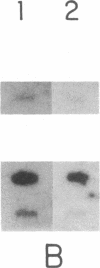
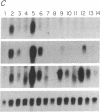
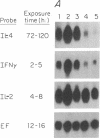
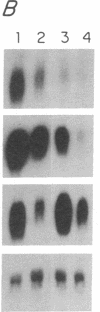
Abstract
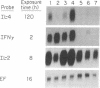
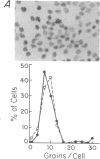
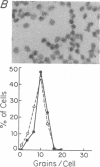
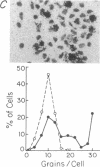
The mechanisms by which T lymphocytes acquire the capacity to produce interleukin 4 (IL-4) and other lymphokines during intrathymic and extrathymic development are poorly understood. To gain insight into this process, we determined the capacity of human neonatal and adult T lineage cell populations to produce IL-4 after polyclonal activation. IL-2 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production were studied in parallel, since their production by neonatal T cells is known to be similar or diminished, respectively, compared to adult T cells. Production of IL-4 by neonatal CD4+ T cells and IFN-gamma by neonatal CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was markedly lower compared with analogous adult cell populations, whereas IL-2 production was similar. Transcription of IL-4, as determined by nuclear run-on assays, and IL-4 mRNA-containing cells, as determined by in situ hybridization, were undetectable in neonatal T cells, whereas both were detectable in adult T cells. IFN-gamma transcription and IFN-gamma mRNA-containing cells were reduced in neonatal T cells compared with adult T cells. Reduced lymphokine production by neonatal T cells correlated with their lack of a CD45R- (putative memory T cell) population; cells with this surface phenotype comprised 30-40% of the adult CD4+ T cells and were highly enriched for IL-4 and IFN-gamma, but not IL-2 production. IL-4, IFN-gamma, and IL-2 mRNA expression by neonatal CD4+CD8- thymocytes was similar to that found in circulating neonatal CD4+ T cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that the extrathymic generation of memory T cells during postnatal life may result in an increased capacity for IL-4 and IFN-gamma gene expression. In addition, IFN-gamma and IL-2 mRNA were significantly more abundant than IL-4 mRNA in activated neonatal CD4+CD8- thymocytes and CD4+ T cells, as well as adult CD4+ CD45R- T cells. Therefore, the capacity of T lineage cells to express the IL-4 gene may be more restricted compared to other lymphokine genes beginning in intrathymic development. This restricted capacity appears to persist during postnatal extrathymic maturation of T cells.
Full text
PDF


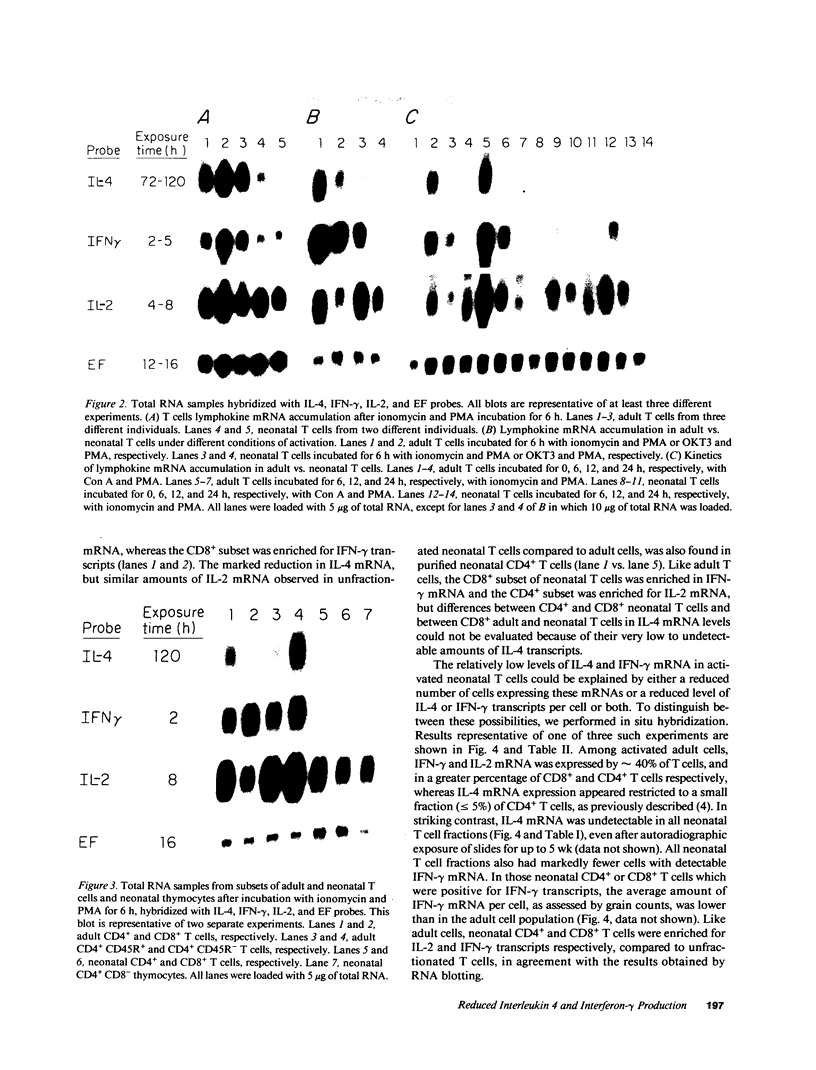
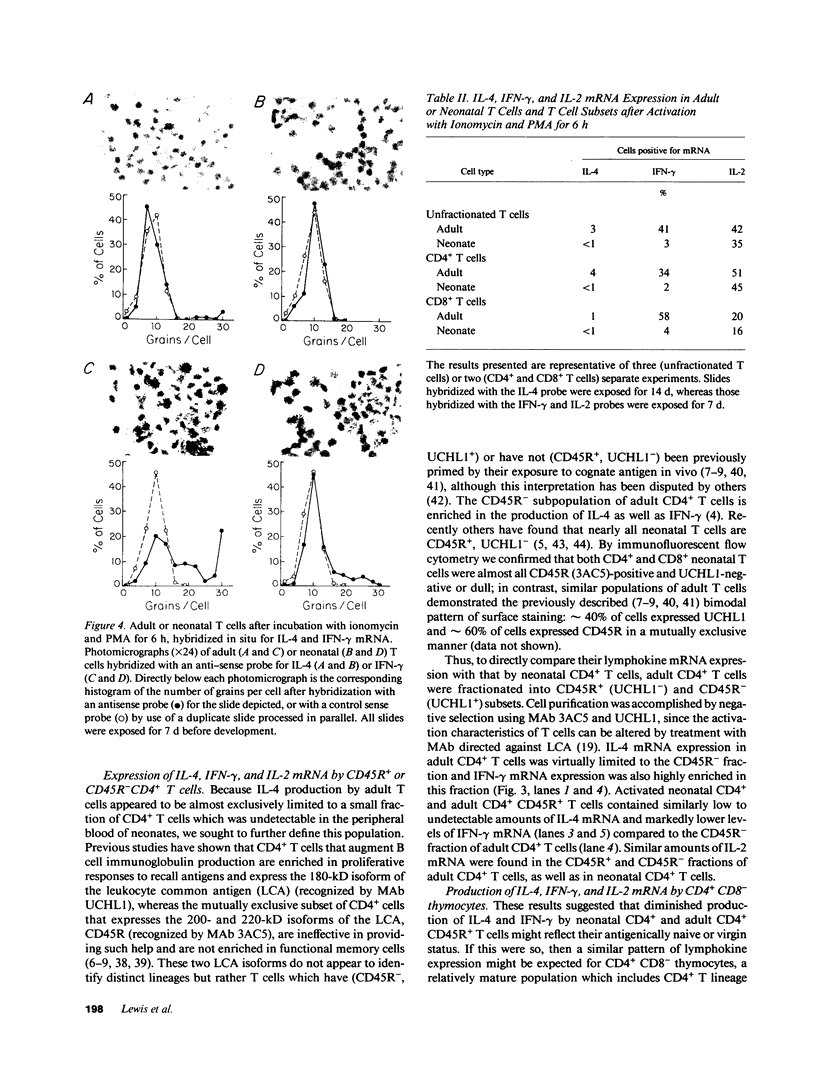




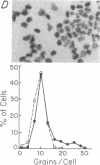
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Winter H. S., Gard S. E., Fischer T. J., Stiehm E. R. Deficiency of immune interferon production by leukocytes of normal newborns. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 15;55(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Cerottini J. C., Horvath C., Bron C., Pedrazzini T., Howe R. C., MacDonald H. R. Distinction of virgin and memory T lymphocytes. Stable acquisition of the Pgp-1 glycoprotein concomitant with antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3120–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Phenotypic identification of memory cytolytic T lymphocytes in a subset of Lyt-2+ cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1009–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Selectively increased production of interferon-gamma by subsets of Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ T cells identified by expression of Pgp-1. