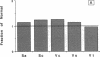Abstract
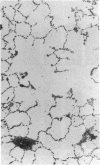
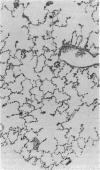
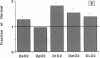
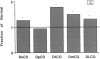
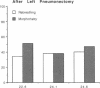
To determine if the functional compensation in diffusing capacity of the remaining lung following pneumonectomy is due to structural growth, we performed morphometric analysis of the right lung in three adult foxhounds approximately 2 yr after left pneumonectomy (removal of 42% of lung) and compared the results to those in normal adult dogs previously studied by the same techniques. Diffusing capacity was calculated by an established morphometric model and compared to physiologic estimates at peak exercise in the same dogs after pneumonectomy. The major structural changes after left pneumonectomy are hyperinflation of the right lung, alveolar enlargement, and thinning of the alveolar-capillary tissue barrier. These changes confer significant functional compensation for gas exchange by reducing the overall resistance to O2 diffusion. The magnitude of compensation in diffusing capacity estimated either morphometrically or physiologically is similar. In spite of morphometric and physiologic evidence of functional compensation, there is no evidence of significant growth of structural components. After pneumonectomy, morphometric estimates of diffusing capacity are on average 23% higher than physiologic estimates in the same dogs at peak exercise. We conclude that the previously reported large differences between morphometric and physiologic estimates of diffusing capacity reflects the presence of large physiologic reserves available for recruitment.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlin J. I., Cassidy S. S., Rajagopal U., Clifford P. S., Johnson R. L., Jr Noninvasive diffusing capacity and cardiac output in exercising dogs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Aug;65(2):669–674. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.2.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin J. I., Hsia C. C., Cassidy S. S., Ramanathan M., Clifford P. S., Johnson R. L., Jr Recruitment of lung diffusing capacity with exercise before and after pneumonectomy in dogs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jan;70(1):135–142. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Crapo R. O. Comparison of total lung diffusion capacity and the membrane component of diffusion capacity as determined by physiologic and morphometric techniques. Respir Physiol. 1983 Feb;51(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Crapo R. O., Jensen R. L., Mercer R. R., Weibel E. R. Evaluation of lung diffusing capacity by physiological and morphometric techniques. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 May;64(5):2083–2091. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.5.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo R. O., Bitterman N., Berlin S. L., Forster R. E. Rate of CO uptake by canine erythrocytes as a function of PO2. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Dec;67(6):2265–2268. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.6.2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., McBride J., Murray G. F., Wilcox B. R., Shallal J. A., Reid L. Structural changes in the canine lung and pulmonary arteries after pneumonectomy. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Oct;53(4):859–864. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J., Bachofen H., Gehr P., Weibel E. R. Alveolar volume-surface area relation in air- and saline-filled lungs fixed by vascular perfusion. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Nov;47(5):990–1001. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.5.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grote J. Die Sauerstoffdiffusionskonstanten im Lungengewebe und Wasser und ihre Temperaturabhängigkeit. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(3):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R. A. Rate at which CO replaces O2 from O2Hb in red cells of different species. Respir Physiol. 1969 Jun;7(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(69)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R. A. Rate of O2 dissociation from O2Hb and relative combination rate of CO and O2 in mammals at 37 degrees C. Respir Physiol. 1969 Jun;7(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(69)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R. A., Shibata H., Scheid P., Piiper J. Kinetics of O2 uptake and release by red cells in stopped-flow apparatus: effects of unstirred layer. Respir Physiol. 1985 Jan;59(1):71–91. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(85)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R. A., van Hezewikj W., Zubzanda J. Velocity of oxygen uptake by partly saturated adult and fetal human red cells. Respir Physiol. 1977 May;29(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(77)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Carlin J. I., Cassidy S. S., Ramanathan M., Johnson R. L., Jr Hemodynamic changes after pneumonectomy in the exercising foxhound. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Jul;69(1):51–57. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Carlin J. I., Ramanathan M., Cassidy S. S., Johnson R. L., Jr Estimation of diffusion limitation after pneumonectomy from carbon monoxide diffusing capacity. Respir Physiol. 1991 Jan;83(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(91)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Carlin J. I., Wagner P. D., Cassidy S. S., Johnson R. L., Jr Gas exchange abnormalities after pneumonectomy in conditioned foxhounds. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Jan;68(1):94–104. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Ramanathan M., Pean J. L., Johnson R. L., Jr Respiratory muscle blood flow in exercising dogs after pneumonectomy. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jul;73(1):240–247. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.1.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSION W. H., CALDWELL D. R., EARLY N. A., SCHILLING J. A. The relationship of dry lung weights to pulmonary function in dogs and humans. J Surg Res. 1962 Sep;2:287–292. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(62)80036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvin G. M., Wood S. C. Effects of capillary red cell density on gas conductance of frog skin. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jul;73(1):224–233. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.1.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAHN H., ROSS B. B. Bronchial tree casts, lobe weights and anatomical dead space measurements in the dog's lung. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jan;10(1):154–157. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAHN H., SADOUL P., FARHI L. E., SHAPIRO J. Distribution of ventalation and perfusion in the lobes of the dog's lung in the supine and erect position. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Jan;8(4):417–426. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.8.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUGHTON F. J., FORSTER R. E., CANDER L. Rate at which carbon monoxide replaces oxygen from combination with human hemoglobin in solution and in the red cell. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Sep;11(2):269–276. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. B., Park H. K. CO uptake kinetics of red cells and CO diffusing capacity. Respir Physiol. 1992 Apr-May;88(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(92)90025-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W. W., Jr, Latham L. P., Capen R. L. Capillary recruitment during airway hypoxia: role of pulmonary artery pressure. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Aug;47(2):383–387. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.2.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Morphometric estimation of pulmonary diffusion capacity. I. Model and method. Respir Physiol. 1970;11(1):54–75. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Taylor C. R., O'Neil J. J., Leith D. E., Gehr P., Hoppeler H., Langman V., Baudinette R. V. Maximal oxygen consumption and pulmonary diffusing capacity: a direct comparison of physiologic and morphometric measurements in canids. Respir Physiol. 1983 Nov;54(2):173–188. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox B. R., Murray G. F., Friedman M., Pimmel R. L. The effects of early pneumonectomy on the remaining pulmonary parenchyma. Surgery. 1979 Aug;86(2):294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Nguyen-Phu D., Scheid P., Piiper J. Kinetics of O2 uptake and release by human erythrocytes studied by a stopped-flow technique. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Apr;58(4):1215–1224. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.4.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]