Abstract
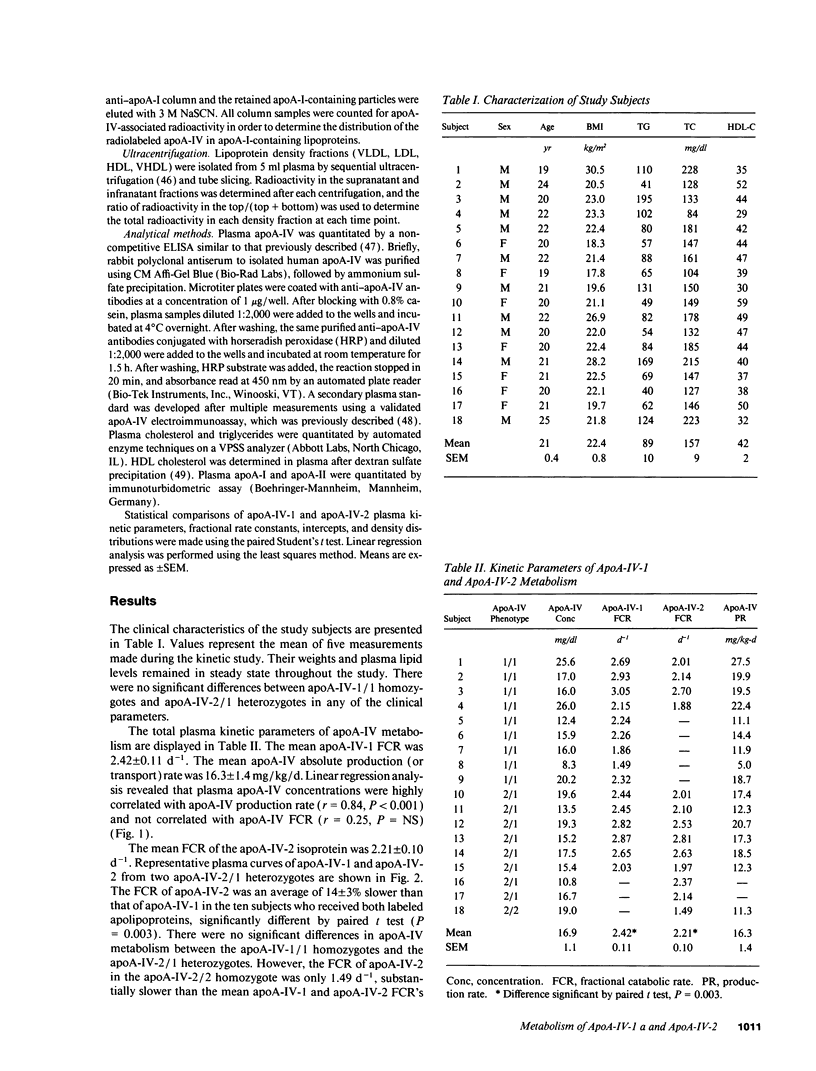
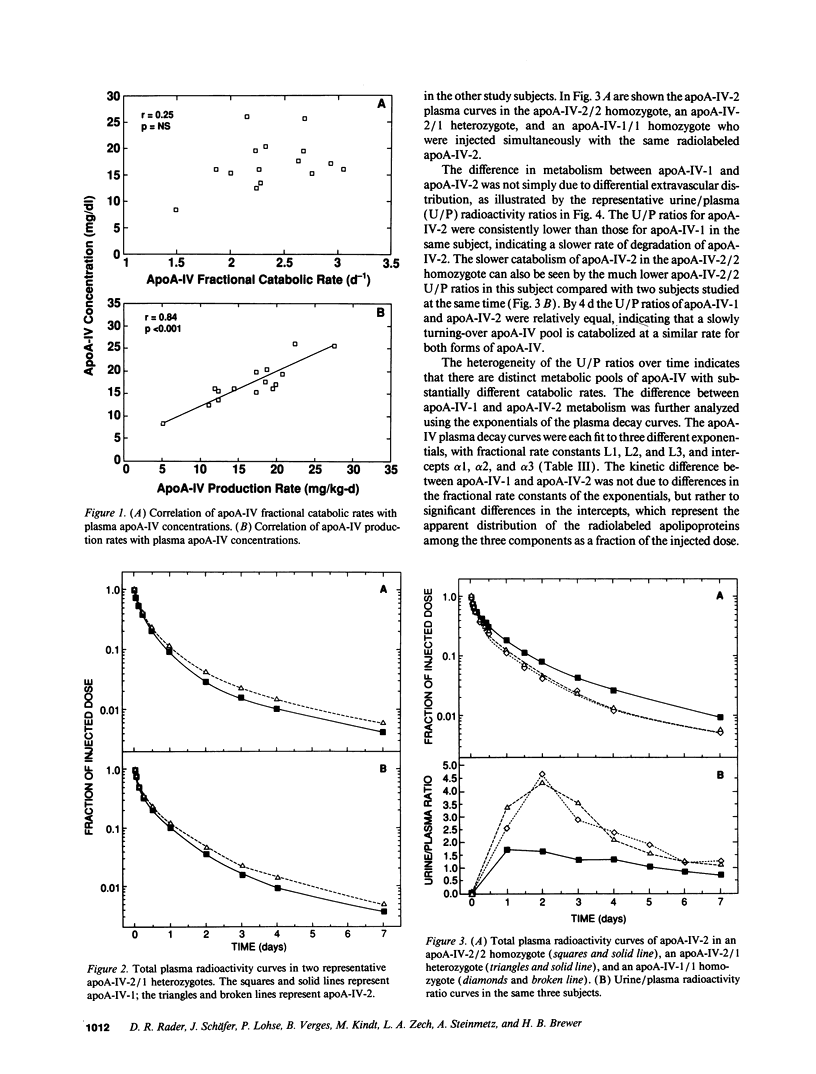
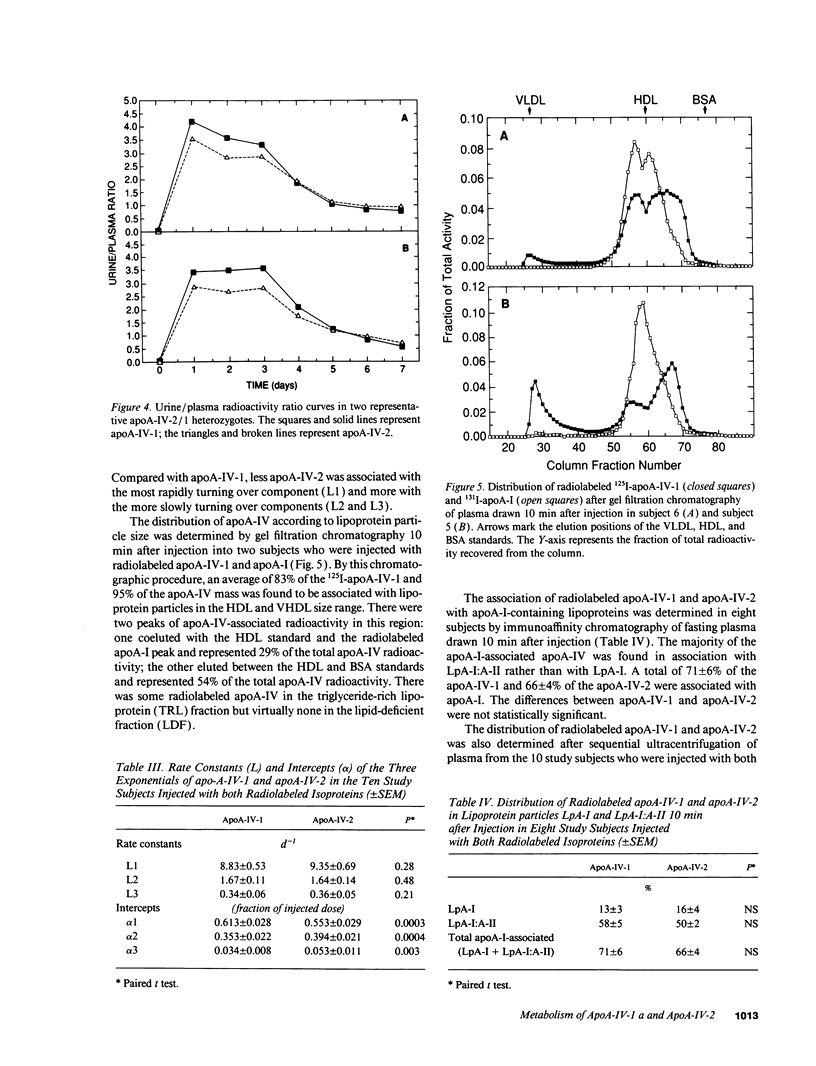
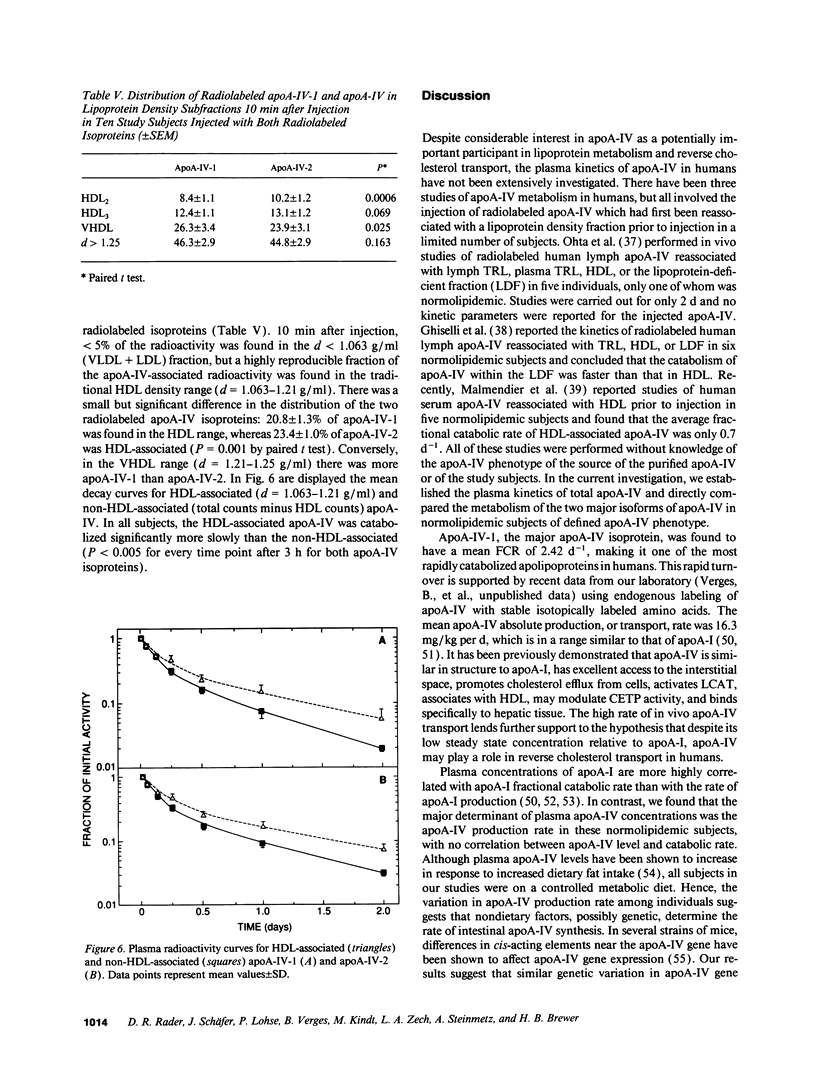
Apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV is a polymorphic, intestinally derived apolipoprotein that is genetically linked to and similar in structure to apoA-I, the major apolipoprotein in high density lipoproteins (HDL). ApoA-IV plays a potentially important role in lipoprotein metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport, but its in vivo metabolism is poorly understood. In order to gain insight into factors modulating apoA-IV metabolism in humans, the in vivo kinetics of the two major human apoA-IV isoproteins apoA-IV-1 and apoA-IV-2 were investigated in normolipidemic human subjects. 131I-apoA-IV-1 and 125I-apoA-IV-2 were reassociated with autologous plasma and injected into study subjects. Analysis of the kinetic data revealed a rapid mean fractional catabolic rate (FCR) for apoA-IV-1 of 2.42 +/- 0.11 d-1. The mean production, or transport, rate of apoA-IV-1 was 16.3 +/- 1.4 mg/kg per d. Plasma apoA-IV concentrations were highly correlated with apoA-IV production rate (r = 0.84, P < 0.001) and not correlated with apoA-IV fractional catabolic rate (r = 0.25, P = NS). The mean FCR of apoA-IV-2 was 2.21 +/- 0.10 d-1. In the ten subjects in whom 131I-apoA-IV-1 and 125I-apoA-IV-2 were simultaneously injected, the FCR of apoA-IV-2 was significantly slower by paired t test (P = 0.003). The FCR of apoA-IV-2 in an apoA-IV-2/2 homozygote was only 1.49 d-1, substantially slower than in all other subjects. We conclude that: (a) apoA-IV is a rapidly catabolized apolipoprotein in humans, with a fractional catabolic rate more than 10 times greater than that of apoA-I; (b) apoA-IV has a high absolute transport rate similar to that of apoA-I; (c) plasma levels of apoA-IV are primarily determined by apoA-IV production rate in normolipidemic subjects; and (d) the fractional catabolic rate of the common variant apoA-IV-2 is slower than that of the wild-type apoA-IV-1.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barter P. J., Rajaram O. V., Chang L. B., Rye K. A., Gambert P., Lagrost L., Ehnholm C., Fidge N. H. Isolation of a high-density-lipoprotein conversion factor from human plasma. A possible role of apolipoprotein A-IV as its activator. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):179–184. doi: 10.1042/bj2540179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Utermann G. An apolipoprotein homolog of rat apolipoprotein A-IV in human plasma. Isolation and partial characterisation. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betard C., Vu-Dac N., Mezdour H., Nestruck A. C., Leroy A., Fruchart J. C. Standardization of an enzymometric assay for apolipoprotein A-I by using mixtures of monoclonal antibodies). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1987 Dec;25(12):893–899. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1987.25.12.