Abstract
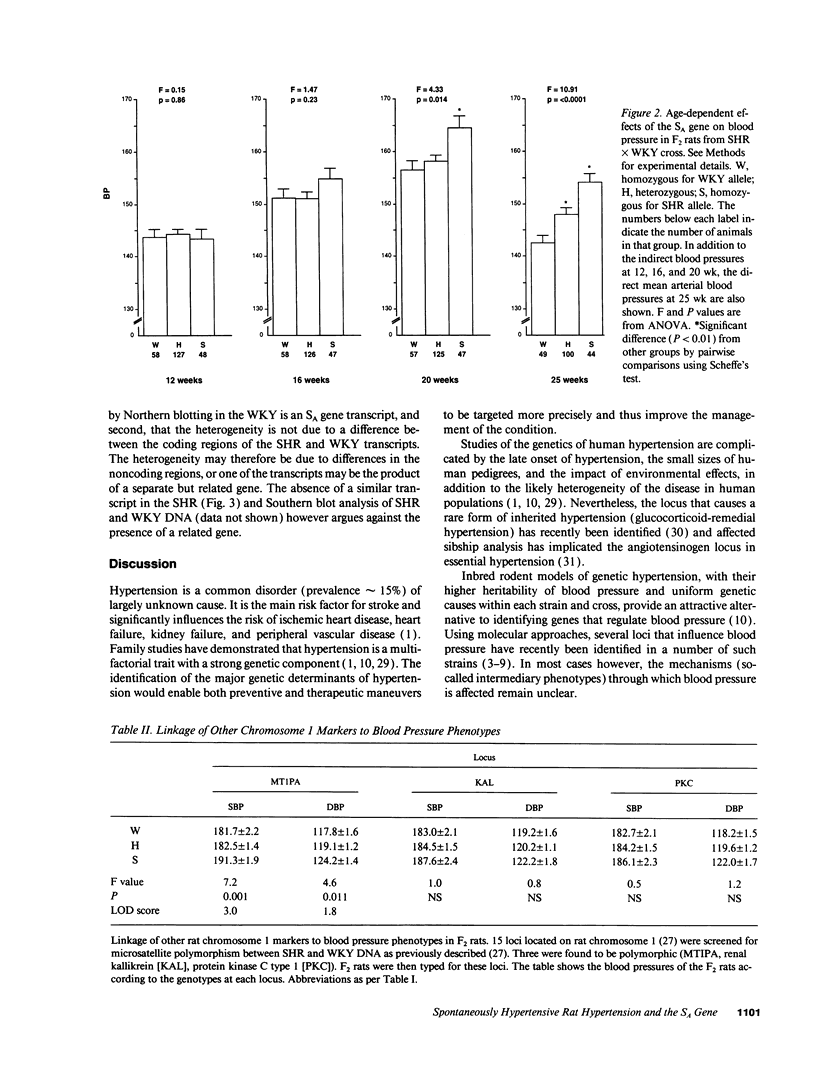
The role of the kidney in initiating hypertension has been much debated. Here we demonstrate that a recently identified gene of yet unknown function, termed SA, which is differentially expressed in the kidney of the spontaneously hypertensive rat, cosegregates with an increase in blood pressure in F2 rats derived from a cross of the spontaneously hypertensive rat with normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rats, accounting for 28 and 21% of the genetic variability in systolic and diastolic blood pressures, respectively. Further, the genotype at this locus appears to determine the level of expression of the gene in the kidney. The findings provide strong evidence for a primary genetic involvement of the kidney in hypertension.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi G., Fox U., Di Francesco G. F., Giovanetti A. M., Pagetti D. Blood pressure changes produced by kidney cross-transplantation between spontaneously hypertensive rats and normotensive rats. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Nov;47(5):435–448. doi: 10.1042/cs0470435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Konecki D. S., Caskey C. T. Expression of human and Chinese hamster hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase cDNA recombinants in cultured Lesch-Nyhan and Chinese hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9593–9596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Y., Rapp J. P. Cosegregation of blood pressure with angiotensin converting enzyme and atrial natriuretic peptide receptor genes using Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):267–272. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustin M. P., Cerutti C., Paultre C. Z. Heterogeneous computer network for real-time hemodynamic signal processing. Comput Biol Med. 1990;20(3):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(90)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Mizelle H. L., Hildebrandt D. A., Brands M. W. Abnormal pressure natriuresis. A cause or a consequence of hypertension? Hypertension. 1990 Jun;15(6 Pt 1):547–559. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.6.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrap S. B., Doyle A. E. Genetic co-segregation of renal haemodynamics and blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Jan;74(1):63–69. doi: 10.1042/cs0740063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert P., Lindpaintner K., Beckmann J. S., Serikawa T., Soubrier F., Dubay C., Cartwright P., De Gouyon B., Julier C., Takahasi S. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):521–529. doi: 10.1038/353521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai N., Inagami T. Identification of a candidate gene responsible for the high blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1992 Oct;10(10):1155–1157. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199210000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai N., Inagami T. Isolation of preferentially expressed genes in the kidneys of hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1991 Feb;17(2):161–169. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai N., Kurtz T. W., Inagami T. Further evidence of the SA gene as a candidate gene contributing to the hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):64–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunemaitre X., Soubrier F., Kotelevtsev Y. V., Lifton R. P., Williams C. S., Charru A., Hunt S. C., Hopkins P. N., Williams R. R., Lalouel J. M. Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90275-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz T. W., Simonet L., Kabra P. M., Wolfe S., Chan L., Hjelle B. L. Cosegregation of the renin allele of the spontaneously hypertensive rat with an increase in blood pressure. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1328–1332. doi: 10.1172/JCI114572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Cook S., Ulick S., Lalouel J. M. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):262–265. doi: 10.1038/355262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongeau J. G. Heredity and blood pressure. Semin Nephrol. 1989 Sep;9(3):208–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pravenec M., Kren V., Kunes J., Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Simonet L., Kurtz T. W. Cosegregation of blood pressure with a kallikrein gene family polymorphism. Hypertension. 1991 Feb;17(2):242–246. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pravenec M., Simonet L., Kren V., Kunes J., Levan G., Szpirer J., Szpirer C., Kurtz T. The rat renin gene: assignment to chromosome 13 and linkage to the regulation of blood pressure. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):466–472. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Wang S. M., Dene H. A genetic polymorphism in the renin gene of Dahl rats cosegregates with blood pressure. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):542–544. doi: 10.1126/science.2563177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig R., Folberth C., Stauss H., Kopf D., Waldherr R., Unger T. Role of the kidney in primary hypertension: a renal transplantation study in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F606–F611. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig R., Stauss H., Folberth C., Ganten D., Waldherr B., Unger T. Hypertension transmitted by kidneys from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 2):F197–F203. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.2.F197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samani N. J., Brammar W. J., Swales J. D. A major structural abnormality in the renin gene of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens. 1989 Apr;7(4):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samani N. J., Swales J. D., Brammar W. J. Expression of the renin gene in extra-renal tissues of the rat. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):907–910. doi: 10.1042/bj2530907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serikawa T., Kuramoto T., Hilbert P., Mori M., Yamada J., Dubay C. J., Lindpainter K., Ganten D., Guénet J. L., Lathrop G. M. Rat gene mapping using PCR-analyzed microsatellites. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):701–721. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulin T., Fagher B., Grabowski M., Ryding E., Elmqvist D., Johansson B. B. Cerebral blood flow in patients with severe hypertension, and acute and chronic effects of felodipine. J Hypertens. 1993 Jan;11(1):83–88. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199301000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]