Abstract
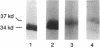
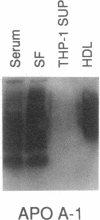
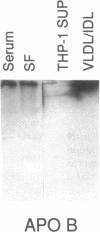
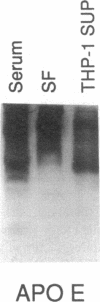
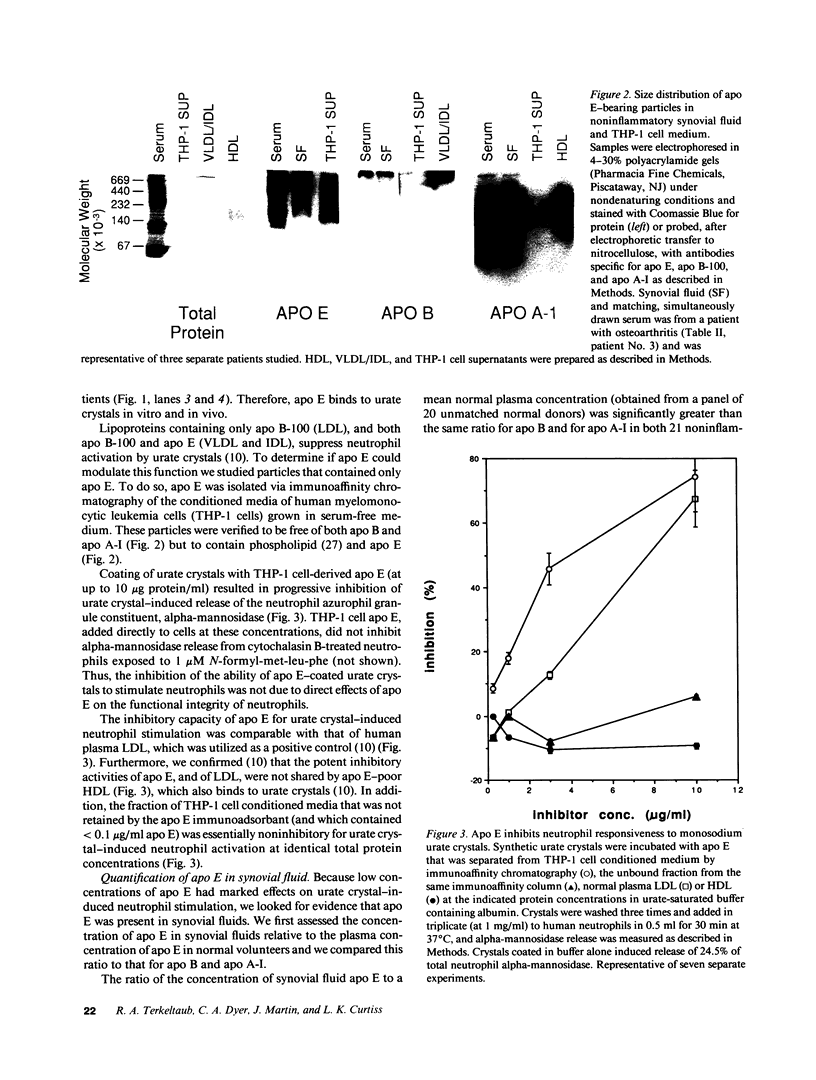
Factors that modulate the ability of monosodium urate crystals to stimulate leukocytes could regulate gouty inflammation. Lipoproteins that bear apo B-100 and apo E bind to urate crystals and suppress crystal-neutrophil interaction. In this study, we observed that urate crystals, coated with apo E of monocyte origin, had a diminished ability to stimulate neutrophils. Apo E was also detected on the surface of urate crystals recovered from gout patients. Thus, we analyzed apo E in noninflammatory synovial fluid, and found it to be associated with particles of heterogeneous size and of predominantly alpha and pre-beta electrophoretic mobility. Local articular synthesis of at least a portion of synovial fluid apo E was suggested because (a) the synovial fluid/plasma concentration ratio of apo E was significantly higher than that for both apo B and apo A-I, which are not widely synthesized by extrahepatic tissues, (b) cultured rheumatoid synovial cells in first passage secreted apo E, (c) a portion of synovial fluid apo E was heavily sialylated. We conclude that synovial fluids contain apo E that appears partly of local origin. Apo E binds to urate crystals and could modulate gouty inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils exposed to monosodium urate. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Feb;25(2):174–180. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo C. A., Schumacher H. R. The synovitis of acute gouty arthritis. A light and electron microscopic study. Hum Pathol. 1973 Jun;4(2):265–279. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(73)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Bilheimer D. W., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Biochemical and genetic studies of the apoprotein E secreted by mouse macrophages and human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9788–9795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Ihrke G., Herz J., Stanley K. K. The LDL-receptor-related protein, LRP, is an apolipoprotein E-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):162–164. doi: 10.1038/341162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanche P. J., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V. Characterization of human high-density lipoproteins by gradient gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyles J. K., Zoellner C. D., Anderson L. J., Kosik L. M., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Hui D. Y., Mahley R. W., Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Ignatius M. J. A role for apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein A-I, and low density lipoprotein receptors in cholesterol transport during regeneration and remyelination of the rat sciatic nerve. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1015–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI113943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D. The effect of synovial hyaluronate on the ingestion of monosodium urate crystals by leukocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Sep 30;55(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Bowlin T. L., Krstenansky J. L. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by synthetic peptides homologous to human plasma apolipoproteins B and E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):741–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Hirose N., Blankenship D. T., Jackson R. L., Harmony J. A., Sparrow D. A., Sparrow J. T. Binding of a high reactive heparin to human apolipoprotein E: identification of two heparin-binding domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):783–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Black A. S., Takagi Y., Plow E. F. New mechanism for foam cell generation in atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):367–373. doi: 10.1172/JCI113081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma high density lipoproteins. Identification with apolipoprotein A-I- and A-II-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2982–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. B., Dahl I. M., Engström-Laurent A., Granath K. Concentration and molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;44(12):817–822. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.12.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giovine F. S., Malawista S. E., Nuki G., Duff G. W. Interleukin 1 (IL 1) as a mediator of crystal arthritis. Stimulation of T cell and synovial fibroblast mitogenesis by urate crystal-induced IL 1. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3213–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dory L., Boquet L. M., Tate C. R., Sloop C. H. Peripheral synthesis and isoform distribution of dog apoprotein E. An in vivo approach. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer C. A., Curtiss L. K. Apoprotein E-rich high density lipoproteins inhibit ovarian androgen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10965–10973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. C., Rubinstein A., Bukberg P. R., Brown W. V. Apolipoprotein E-enriched lipoprotein subclasses in normolipidemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):886–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Formation of cholesterol- and apoprotein E-enriched high density lipoproteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6202–6212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerne P. A., Terkeltaub R., Zuraw B., Lotz M. Inflammatory microcrystals stimulate interleukin-6 production and secretion by human monocytes and synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Nov;32(11):1443–1452. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher P., Schumacher H. R. Immunoglobulin in tophi and on the surface of monosodium urate crystals. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):353–361. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose N., Blankenship D. T., Krivanek M. A., Jackson R. L., Cardin A. D. Isolation and characterization of four heparin-binding cyanogen bromide peptides of human plasma apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5505–5512. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle D. M., Smith R. S., Curtiss L. K. Quantitation of plasma apolipoprotein A-I using two monoclonal antibodies in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Lipid Res. 1988 Sep;29(9):1221–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Immunoregulatory plasma lipoproteins. Role of apoprotein E and apoprotein B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11775–11781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Malmnäs Tjernlund U. K., Kabelitz D., Wigren A. Appearance of anti-HLA-DR-reactive cells in normal and rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Aug;14(2):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozin F., Ginsberg M. H., Skosey J. L. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte responses to monosodium urate crystals: modification by adsorbed serum proteins. J Rheumatol. 1979 Sep-Oct;6(5):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Somerville J. A. Permeability of human synovial membrane to plasma proteins. Relationship to molecular size and inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Sep-Oct;14(5):560–570. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Xu Y. F., Wu J. Y., Chan L. Immunoreactive apolipoprotein E is a widely distributed cellular protein. Immunohistochemical localization of apolipoprotein E in baboon tissues. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):947–958. doi: 10.1172/JCI112685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Gump H., Diller P., Getz G. S. Macrophage free cholesterol content regulates apolipoprotein E synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11657–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J. Crystal identification in human synovial fluids. Methods and interpretation. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Aug;14(2):253–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe M. G., Curtiss L. K. Apolipoprotein E is a biologically active constituent of the normal immunoregulatory lipoprotein, LDL-In. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3716–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Boyles J. K., Lee S. H., Hui D., Weisgraber K. H. Lipoproteins and their receptors in the central nervous system. Characterization of the lipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid and identification of apolipoprotein B,E(LDL) receptors in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14352–14360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Carey M., Forte T., Vega G. L. Apolipoproteins in human cerebrospinal fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4646–4649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALL D. M., COHEN A. S., SCHMID K. LIPOPROTEINS OF SYNOVIAL FLUID AS STUDIED BY ANALYTICAL ULTRACENTRIFUGATION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2070–2079. doi: 10.1172/JCI105081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOKOLOFF L. The pathology of gout. Metabolism. 1957 May;6(3):230–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Levy R. I. Pathogenesis and management of lipoprotein disorders. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1300–1310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Hamilton R., Krause B. R., Roheim P. S. Characterization of dog peripheral lymph lipoproteins: the presence of a disc-shaped "nascent" high density lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1983 Nov;24(11):1429–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Roheim P. S. Interstitial fluid lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1987 Mar;28(3):225–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi Y., Dyer C. A., Curtiss L. K. Platelet-enhanced apolipoprotein E production by human macrophages: a possible role in atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):859–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Werb Z. Modulation of apoprotein E secretion in response to receptor-mediated endocytosis in resident and inflammatory macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):167–178. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Curtiss L. K., Tenner A. J., Ginsberg M. H. Lipoproteins containing apoprotein B are a major regulator of neutrophil responses to monosodium urate crystals. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1719–1730. doi: 10.1172/JCI111380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Martin J., Curtiss L. K., Ginsberg M. H. Apolipoprotein B mediates the capacity of low density lipoprotein to suppress neutrophil stimulation by particulates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15662–15667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Smeltzer D., Curtiss L. K., Ginsberg M. H. Low density lipoprotein inhibits the physical interaction of phlogistic crystals and inflammatory cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):363–370. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Tenner A. J., Kozin F., Ginsberg M. H. Plasma protein binding by monosodium urate crystals. Analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jun;26(6):775–783. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr Human apolipoprotein B-100 heparin-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11097–11103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Sparrow J. T. Human apolipoprotein E. Determination of the heparin binding sites of apolipoprotein E3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2068–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Endotoxin suppresses expression of apoprotein E by mouse macrophages in vivo and in culture. A biochemical and genetic study. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10642–10648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette-Hammond M. E., Lauer S. J., Corsini A., Walker D., Taylor J. M., Rall S. C., Jr Glycosylation of human apolipoprotein E. The carbohydrate attachment site is threonine 194. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Smith R. S., Hogle D. M., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Two new monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked assays of apolipoprotein B. Clin Chem. 1986 Aug;32(8):1484–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]