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Sachdev O. P., Lee E. S., Williams K. J., Blum C. B., Glickman R. M. Effect of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV among lipoproteins of human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Sachdev O. P., Megna L., Glickman R. M. Distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):11–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Siebenkas M. V., Hesler C. B., Swenson T. L., Blum C. B., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Glickman R. M., Tall A. R. Effect of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody to cholesteryl ester transfer protein on the redistribution of apolipoproteins A-IV and E among human lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):1025–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Visvikis S., Chan L. Two polymorphisms for amino acid substitutions in the APOA4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4966–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton E. A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. A low-fat diet decreases high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels by decreasing HDL apolipoprotein transport rates. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):144–151. doi: 10.1172/JCI114405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton E. A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Elevated high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels correlate with decreased apolipoprotein A-I and A-II fractional catabolic rate in women. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):262–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI114149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton E. A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Increased apo A-I and apo A-II fractional catabolic rate in patients with low high density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels with or without hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):536–544. doi: 10.1172/JCI115028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Albers J. J. Activation of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase by apolipoproteins E-2, E-3, and A-IV isolated from human plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 2;836(3):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duverger N., Ghalim N., Ailhaud G., Steinmetz A., Fruchart J. C., Castro G. Characterization of apoA-IV-containing lipoprotein particles isolated from human plasma and interstitial fluid. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Jan;13(1):126–132. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duverger N., Ghalim N., Theret N., Duchateau P., Aguie G., Ailhaud G., Castro G., Fruchart J. C. Lipoprotein A-I containing particles. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;285:93–99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5904-3_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Gorder N. L., Benson D. M., Gotto A. M., Jr Apolipoprotein A-IV. A determinant for binding and uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15714–15718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner J. E., Kuller L. H., Ferrell R. E., Kamboh M. I. Phenotypic effects of apolipoprotein structural variation on lipid profiles: II. Apolipoprotein A-IV and quantitative lipid measures in the healthy women study. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(4):493–499. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Boguski M. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. The nucleotide and derived amino acid sequence of human apolipoprotein A-IV mRNA and the close linkage of its gene to the genes of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):1998–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Krishnan S., Beigel Y., Gotto A. M., Jr Plasma metabolism of apolipoprotein A-IV in humans. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):813–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Scheraldi C. A., Yacoub L. K., Saxena U., Bisgaier C. L. Lipoprotein ApoC-II activation of lipoprotein lipase. Modulation by apolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4266–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W., Quinet E. Human apolipoprotein A-IV. Intestinal origin and distribution in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI109745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Saudek C. D., Blum C. B., Tall A. R. Human intestinal lipoproteins. Studies in chyluric subjects. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):233–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamboh M. I., Ferrell R. E. Genetic studies of human apolipoproteins. I. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein A-IV. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;41(2):119–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Oettgen P., Haddad I. A., Antonarakis S. E. Structure, evolution, and polymorphisms of the human apolipoprotein A4 gene (APOA4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Yunis I., Zannis V. I. Structure, evolution, and tissue-specific synthesis of human apolipoprotein AIV. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3962–3970. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hoppichler F., Vogel W., Utermann G. Changes of genetic apolipoprotein phenotypes caused by liver transplantation. Implications for apolipoprotein synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):137–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI113849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrost L., Gambert P., Boquillon M., Lallemant C. Evidence for high density lipoproteins as the major apolipoprotein A-IV-containing fraction in normal human serum. J Lipid Res. 1989 Oct;30(10):1525–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrost L., Gambert P., Dangremont V., Athias A., Lallemant C. Role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) in the HDL conversion process as evidenced by using anti-CETP monoclonal antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1569–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Kindt M. R., Rader D. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Genetic polymorphism of human plasma apolipoprotein A-IV is due to nucleotide substitutions in the apolipoprotein A-IV gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10061–10064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Kindt M. R., Rader D. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Human plasma apolipoproteins A-IV-0 and A-IV-3. Molecular basis for two rare variants of apolipoprotein A-IV-1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12734–12739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmendier C. L., Lontie J. F., Lagrost L., Delcroix C., Dubois D. Y., Gambert P. In vivo metabolism of apolipoproteins A-IV and A-I associated with high density lipoprotein in normolipidemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1991 May;32(5):801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Boerwinkle E., Schrangl-Will S., Utermann G. Human apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism: frequency and effect on lipid and lipoprotein levels. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):368–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00282179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kövary P. M., Assmann G. Apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism in man. Hum Genet. 1982;62(4):349–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00304554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Sigurdsson G., Boerwinkle E., Schrangl-Will S., Dieplinger H., Utermann G. Frequency and effect of human apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism on lipid and lipoprotein levels in an Icelandic population. Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;84(4):344–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00196231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Characterization of apolipoprotein A-IV complexes and A-IV isoforms in human lymph and plasma lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14888–14893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Studies on the in vivo and in vitro distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV in human plasma and lymph. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1252–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI112081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader D. J., Castro G., Zech L. A., Fruchart J. C., Brewer H. B., Jr In vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein A-I on high density lipoprotein particles LpA-I and LpA-I,A-II. J Lipid Res. 1991 Nov;32(11):1849–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosseneu M., Michiels G., De Keersgieter W., Bury J., De Slypere J. P., Dieplinger H., Utermann G. Quantification of human apolipoprotein A-IV by "sandwich"-type enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem. 1988 Apr;34(4):739–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Gamliel A. Binding of apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein A-IV to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):178–186. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Zech L. A., Jenkins L. L., Bronzert T. J., Rubalcaba E. A., Lindgren F. T., Aamodt R. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein A-I and A-II metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):850–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Krause B. R., Castle C., Roheim P. S. Lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in peripheral lymph of normal and cholesterol-fed dogs. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Oct;49(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y., Lefevre M., Roheim P. S. The role of apolipoprotein A-IV in reverse cholesterol transport studied with cultured cells and liposomes derived from an ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 14;878(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Barbaras R., Ghalim N., Clavey V., Fruchart J. C., Ailhaud G. Human apolipoprotein A-IV binds to apolipoprotein A-I/A-II receptor sites and promotes cholesterol efflux from adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7859–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Clavey V., Vu-Dac N., Kaffarnik H., Fruchart J. C. Purification of human apolipoprotein A-IV by fast protein liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1989 Jan 27;487(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Czekelius P., Thiemann E., Motzny S., Kaffarnik H. Changes of apolipoprotein A-IV in the human neonate: evidence for different inductions of apolipoproteins A-IV and A-I in the postpartum period. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Jan;69(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Utermann G. Activation of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase by human apolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2258–2264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenkanen H., Lukka M., Jauhiainen M., Metso J., Baumann M., Peltonen L., Ehnholm C. The mutation causing the common apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism is a glutamine to histidine substitution of amino acid 360. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jul-Aug;11(4):851–856. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Beisiegel U. Apolipoprotein A-IV: a protein occurring in human mesenteric lymph chylomicrons and free in plasma. Isolation and quantification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Feussner G., Franceschini G., Haas J., Steinmetz A. Genetic variants of group A apolipoproteins. Rapid methods for screening and characterization without ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnick G. R., Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Comparison of current methods for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol quantitation. Clin Chem. 1979 Apr;25(4):596–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Dantzker C., Patton C. S. Sensitivity of serum apolipoprotein A-IV levels to changes in dietary fat content. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jan;98(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91285-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Ibdah J. A., Phillips M. C. Adsorption of apolipoprotein A-IV to phospholipid monolayers spread at the air/water interface. A model for its labile binding to high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8977–8983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Jordan M. K., Steinmetz A. Distinctive structure and function of human apolipoprotein variant ApoA-IV-2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18372–18378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Patton C. S. Binding of human apolipoprotein A-IV to human hepatocellular plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1044(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90311-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Scanu A. M. Isolation and characterization of human apolipoprotein A-IV from lipoprotein-depleted serum. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):52–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Spector M. S. The self-association of human apolipoprotein A-IV. Evidence for an in vivo circulating dimeric form. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14279–14286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of an apoprotein from the d less than 1.006 lipoproteins of human and canine lymph homologous with the rat A-IV apoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):287–292. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Grant S. G., Reue K., Carrasquillo B., Lusis A. J., Kinniburgh A. J. cis-acting determinants of basal and lipid-regulated apolipoprotein A-IV expression in mice. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19009–19016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Knijff P., Rosseneu M., Beisiegel U., de Keersgieter W., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism and its effect on plasma lipid and apolipoprotein concentrations. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1621–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein A., Funke H., Schulte M., Erren M., Schulte H., Assmann G. Nonsynonymous polymorphic sites in the apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV gene are associated with changes in the concentration of apo B- and apo A-I-containing lipoproteins in a normal population. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1115–1128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