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3583–3586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., McKinney S., Liu V., Kung P. C., Vilcek J., Le J. Use of monoclonal antibodies as sensitive and specific probes for biologically active human gamma-interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilmonczyk B. A., Levin M. J., McDuffy R., Hayward A. R. Characterization of the human newborn response to herpesvirus antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4184–4188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Yamashita N., Martin A. M. The functionally distinct subpopulations of human CD4+ helper/inducer T lymphocytes defined by anti-CD45R antibodies derive sequentially from a differentiation pathway that is regulated by activation-dependent post-thymic differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1464–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Kaempfer R. Control of biologically active interleukin 2 messenger RNA formation in induced human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2601–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Pilo S., Kaempfer R. Kinetics of induction and molecular size of mRNAs encoding human interleukin-2 and gamma-interferon. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):236–239. doi: 10.1038/297236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English B. K., Burchett S. K., English J. D., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Wilson C. B. Production of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor by human neonatal mononuclear cells. Pediatr Res. 1988 Dec;24(6):717–722. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198812000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes B. J., Pardoll D. M. Molecular and cellular events of T cell development. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:207–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60643-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel L., Bryson Y. J. Ontogeny of phytohemagglutinin-induced gamma interferon by leukocytes of healthy infants and children: evidence for decreased production in infants younger than 2 months of age. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerli R., Rambotti P., Cernetti C., Velardi A., Spinozzi F., Tabilio A., Martelli M. F., Grignani F., Davis S. A mature thymocyte-like phenotypic pattern on human cord circulating T-lymphoid cells. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Nov;4(6):461–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00916576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R. Murine CD4+ T cell subsets defined. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1825–1838. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R. Phenotypic and functional alteration of CD4+ T cells after antigen stimulation. Resolution of two populations of memory T cells that both secrete interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2245–2250. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lee J., Beverley P. C. Ontogeny of expression of UCHL1 antigen on TcR-1+ (CD4/8) and TcR delta+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):771–773. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercend T., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Comparative expression of T9, T10, and Ia antigens on activated human T cell subsets. Hum Immunol. 1981 Nov;3(3):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Inhibitory influence of IL-4 on human B cell responsiveness. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):164–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karray S., DeFrance T., Merle-Béral H., Banchereau J., Debré P., Galanaud P. Interleukin 4 counteracts the interleukin 2-induced proliferation of monoclonal B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):85–94. