Abstract
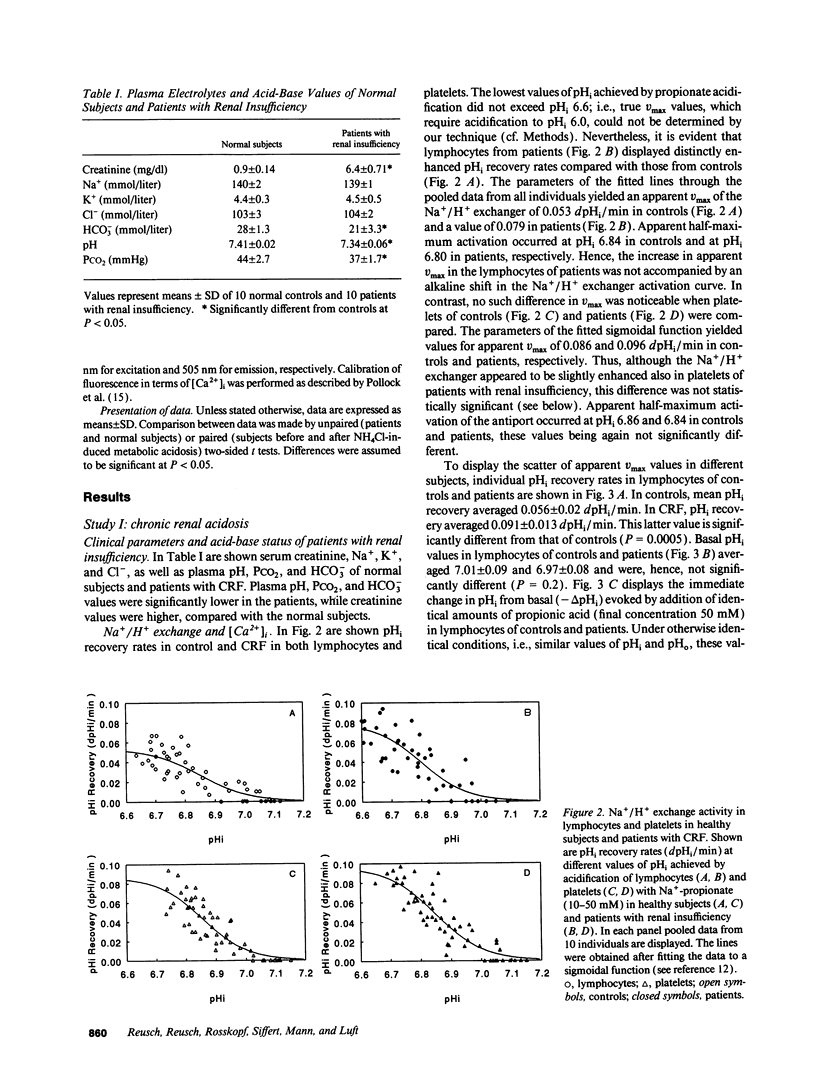
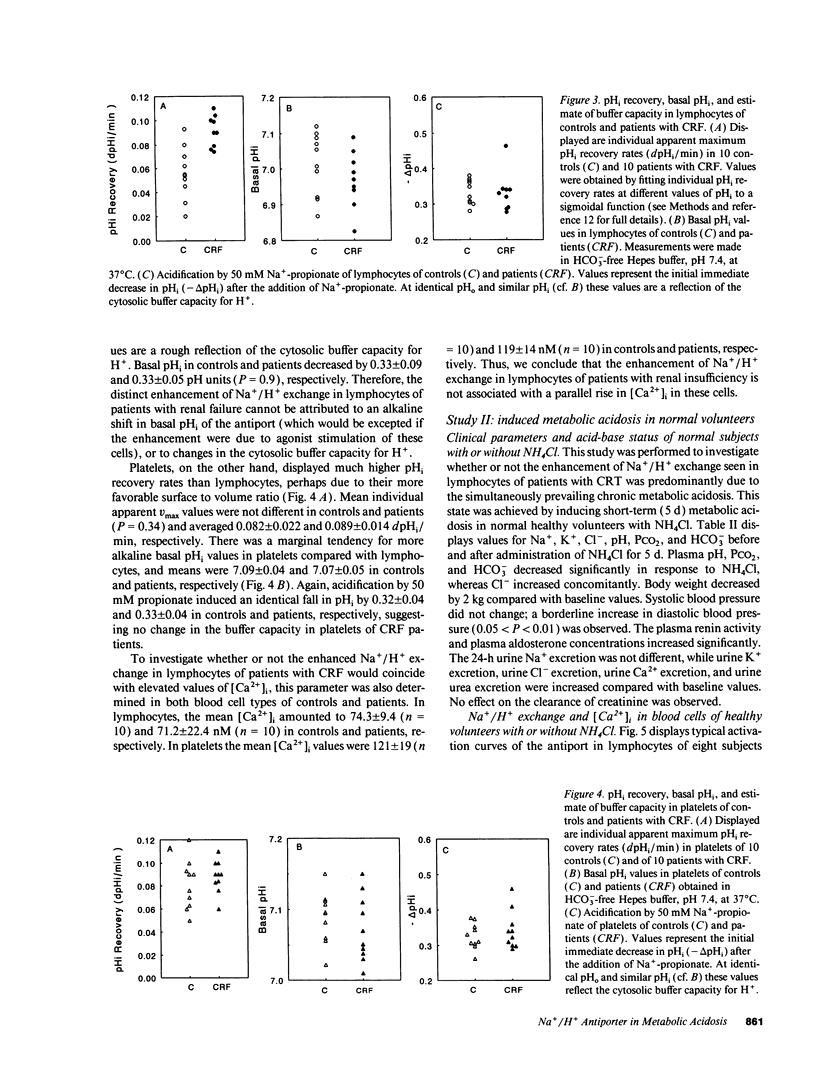
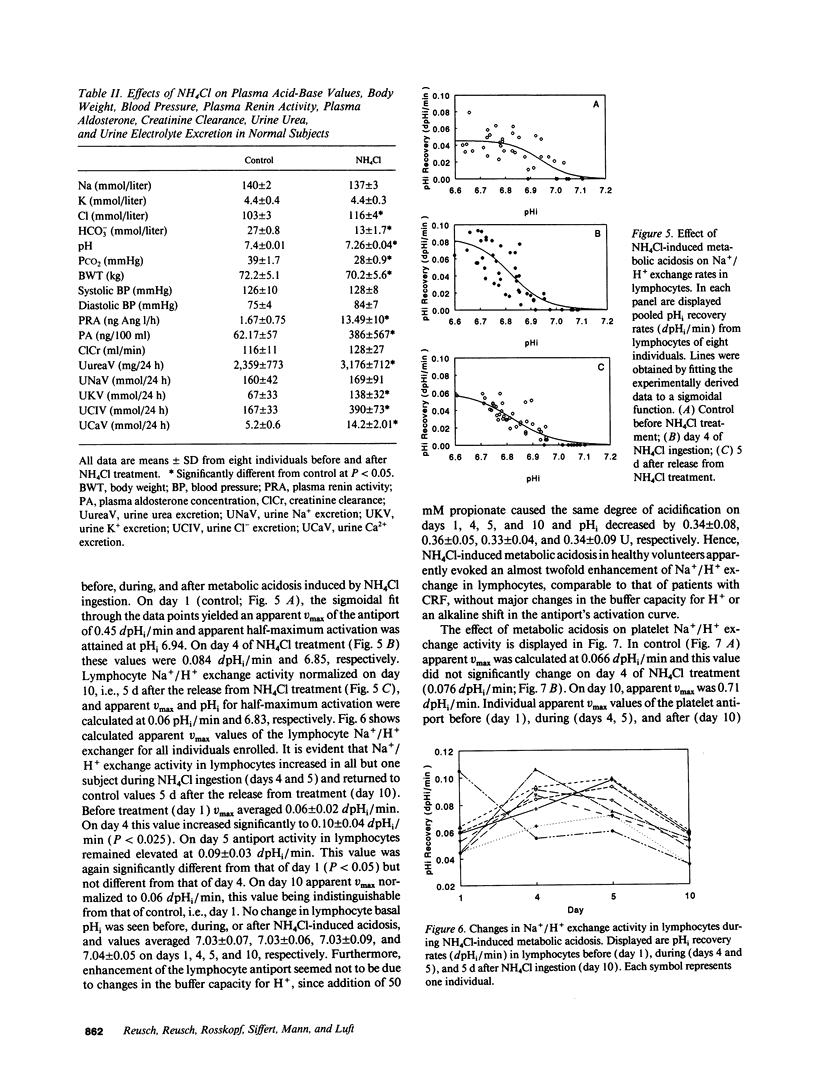
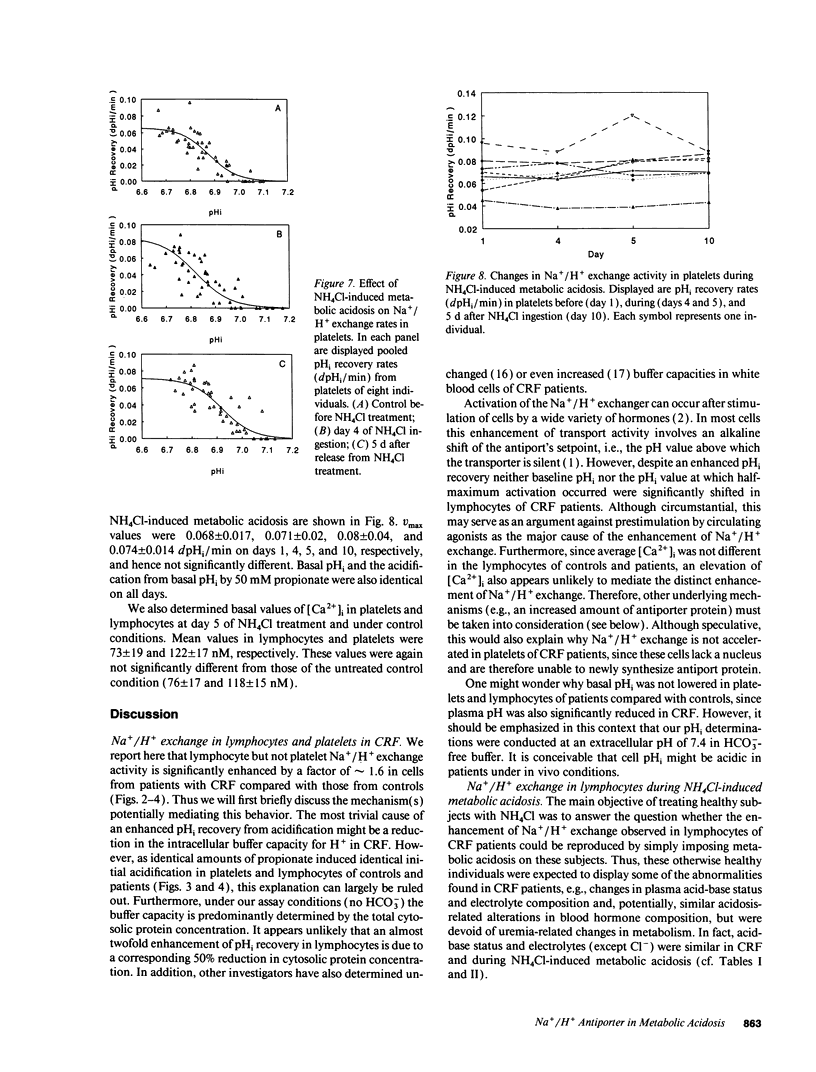
The effect of acid-base disturbances on sodium/proton (Na+/H+) exchange has been examined in animal models; however, few data are available from human studies. To test the effect of metabolic acidosis on Na+/H+ exchange in man, as well as to examine the relationship between Na+/H+ exchange and cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]i), we measured both variables in patients with decreased renal function with mild metabolic acidosis (pH 7.34 +/- 0.06), in normal control subjects (pH 7.41 +/- 0.02), and in subjects before (pH 7.40 +/- 0.01), and after (pH 7.26 +/- 0.04) ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) 15 g for 5 d. Lymphocytes and platelets were loaded with the cytosolic pH (pHi) indicator 2'-7'-bis(carboxyethyl)-5,6-carboxyfluorescein and acidified to pH approximately 6.6 with propionic acid. To quantitate Na+/H+ exchange, dpHi/dt was determined at 1 min. [Ca2+]i was measured with fura-2. Na+/H+ exchange was significantly increased only in lymphocytes of patients with renal insufficiency. Neither intracellular pH (pHi) nor [Ca2+]i was different from controls. NH4Cl resulted in a significant increase in Na+/H+ exchange in lymphocytes, but not in platelets of normal subjects. Values of pHi and [Ca2+]i in either cell type remained unaffected. Since metabolic acidosis influenced Na+/H+ only in lymphocytes, but not in platelets, it is possible that protein synthesis may be involved in increasing Na+/H+ exchange.