Abstract
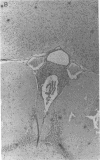
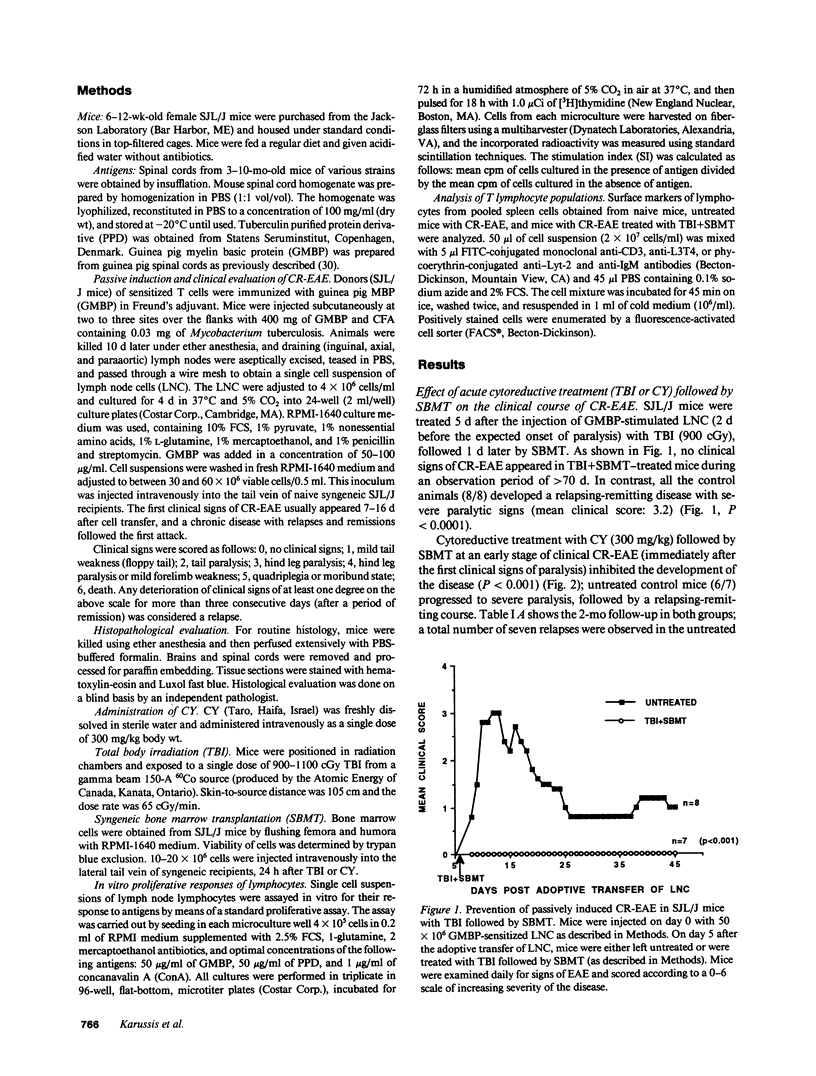
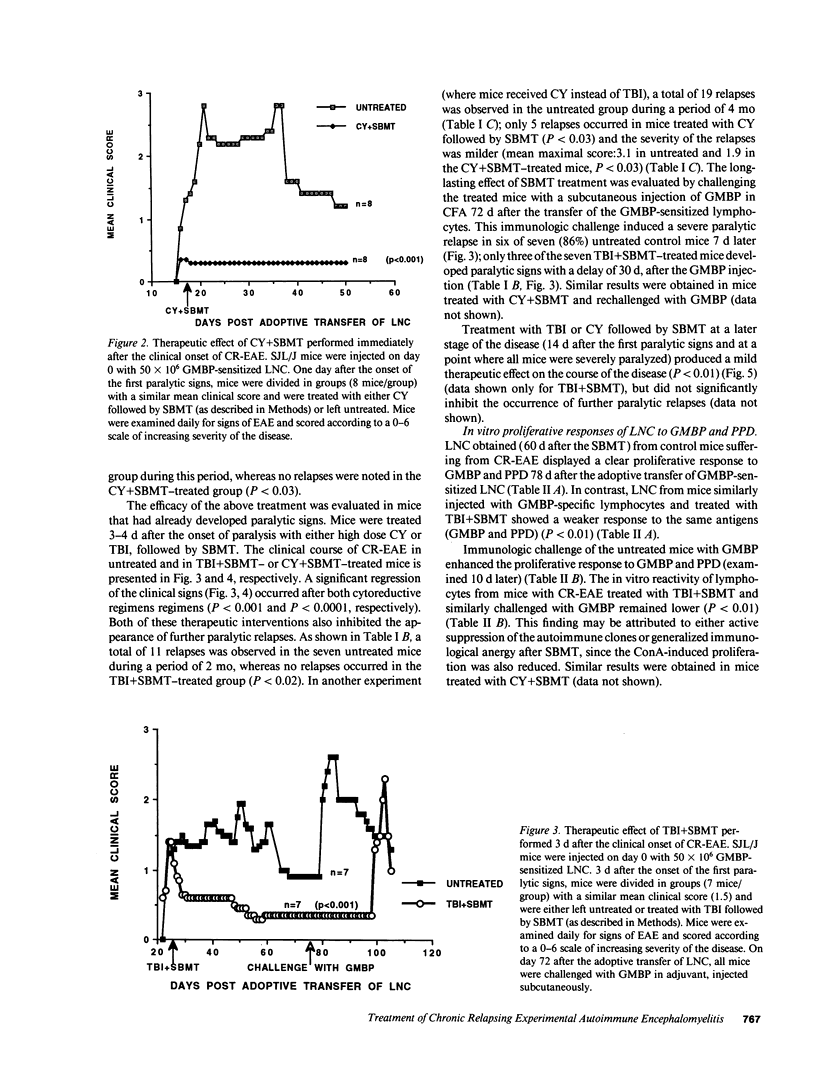
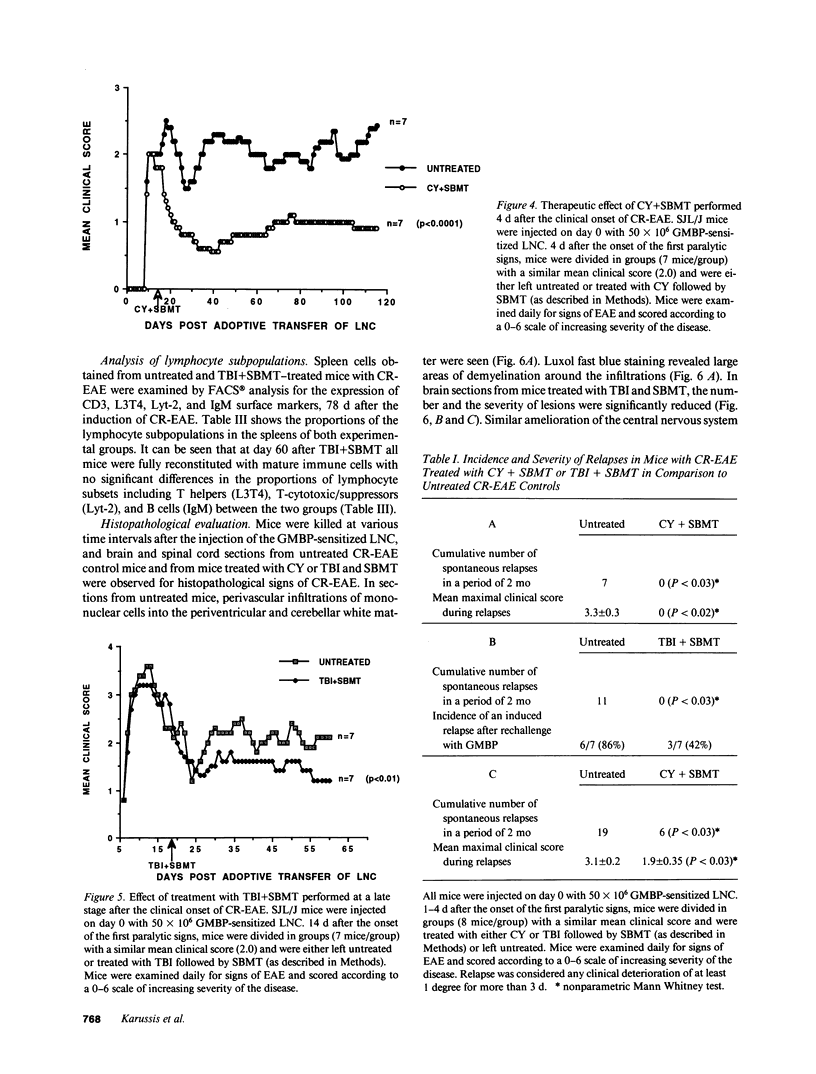
A chronic relapsing form of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (CR-EAE) was induced in SJL/J mice by adoptive transfer of lymph node cells (LNC) sensitized to guinea pig myelin basic protein (GMBP). We examined the efficacy of high dose immunosuppressive regimens (cyclophosphamide [CY] 300 mg/kg or total body irradiation [TBI] 900 cGy) followed by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation (SBMT) in prevention and treatment of already established CR-EAE. Treatment with TBI and SBMT on day 5 after the induction of CR-EAE, just before the onset of clinical signs, completely inhibited the appearance of the paralytic signs. The same treatment, applied 4 d after the clinical onset of the disease, led to a significant regression of the paralytic signs and to a total inhibition of spontaneous relapses during a follow-up period of 2 mo. Challenge of mice with GMBP+CFA 78 d after the passive induction of CR-EAE induced a relapse of the disease 7 d later in almost all of the untreated mice; in contrast, the same challenge given to TBI+SBMT-treated mice caused a delayed relapse (30 d later) in only a minority (3/7) of the challenged mice. In vitro lymphocytic proliferative responses to GMBP and purified protein derivative were significantly lower in TBI/SBMT-treated mice before and after the GMBP challenge, although these mice were fully immunocompetent, as evidenced by their normal lymphocytic proliferation to concanavalin A (ConA) and the FACS analysis of their lymphocytic subpopulations. A similar beneficial therapeutic effect was observed in mice treated with CY followed by SBMT, after the onset of CR-EAE. Our results could support possible clinical applications of similar therapeutic strategies, involving acute immunosuppression followed by stem cell transplantation and retolerization of the reconstituting immune cells in life-threatening neurological and multisystemic autoimmune diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Olson G. B., Autry J. R., Howarth J. L., Troup G. M., Bartels P. H. Radiosensitivity of T and B lymphocytes. IV. Effect of whole body irradiation upon various lymphoid tissues and numbers of recirculating lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1191–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Nun A., Lando Z. Detection of autoimmune cells proliferating to myelin basic protein and selection of T cell lines that mediate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard C. C., Leydon J., Mackay I. R. T cell necessity in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Sep;6(9):655–660. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brod S. A., al-Sabbagh A., Sobel R. A., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin antigens: IV. Suppression of chronic relapsing disease in the Lewis rat and strain 13 guinea pig. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):615–622. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Mason D. W. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: successful treatment in vivo with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes T helper cells. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1938–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., McFarlin D. E. Relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the SJL/J mouse. Lab Invest. 1981 Sep;45(3):278–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Chronologic neuropathology of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):171–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Mayumi H., Tomita Y., Yoshikai Y., Nishimura Y., Maeda T., Ando T., Nomoto K. Specific destruction of host-reactive mature T cells of donor origin prevents graft-versus-host disease in cyclophosphamide-induced tolerant mice. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1402–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Mayumi H., Tomita Y., Yoshikai Y., Nomoto K. Intrathymic clonal deletion of V beta 6+ T cells in cyclophosphamide-induced tolerance to H-2-compatible, Mls-disparate antigens. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):97–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD E. J., MILLER H. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: comparison of protective effects of prednisolone and corticotrophin. Br Med J. 1962 Mar 24;1(5281):843–844. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5281.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feurer C., Chow L. H., Borel J. F. Preventive and therapeutic effects of cyclosporin and valine2-dihydro-cyclosporin in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):219–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. B., Chou C. H., McFarlin D. E. Relapsing murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced by myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1024–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig M. E., Gibbons A. J., Elliott G. A. A comparison of the effects of melengestrol acetate and hydrocortisone acetate on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 May;173(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Physico-chemical state of lipids in intestinal content during their digestion and absorption. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBLER R. F. LARGE DOSE CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY OF EXPERIMENTAL AND HUMAN DEMYELINATING DISEASES. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:469–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komarek A., Dietrich F. M. Chemical prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats: a quantitative evaluation of steroids and various non-steroid drugs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1971 Oct;193(2):249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Suppression of the hyperacute form of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by drugs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1977 Dec;230(2):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lider O., Reshef T., Beraud E., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Anti-idiotypic network induced by T cell vaccination against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):181–183. doi: 10.1126/science.2447648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin F. D. Immunomodulation of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 1984 Dec;34(12):1615–1617. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.12.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin F. D., Maurer P. H., Berry R. G., Tippett D. Delayed, relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):819–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki G., Yoshikai Y., Ogimoto M., Kishihara K., Nomoto K. Clonal deletion of self-reactive T cells at the early stage of T cell development in thymus of radiation bone marrow chimeras. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtarian F., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Adoptive transfer of myelin basic protein-sensitized T cells produces chronic relapsing demyelinating disease in mice. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):356–358. doi: 10.1038/309356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morecki S., Leshem B., Eid A., Slavin S. Alloantigen persistence in induction and maintenance of transplantation tolerance. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1468–1480. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Cornford E. M. A comparison of total body and local spinal cord irradiation in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Jan;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197701000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y., BEISAW N. E. EFFECT OF WHOLE BODY X-IRRADIATION ON INDUCTION OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS IN RATS. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:532–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Drobish D. G. Cyclophosphamide: effect on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. Science. 1969 Jul 11;165(3889):191–192. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3889.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Hanson M. A., Gerner E. W. Cyclophosphamide inhibition of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Wistar rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Mar;124(3):928–932. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Harvey J. M. Irradiation potentiation of cellular transfer of EAE: time course and locus of effect in irradiated recipient Lewis rats. Cell Immunol. 1978 Dec;41(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Richarson W. P., Drobish D. G. Cellular transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: altered disease pattern in irradiated recipient lewis rats. Cell Immunol. 1975 Mar;16(1):48–59. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinelli C. B., McFarlin D. E. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice after in vitro activation of lymph node cells by myelin basic protein: requirement for Lyt 1+ 2- T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1420–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S. Biology of disease. Analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):608–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthale M. E., Datko L. J., Kassarich J., Schneider F. Chemotherapy of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1969 Jun;179(2):251–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller-Levis G. B., Kozlowski P. B., Wisniewski H. M. Cyclosporin A treatment of an induced attack in a chronic relapsing model of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Aug;40(2):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser D. E., Chvatchko Y., Zinkernagel R. M., MacDonald H. R. Distinct fates of self-specific T cells developing in irradiation bone marrow chimeras: clonal deletion, clonal anergy, or in vitro responsiveness to self-Mls-1a controlled by hemopoietic cells in the thymus. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1305–1314. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Roberts C. A. Treatment of established chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with anti-L3T4 antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4464–4469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Solomon D., Rouse R. V., Steinman L. Identification of T cell subsets and B lymphocytes in mouse brain experimental allergic encephalitis lesions. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1649–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staykova M., Goranov I., Nikolov T. L'influence du cyclophosphamide sur le développement de l'encéphalomyélite autoimmune expérimentale. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1978 Feb-Mar;129(2-3):415–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Brenner T., Mizrachi-Kol R., Abramsky O. Development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis during steroid administration. Outcome of neurological immune-mediated disorders under immunosuppressive therapy. Isr J Med Sci. 1991 Jul;27(7):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman G. D., Heim L. R., South M. A., Trentin J. J. Differential effects of cyclophosphamide on the B and T cell compartments of adult mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):277–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober S., Kotzin B., Field E., Hoppe R., Myers B., Tanay A. Treatment of autoimmune disease with total lymphoid irradiation. Cellular and humoral mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;475:285–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tochner Z., Slavin S. Immune modulation by ionized irradiation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1988 Dec;1(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visakorpi R., Kosunen T. U. The effect of whole body x-irradiation on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1972;50(2):95–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale B., Allegretti N., Matosić M. Influence of x-irradiation on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Radiat Res. 1966 Aug;28(4):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., Hardy R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Lanier L., Lim M., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with monoclonal antibody to a T-cell subset marker. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3155574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bekkum D. W., Bohre E. P., Houben P. F., Knaan-Shanzer S. Regression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats following bone marrow transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10090–10094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]