(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Miskin R. Plasminogen activator in the rodent brain. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 20;216(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. LOCALIZATION OF FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN TISSUES. Br Med Bull. 1964 Sep;20:210–212. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand W. E., Wagner S. L., Farrow J. S., Cunningham D. D. Immunopurification and protease inhibitory properties of protease nexin-2/amyloid beta-protein precursor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9591–9594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand W. E., Wagner S. L., Suzuki M., Choi B. H., Farrow J. S., Geddes J. W., Cotman C. W., Cunningham D. D. Protease nexin-II, a potent antichymotrypsin, shows identity to amyloid beta-protein precursor. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):546–549. doi: 10.1038/341546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA for the rat plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]