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster H. V., Dempsey J. A., Thomson J., Vidruk E., DoPico G. A. Estimation of arterial PO2, PCO2, pH, and lactate from arterialized venous blood. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Jan;32(1):134–137. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes A. P., Daniels I., Porter C., Fletcher J., Morgan A. G. Abnormal cytoplasmic pH regulation during activation in uremic neutrophils. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):690–699. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Yamaji Y., Cano A., Miller R. T., Alpern R. J. Role of protein kinase C and transcription factor AP-1 in the acid-induced increase in Na/H antiporter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5236–5240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huot S. J., Aronson P. S. Na(+)-H+ exchanger and its role in essential hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1991 Jun;14(6):521–535. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.6.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen T. A., Welch W. J., Lorenz J. N., Ott C. E. Renal tubular chloride and renin release. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Nov;110(5):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Beeler I., Hertner D., Hulter H. N. Chronic respiratory alkalosis. The effect of sustained hyperventilation on renal regulation of acid-base equilibrium. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1394–1401. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Pearce D., Lynch C., Xi X. P., Reudelhuber T. L., Pouysségur J., Rector F. C., Jr Expression of rat renal Na/H antiporter mRNA levels in response to respiratory and metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI115057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. W., Miller R. T., Horie S., Cano A., Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Differential regulation of Na/H antiporter by acid in renal epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1703–1708. doi: 10.1172/JCI115487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perper R. J., Zee T. W., Mickelson M. M. Purification of lymphocytes and platelets by gradient centrifugation. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Nov;72(5):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli de Figueiredo C. E., Ng L. L., Garrido M. C., Davies J. E., Ellory J. C., Hendry B. M. Leukocyte intracellular pH and Na/H antiporter activity in uraemia and type I diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1991;6(9):615–620. doi: 10.1093/ndt/6.9.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., SHELBURNE P. F., TALMAN A. Profound acidosis resulting from excessive ammonium chloride in previously healthy subjects. A study of two cases. N Engl J Med. 1961 Apr 27;264:848–852. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196104272641703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosskopf D., Siffert G., Osswald U., Witte K., Düsing R., Akkerman J. W., Siffert W. Platelet Na(+)-H+ exchanger activity in normotensive and hypertensive subjects: effect of enalapril therapy upon antiport activity. J Hypertens. 1992 Aug;10(8):839–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Siffert G., Scheid P. Activation of Na+/H+ exchange in human platelets stimulated by thrombin and a phorbol ester. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):301–303. doi: 10.1042/bj2410301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Siffert G., Scheid P., Akkerman J. W. Na+/H+ exchange modulates Ca2+ mobilization in human platelets stimulated by ADP and the thromboxane mimetic U 46619. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):719–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. O. Sodium intake, body sodium, and sodium excretion. Lancet. 1988 Jul 2;2(8601):25–29. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92954-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strazzullo P., Canessa M. Kinetics of the human lymphocyte Na(+)-H+ exchanger. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Nov;79(5):531–536. doi: 10.1042/cs0790531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger M. H., Ramsdell J. W., Rosner D. R., Geddes J. J. Effect of chlorothiazide and sodium on vascular responsiveness to angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1049–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


