Abstract
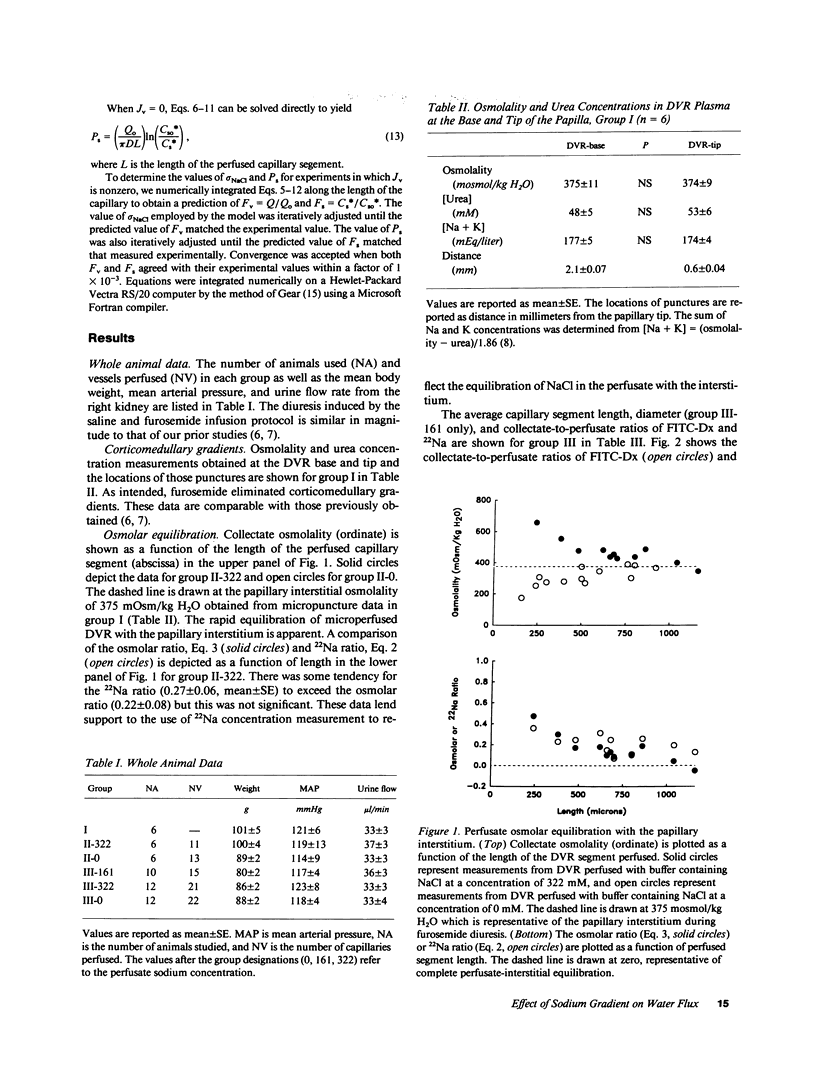
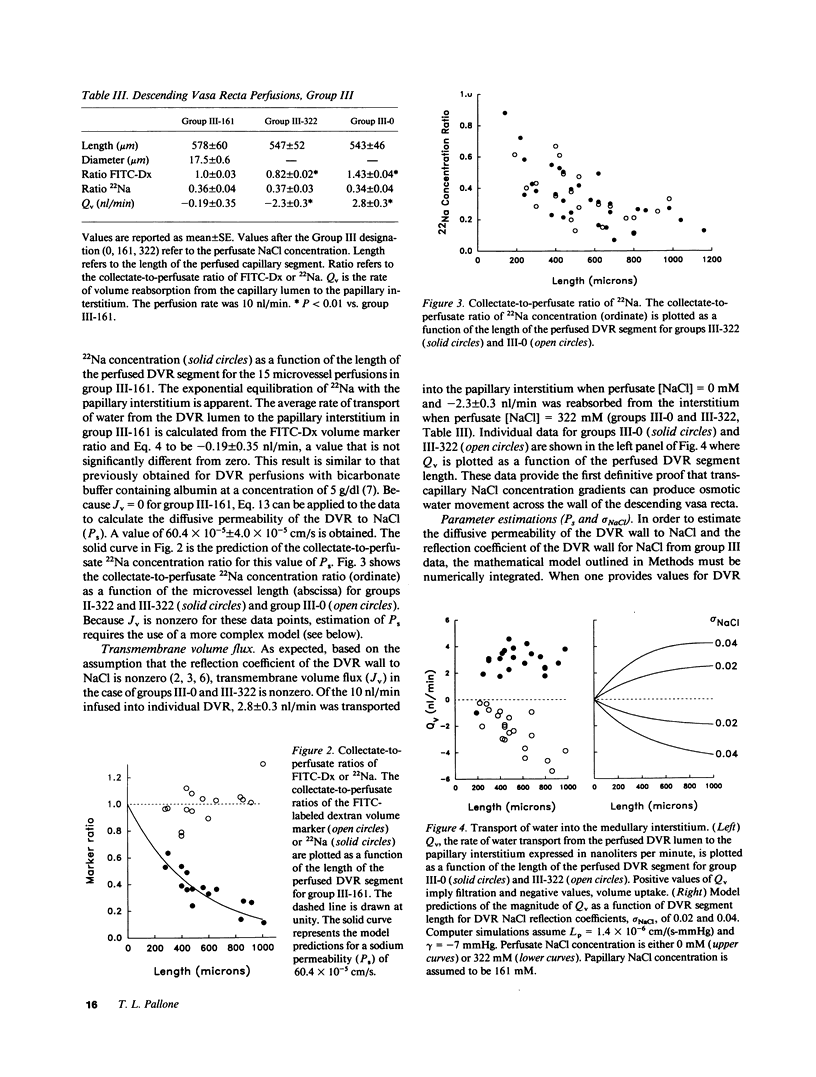
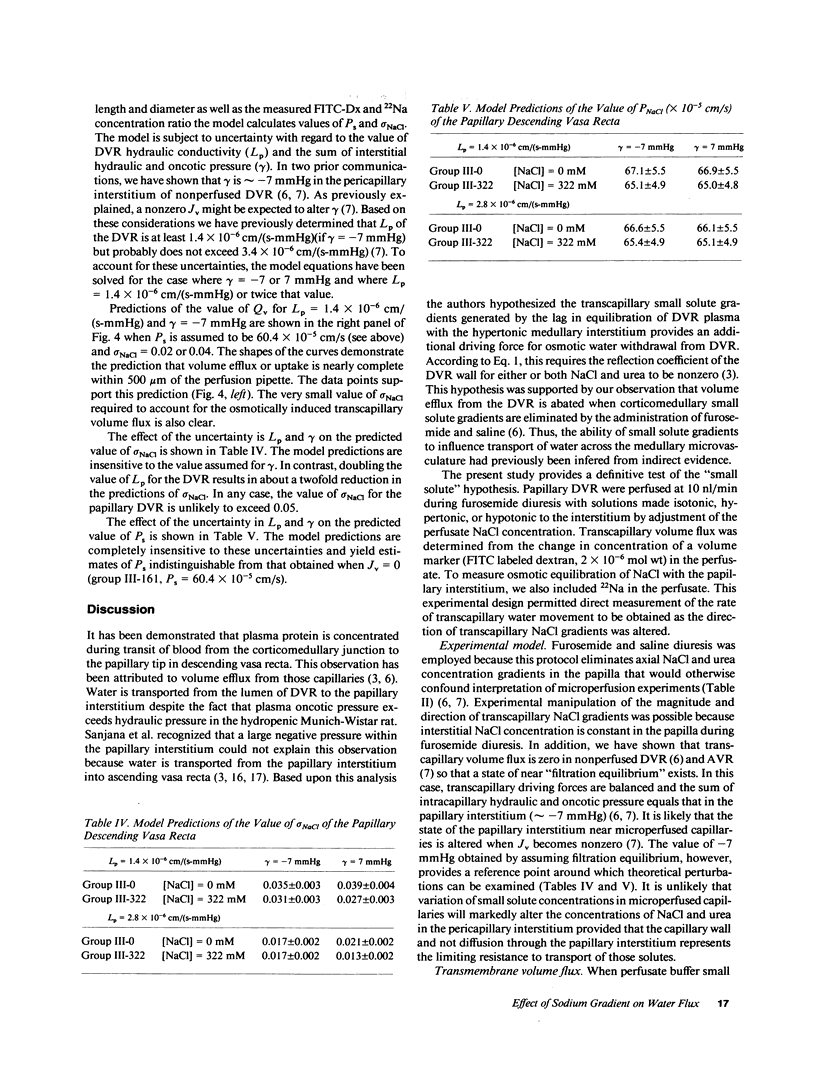
In the hydropenic kidney, volume efflux from descending vasa recta (DVR) occurs despite an intracapillary oncotic pressure that exceeds hydraulic pressure. That finding has been attributed to small solute gradients which may provide an additional osmotic driving force favoring water transport from DVR plasma to the papillary interstitium. To test this hypothesis, axial gradients of NaCl and urea in the papilla were eliminated by administration of furosemide and saline. DVR were then blocked with paraffin and microperfused at 10 nl/min with a buffer containing albumin, fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled dextran (FITC-Dx), 22Na, and NaCl in a concentration of 0 (hypotonic to the interstitium), 161 (isotonic) or 322 mM (hypertonic). Collectate was obtained from the perfused DVR by micropuncture and the collectate-to-perfusate ratios of FITC-Dx and 22Na were measured. A mathematical model was employed to determine DVR permeability (Ps) and reflection coefficient to NaCl (sigma NaCl). The rate of transport of water from the DVR lumen to the papillary interstitium was 2.8 +/- 0.3 (Nv = 22), -0.19 +/- 0.4 (Nv = 15), and -2.3 +/- 0.3 nl/min (Nv = 21) (mean +/- SE) when perfusate NaCl was 0, 161, or 322 mM, respectively (Nv = number of DVR perfused). The collectate-to-perfusate 22Na concentration ratios were 0.34 +/- 0.04, 0.36 +/- 0.04 and 0.37 +/- 0.03 for those groups, respectively. Based on these data, Ps is calculated to be 60.4 x 10(-5) +/- 4.0 x 10(-5) cm/s and sigma NaCl less than 0.05. The results of this study confirm that transcapillary NaCl concentrations gradients induce water movement across the wall of the DVR.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curry F. E., Michel C. C., Mason J. C. Osmotic reflextion coefficients of capillary walls to low molecular weight hydrophilic solutes measured in single perfused capillaries of the frog mesentery. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):319–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutsche H. U., Müller-Surr R., Hegel U., Hierholzer K., Lüderitz S. A new method for intratubular blockade in micropuncture experiments. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(2):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00579949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):229–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. J., Segel L. A. Analysis of countercurrent diffusion exchange in blood vessels of the renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):817–828. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G. Structure and formation of pores in fenestrated capillaries. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Sep;36(5):768–782. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. Permeability of the loop of Henle, vasa recta, and collecting duct to water, urea, and sodium. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):108–115. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Jamison R. L. Effect of ureteral excision on inner medullary solute concentration in rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1225–F1229. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Morgenthaler T. I., Deen W. M. Analysis of microvascular water and solute exchanges in the renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F303–F315. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Robertson C. R., Jamison R. L. Renal medullary microcirculation. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):885–920. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Work J., Jamison R. L. Resistance of descending vasa recta to the transport of water. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F688–F697. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Yagil Y., Jamison R. L. Effect of small-solute gradients on transcapillary fluid movement in renal inner medulla. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):F547–F553. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.4.F547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Goldstein D. A., Hoffman J. F. The flow of solute and solvent across a two-membrane system. J Theor Biol. 1963 Nov;5(3):426–442. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjana V. M., Johnston P. A., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M., Jamison R. L. Hydraulic and oncotic pressure measurements in inner medulla of mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1921–1926. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjana V. M., Johnston P. A., Robertson C. R., Jamison R. L. An examination of transcapillary water flux in renal inner medulla. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):313–318. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. M., Karnovsky M. J., Vehkatachalam M. A. Ultrastructural differences between rat inner medullary descending and ascending vasa recta;. Lab Invest. 1976 Aug;35(2):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. L. Concentration of urine in a central core model of the renal counterflow system. Kidney Int. 1972 Aug;2(2):85–94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vurek G. G., Knepper M. A. A colorimeter for measurement of picomole quantities of urea. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):656–658. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerhackl B., Robertson C. R., Jamison R. L. Fluid uptake in the renal papilla by vasa recta estimated by two methods simultaneously. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):F347–F353. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.3.F347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