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Allison J. P., Phillips J. H. Correlation of cell surface antigen expression on human thymocytes by multi-color flow cytometric analysis: implications for differentiation. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2501–2507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Rose L. M., Spooner C. E., Beatty P. G., Martin P. J., Clark E. A. Antibodies to common leukocyte antigen p220 influence human T cell proliferation by modifying IL 2 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1819–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Larsen A., Wilson C. B. Reduced interferon-gamma mRNA levels in human neonates. Evidence for an intrinsic T cell deficiency independent of other genes involved in T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1018–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., De Plaen E., Van Snick J. A simple panning method for the selection of cell surface antigen transfectants. J Immunol Methods. 1985 May 10;79(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Seki H., Taga K., Sato H., Taniguchi N. Dissociated production of interleukin-2 and immune (gamma) interferon by phytohaemagglutinin stimulated lymphocytes in healthy infants. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):505–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarangelo L. D., Panina P., Imberti L., Malfa P., Ugazio A. G., Albertini A. Neonatal T4+ lymphocytes: analysis of the expression of 4B4 and 2H4 antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jan;46(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN J. J., DANCIS J., JULIA J. F. Studies of the immunology of the newborn infant. I. Age and antibody production. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Fowlkes B. J., Lechler R. I., Germain R. N., Schwartz R. H. Early genetic events in T cell development analyzed by in situ hybridization. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1624–1638. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Ohara J. B-cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:429–459. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Pleiotropy and redundancy: T cell-derived lymphokines in the immune response. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Mangoni L., Engers H. D., Trinchieri G. Interferon production by human and murine lymphocytes in response to alloantigens. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1589–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers G. D., Abbas A. K., Miller R. A. Frequencies of IL-2- and IL-4-secreting T cells in naive and antigen-stimulated lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3352–3357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powrie F., Mason D. The MRC OX-22- CD4+ T cells that help B cells in secondary immune responses derive from naive precursors with the MRC OX-22+ CD4+ phenotype. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):653–662. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Inaba K., Metlay J. Lymphokine production by murine T cells in the mixed leukocyte reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):795–800. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. M., Ginsberg A. H., Rothstein T. L., Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. Selective loss of a subset of T helper cells in active multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7389–7393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki H., Taga K., Matsuda A., Uwadana N., Hasui M., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of active suppressor cells against IFN-gamma production in PHA-stimulated cord blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3158–3161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra H. M., Krowka J. F., Ledbetter J. A., Pilarski L. M. Loss of CD45R (Lp220) represents a post-thymic T cell differentiation event. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1435–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Funa K., Zalcberg-Quintana I., Xanthopoulos K. G., Kisielow P., Palacios R. Analysis by in situ hybridization of cells expressing mRNA for interleukin 4 in the developing thymus and in peripheral lymphocytes from mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):218–221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Brown M. H., Rowe D., Callard R. E., Beverley P. C. Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):63–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. J., Merćep M., Saito T., Germain R. N., Bonvini E., Ashwell J. D. Dissociation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Ca2+ fluxes from the biological responses of a T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):625–628. doi: 10.1038/334625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., McKenzie D. T., Weinberg A. D., Hancock W. Characterization of T helper 1 and 2 cell subsets in normal mice. Helper T cells responsible for IL-4 and IL-5 production are present as precursors that require priming before they develop into lymphokine-secreting cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3445–3455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Regulation of cytokine gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:439–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Clement L. T., Cooper M. D. Human lymphocyte differentiation antigens HB-10 and HB-11. I. Ontogeny of antigen expression. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Cooper M. D., Clement L. T. Human lymphocyte differentiation antigens HB-10 and HB-11. II. Differential production of B cell growth and differentiation factors by distinct helper T cell subpopulations. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2989–2994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu D. T., Jabara H. H., DeKruyff R. H., Abbas A. K., Abrams J. S., Geha R. S. Functional heterogeneity among human inducer T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4211–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Sanceau J., Sondermeyer P., Falcoff R. Kinetics of messenger accumulation coding for IFN gamma, related to modifications in the poly(A) RNA population of activated human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2629–2640. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi N., Virelizier J. L. Defective IFN-gamma production in the human neonate. I. Dysregulation rather than intrinsic abnormality. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):167–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Acres R. B., Sassenfeld H. M., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic cell populations from human peripheral blood by B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4). J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Remington J. S. Effects of monocytes from human neonates on lymphocyte transformation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jun;36(3):511–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Westall J., Johnston L., Lewis D. B., Dower S. K., Alpert A. R. Decreased production of interferon-gamma by human neonatal cells. Intrinsic and regulatory deficiencies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):860–867. doi: 10.1172/JCI112383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Rosen F. S., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Ontogeny of human T and B lymphocytes during stressed and normal gestation: phenotypic analysis of umbilical cord lymphocytes from term and preterm infants. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Oct;37(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]